Professional Documents
Culture Documents
17 - Technology and Innovation Report 2021
Uploaded by
Aprndz AprendizCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
17 - Technology and Innovation Report 2021
Uploaded by
Aprndz AprendizCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER II
Forging ahead at the digital frontiers
There is no single definition of frontier technologies, but they are generally understood to be new
and rapidly developing technologies that take advantage of digitalization and connectivity. These
technologies can have dramatic impacts on economies and societies as well as on the development
of other technologies.1 This report covers 11 such technologies: artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet
of things (IoT), big data, blockchain, 5G, 3D printing, robotics, drones, gene editing, nanotechnology
and solar photovoltaic (Solar PV) (Table II 1). Most of these technologies have emerged in a period of
dramatic falls in the prices of data storage and solar energy.2
Frontier technologies can increase productivity and improve livelihoods.3 AI, for example, combined
with robotics can transform production and business. 3D printing allows faster and cheaper
low-volume production and rapid iterative prototyping of new products. Using these and other
innovations, enterprises in developing countries can leapfrog previous paradigms and move ahead
rapidly.4 Despite low resources and capabilities, many firms and farms are already doing so. In Nigeria,
for example, IoT is being used to generate advice on farming techniques. And in Colombia 3D printers
are being used to create fashion items such as caps, bracelets, and dresses.5 6
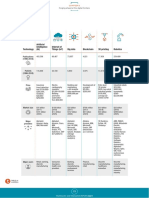
Table II 1
Frontier technologies covered in this report
Technology Description
Artificial AI is normally defined as the capability of a machine to engage in cognitive activities typically performed
intelligence (AI) by the human brain. AI implementations that focus on narrow tasks are widely available today, used for
example, in recommending what to buy next online, for virtual assistants in smartphones, and for spotting
spam or detecting credit card fraud. New implementations of AI are based on machine learning and
harness big data.
Internet of Things IoT refers to myriad Internet-enabled physical devices that are collecting and sharing data. There is a vast
(IoT) number of potential applications. Typical fields include wearable devices, smart homes, healthcare, smart
cities and industrial automation.
Big data Big data refers to datasets whose size or type is beyond the ability of traditional database structures to
capture, manage and process. Computers can thus tap into data that has traditionally been inaccessible
or unusable.
Blockchain A blockchain refers to an immutable time-stamped series of data records supervised by a cluster of
computers not owned by any single entity. Blockchain serves as the base technology for cryptocurrencies,
enabling peer-to-peer transactions that are open, secure and fast.
5G 5G networks are the next generation of mobile internet connectivity, offering download speeds of around
1-10 Gbps (4G is around 100 Mbps) as well as more reliable connections on smartphones and other devices.
3D printing 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, produces three-dimensional objects based on a digital
file. 3D printing can create complex objects using less material than traditional manufacturing.
Robotics Robots are programmable machines that can carry out actions and interact with the environment via sensors
and actuators either autonomously or semi-autonomously. They can take many forms: disaster response
robots, consumer robots, industrial robots, military/security robots and autonomous vehicles.
Drones A drone, also known as unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) or unmanned aircraft systems (UAS), is a flying
robot that can be remotely controlled or fly autonomously using software with sensors and GPS. Drones
have been often used for military purposes, but they also have civilian uses such as in videography,
agriculture and in delivery services.
Gene editing Gene editing, also known as genome editing, is a genetic engineering tool to insert, delete or modify the
genome in organisms. Potential applications include drought-tolerant crops or new antibiotics.
Nanotechnology Nanotechnology is a field of applied science and technology dealing with the manufacturing of objects in
scales smaller than 1 micrometre. Nanotechnology is used to produce a wide range of useful products
such as pharmaceuticals, commercial polymers and protective coatings. It can also be used to design of
computer chip layouts.
Solar photovoltaic Solar photovoltaic (Solar PV) technology transforms sunlight into direct current electricity using
(Solar PV) semiconductors within PV cells. In addition to being a renewable energy technology, solar PV can be used
in off-grid energy systems, potentially reducing electricity costs and increasing access.
Source: UNCTAD.
TABLE OF
CONTENT
17
TECHNOLOGY AND INNOVATION REPORT 2021
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Credit Card Generator & Validator - Valid Visa Numbers - CardGuruDocument8 pagesCredit Card Generator & Validator - Valid Visa Numbers - CardGuruRahul Singh BhatiNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- PaascheAirbrushCat 2014 PDFDocument24 pagesPaascheAirbrushCat 2014 PDFDavid ZimmermanNo ratings yet
- Creating Instructional Materials: Learning TaskDocument13 pagesCreating Instructional Materials: Learning TaskMike jeron martinez50% (2)
- 9 - Proteção em Redes Ópticas ElásticasDocument9 pages9 - Proteção em Redes Ópticas ElásticasAprndz AprendizNo ratings yet
- 18 - Technology and Innovation Report 2021Document1 page18 - Technology and Innovation Report 2021Aprndz AprendizNo ratings yet
- 23 - Technology and Innovation Report 2021Document1 page23 - Technology and Innovation Report 2021Aprndz AprendizNo ratings yet
- 135 - Technology and Innovation Report 2021Document1 page135 - Technology and Innovation Report 2021Aprndz AprendizNo ratings yet
- Tab Comp PONDocument3 pagesTab Comp PONAprndz AprendizNo ratings yet
- SIEPON Alignment With SIEPON Alignment With Broadband Forum Requirements Broadband Forum Requirements Q QDocument23 pagesSIEPON Alignment With SIEPON Alignment With Broadband Forum Requirements Broadband Forum Requirements Q QAprndz AprendizNo ratings yet
- P O N S: Assive Ptical EtworkDocument94 pagesP O N S: Assive Ptical EtworkAprndz AprendizNo ratings yet
- IEEE 1904.1 (SIEPON) Architecture and Model: Marek Hajduczenia ZTE CorporationDocument15 pagesIEEE 1904.1 (SIEPON) Architecture and Model: Marek Hajduczenia ZTE CorporationAprndz AprendizNo ratings yet
- Smith Chart: © Copr. 1949-1998 Hewlett-Packard CoDocument16 pagesSmith Chart: © Copr. 1949-1998 Hewlett-Packard CoAlessandro VinassaNo ratings yet
- QW-QAL-626 - (Rev-00) - Prod. and QC Process Flow Chart - Ventura Motor No. 13 (35804)Document6 pagesQW-QAL-626 - (Rev-00) - Prod. and QC Process Flow Chart - Ventura Motor No. 13 (35804)Toso BatamNo ratings yet
- Gloucester MT Extra Condensed (TrueType)Document1 pageGloucester MT Extra Condensed (TrueType)dgw0512No ratings yet
- Chap 2 Linux Sysadmin Part 3 Users and Group Management Students VersionDocument11 pagesChap 2 Linux Sysadmin Part 3 Users and Group Management Students VersionniccinchamiNo ratings yet
- Steps For Signing Up On The NGO-DARPAN Portal New UserDocument1 pageSteps For Signing Up On The NGO-DARPAN Portal New UserGaurav TiwariNo ratings yet
- Ydflp-6 V1Document26 pagesYdflp-6 V1Info PLSNo ratings yet
- ABB Ellipse APM Edge - BrochureDocument8 pagesABB Ellipse APM Edge - BrochureCarlos JaraNo ratings yet
- Siddu SeminarDocument19 pagesSiddu SeminarVenkat SaiNo ratings yet
- Asrat Simru AppDocument36 pagesAsrat Simru Apptadiso birkuNo ratings yet
- RTIRDocument19 pagesRTIRHatem GharbiNo ratings yet
- Light Is Life: Osram PlantastarDocument2 pagesLight Is Life: Osram Plantastardingeo11No ratings yet
- Frameless Snubbing UnitDocument16 pagesFrameless Snubbing UnitDean ReinNo ratings yet
- Airways - Multilateration Phase I Gen PDFDocument18 pagesAirways - Multilateration Phase I Gen PDFmavv5455No ratings yet
- Quotation: Sinoma Science & Technology (Chengdu) Co., LTDDocument1 pageQuotation: Sinoma Science & Technology (Chengdu) Co., LTDjuan alarconNo ratings yet
- Vivid E95: Patient Care. ElevatedDocument5 pagesVivid E95: Patient Care. Elevatedfarouk beNo ratings yet
- Module 6: Influence Lines Lecture 5: Müller-Breslau PrincipleDocument4 pagesModule 6: Influence Lines Lecture 5: Müller-Breslau Principlevenkat27081995No ratings yet
- The Innovation Management of Microsoft: Submitted byDocument16 pagesThe Innovation Management of Microsoft: Submitted byCarolina Moncada ValderramaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document71 pagesLecture 2Bandar AlmaslukhNo ratings yet
- Catalogo PistonesDocument196 pagesCatalogo PistonesalexjoseNo ratings yet
- Eaap Module 2Document4 pagesEaap Module 2Kyzer GaliNo ratings yet
- Iu-At-137 - Iii - Eng Aspel 308 AbpmDocument37 pagesIu-At-137 - Iii - Eng Aspel 308 AbpmEla MihNo ratings yet
- 6 RedHatDocument20 pages6 RedHatkoenjavaNo ratings yet
- B - Namrata Karuna - Mit Chandya U21172 - Kalyan Mudris U21064Document8 pagesB - Namrata Karuna - Mit Chandya U21172 - Kalyan Mudris U21064Mit ChandyaNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Taylor & Francis Author Template Microsoft Word Mac 2008Document3 pagesInstructions For Taylor & Francis Author Template Microsoft Word Mac 2008samuel mechNo ratings yet
- Yealink W70B DECT IP Phone Release Notes of Version 85Document9 pagesYealink W70B DECT IP Phone Release Notes of Version 85tristan.zfrNo ratings yet
- Resume ScreeningDocument5 pagesResume Screeningafmrokptolziea100% (1)
- PSS Inv Manual 2020Document1,117 pagesPSS Inv Manual 2020ArifAzriNo ratings yet