0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views23 pagesIntroduction To Manufacturing Process
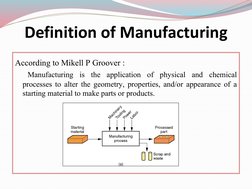
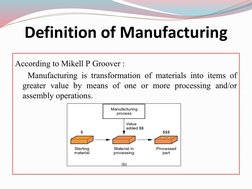
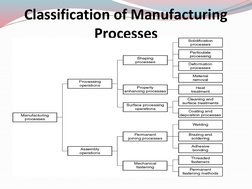
The document provides an overview of manufacturing processes. It defines manufacturing as the process of converting raw materials into products, which includes design, material selection, and the manufacturing sequence. Manufacturing processes transform raw materials through steps like treating, machining, and reshaping materials. Key processes discussed include subtractive processes like milling; additive processes like welding; continuous processes like extrusion; and net shape processes like casting. The document also outlines basic manufacturing processes like casting, forming, machining, joining and assembly, and rapid prototyping.
Uploaded by
Gan Chong YaoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views23 pagesIntroduction To Manufacturing Process
The document provides an overview of manufacturing processes. It defines manufacturing as the process of converting raw materials into products, which includes design, material selection, and the manufacturing sequence. Manufacturing processes transform raw materials through steps like treating, machining, and reshaping materials. Key processes discussed include subtractive processes like milling; additive processes like welding; continuous processes like extrusion; and net shape processes like casting. The document also outlines basic manufacturing processes like casting, forming, machining, joining and assembly, and rapid prototyping.
Uploaded by
Gan Chong YaoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd