Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Historical Background (Not Completed)
Uploaded by
Paopao Macalalad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Historical Background(not completed)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesHistorical Background (Not Completed)
Uploaded by
Paopao MacalaladCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Historical Background
(https://infectious-diseases-and-treatment.imedpub.com/antibacterial-effect-of-garlic-allium-
sativumagainst-clinical-isolates-of-staphylococcusaureus-and-escherichia-coli-from-patientsa.php?
aid=17777) In the study conducted by Abiy, Ephrem, and Berhe, Asefaw in 2016, in today’s generation,
the use of higher plants and preparations from them to treat infections is an age-old practice. Interests in
plants with antimicrobial properties have come to use again because of the emergence of resistant strains
against antimicrobials.
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3874089/) As stated in the study of Aghajanshakeri et al
in 2013, Garlic(Allium sativum) is under the family Liliaceae, like mountain onion and shallot, and also
has antibacterial activity against many common pathogenic bacteria. Garlic is a hardy perennial member
of the onion family. Studies explain that it may be originally native to Asia, but has long been naturalized
to Europe northern Africa, Mexico, and all over the world. It is an erect annual herb with superficial
adventitious roots, bulbs composed of a disk-like stem.
(https://openventio.org/wp-content/uploads/Therapeutic-Value-of-Garlic-Allium-sativum-A-Review-
AFTNSOJ-5-162.pdf) These chemicals were used for the treatment of inflammation, cancer, blood
pressure, atherosclerosis, and hyperlipidemia as praised by several authors. Additionally, extracts of
garlic have been used to treat various diseases and have shown anti-viral, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal,
anticoagulative, and antioxidant effects. However, few adverse effects have been found with garlic are
nausea and vomiting when a high quantity is consumed.
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3249897/#ref3) According to the study conducted by
Cekovska, Svetlana and Petrovska, Biljana Bauer in 2010,Garlic is nicknamed as Russian penicillin due
to its widespread use as a topical and systemic antimicrobial agent; it is commonly used in many cultures
as excitement and reputation of healing power. Most of its prophylactic and therapeutic effects are
ascribed to specific oil- and water-soluble organosulfur compounds, which are responsible for the typical
odor and flavor of garlic (Block, 1985). During crushing or cutting of the clove, the odorless amino acid
alliin, present in the garlic clove, is metabolized by the enzyme alliinase (a cysteine sulfoxide lyase) to
yield allicin and other thiosulfinates that are the source of the characteristic odor of garlic. Thiosulfinates
and other secondary metabolites of garlic, including 7-glutamyl peptides, scordinins, steroids, terpenoids,
flavonoids, and other phenols, may be responsible for the range of therapeutic effects reported for garlic.
Reuter et al. (1996) recently reviewed the therapeutic effects of garlic, namely, effects on the
cardiovascular system, antibiotic, anticancer, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory,
hypoglycemic, and hormone-like effects.
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4103721/) As stated in the study of Bayan,
Leyla, Gorji, Ali Koulivand, and Peir Hossain in 2014,Garlic has antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, and
antiseptic properties from allicin. Allicin is the main biologically and biochemically active component of
freshly crushed garlic which can easily be decomposed under the influence of heat and time into stable
compounds. 2-propenesulfenic acid and tioacrolein are two important molecules derived from garlic,
which in turn result in the formation of greater molecules including diallyl trisulfide and dithiin.
Generally, garlic is a potent antibiotic and shows an effective performance against the bacteria resistant to
pharmaceutical antibiotics. Garlic also has thiosulfinates, which can act as an antimicrobial.
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4103721/) According to the study of Avicenna J
Phytomed in 2014, it has been reported that fresh garlic ingestion or intravenous preparation of its
extracts is used to treat various viral infections or cryptococcal meningitis patients, respectively, in China
(Tsai et al., 1985). In Asia and Europe, garlic is used to treat the common cold, fever, coughs, asthma, and
wounds (Rehman et al., 2019). Garlic oil has also been used to relieve pain due to ear infections (Al
Abbasi, 2008). Garlic has been used in African traditional medicine, such as in Ethiopia and Nigeria, to
treat several infections including sexually transmitted diseases, tuberculosis, respiratory tract infection,
and wounds (Abiy & Asefaw, 2016; Gebreyohannes & Mebrahtu, 2013). Garlic has been reported to have
antiviral activity against human, animal, and plant viral infections. Further, randomized clinical trials on
different commercial garlic preparations also showed that garlic plays a significant therapeutic role in
various viral infections such as cold and flu, viral-induced hepatitis, viral-associated warts, as well as
immune-enhancing activity in viral infected patients. The proposed mechanism of their antiviral activity
was reported to be the inhibition of the viral cell cycle, enhancing host immune response or reduction of
cellular oxidative stress.
(https://www.globalsafe.com.au/what_are_disinfectants.php) Based from Global Safe Technology
Australia, disinfectants are chemical substances used to destroy viruses and microbes (germs), such as
bacteria and fungi, as opposed to an antiseptic which can prevent the growth and reproduction of various
microorganisms, but does not destroy them. The ideal disinfectant would offer complete sterilization,
without harming other forms of life, be inexpensive, and non-corrosive. Unfortunately ideal disinfectants
do not exist. Many disinfectants are only able to partially sterilize. The most resistant pathogens are
bacteria spores but some viruses and bacteria are also highly resistant to many disinfectants.
Disinfection is the process of eradicating pathogens on the environmental surfaces, reusable medical
devices and other inanimate objects. It can be accomplished by using chemical or physical agents.
Increasing clinical evidences have shown proper disinfection able to disrupt the transmission pathways.
Those evidence based infection prevention studies warrants the importance of proper disinfection of
environmental surfaces.
(https://www.globalsafe.com.au/what_are_disinfectants.php) Based from Global Safe Technology
Australia, all disinfectants are also, by their very nature, potentially harmful (even toxic) to humans or
animals. They should be treated with appropriate care. Most come with safety instructions printed on the
packaging, which should be read in full before using the disinfectant. Most modern household
disinfectants contain Bitrex, an exceptionally bitter substance designed to discourage ingestion, as an
added safety measure. Those that are used in people's homes should never be mixed with other cleaning
products as chemical reactions can occur. They are frequently used in hospitals, dental surgeries, kitchens
and bathrooms to kill infectious organisms.
The proper use of disinfectants can help contain and prevent the spread of harmful bacteria and viruses.
Many infectious diseases can be halted in their tracks by the proper use of disinfectant products, and by
the routine disinfection. To minimise number of organisms in the population worldwide. The method of
disinfection is used internationally for the safety of humans, to decrease the scale of transmission of
diseases. A large emphasis of sterilisation and disinfection has been placed in the food industry, water
sanitisation and medical care and hospitals. As these have found to be largest affected organisations with
microorganisms and modes of transmission amongst the population.
Garlic is a powerful remedy to protect against infections of many bacteria, fungi, and viruses, using garlic
extract as an alternative disinfectant or chemical agents designed to inactivate or destroy microorganisms
on inert surfaces will be effective since it was a given that it can kill and reduce viruses and
microorganism. The aim of the study is to help citizens to understand the components of the garlic that
helps in reducing viruses, this research will also allow them to utilize the extract of this everyday spice
that can be found in every kitchen or household, to be used as an alternative disinfectant in a very
straightforward and simple way. It will also save people money from buying expensive disinfectant since
the materials that will be needed will not cause that much. Since store-bought disinfectants have a smell
that some people don't prefer, this research will help them create their disinfectant in their preferred scent.
It will make people feel safe from their environment and from the things they will or they are touching
especially during a pandemic.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Diseases WorksheetDocument3 pagesDiseases Worksheetapi-408461912No ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension: Know Protective MeasuresDocument3 pagesReading Comprehension: Know Protective MeasuresMauricio Bellido50% (2)
- What Is Science?: The Nature of ScienceDocument15 pagesWhat Is Science?: The Nature of SciencePaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Communication and GlobalizationDocument6 pagesCommunication and GlobalizationPaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Key Terms: Pambansang Alagad NG Sining NG Pilipinas (Philippine National Artists)Document110 pagesKey Terms: Pambansang Alagad NG Sining NG Pilipinas (Philippine National Artists)Paopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere 3.1Document22 pagesAtmosphere 3.1Paopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Motivations For Participation in Physical Activity Across The LifespanDocument16 pagesMotivations For Participation in Physical Activity Across The LifespanPaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Smartphone Use During The COVID-19 Pandemic: Social Versus Physical DistancingDocument8 pagesSmartphone Use During The COVID-19 Pandemic: Social Versus Physical DistancingPaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Body Fluids: Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and AnimalsDocument16 pagesRegulation of Body Fluids: Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and AnimalsPaopao Macalalad100% (4)
- Methodology Research Design: Table 1. Amount of Garlic Extract Present in The Alternative DisinfectantDocument14 pagesMethodology Research Design: Table 1. Amount of Garlic Extract Present in The Alternative DisinfectantPaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- IV. Target Customers and The Main Value Proposition To The CustomersDocument2 pagesIV. Target Customers and The Main Value Proposition To The CustomersPaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow 123Document1 pageCash Flow 123Paopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Conceptual FrameworkDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Conceptual FrameworkPaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
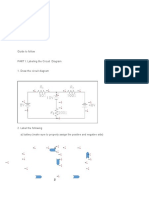
- Solve For I1, I2, and I3: Jan Paolo M. Macalalad 12-NarraDocument7 pagesSolve For I1, I2, and I3: Jan Paolo M. Macalalad 12-NarraPaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Department Sy: 2019-2020Document26 pagesSenior High School Department Sy: 2019-2020Paopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Coping With Alcoholic ParentsDocument11 pagesCoping With Alcoholic ParentsPaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Pe 2Document5 pagesPe 2Paopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 DraftDocument6 pagesChapter 3 DraftPaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- RESEARCHDocument31 pagesRESEARCHPaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Green Holiday TipsDocument12 pagesGreen Holiday TipsPaopao Macalalad67% (3)
- Reading and Writing Lesson 4 3Document31 pagesReading and Writing Lesson 4 3Paopao Macalalad100% (1)
- Activity 8: Reason OutDocument1 pageActivity 8: Reason OutPaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Summary of Findings and RecommendationsDocument5 pagesSummary of Findings and RecommendationsPaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Materia Medica Sanum PDFDocument354 pagesMateria Medica Sanum PDFPaulo de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- AQA Immunity BookletDocument7 pagesAQA Immunity Bookletsu966No ratings yet
- Bacteria Concepts Practice BookletDocument7 pagesBacteria Concepts Practice BookletEli GlassNo ratings yet
- 04 Thinking Outside of AgriTech - Amy Romaniuk Innovate UK KTNDocument12 pages04 Thinking Outside of AgriTech - Amy Romaniuk Innovate UK KTNlucy.hughesNo ratings yet
- LegionellaDocument13 pagesLegionellaBam ManNo ratings yet
- Medical AsepsisDocument16 pagesMedical AsepsisAnita Mann0% (1)
- Mep Cover Infected - Indd 1 19/10/11 12:12:38Document32 pagesMep Cover Infected - Indd 1 19/10/11 12:12:38ZMGNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project - Viral Diseases PDFDocument14 pagesBiology Investigatory Project - Viral Diseases PDFNishita0% (1)
- Trans-Savi-Med2-Lec 28-Introduction-to-Infectious-Diseases-1st-SemesterDocument7 pagesTrans-Savi-Med2-Lec 28-Introduction-to-Infectious-Diseases-1st-SemesterAdrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Fall IllDocument8 pagesWhy Do We Fall IllSukhda TrivediNo ratings yet
- Book Slides Managing Epidemic WHODocument255 pagesBook Slides Managing Epidemic WHOAatif HussainNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and ZoonosesDocument149 pagesEpidemiology and ZoonosesAbhijith SP100% (1)
- Human Health and Disease Practice TestDocument11 pagesHuman Health and Disease Practice TestIndu YadavNo ratings yet
- Tutorials 20156Document6 pagesTutorials 20156Everton KingNo ratings yet
- Natural History of DiseaseDocument31 pagesNatural History of Diseasegabo dasNo ratings yet
- HKDSE Biology Part 3 Health & DiseasesDocument17 pagesHKDSE Biology Part 3 Health & DiseasesTSZ YAN CHEUNGNo ratings yet
- Avenue of Penetration by Plant PathogenDocument8 pagesAvenue of Penetration by Plant Pathogenshyamsunder68100% (1)
- Advanced Crop Protection Hand-OutsDocument21 pagesAdvanced Crop Protection Hand-OutsDaphne Cuaresma100% (1)
- Measures and Effective Methods of Treatment Against Ichthyobodosis (Costiosis) Disease of FishDocument4 pagesMeasures and Effective Methods of Treatment Against Ichthyobodosis (Costiosis) Disease of FishAcademic JournalNo ratings yet
- CMMC Case Invasive Fungal Infections Identification Matters Fusarium 3Document11 pagesCMMC Case Invasive Fungal Infections Identification Matters Fusarium 3kaseera musaNo ratings yet
- DENR - Proper Handling of Hazardous WasteDocument16 pagesDENR - Proper Handling of Hazardous WasteNisha HernandezNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Farming of The Mealworm Tenebrio Molitor For The Production of Food and FeedDocument13 pagesSustainable Farming of The Mealworm Tenebrio Molitor For The Production of Food and Feedraziel alvarezNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of Insects and Vertebrate PestsDocument10 pagesPathogens of Insects and Vertebrate PestsRozele RomNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 18 MicrobiologyDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 18 MicrobiologyApryll DarlineNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia (Overview Journal)Document12 pagesPneumonia (Overview Journal)Ayu Baitul MNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Micropara LecDocument5 pagesQuiz 2 Micropara LecAbby CruzNo ratings yet
- Communicale Chaper OneDocument26 pagesCommunicale Chaper OneAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Imp. Points PathoDocument4 pagesImp. Points PathoPawan TiwariNo ratings yet