Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9.5 Notes B - Vertex Form
Uploaded by
Charlie Williamson0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesThe document discusses the vertex form of a quadratic equation. It explains that the standard form is y = ax2 + bx + c, while the vertex form is y = (x - h) + k, where (h, k) is the vertex. It provides examples of completing the square to write quadratic equations in vertex form and find the vertex. Students are given practice problems to determine the vertex by writing quadratic functions in vertex form.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the vertex form of a quadratic equation. It explains that the standard form is y = ax2 + bx + c, while the vertex form is y = (x - h) + k, where (h, k) is the vertex. It provides examples of completing the square to write quadratic equations in vertex form and find the vertex. Students are given practice problems to determine the vertex by writing quadratic functions in vertex form.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pages9.5 Notes B - Vertex Form
Uploaded by
Charlie WilliamsonThe document discusses the vertex form of a quadratic equation. It explains that the standard form is y = ax2 + bx + c, while the vertex form is y = (x - h) + k, where (h, k) is the vertex. It provides examples of completing the square to write quadratic equations in vertex form and find the vertex. Students are given practice problems to determine the vertex by writing quadratic functions in vertex form.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
9-5 Notes B Algebra
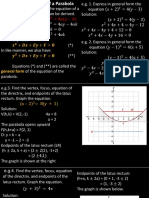
Vertex Form of a Quadratic Equation
Standard form of a parabola: y = ax2 + bx + c
Vertex form of a parabola: 𝑦 = (𝑥 − ℎ) + 𝑘 where (h, k) is the vertex.
Example 1 – Finding the VERTEX of a parabola by completing the square.
Find the vertex of the parabola: 𝒚 = 𝒙𝟐 + 𝟔𝒙 + 𝟖
Step 1: Isolate both x2 and bx terms on one side of the equal sign.
Step 2: Complete the square by finding (b/2)2 .
Step 3: Add this number both sides of the equation.
Step 4: Factor the perfect-square trinomial.
Step 5: Solve for y to put into vertex form.
Step 6: Determine the vertex (h, k). *Note: Use opposite sign for h.
You Try: Find the vertex of the following quadratic functions:
a.) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 4𝑥 + 10 b.) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 12𝑥 + 34
Practice:
Determine the coordinates of the vertex of the parabola by writing the equation in vertex form.
1. y = x2 + 10x + 7 2. y = x2 + 6x – 3 3. y = x2 – 4x + 12
4. y = x2 + 6x + 2 5. y = x2 + 2x – 5 6. y = x2 – 8x – 1
7. y = x2 + 20x + 30 8. y = x2 - 12x – 7 9. y = x2 – 16x + 10
Hint for #10,11, and 12: Divide each term by the GCF first.
10. 2y = 2x2 + 8x + 6 11. 3y = 3x2 + 6x – 3 12. -y = -x2 – 6x + 2
You might also like
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- 9.5 Notes B - Vertex FormDocument2 pages9.5 Notes B - Vertex FormCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Math Las G9 Q1 WK1 PDFDocument29 pagesMath Las G9 Q1 WK1 PDFJezreel TanNo ratings yet
- Math-9 Q1 Sept.-6Document25 pagesMath-9 Q1 Sept.-6James Kevin MarananNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Homework 3Document1 pagePrecalculus Homework 3Mr OrrNo ratings yet
- Translating Conic SectionsDocument15 pagesTranslating Conic SectionsNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Hand-Outs in MATH 9Document9 pagesHand-Outs in MATH 9Lee EspeletaNo ratings yet
- Study Paper of 2Nd Year Mathematics: UNDER THE SUPERVISION of Professors & LecturersDocument2 pagesStudy Paper of 2Nd Year Mathematics: UNDER THE SUPERVISION of Professors & LecturersDanish Naeem BhattiNo ratings yet
- Math 9 ReviewerDocument23 pagesMath 9 ReviewerLorica John LuisNo ratings yet
- AT-4e Chapter 1 FormsDocument27 pagesAT-4e Chapter 1 FormsmgestaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 TestDocument6 pagesChapter 3 TestJose SegalesNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Graphing Solving QuadraticsDocument14 pagesUnit 8 Graphing Solving Quadraticsapi-310051256No ratings yet
- Quadratics Worksheet Sept 2017 QDocument8 pagesQuadratics Worksheet Sept 2017 QnatalieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 TestDocument16 pagesChapter 4 TestKloe-Rose LemmonNo ratings yet
- Ch10 The Quadratic FunctionDocument36 pagesCh10 The Quadratic Functiontrantuanan123No ratings yet
- m9 - Week 1 - Quadratic Equations. - Module 2pptxDocument32 pagesm9 - Week 1 - Quadratic Equations. - Module 2pptxprilyn albaricoNo ratings yet
- Math First Periodical ReviewerDocument3 pagesMath First Periodical Reviewerluluhbelle cruzNo ratings yet
- 524.higher Maths Assnmt1 Jan-June 2021Document5 pages524.higher Maths Assnmt1 Jan-June 2021joseph.kabaso96No ratings yet
- Revision Quadratic Equations Challenging: A) X X B) X XDocument5 pagesRevision Quadratic Equations Challenging: A) X X B) X XStijn WinkelerNo ratings yet
- Maths in Focus - Margaret Grove - ch9Document34 pagesMaths in Focus - Margaret Grove - ch9Sam Scheding0% (1)
- How To Identify Conic Sections PDFDocument31 pagesHow To Identify Conic Sections PDFkaskaraitNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Functions: A A Shape ParameterDocument8 pagesQuadratic Functions: A A Shape ParameterAna Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Q1 W4 LAS4 Vertex FormDocument7 pagesQ1 W4 LAS4 Vertex FormCraig Dale B. GriponNo ratings yet
- Aga A1 0905 ApDocument1 pageAga A1 0905 Apdeepaksharma1976No ratings yet
- L3 Algebra Class 3Document9 pagesL3 Algebra Class 3nie leonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1a TestDocument2 pagesChapter 1a Testspeterlee6253No ratings yet
- Quadratic Functions and Equations in One Variable: Form 4 MathsDocument16 pagesQuadratic Functions and Equations in One Variable: Form 4 MathsGGy Joe YeeNo ratings yet
- Nichols School Mathematics Department Summer Work AssignmentDocument5 pagesNichols School Mathematics Department Summer Work AssignmentVladanNo ratings yet
- Vedantu Telugu Jee Channel Kiran Sir Maths: Section-ADocument2 pagesVedantu Telugu Jee Channel Kiran Sir Maths: Section-Akc802220No ratings yet
- Worksheet No.1-Quadratic EquationDocument4 pagesWorksheet No.1-Quadratic EquationGeneroso SiaNo ratings yet
- 9-2 Solving Quadratic Equaions by GraphingDocument27 pages9-2 Solving Quadratic Equaions by GraphingJojie CastilloNo ratings yet
- ch10 PDFDocument36 pagesch10 PDFcathyNo ratings yet
- SIM GeometryDocument11 pagesSIM GeometryJashey Dee83% (6)
- Module 2 Conics NotesDocument8 pagesModule 2 Conics NotesFons Roxas-ChuaNo ratings yet
- Graph of Quadratic FunctionDocument66 pagesGraph of Quadratic FunctionMxllowsNo ratings yet
- Aga A2 0205 ApDocument1 pageAga A2 0205 Apdeepaksharma1976No ratings yet
- Mathematics 9 - Quadratic Equation ReviewerDocument3 pagesMathematics 9 - Quadratic Equation ReviewerJames Russel MariNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICSDocument11 pagesMATHEMATICSTEMIDIRE OLAYINKANo ratings yet
- Maths Sa1 Sp2Document15 pagesMaths Sa1 Sp2Shivam PandeyNo ratings yet
- ps42 n3cs19 SDocument2 pagesps42 n3cs19 Sapi-234377298No ratings yet
- Quadratics Lecture NotesDocument13 pagesQuadratics Lecture NotesKaness Mathz100% (1)
- Completing The Square 2019Document10 pagesCompleting The Square 2019Amie S. BabieraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1, Part 2 Chapter 4: Quadratic EquationsDocument16 pagesUnit 1, Part 2 Chapter 4: Quadratic EquationsZlata OsypovaNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document14 pagesWeek 1Rizza Mae ReponteNo ratings yet
- 18 Quadratic EquationsDocument9 pages18 Quadratic EquationsShyam PatelNo ratings yet
- Test 7ADocument6 pagesTest 7AJasmina Angelevska KostadinoskaNo ratings yet
- Elimination Round QuestionsDocument2 pagesElimination Round QuestionsAnie BrabangcoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Notes Gr.11Document59 pagesMathematics Notes Gr.11iyermagsNo ratings yet
- Parabola 3Document6 pagesParabola 3Aly FayeNo ratings yet
- Maths Final Revision PDFDocument56 pagesMaths Final Revision PDFKishori KumariNo ratings yet
- MATH 9 Q1 Week 7 Module 7A Riza SibayanDocument15 pagesMATH 9 Q1 Week 7 Module 7A Riza Sibayanjojo diazNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Quarter 1Document34 pagesMath 9 Quarter 1Janinne Villa Del Rey100% (1)
- Chap 6Document24 pagesChap 6Dawood MNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Revision Maths Final Exam Term 1Document5 pagesGrade 8 Revision Maths Final Exam Term 1Ria MandasariNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 9 August 8Document3 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics 9 August 8Reynaldo Billones100% (2)
- 12 Maths Mission 100% (2marks)Document10 pages12 Maths Mission 100% (2marks)Jagdev SinghNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Lesson 1 Quadratic EquationDocument15 pagesMath 9 Lesson 1 Quadratic EquationJosielyn ValladolidNo ratings yet
- Slope of A Line Given EquationDocument4 pagesSlope of A Line Given EquationJohn PaulNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Functions: A A Shape ParameterDocument8 pagesQuadratic Functions: A A Shape ParameterMuhammad Syarif100% (1)
- Sharn Inquisitive: at The Mercy of MercenariesDocument1 pageSharn Inquisitive: at The Mercy of MercenariesCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- First Law of MotionDocument2 pagesFirst Law of MotionCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Sharn Inquisitive: Noble-Napped! Abducted Aristocrat Found!Document1 pageSharn Inquisitive: Noble-Napped! Abducted Aristocrat Found!Charlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Philosopher - ClassesDocument5 pagesPhilosopher - ClassesCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- #06 World's Fastest AntsDocument3 pages#06 World's Fastest AntsCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Atavist, Fourth DraftDocument13 pagesAtavist, Fourth DraftCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Military Leaders: Tecumseh: Early LifeDocument3 pagesMilitary Leaders: Tecumseh: Early LifeCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Light On A Clear Blue Morning SATBDocument9 pagesLight On A Clear Blue Morning SATBCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- The Economy and You: Unit 1Document18 pagesThe Economy and You: Unit 1Charlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Step 3 Sources - Women in The 1950sDocument4 pagesStep 3 Sources - Women in The 1950sCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 REVIEW: Name Class DateDocument4 pagesChapter 9 REVIEW: Name Class DateCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Eberron Mood Kits - ThraneDocument16 pagesEberron Mood Kits - ThraneCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- T3-8.3 Trig Intro SohcahtoaDocument2 pagesT3-8.3 Trig Intro SohcahtoaCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Givens:: Matching-Statements and ReasonsDocument2 pagesGivens:: Matching-Statements and ReasonsCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Lesson 1a - SegmentsDocument3 pagesUnit 2-Lesson 1a - SegmentsCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Lesson 1a - Segments - Worksheet: Geometry HonorsDocument2 pagesUnit 2-Lesson 1a - Segments - Worksheet: Geometry HonorsCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- 2 A R R A R R A R Ra A A A A Ar: 1 R R R 4 A A R R R R A A A R RDocument1 page2 A R R A R R A R Ra A A A A Ar: 1 R R R 4 A A R R R R A A A R RCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Eberron Mood Kits - The MournlandDocument18 pagesEberron Mood Kits - The MournlandCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Eberron Mood Kits - The MournlandDocument18 pagesEberron Mood Kits - The MournlandCharlie WilliamsonNo ratings yet