Professional Documents
Culture Documents
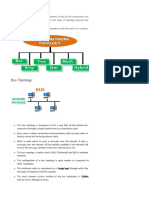
Bus Network Topology: 1. 2. 3. Disadvantages of
Bus Network Topology: 1. 2. 3. Disadvantages of
Uploaded by
Rezwan Ahmed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesThis document describes four common network topologies: bus, star, ring, and mesh. The bus topology connects all nodes to a single cable. The star topology connects each node to a central hub. The ring topology arranges the nodes in a circular fashion passing data in one direction. The mesh topology allows for multiple connections between nodes. Advantages and disadvantages are listed for each but not described. A hybrid topology combines two or more standard topologies.
Original Description:
Original Title
Bus Network Topology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes four common network topologies: bus, star, ring, and mesh. The bus topology connects all nodes to a single cable. The star topology connects each node to a central hub. The ring topology arranges the nodes in a circular fashion passing data in one direction. The mesh topology allows for multiple connections between nodes. Advantages and disadvantages are listed for each but not described. A hybrid topology combines two or more standard topologies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesBus Network Topology: 1. 2. 3. Disadvantages of
Bus Network Topology: 1. 2. 3. Disadvantages of
Uploaded by
Rezwan AhmedThis document describes four common network topologies: bus, star, ring, and mesh. The bus topology connects all nodes to a single cable. The star topology connects each node to a central hub. The ring topology arranges the nodes in a circular fashion passing data in one direction. The mesh topology allows for multiple connections between nodes. Advantages and disadvantages are listed for each but not described. A hybrid topology combines two or more standard topologies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
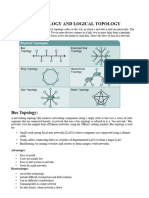
Bus Network Topology
In Local Area Networks (LAN) where bus topology is used, each node is
connected to a single cable. Each computer or server is connected to the single
bus cable. A signal from the source travels in both directions to all machines
connected on the bus cable until it finds the intended recipient. If the machine
address does not match the intended address for the data, the machine ignores
the data.
Advantages of Bus Network Topology:
1.
2.
3.
Disadvantages of Bus Network Topology:
1.
2.
3.
Star network topology
In local area networks with a star topology, each network host is connected to a
central hub with a point-to-point connection. In Star topology every node
(computer workstation or any other peripheral) is connected to central node
called hub or switch. The switch is the server and the peripherals are the clients.
The network does not necessarily have to resemble a star to be classified as a
star network, but all of the nodes on the network must be connected to one
central device.
Advantages of Star Network Topology:
1.
2.
3.
Disadvantages of Star Network Topology:
1.
2.
3.
Ring network topology
A network topology that is set up in a circular fashion in which data travels
around the ring in one direction and each device on the right acts as a repeater
to keep the signal strong as it travels. Each device incorporates a receiver for the
incoming signal and a transmitter to send the data on to the next device in the
ring. The network is dependent on the ability of the signal to travel around the
ring
Advantages of Ring Network Topology:
1.
2.
3.
Disadvantages of Ring Network Topology:
1.
2.
3.
Mesh network topology
The value of fully meshed networks is proportional to the exponent of the number
of subscribers, assuming that communicating groups of any two endpoints, up to
and including all the endpoints, is approximated by Reed's Law.
Advantages of Mesh Network Topology:
1.
2.
3.
Disadvantages of Mesh Network Topology:
1.
2.
3.
Mesh network topology
Hybrid networks use a combination of any two or more topologies in such a way
that the resulting network does not exhibit one of the standard topologies (e.g.,
bus, star, ring, etc.). For example, a tree network connected to a tree network is
still a tree network topology. A hybrid topology is always produced when two
different basic network topologies are connected.
Advantages of Mesh Network Topology:
1.
2.
3.
Disadvantages of Mesh Network Topology:
1.
2.
3.
You might also like
- 1.2.2 Topology FactsDocument2 pages1.2.2 Topology FactsSaypiseth SeangNo ratings yet
- Networking 1.2Document7 pagesNetworking 1.2Echo greenNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document13 pagesUnit 2Nihal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce 1-5QNS FinalDocument20 pagesEcommerce 1-5QNS FinalMAGOMU DAN DAVIDNo ratings yet
- Home Ccatcracker Pyapps Ccatcracker Ccatcracker Networking PDFDocument92 pagesHome Ccatcracker Pyapps Ccatcracker Ccatcracker Networking PDFTejas RaneNo ratings yet
- Cables and TopologiesDocument9 pagesCables and TopologiesRafayetNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of Network Topology in Computer NetworksDocument4 pagesDifferent Kinds of Network Topology in Computer Networksmuna cliffNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Topologies - JavatpointDocument8 pagesComputer Network Topologies - JavatpointP DNo ratings yet
- Cne Chapter2 NotesDocument24 pagesCne Chapter2 Noteskirantamanna63No ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument7 pagesNetwork TopologyJayvee Puntalba CalinogNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument7 pagesNetwork TopologyBijay NagNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 2 & 16 MarksDocument26 pagesUnit 1 - 2 & 16 MarksGautamNo ratings yet
- IT ERA Lesson 6Document9 pagesIT ERA Lesson 6rizielpingcas82No ratings yet
- Network TopologiesDocument4 pagesNetwork TopologieskaranmaddiNo ratings yet
- Network Devices & Network TopologyDocument2 pagesNetwork Devices & Network TopologyAabbuu MynNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument24 pagesNetwork TopologyVahough BhielhattNo ratings yet
- Network Topology YashuDocument7 pagesNetwork Topology YashuyashuNo ratings yet
- TopologyDocument5 pagesTopologykirtanpkNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document9 pagesUnit 6Farhan PatelNo ratings yet
- Study About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanDocument11 pagesStudy About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanAnonymous aQxekTRNo ratings yet
- DcnsDocument19 pagesDcnsYogesh KambleNo ratings yet
- Types of Network TopologyDocument24 pagesTypes of Network TopologyVishnu PujariNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Lab RecordDocument62 pagesComputer Networks Lab Record'Mahadevan Govindakrishnan'No ratings yet
- Unit 02 Network Topologies and Networking DevicesDocument9 pagesUnit 02 Network Topologies and Networking Devicesroysayanccp05No ratings yet
- TopologyDocument6 pagesTopologyParidhi GaurNo ratings yet
- Network TopologiesDocument9 pagesNetwork TopologiesshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- 1.2.2 Topology FactsDocument2 pages1.2.2 Topology FactsSaypiseth SeangNo ratings yet
- What Is Network TopologyDocument4 pagesWhat Is Network TopologyGoldy BatraNo ratings yet
- Cchapter 1 - Part IIDocument39 pagesCchapter 1 - Part IIBezabh AbebawNo ratings yet
- Network Topology 1Document10 pagesNetwork Topology 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- C PPPPPP PPP PPDocument9 pagesC PPPPPP PPP PPahils100% (1)
- Topology: Computer Networks (Introduction)Document12 pagesTopology: Computer Networks (Introduction)Anjana MagantiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document10 pagesUnit 1pratyay dhondNo ratings yet
- Presented by Vinay Shukla Cs 3rd Year: Guided By:-Sudhanshu NayakDocument23 pagesPresented by Vinay Shukla Cs 3rd Year: Guided By:-Sudhanshu NayakVinay ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Ii: Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesAssignment - Ii: Computer NetworksAashish RaghunathNo ratings yet
- Network TopologiesDocument43 pagesNetwork Topologiesayunik615No ratings yet
- TopologyDocument11 pagesTopologyAdilet KenesovNo ratings yet
- TECHNOLOGY IN BANKING OPERATIONS Explain The Concept of Network Topology and Its Various TypesDocument6 pagesTECHNOLOGY IN BANKING OPERATIONS Explain The Concept of Network Topology and Its Various TypesAbhishek AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Advanced NetworkingDocument15 pagesAdvanced NetworkingdisgruntledattitudeNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies: Lecture # 2Document21 pagesNetwork Topologies: Lecture # 2Monika RehmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 1 and 2 21Document17 pagesChapter 2 1 and 2 2119Siddhesh DhumalNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By:: Sir Saif Ali Bajwa Muhammad Saad Majeed 2ND SemesterDocument8 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By:: Sir Saif Ali Bajwa Muhammad Saad Majeed 2ND SemesterSaad MajeedNo ratings yet
- CSE Fundamental - TopologyDocument14 pagesCSE Fundamental - TopologySYED FARHAN REZANo ratings yet
- Internetworking Devices: Cables Repeaters Hubs Bridges Switches RoutersDocument13 pagesInternetworking Devices: Cables Repeaters Hubs Bridges Switches RoutersPrashanth PrashuNo ratings yet
- Homewrok Assignment1Document12 pagesHomewrok Assignment1Takudzwa SibandaNo ratings yet
- Physical Topology and Logical TopologyDocument3 pagesPhysical Topology and Logical TopologyNO NameNo ratings yet
- Network Basics: Network Topology: Node: A NodeDocument3 pagesNetwork Basics: Network Topology: Node: A Nodemanohar reddyNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Concepts of Lan & DLL Protocols: Categores of Computer NetworksDocument15 pagesUNIT-1 Concepts of Lan & DLL Protocols: Categores of Computer NetworksDinesh PalavalasaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Network Topologies& DevicesDocument61 pagesChapter 4 Network Topologies& DevicesManofwarriorNo ratings yet
- Ring Topology: Name Kajal Class:-Fybsc (It) /B ROLL NO:-90Document8 pagesRing Topology: Name Kajal Class:-Fybsc (It) /B ROLL NO:-90jyotiNo ratings yet
- 02 Computer NetworksDocument43 pages02 Computer NetworksShalini Kumari GuptaNo ratings yet
- Network TopologiesDocument43 pagesNetwork TopologiesKunal Sah100% (1)
- Basic Concepts of Computer Networks: Network TopologyDocument25 pagesBasic Concepts of Computer Networks: Network TopologyAmritansh SinghNo ratings yet
- 173462129-Atikur Rahman PDFDocument3 pages173462129-Atikur Rahman PDFAtikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- It 111: Introduction To Information TechnologyDocument33 pagesIt 111: Introduction To Information TechnologyJay JembeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Computer NetworksDocument33 pagesLecture 2 Computer NetworksJay JembeNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks and Data Communication: Definition of Terms I) NetworkDocument9 pagesComputer Networks and Data Communication: Definition of Terms I) NetworkJamesNo ratings yet
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsFrom EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- GSM Signalling ProcedureDocument60 pagesGSM Signalling ProcedureSudheera IndrajithNo ratings yet
- Technical QuestionsDocument6 pagesTechnical Questionspitchrks19841No ratings yet
- MXK-Gpon-Unified Prov PPPoE - Telbo Rev1Document6 pagesMXK-Gpon-Unified Prov PPPoE - Telbo Rev1Abdulfatah Kasim ImanNo ratings yet
- Call Debug Cube AsrDocument3 pagesCall Debug Cube AsrtheajkumarNo ratings yet
- Blue Coat ProxySGDocument70 pagesBlue Coat ProxySGHitesh RahangdaleNo ratings yet
- 28-BGP Split HorizonDocument3 pages28-BGP Split HorizonprakashrjsekarNo ratings yet
- Backtrack Tool NotesDocument17 pagesBacktrack Tool NotesShahin ShahsavaraniNo ratings yet
- School Management System MCS 2010Document14 pagesSchool Management System MCS 2010Koetlisi Makhaola Elliott ThekoNo ratings yet
- HTTP Codes SelfDocument7 pagesHTTP Codes SelfKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- All About Java MailDocument175 pagesAll About Java MailNavneet100% (26)
- DS K1A340 DS K1T343 Series Face Recognition Terminal FlyerDocument2 pagesDS K1A340 DS K1T343 Series Face Recognition Terminal Flyerzwelinoo.itNo ratings yet
- Ubiquiti Nanostation2 Loco 8dbi APDocument5 pagesUbiquiti Nanostation2 Loco 8dbi APFlorencio CancheNo ratings yet
- F8936-L Series Router Technical Specification V1.0.1Document5 pagesF8936-L Series Router Technical Specification V1.0.1Xiamen Four-Faith Industrial Router supplierNo ratings yet
- IT6201 Data Communications & Network 1Document96 pagesIT6201 Data Communications & Network 1Mark De Guzman100% (1)
- SIM7020 Series - AT Command Manual - V1.05Document331 pagesSIM7020 Series - AT Command Manual - V1.05Isak EscobarNo ratings yet
- Juniper Practice Questions PDFDocument32 pagesJuniper Practice Questions PDFBiruk TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Fatima Jinnah Women University: Items DescriptionDocument5 pagesFatima Jinnah Women University: Items DescriptionfaizaNo ratings yet
- Websense Content Gateway - WCG - Help-V7.6Document467 pagesWebsense Content Gateway - WCG - Help-V7.6getriazkhanNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking Thesis SampleDocument7 pagesComputer Networking Thesis SamplePaperWritingServicePortland100% (2)
- Paket 4Document1 pagePaket 4Himawan Sutanto SMK Yapalis Krian SidoarjoNo ratings yet
- SSHD - Config WindowsDocument2 pagesSSHD - Config Windows1martinez100% (2)
- 3-The Session Initiation ProtocolDocument42 pages3-The Session Initiation ProtocolRaytheeshMonNo ratings yet
- Data Link Control: B. R. Chandavarkar CSE Dept., NITK SurathkalDocument37 pagesData Link Control: B. R. Chandavarkar CSE Dept., NITK SurathkalSoham Raje PatilNo ratings yet
- BGP: Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument14 pagesBGP: Frequently Asked QuestionsMustafa HussienNo ratings yet
- How To Enable Remote Connections To SQL ServerDocument18 pagesHow To Enable Remote Connections To SQL Servernacho altamirandaNo ratings yet
- DLR Push Api Specifications (Version:1.0.0, July 10,2012)Document3 pagesDLR Push Api Specifications (Version:1.0.0, July 10,2012)Atty RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- KN519ADocument3 pagesKN519AGarySinisterraNo ratings yet
- Meru MC5000 Data SheetDocument2 pagesMeru MC5000 Data Sheetvs6xra8308No ratings yet
- Group A CN Assignment 3Document13 pagesGroup A CN Assignment 3Usama RaheemNo ratings yet
- OAW-AP1251 (Outdoor WIFI AP)Document5 pagesOAW-AP1251 (Outdoor WIFI AP)gustavoac834217No ratings yet