Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carbon Cycle: Carbon Dioxide Balance Sheet Per Year
Uploaded by
Hooriya Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThe carbon cycle describes how carbon is exchanged between the atmosphere, biosphere, and oceans through natural processes. Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere are regulated by its absorption into the oceans as bicarbonate minerals and by photosynthesis in plants. Each year, emissions from fossil fuels and land use changes add around 11 billion tons of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, despite uptake by the oceans and photosynthesis by plants. The oceans contain over 50 times more carbon dioxide than the atmosphere.
Original Description:
Original Title
Document (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe carbon cycle describes how carbon is exchanged between the atmosphere, biosphere, and oceans through natural processes. Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere are regulated by its absorption into the oceans as bicarbonate minerals and by photosynthesis in plants. Each year, emissions from fossil fuels and land use changes add around 11 billion tons of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, despite uptake by the oceans and photosynthesis by plants. The oceans contain over 50 times more carbon dioxide than the atmosphere.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesCarbon Cycle: Carbon Dioxide Balance Sheet Per Year
Uploaded by
Hooriya KhanThe carbon cycle describes how carbon is exchanged between the atmosphere, biosphere, and oceans through natural processes. Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere are regulated by its absorption into the oceans as bicarbonate minerals and by photosynthesis in plants. Each year, emissions from fossil fuels and land use changes add around 11 billion tons of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, despite uptake by the oceans and photosynthesis by plants. The oceans contain over 50 times more carbon dioxide than the atmosphere.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
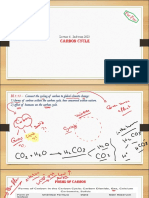
Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle is the process in which carbon travels from the
atmosphere into organisms and the Earth and then back into the
atmosphere. As carbon is the backbone of biological chemistry,
the carbon cycle is a very important chemical cycle. The
atmosphere is the minor reservoir of carbon dioxide while the
oceans are the major reservoir, containing as much as 50 times
more as that of air where it is stored as bicarbonate mineral
deposit on the ocean floor. The latter regulates the carbon dioxide
level in the atmosphere. The cycle operates in the form of carbon
dioxide exchanging among the atmosphere, biosphere and the
ocean
Carbon dioxide balance sheet per year :
(i) emissions by fossil fuel 20 billion tons,
(ii) emissions by deforestation and changes in land use 5.5 billion
ton.
(iii) uptake in the oceans 5.5. billion tons,
(iv) uptake by carbon dioxide fertilization, i.e. photo-synthesis 7.3
billion tons.
Thus there is a net increase of carbon dioxide in the
atmosphere of 11 billion tons per year.
Concentration of carbon dioxide: The atmosphere contains 2700
billion tons of carbon dioxide; biosphere, vegetation and soil
about 6600 billion tons and the oceans about 1,36,000 billion tons
of carbon dioxide.
STEPS OF CARBON CYCLE:
Photosynthesis:
During photosynthesis plants, algae and
You might also like
- Carbon Cycle: Dela Cruz, Ma. Angelica F. BSCE-4Document13 pagesCarbon Cycle: Dela Cruz, Ma. Angelica F. BSCE-4Angelica F. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument2 pagesThe Carbon CycleFoisal SwarupNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument3 pagesThe Carbon CycleFoisal SwarupNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument5 pagesCarbon CycleAkshat KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Main Components: Carbon Biosphere Geosphere Hydrosphere Atmosphere Nitrogen Cycle Water Cycle BiosphereDocument3 pagesMain Components: Carbon Biosphere Geosphere Hydrosphere Atmosphere Nitrogen Cycle Water Cycle BiosphereJosueNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Climate ScienceDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Climate ScienceRAHIL BHADOONo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle: Dioxide (CODocument4 pagesCarbon Cycle: Dioxide (COOryx PerfectioNo ratings yet
- Screenshot (1247)Document2 pagesScreenshot (1247)schoolworks IrishNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument11 pagesCarbon CycleUmar Saleh GwaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PDF For Msce Used in MalawiDocument6 pagesChemistry PDF For Msce Used in Malawiwitnesschirombo3No ratings yet
- Big Picture: Big Picture in Focus: Uloa. Describe The Paths in Which Carbon Move Throughout The EnvironmentDocument17 pagesBig Picture: Big Picture in Focus: Uloa. Describe The Paths in Which Carbon Move Throughout The Environmentjapheth louie m. gofredoNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument3 pagesThe Carbon CycleRochelle BautistaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle - WikipediaDocument172 pagesCarbon Cycle - WikipediasubhajitparichhaNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument28 pagesCarbon CyclejosevitorromualdoNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument9 pagesThe Carbon CycleNurmeilyRachmawatiNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide DoublingDocument7 pagesCarbon Dioxide DoublingAishah AhmedNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument2 pagesCarbon Cycleisaac.lemer2No ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument15 pagesCarbon CycleVaishnavi Kalantri100% (1)
- Name: Swagato Das Student ID: 181001102011 Subject: EVS AssignmentDocument5 pagesName: Swagato Das Student ID: 181001102011 Subject: EVS AssignmentAnkush HalderNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle: Lecture 6.. 2nd Term 2023Document33 pagesCarbon Cycle: Lecture 6.. 2nd Term 2023Adam Saeed FNo ratings yet
- Microbiological DiversityDocument30 pagesMicrobiological DiversityAndrew SalazarNo ratings yet
- Global Carbon Cycle Project: ENGR 3520Document18 pagesGlobal Carbon Cycle Project: ENGR 3520wrona2983No ratings yet
- The Oxygen Cycle and The Carbon Dioxide CycleDocument3 pagesThe Oxygen Cycle and The Carbon Dioxide Cyclevincent gavinNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle2Document2 pagesCarbon Cycle2The King studioNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument16 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesMadeline Castro PangilinanNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument8 pagesThe Carbon Cycleapi-287827705No ratings yet
- Bio-Geo-Chemical CycleDocument24 pagesBio-Geo-Chemical CycleGovind rajgorNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument12 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesFazilaNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles: Dhruv Rawat Ix-ADocument11 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles: Dhruv Rawat Ix-ADhruv rawatNo ratings yet
- Soil CarbonDocument3 pagesSoil CarbonNag NaniNo ratings yet
- Biogeological CyclesDocument16 pagesBiogeological CyclesMark Vincent Salcedo CardinalNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument44 pagesCarbon CycleluisianamzNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle.Document13 pagesCarbon Cycle.ayantumegerssa80No ratings yet
- Explain The Processess Involve In: (5Pts Each)Document2 pagesExplain The Processess Involve In: (5Pts Each)Anna Marie LaganzonNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument32 pagesCarbon CycleTenzin Kuenzey GyeltshenNo ratings yet
- Where Is Carbon Stored? How Does It Flow?Document5 pagesWhere Is Carbon Stored? How Does It Flow?api-351842772No ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle: Carbon Biosphere Pedosphere Geosphere Hydrosphere Atmosphere Nitrogen Cycle Water CycleDocument1 pageCarbon Cycle: Carbon Biosphere Pedosphere Geosphere Hydrosphere Atmosphere Nitrogen Cycle Water CycleJane KatigbakNo ratings yet
- The Carbon CycleDocument3 pagesThe Carbon Cycleakeem babbNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources Biogeochemical CyclesDocument4 pagesNatural Resources Biogeochemical Cyclesboris pocusNo ratings yet
- What Is Carbon Dioxide and How Is It DiscoveredDocument5 pagesWhat Is Carbon Dioxide and How Is It DiscoveredVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 Biogeochemical CyclesDocument12 pagesLec 7 Biogeochemical CyclesKhaled Hasan Khan100% (1)
- Carbon Cycle: AtmosphereDocument1 pageCarbon Cycle: AtmosphereAnggi FahrunnisaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Carbon Dioxide by Humans-Amy Lin 625Document4 pagesApplications of Carbon Dioxide by Humans-Amy Lin 625Alexis ChangNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Carbon Cycle The Greenhouse EffectDocument3 pagesWorksheet Carbon Cycle The Greenhouse Effectapi-235658421No ratings yet
- ES Lecture 6Document15 pagesES Lecture 6Erico TambanganNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document10 pagesLecture 6Naga Varshini MeenakshisundaramNo ratings yet
- Environmental SciencesDocument17 pagesEnvironmental SciencesSayan GhoshNo ratings yet
- 02.understanding Process Equipment For Operators & Engineers-65Document5 pages02.understanding Process Equipment For Operators & Engineers-65Aatish ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- Natural Biogeochemical Cycles Biogeochemical CyclesDocument2 pagesNatural Biogeochemical Cycles Biogeochemical CyclesKAINAT YASEENNo ratings yet
- CARBON CYCLE March 2, 2021Document19 pagesCARBON CYCLE March 2, 2021resita nanaNo ratings yet
- Energy & Climate Change - Lect-6 (28.09.2021)Document25 pagesEnergy & Climate Change - Lect-6 (28.09.2021)humza abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle DiagramDocument3 pagesCarbon Cycle DiagramRommel Villaroman EstevesNo ratings yet
- Uses of Oxygen: Nitrogen CycleDocument7 pagesUses of Oxygen: Nitrogen CycleSyed Sulman SheraziNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Siklus KarbonDocument13 pagesJurnal Siklus KarbonKhina ChyaNkk Khirah100% (1)
- Terjemah Karya Tulis RIKADocument17 pagesTerjemah Karya Tulis RIKAKeyla AishaNo ratings yet
- Earths Cycles (Lecture 06) - Part 02Document39 pagesEarths Cycles (Lecture 06) - Part 02Binthan RamzeeniNo ratings yet
- Climate Change & Carbon Sequestration: What Is Global Warming?Document3 pagesClimate Change & Carbon Sequestration: What Is Global Warming?ShaunnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 29 MooKitDocument12 pagesLecture 29 MooKitsumanaditya2022No ratings yet