Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IM Typed Hehe
Uploaded by
Kathleen Grace Maniago0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views12 pagesOriginal Title
IM typed hehe
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views12 pagesIM Typed Hehe
Uploaded by
Kathleen Grace ManiagoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
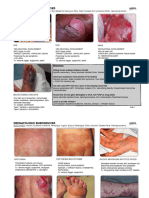
IM DERMA LUPUS VULGARIS: APPLE JELLY
ERYTHRASMA: CORAL RED
Measles (Rubeola): Koplik spots fever+rash ATOPIC DERMATITIS: Clinical features:3 or 4
sabay PCF LA(pruritus, chronic relapsing, Family hx
RUBELLA: prodrome the n rash _ atopy, location and appearance)
forscheimer spots (soft palate and uvula) SEBORRHEIC DERMATITIS: scalp eyebrows,
EXANTHEM SUBITUM: Human herpesvirus 6 nasolabial folds, side burn areas, flexural,
◊ Palpebral edema “stress”
◊ Nagayama spots(erythematous STASIS DERMATITIS:
papules in soft palate) ◊ Lesion in medial ankle (distended
◊ Exanthema: 1 before to 1-2 days vein)
after fever fades lasts for 3-5 days ◊ Bipedal edema
◊ Rose red macules or papules with IRRITANT CONTACT DERMATITIS
WHITE HALO (neck and trunk) ◊ Non-allergic inflammatory
◊ NO desquamation ◊ Irritating substance(detergents)
HERPANGINA: ERYTHRODERMA
◊ Coxsackievirus ◊ Widespread erythematous scaling
◊ Fever sorethroat headache, ab pain patches
vomiting and body aches PSORIASIS
◊ Yellow white with ◊ Red scaling
erythemaerosons on anterior ◊ Elbows and knees
pillars of tonsillar fauces(uvula, ◊ Mild: Glucocrotocids, Topical
tonsils and soft palate) ◊ Moderate to Severe: Systemics and
VARICELLA ZOSTER Biologicals, Phototherapy
◊ Facetrunk ◊ Associated ARTHRITIS AND
◊ SPARE EXTREMITIES METABOLIC SYNDROME
◊ Dewdrop on rose petal ◊ Increased risk of <3 dses
◊ Umbulicated pustule and crust NECROLYTIC MIGRATORY ERYTHEMA (NME)
HERPES ZOSTER ◊ Pancreatic glucagonoma
◊ Unilateral and along a single sensory ◊ Alpha cell
ganglion DERMATOMYOSITIS
◊ V1 ◊ Muscle weakness
◊ T3 to L2 ◊ Gottron papules: IP &/ MCP
HERPES SIMPLEX JAUNDICE: scleara and hard palate bilirubin
◊ HSV 1: orofacial SWEET SYNDROME:
◊ HSV 2: genital ◊ Red plaque on face, neck, upper
MOLLUSCUM CONTAGIOSUM trunk, extremities
◊ Molluscipoxvirus ◊ Leukocytosis
◊ Central umbilication ◊ Acute myelogenous leukemia
◊ Koebnerization ACANTHOSIS NIGRICANS
PEDICULOSIS CAPITIS ◊ Thickening of the skin induced by
◊ Scalp with nits insulin-like growth factors
◊ Itching: saliva by louse XANTHELASMA PALEBRARUM
TINEA CAPITIS ◊ associated with dyslipidemia
◊ Dermatophytosis NECROBIOSIS LIPOIDICA
Piedra: ◊ Yellowish annular plaques with
◊ Fungal, asymptomatic atrophic enter
◊ Trichomycosis ◊ Telangiectasia
◊ Pre-tibial Ampicillin
◊ Represents; degeneration of Azithro
collagen in the dermis Ceftriaxone
PEUTZ JEGHER’S Cefotaxime
◊ Multiple intestinal polyps TYPHOID
◊ Brown oval macules on lip and ◊ Blood culture 40-80%, : GOLD
buccal mucosa STANDARD FIRST WEEK OF ILLNESS
IM INFECTIOUS DISEASES ◊ Stool cultures (+) during 3rd week of
CONTACT PRECAUTIONS: skin! Poop infection,
AIRBORNE PRECAUTIONS: Measles, ◊ Bone marrow highest sensitivity,
varicella, TB, Bird flu yield NOT reduced up to 5 days Ab
DROPLET: INFLUENZA! PNEUMONIA, therapy
meningitis, pharyngitis, mumps ◊ Salmonella can be cultured from
Strongly recommended for Filipino rose spots
healthcare workers: Tdap, Hep B, Influenza, ◊ Hyperplasia, ulceration and necrosis
Varicella, MMR of ileocecal Peyer’s patches at initial
LEPTOSPIROSIS site of Salmonella infiltration
◊ Post exposure prophylaxis symptoms
Low-risk ◊ CIPROFLOXACIN: most cost effective
Single exposure ◊ Fluoroquinolones: most effective
No wounds class of agents
Doxycycline 2 caps TETANUS
100mg in 1-3 days ◊ Clostridium tetani obligate anerobic
Moderate risk gram + with mult flagellae
Single ◊ 2nd week of severe tetanus:
(+) Wounds cuts Autonomic disturbance
Doxycycline 2 caps for ◊ TETANOSPASMIN: responsible for
3-5 days clinical manifestation
High risk ◊ Culture not useful
Continuous exposure ◊ Kille dby iodine, glutaraldehyde,
Doxycycline 2 caps agua oxinada, autoclaving
once weekly until end ◊ COLE STAGING
of exposure ◊ Stage I
◊ LEPTOMAT: when negative request >14 d incbation
for repeat LEPTO MAT, increase mild/localized stiffness
sensitivity 10-12 days mild brief transient spasm
◊ Renal fxn returns to normal in ◊ Stage II
survivors 10-14 d
◊ Jaundice but no heaptic necrosis moderate trismus,
◊ *conjunctival suffusion pronounced rigidity with
◊ Treatment opisthotonus
Mild more severe and longer
Doxycycline 100mg spasms
Amox ◊ Stage III
Azithromycin <10 days
dehydrate RISUS SARDONICUS
Moderate-severe Aspiration
Pen G 1.5 MU Veretbrla fracture
Violent spasms ◊ Paralytic/dumb flaccid paralysis
SYMPATHETHIC NERVOUS ◊ 5 injections
SYSTEM OVERACTIVITY FILARIASIS
◊ Tx ◊ OBSTRUCTION: GRANULOMATOUS
◊ Prevent exotoxin and PROLIFERATIVE PROCESSES to
Aq Pen G 5M ADULT WORM (Schistosoma to egg)
Metronidazole 500 mg ◊ Big balls (big belly schistosomiasis)
◊ Tetanus immune globulin or equine SCHISTOSOMIASIS
antitoxin: neutralized unbound ◊ Onchomelania (snails)
toxins ◊ DOC Praziquantel
Syndromic approach: best and practical ◊ Symptoms from granulomatous host
Etiologic approach: ideal immune response to EGGS
GONOCOCCAL deposited In tissues
◊ N. gonorrhea ◊ Kato thick smears miss light infxns
◊ Mucopurulent Urethral discharge MALARIA
◊ Cefixime ◊ P falciparum: trophozoites and
◊ Doxycycline schizonts in vital organs
◊ INTRACELLULAR gram negative ◊ See page 15 2017 ratio
diplococci ◊ CQ+SP: not severe
◊ + leukocyte esterase ◊ Co-Artem: 2nd line
CHLAMYDIA ◊ Quinine: cerebral malaria
◊ Mucopurulent Urethral discharge ◊ Primaquine+Chloroquine: confirmed
◊ Azithromycin and Doxycycline vivax
HERPES Aspergillosis
◊ Painful genital ulcer ◊ Aspergilloma: surgical rsection
SYPHILIS ◊ Invasive aspergillosis: Voriconazole+
◊ Painless genital ulcer Ampho B
◊ VDRL: DIAGNOSTIC TEST OF CHOICE Cryptococcosis
FOR NEUROSYPHILIS ◊ Ampothericin B + Flucytosine
VDRL and RPR Correlate with ◊ India ink
disease activity See page 18 2017 ratio
◊ Primary: Chancre GI SYSTEM 1
◊ Secondary skin PREFORMED TOXIN (B cerecus. S aureus C
◊ Late cardiac ophthalmic gumma perfringens) & ENTEROTOXIN( V cholatr,
Vaginal discharge ETC, Klebsiella, Aeromonas) VOMITING,
◊ Trichomonas WATERY DIARRHEA
◊ Bacterial vaginosis ENTEROADHERENT( EPEC, EAEC, Giardia,
◊ Candidiasis Cryptospordiosis, Helminths): AB PAIN +
TB MUSHY DIARRHEA
◊ Pan susceptible: sensitive to all Cytotoxin (Clostridium difficile, EHEC):
◊ MDR: >2 drugs (with INH and RFP) ABDOMINAL PAIN, WATERY THEN
◊ XDR: >4 drugs (INH RFP KM FQ) BLOODY(QUICKLY: EHEC, OCCULT: DIFFI)
◊ TB meningitis, military, bone/joint: 2 Invasive (Rota, Norwalk, salmonella,
HRZE/ 10 HR (12 mos) campylobacter, yersionia parahemolyticus):
RABIES FEVER, WATERY DIARRHEA
◊ Can be confirmed by IFAT SEVERE: Shigella, EIEC, Entamoeba
◊ Encephalitic/furiosu type: histolytica, AB PAIN FEVER AND BLOOFY
aerophobia nd hydrophobia DIARRHEA
SECRETORY: derangemet in fluid and NON MECHANICAL /ADYNAMIC ILEUS: (-)
electrolyte transport, kahit di kumain may colicky pain, discomfort from distention,
diarrhea, frequent vomiting
◊ Painless, watery large volume PULMONARY
PERSISTS WITH FASTING TB
◊ Stimulant laxatives, bowel resection, PRESUMPTIVE TB: signs/symptoms
mucosal disease or enterocolic BACTERIOLOGICALLY CONFIRMED
fistula, metastatic GIT carcinoid CLINICALLY DIAGNOSED: diagnosed with
tumors, gastrinom, panc cholera, active TB: abnormal chest Xray findings
OSMOTIC: ingested poorly absorbable LATENT TB/TB INFECTION: POSITIVE TST (no
osmotically active solutes fluid lumenward s sx)
to exceed resorption of colon TB EXPOSURE: close contact
◊ STOPS with FASTING TB DISEASE: presumptive+clinical and
◊ Health supplements, osmotic diagnostic CONFIRMATION
laxatives, CHO malabsorption
STEATORRHEAL: greasy foul smelling diff to
DRTB
flush,weight loss and nutritional deficiencies
CURED: (-) smear at last *18 mos tx, no
◊ FAT MALABSORPTION
month of tx & 1 in failure
◊ Pancreatic
continuation phase, *>3 cultures, 30
◊ Celiac sprue, post mucosal lymphatic
days (-) after
obstruction
intensive phase
INFLAMMATORY:
TREATMENT No record
◊ pain fever and bleeding
COMPLETED: complete culture taken
◊ ANASARCA,
no record
◊ (+) LEUKOCYTES or leukocyte
TREATMENT FAILURE: (+) *need for
derived protein
smear 5 months or later permanent
◊ Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis: Charcot
in tx, not show clinical regimen change
Leyden crystals
improvement of at least 2
◊ Hypogammaglobulinemia antiTB drugs:
DYSMOTILITY ADRs, lack
◊ Rapid transit either secondary or conversion,
contributory bacteria revr
◊ IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME LOST TO FOLLOW UP:
◊ HYPERTHYROIDISM AND DIABETES interrupted for 2
FACTITIAL consecutive months or
◊ Munchausen more
◊ Bulimia Isoniazid preventive therapy
◊ Decreased stool osmolality(H2O ◊ With HIV
added) ◊ <5 years old
◊ Increase urea(urine contaminated) COAL WORKERS PNEUMOCONIOSIS: chest
◊ Increased mg (laxative) Xray looks worse than the patient
ADHESIONS: prior surgery Silicosis and Caplan syndrome: progressive
Vomiting more profuse: higher obstruction assive fibrosis
COLICKY PAIN, MECHANICAL BOWEL SILICOSIS
OBSTRUCTION ◊ Upper lobes
OBSTIPATION: complete lower gut VARY among individuals: immunological rxn
obstruction EVERYONE: toxic exposure
WORSENING DURING WEEKDAYS: ◊ Chest xray finding of bilateral
occupational asthma, sick building infiltrates consistent with pulmo
syndrome, stress-related asthma edema
ASBESTOSIS ◊ PaO2/FiO2 ratio <= 300mmHg
◊ LOWER LOBES ◊ Respi failure cannot be fully
◊ PLEURAL PLAQUES and effusion explained by <3 failure
◊ LATE(dose dependent) ◊ + Neuromuscular blockade
RECURRENT HYPERSENISITIVITY TIDAL VOLUME <=6ML/KG: low mortality
PNEUMONITIS TYPE 1
◊ Even with psych ◊ HYPOXEMIC RF
POSITIVE METACHOLINE TEST ◊ PaO2 <60
◊ Asthma ◊ PNEUMONIA,sepsis, near drowning,
◊ Reactive airways dysfunction muly blood transfusions and panx
syndrome TYPE 2
PFT ◊ Hypercapneic
◊ FEV1 and FVC LOW; FEV1/FVC: ◊ Severe respi acidosis normal
normal: RESTRICTIVE PATTERN oxygenation to mild hypoxemia
◊ Normal FVC,FEV1/FVC: TYPE 3
lowobstruction ◊ Peri operative RF
CURB 65 ◊ POST OP
◊ Confusion ◊ Post anesthetic depression
◊ Urea >7mmol/L TYPE 4
◊ RR >= 30 bpm ◊ Hypoperfusion
◊ BP <=90/60 mmHg ◊ Shock
◊ Age >=65 years BRONCHIAL ASTHMA
Tx ◊ (Actual post BD-Actual pre BD )/
◊ 0-1 home Actual pre
◊ 2:hospital supervised, admit ward IV Intermittent: daytime monthly,nocturnal
antibiotic awakening less than monthly, agonist use
◊ 3+: manage in hospital ssevere less weekly, PEF or FEV1 >80%
pneumonia, assess ICU admission ◊ Tx: occasional prn B2 only
(CURB 4 or 5) Mild to Moderate Persistent: PEF FEV1: 60-
BRONCHIECTASIS 80% predicted
◊ Focal:obstruction ◊ Tx: regular ICS +LABA
◊ Diffuse: widespread Severe Persistent: PEF FEV1: <60%
◊ Persistent productive cough with ◊ Tx: ICS+ LABA+OCS
prod of thick tenacious sputum Symbicort: Formoterol+Budesonide
◊ HRCT ◊ Single inhaler maintenance and
◊ CYLINDRICAL MOST COMMON relief therapy strategy
LUNG ABSCESS STEP 3: RELIEVER MEDICATION + 1 OR 2
◊ Primary: aspirate and anaerobic CONTROLLERS
bacteria (H. INFLUENZAE AND VARIABLE EXPIRATORY FLOW:
PSEUDOMONAS AEROGINOSA) bronchoconstriction, airway thickening and
◊ Secondary: underlying increased mucus
ARDS Typical presentation: cough + wheeze and
◊ Acute onset chest tightness
Controlled: no s/sx
Partly: <3
Uncontrolled: 3 or more ◊ Ocula rinvolvement
Post bronchodilator improve = 12% ◊ NEUTROPHIL infiltration
Risk factors for developing future asthma ◊ ENDOTHELIAL SWELLING
◊ FEV1 low ◊ Involve all kinds of vessels small me
◊ Near fatal asthma dand large
Pulmonary vascular diseases Takayasu arteritis
D-dimer ◊ Pulseless disease
◊ DVT or Pulmonary embolism ◊ Panarteritis with inf mononuclear
◊ Virchows triad(SHE) and occasional giant cells
Stasis (confinement) ◊ Medium and large
Hypercoagulable Pulmonary arterial hypertension
Endothelial ◊ Responsive to NO
dysfxn(smoking/surgery) ◊ Tx: Ca channel blocker: Nifedipine
◊ Not use: INCREASED in AML, sepsis, ◊ Increased PAP
Pneumonia, CA, post-op and ◊ Normal PCWP
pregnancy Pulmonary venous HPN
◊ (CA P P P) ◊ No effective therapy
◊ Increased PAP and PWP
Venous UTS LUNG NEOPLASMS
◊ GOLD STANDARD FOR SCLC : central
DIAGNOSISNG DVT ◊ LIMITED: chemoradio
◊ NO PULMO SX One hemithorax
◊ RFs:immbolization, Regional lymph nodes
pregnant,polycythemia ◊ EXTENSIVE: chemo
Ct angiogram of lung Exceed boundaries
◊ Principal imaging test for diagnosing
PE ◊ No surgery
◊ Pulmo sx. NSCLC: peripheral
◊ Note Ci to D dimer ◊ TNM
Ventilation/perfusion lung scan CHEMOTHERPAY ALONE
◊ If allergic to dye and CI to d-dimer RADIOTHERPAY ALONE
◊ Pulmonary embolism ◊ NSCLC Stage IV
◊ Alternative is MRI SURGICLA RESECTION ALONE
Wegener Syndrome CHEMO +RADIO
◊ Glomerulonephritis ◊ Small cell CA
◊ Granulomatosis vasculitis ◊ LIMITED: one hemithorax, ipsi
mediastinal
Microscopic Polyangitis ◊ NSCLC:
◊ Glomerulonephritis N2 nodes: subcaribal
◊ Necrotizing vasculitis mediastinal STAGE 3A
◊ capillaries and venules N3 nodes: CONTRALATERAL
Churg-Staruss Syndrome STAGE 3B
◊ ASTHMA SURGERY+CHEMO+RADIO
◊ EOSINOPHILIA ◊ NSCLC Stage 2b
◊ Extravascular granuloma T2b(5-7cm) N1 M0
Behcet’s syndrome Squamous: hypercalcemia as
◊ Recurrent oral and genital paraneoplastic, EGFR mutation
ulcerations + AdenoCA EGFR mutation
Small cell: MYC mutation, other ◊ Normal >1
paraneoplastic expt hyper ca ◊ Peripheral arterial disease: <1
SOLITARY PULMONARY NODULE ◊ Severe ischemia: <0.5
◊ Calcifictaion Peripheral arterial disease
Bull’s eye: granuloma: AFB ◊ INTERMITTENT CLAUDICATION
smear ◊ DEATH: CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
Popcorn: hamartoma PAD TO CAD
◊ Prev Xray or PET ◊ CILOSTAZOL: PDE-I vasodilator and
◊ Non smoking <35: serial CT antiplatelet, impro QOL
◊ Smoking >35: biopsy Thromboangitis obliterans NOT
Pneumomediastinum sclerodactyly
◊ Hamman’s: SubQ emphysema ◊ Claudication, raynaud’s
◊ Supplemental oxygen phenomenon, migratorysuperficial
Pleural effusion: base, dull percussion, lag, vein thrombophlebitis
absent breath sounds Fibromuscular dysplasia: string of beads
◊ XrayUTS (quantify) APS sys
Pneumothorax: hyperresonant percussion Daya APR
◊ Spontaneous primary pneumothorax Increased risk of arterial embolization
Pulmo thickening: decreased breath sounds ◊ S. aureus
Pleurodesis for malignant effusion ◊ Vegetations >10mm
Heart diseases ◊ Infection involve mitral valve
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy:LVOT >60 Major criteria
mmHg ◊ Positive blood culture
◊ Sustained ventricular tachycardia: 2 separate cultures
most common cause of death ◊ Endocardial involvement : +
Fulminant myocarditis: fever echocardiogram,new valve regurg
malaiseshock Minor (PF, VIM)
◊ Trypanosoma cruzi(Chagas) ◊ Predisposition (<3 conditon or Iv
Acute viral myocarditis: left ventricular drug use)
segmental hypokinesia ◊ Fever
Clostridial myocarditis: gas bubbles ◊ Vascular (janeway)
Mesothelioma: primary malignant tumor of ◊ Immunologic (osler, roths)
the pericardium ◊ Microbiologic evidence
Stage 1: diffuse ST elevation ( Convex: Dx: 2 major/ 1 major and 3 minor/ 5 minor
MI,Concave: Acute Pericarditis) TTE: not image <2mm
Stage 2: ST baseline TEE: safe vegetatios >90%
Stage 3: T wave inversions IE defervecence 5-7 days
Stage 4: ECG returns to normal LDL-C= Total- (TG/5)-HDL
Beck’s triad: cardiac tamponade: Cholesterol absorption inhibitor:
hypotension, distended neck veins and Sitosterolemia (anemia, enlarged spleen,
muffled or absent heart sounds, ECG: cardiomegaly)
electrical alternans
◊ Prominent X, absent Y
Chronic constrictive pericarditis
◊ PROMINENT X AND Y DESCENT
RV infarction absent y descent
Acute pericarditis: friction rub
ABI:
Abetalipoproteinemia: recurrent diarrhea, ◊ PR prolongedslowpathwayfast
deficiency in vit A, K and E rhythm
Ventricular Premature Beat: wide QRS
complex+bundle branch w/ negative T wave
Ventricular Tachycardia: >= 3 consecutive
beats at rate faster than 100 beats/min
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome:
supraventricular rhythm + wide QRS
complex due to pre-excitation
P wave atrial depo
QRS ventricular depo
ST ventricular repo
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: irregularly irregular
◊ Supraventricular
◊ Irregular RR
◊ No discernible P waves
Sinus tachycardia: regular
Junctional tachycardia: narrow QRS with VA
block
Ventricular Tachycardia: regular rhythm
faster than 100 beats/min from bundle of
His
MULTIFOCAL ATRIAL TACHYCARDIA
◊ Irregular <3 rhythm
◊ 3 distinct P wave morphologies
◊ 100-150 beats/min
Tangier disease: hepatosplenomegaly BLOOD PRESSURE
+enlarged orange tonsils ◊ Office: >= 140/90
COMPLETE HEART BLOCK/3rd degree AV ◊ Ambulatory
block: bradyarrhythmia due to slow of Daytime >=135/85
conduction of AV node Nighttime >=120/70
Bradyarrythmia: AV node dysfuncion and 1st 24 hr: 130/80
and 2nd degree AV block ◊ Home: >=135/85
SINUS EXIT BLOCK: intermittent failure of Canadian Cardiovascular Fxnal
conduction from SA node Classification: severity of ANGINA
Automaticity: result of net inward ionic NYHA: <3 dse on fxnal capacity
current (phase 4) STEMI: FIBRIN RICH,
Reentry: impulse circuited back to reentrant ◊ Responsive to streptokinase
portion & disorder of impulse propagation ◊ Q waves
NSTEMI
Accessory pathway: abnormal connections ◊ No ST elev
that allow conduction between atrium and ◊ Myocardial necrosis
ventricles across the AV ring ◊ UA
TRIGGERED ACTIVITY: oscillations in the PLAQUE RUPTURE: MC mechanism for
RMP during phase 3 acute coronary syndrome
AV NODE REENTRY: slow and fast pathways Anginal equivalents: dyspnea, epi
◊ P waves embedded in QRS complex discomfort etc, esp in women, diabetics and
elderly
Troponin released in 2-4 hrs/ persist 7-10 inflammation, demyelination, gliosis
days (scarring), and neuronal loss
CPKMB/ elev 4-6 hrs/ persists 2-3 days ◊ perpendicular oriented white matter
PINSAN: hyperintensities
◊ Parasympatheticinferior wall ◊ Tx: High dose IV methylprednisolone
infarction and plasmapheresis
◊ Sympatheticanterior wall ◊ Disease modifying agents: interferon
infarction ◊ T cells and macrophages
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS UMN/supranuclear: spastic hyperactive
◊ Relapsing Remitting: discrete attacks DTRs, babinski
that evolve over days to weeks LMN/intranuclear: fasciculations,flaccid and
◊ PRIMARY PROGRESSIVE: No hypotonic
attacks/steady fxnal decline Vasogenic edema: from blood vessels (inc
◊ Secondary progressive: steady permeability of BBB), tumor
deterioration in fxn not associated Intersititial edema: obstruction of
with acute attacks ventricular flow
Begin with RRMS Cytotoxic: inflammation or increased amt of
◊ Progressive/relapsing: steady fluid inside cells
deterioration in condition, but with TB tubercles burst into subpial and
occasional attack superimposed on subependymal areasTB meningitis
progressive course Rifampicicn: prophylaxis contact with
NEUROMYELITIS OPTICA: vasculocentric meningococcal meningitis
inflammation with antibody and Neiseria gonor meningitis: PenG or
complement deposition Ampicillin
◊ Astrocyte: Aquaporin-4 Bacterial meningitis wo rashes: 3rd gen
◊ Complete transverse myelopathy cephalosporin and vancomycin
◊ Tx. Acute exacerbation (IV METHYL MINIMALLY CONSCIOUS STATE: mutism,
PREDNISOLONE) unresponsiveness, unawareness of
◊ If refractory: plasma exchange and environment, inability to sustain social
IV immunoglobulin interaction
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Heptic encephalopathy: accumulation of
(ADEM) intracerebral manganese
◊ Polysymptomatic demyelination Heavy alcohol consumption: GLUTAMYL
with encephalopathy TRANSFERASE
◊ MULTIFOCAL WHITE MATTER HIPPOCAMPUS: most susceptible to
LESIONS WITH NO MASS EFFECT ischemia
◊ Perivenous localization WERNICKE ENCEPHALOPATHY: mental
◊ Exanthema (post infection) status change, ophthalmoplegia and ataxia
◊ Post vaccination: MEASLES KORSAKOFF: inability to incorporate new
◊ Area postrema syndrome: memories, immediate recall intact,
intractable hiccups, nausea, presence of confabulation
vomiting Contraindications for administration of rtPA
◊ Optic neuritis: extensive, frequent ◊ Sustained BP >185/110
posterior involvement, bilateral ◊ Platelets <100,000
Multiple Sclerosis: dissemination in time ◊ HCT <25%
and space ◊ Glucose <50 >400
◊ autoimmune disease of the CNS ◊ Heparin 48 h
characterized by chronic ◊ Prolonged PTT
◊ Elevated INR Central facial palsy + ipsilateral weakness
◊ Rapidly improving symptoms =SUPRATENTORIAL
◊ Prior stroke or head injury win 3 ABCDD for stroke
mos prior intracranial hemorrhage ◊ Age >=60,BP >140/90,Clinsx,
◊ Major surg preceding 14 days unilateral weakness(2), speech
◊ Minor stroke symptoms disturbance only (1), Duration >=60
◊ GI bleeding prec 21 days min (2),10-59 (1), Diabetes
◊ Recent MI MRI: Infarction
◊ Coma/stupor RHEUMA
Amyloid angiopathy: recurrent lobar EBV: associated trigger of SLE
hemorrhages in elderly Hydroxycholoroquine: mainstay in long
PUTAMEN: MC site hypertensive term tx of SLE
intraparenchymal hemorrhage Methylprednisilone: safest in pregnancy
PARKINSONS: MCC of resting tremor Anti-histone: drug induced lupus
DYSTONIA: hyperkinetic, involuntary, ◊ HYDRALAZINE
repetitive contractions, twisting movement Causes of stroke in lupus patient
and abnormal posture ◊ B2 glycoprotein antibody
TIC : repetitive stereotyped movement ◊ Systemic vasculitis
longer in duration than mycolic jerk ◊ Libman Sacks endocarditis
MMSE dementia; 22 (LESS THAN 24) SLE monitor for Tx side effects
HYPOGLYCEMIA: MCC treatable coma ◊ CBC
Pseudo coma vs. Coma ◊ FBS
◊ Eyelid-release test ◊ Annual ophthalmologic exam
◊ Flaccidity of the cheek Pulmonary hypertension
◊ Limb dropping test ◊ Systemic sclerosis and SLE
VASOVAGAL SYNCOPE: peripheral Osteoarthritis
vasodilation drop in BPloss of ◊ Pain
consciousness ◊ Weight bearing
LAMOTRIGINE: generalized TC normal bg ◊ Relieved with rest
activity w gen polyspike waves ◊ Immobilitystiffness
CARBAMAZEPINE, PHENYTOIN AND ◊ Minimal inflammation
PHENOBARBITAL AVOID ◊ BONE ENLARGENEMT DEFORMITIES
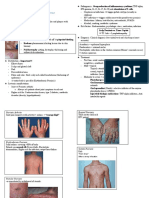
Sjs and ten related to ◊ Bouchard and Heberden node?
carbamazepinePOSITIVE ALLELE HLA ◊ Hyaline articular cartilage loss
B015 ◊ Increase thickness and sclerosis of
* Valproic acid: highest teratogenic subchondral bone
potential ◊ Outgrowth of osteophytes at joint
*Carbamazepine and phenytoin: dizziness margin
and ataxia ◊ Meniscal degeneration
*Gabapentin and Leviteracetam: NOT SEPTIC/ BACTERIAL ARTHRITIS
hepatotoxic ◊ Negative orNORMAL CUTURE: LOW
decussations POSSIBILITY
SPINOTHALAMIC TRACT: 1-2 spinal nerve Rheumatoid arthritis
segments above its point of entry in the ◊ PANNUS FORMATION
SPINAL CORD ◊ CIGARETTE SMOKING
◊ Pain and temp ◊ ANTI CYCLIC CITRULLINATED
Fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus and PEPTIDE
corticospinal tract: MEDULLA ◊ Fusiform swelling of fingers
◊ Spared wrist elbow and ankle TRANSCUTANEOUS ELECTRICAL
◊ Chronic deformities: boutonniere, STIMUATION(TES): lessen exposure to toxic
swan neck and Zline side effects of Analgesics
◊ MC cause of death CV disease Renal Medicine
Gouty arthritis GLOMERULAR CAPILLARY HYDROSTATIC
◊ SYNOVIAL FLUID LEUKOCYTE ARE PRESSURE
ELEVATED 2K-60K ◊ Primary driving force for glomerular
◊ CONTROL INFLAMMATION: filtration
PRIORITY GLOMERULAR CPILLARY ONCOTIC
◊ WARM RED TENDER PRESSURE
◊ Attacks can be triggered by rapid ◊ CONCENTRATION OF UNFILTERED
changes in urate levels PLASMA PROTEINS
◊ NSAID, colchicine, glucocorticoids ◊ PARTIALLY OFFSETS HYDROSTATIC
Ankylosing spondylitis PRESSURE
◊ ENTHESITIS: main patho ◊ OPPOSES FILTRATION
◊ Sacroilitis: earliest AS MYOGENIC REFLEX
◊ Syndesmophytes:AS &PA ◊ First line defense against
◊ Dactylitis ◊ Trigger:fluctuations in renal blood
Psoriatic arthritis flow
◊ Syndesmophytes ◊ Afferent arteriole
◊ Dactylitis ◊ HPNconstrict afferent arteriole
FIBROMYALGIA TUBULOGLOMERULAR FEEDBACK
◊ WIDESPREAD PAIN ◊ Mediated by macula densa
Systemic sclerosis: CREST syndrome ◊ Trigger: NaCl in urine
Dermatomyositis HIV-ASSOCIATED: FSGS
◊ Heliotrpe rash IGA NEPHROPATHY: cardiac(murmur) and
◊ Gottron’s sign renal
◊ Colon CA ◊ Dysmorphic RBCs
Rehab Medicine Pauci immune: Wegener, Churg Strauss,
Disability: restriction/lack capacity Microscopic polyangitis
Impairment: body function or structure TYPE 1 DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY: early
Activity: execution of task increase in GFR then inexorable decline+
Participation: involvement increasing proteinuria
Rehab Goals #1: PAIN, #5 Conserve CYSTATIN C: biomarkers in CKD assess
energy(easy fatigability) kidney fxn better
PLATFORM WALKER AND FORE-ARM DISTAL RTA ( hypokalemic acidosis (low K
CRUTCHES: Commonly used mobility asitive citrate and high Ca (stone)
devices ENDO HUHU
PULMONARY EMBOLISM: complication in PARATHYROID HORMONE-RELATED
hours, stasis PROTEIN: released by CAincreased bone
ISOTONIC ALL LIMB AND TRUNK (large resorptionhypercalcemia
muscles): diabetic ANTICONVULSANTSincreased catabolism
MODERATE AEROBIC CONDITIONING of vit D
EXERCISE: Renal transplant overcome Calcium reqt
chronic anemia and abnormal bone ◊ 500 young children
metabolism ◊ 800 older children
◊ 1,300 adolescents and young adults
◊ 1,000 19-50
◊ 1,200 >50
You might also like
- Internal Medicine Finals ReviewerDocument8 pagesInternal Medicine Finals ReviewerRojales FrancisNo ratings yet
- Peds EORDocument17 pagesPeds EORRachel BarrosNo ratings yet
- Papulosquamous DisordersDocument6 pagesPapulosquamous DisordersWoo Rin ParkNo ratings yet
- Skin and MSK EverythingDocument31 pagesSkin and MSK EverythingBernard HernandezNo ratings yet
- Erythema Multiforme and Drug EruptionDocument5 pagesErythema Multiforme and Drug EruptionAdparizby FachryNo ratings yet
- Hippo Education Hippo EM - Dermatology Written SummaryDocument7 pagesHippo Education Hippo EM - Dermatology Written Summarykaylawilliam01100% (1)
- 10a Dermatitis AtopikDocument27 pages10a Dermatitis Atopikwuryan dewiNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis and EczemaDocument6 pagesDermatitis and EczemaWoo Rin ParkNo ratings yet
- Urticaria and ErythemaDocument5 pagesUrticaria and ErythemaAdparizby FachryNo ratings yet
- Urticaria and ErythemaDocument5 pagesUrticaria and ErythemaWoo Rin ParkNo ratings yet
- Notes: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument4 pagesNotes: Mycobacterium TuberculosisAniket SinghNo ratings yet
- Dermatosis Erythrosquamous: Def: Disease Are Characterized by Erythema and Scale (Squama)Document16 pagesDermatosis Erythrosquamous: Def: Disease Are Characterized by Erythema and Scale (Squama)Rizky FajriNo ratings yet
- Impetigo, Erysipela S, Cellulitis: Rasay, Joana Mikee DDocument48 pagesImpetigo, Erysipela S, Cellulitis: Rasay, Joana Mikee DJoana Mikee RasayNo ratings yet
- Arena VirusesDocument2 pagesArena VirusesWoo Rin ParkNo ratings yet
- Notes: Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus (LCMV)Document2 pagesNotes: Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus (LCMV)Vivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- CH 2180.table 4Document5 pagesCH 2180.table 4Nirav CHOVATIYANo ratings yet
- Differentials: Less Common InfectionsDocument6 pagesDifferentials: Less Common InfectionsTaeyomiNo ratings yet
- 12 KULIT KELAMIN Viral Diseases of The Oral Cavity-1Document79 pages12 KULIT KELAMIN Viral Diseases of The Oral Cavity-1NAOMI SINAGANo ratings yet
- Cornea and External DiseaseDocument26 pagesCornea and External Diseaserajeshwari saravananNo ratings yet
- Tabel Preventable Disesase-Week 3Document3 pagesTabel Preventable Disesase-Week 3Tiffany NicolèNo ratings yet
- Notes: Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus (Eeev)Document5 pagesNotes: Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus (Eeev)Woo Rin ParkNo ratings yet
- MergedDocument17 pagesMergedJack Ortega PuruggananNo ratings yet
- PapulosquamousDocument5 pagesPapulosquamousMinh ChâuNo ratings yet
- Notes: Chlamydia Species (Pneumonia)Document3 pagesNotes: Chlamydia Species (Pneumonia)Woo Rin ParkNo ratings yet
- By:Zairrabasig: Rheumatic FeverDocument3 pagesBy:Zairrabasig: Rheumatic FeverJuviely PremacioNo ratings yet
- ArenaviridaeDocument2 pagesArenaviridaeWoo Rin ParkNo ratings yet
- 2018 Prof. Harijono DermatitisDocument62 pages2018 Prof. Harijono DermatitisDEWI MULYANI100% (1)
- Lyell) 30%. SCORTEN: Usia 40: Pepper (Hipo Dan Hiperpigmentasi), Hipo/anhidrosis. ANA + - Komplikasi: Fibrosis ParuDocument14 pagesLyell) 30%. SCORTEN: Usia 40: Pepper (Hipo Dan Hiperpigmentasi), Hipo/anhidrosis. ANA + - Komplikasi: Fibrosis Parutessa thenNo ratings yet
- Skin Summary ChartDocument7 pagesSkin Summary ChartMarco HernandezNo ratings yet
- LCD Kuliah Dermatitis Wa2008Document32 pagesLCD Kuliah Dermatitis Wa2008Made Wardhana100% (2)
- Cutaneous Fungal Infections PDFDocument3 pagesCutaneous Fungal Infections PDFRch 19No ratings yet
- Burns and FrostbiteDocument9 pagesBurns and FrostbiteAli 10No ratings yet
- Kukel WerdDocument3 pagesKukel WerdRicky YurdanaNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue FinalsDocument3 pagesConnective Tissue FinalsVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous BacteriaDocument5 pagesMiscellaneous BacteriaFaithNo ratings yet
- MycoplasmaDocument2 pagesMycoplasmaaminshafihassan902No ratings yet
- Fever and Rash: Alvin Germo PasuquinDocument70 pagesFever and Rash: Alvin Germo PasuquinAlvin Germo PasuquinNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument27 pagesParasitologySantosh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Micky Infectious NotesDocument10 pagesMicky Infectious NotesNoelani-Mei AscioNo ratings yet
- LeptospirosisDocument2 pagesLeptospirosisSeff CausapinNo ratings yet
- Dermatosis ErythrosquamousDocument25 pagesDermatosis ErythrosquamousDeny IndahwatyNo ratings yet
- PapulosquamousDocument5 pagesPapulosquamousMinh ChâuNo ratings yet
- Nonvenomous Insect BitesDocument18 pagesNonvenomous Insect BitesYang JunNo ratings yet
- IT-11 DERMATOMIKOSIS SUPERFISIALIS Edit 8 OktDocument69 pagesIT-11 DERMATOMIKOSIS SUPERFISIALIS Edit 8 Oktputri.SpANo ratings yet
- Term Example Discoloration Flat,: Patch ( 1cm) Papule ( 1cm)Document4 pagesTerm Example Discoloration Flat,: Patch ( 1cm) Papule ( 1cm)Almira PutriNo ratings yet
- Race Dermatology 2024 by DR AshishDocument29 pagesRace Dermatology 2024 by DR AshishdrshekarforyouNo ratings yet
- EczemaDocument1 pageEczemaKaniz WahabNo ratings yet
- Eponyms in DermatologyDocument2 pagesEponyms in DermatologyJamesNo ratings yet
- Measles and Scarlet Fever Kawasaki Disease: Fatin & EileenDocument30 pagesMeasles and Scarlet Fever Kawasaki Disease: Fatin & EileenbyteNo ratings yet
- Infectii CutanateDocument24 pagesInfectii CutanateMaria Minodora PascuNo ratings yet
- 5 Drug EruptionsDocument50 pages5 Drug EruptionsCharl UnalNo ratings yet
- Skin, Hair and Nails Ok - CompressedDocument67 pagesSkin, Hair and Nails Ok - CompressedFelya Elsa Pratiwi KurniaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYS - DermatologyDocument19 pagesPATHOPHYS - Dermatologyaagioaa100% (1)
- Trematodes (Flatworms)Document6 pagesTrematodes (Flatworms)Woo Rin ParkNo ratings yet
- Emed - Pedia 1Document7 pagesEmed - Pedia 1Princess Cate MercadoNo ratings yet
- Assalamu'alikum WR WB: Harijono KariosentonoDocument59 pagesAssalamu'alikum WR WB: Harijono KariosentonoDhiastikaNo ratings yet
- MODALITIES To Print Small PaperDocument4 pagesMODALITIES To Print Small PaperLeah DeeNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandDermatology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Dermatology Atlas for Medical StudentsFrom EverandDermatology Atlas for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Alex P. Bello MDDocument8 pagesPersonal Protective Equipment (PPE) Alex P. Bello MDKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- ARMY ScienceDocument3 pagesARMY ScienceKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Uterine AtonyDocument4 pagesUterine AtonyKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid PhysiologyDocument25 pagesThyroid PhysiologyKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- When Your Anxiety Is Getting The Best of YouDocument1 pageWhen Your Anxiety Is Getting The Best of YouKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Basic Knot TyingDocument10 pagesBasic Knot TyingKathleen Grace Maniago100% (1)
- Reviewer On Immunization (KMBM)Document8 pagesReviewer On Immunization (KMBM)Kathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound RotationDocument4 pagesUltrasound RotationKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- New Doc NewDocument1 pageNew Doc NewKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- The Intern Pocket Card Surviving GraysDocument2 pagesThe Intern Pocket Card Surviving GraysKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Anes Drugs TableDocument20 pagesAnes Drugs TableKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Chap2 OutoutlinelineDocument7 pagesChap2 OutoutlinelineKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Commed SummaryDocument19 pagesCommed SummaryKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Ent 3Document3 pagesEnt 3Kathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- With Notesent 1Document8 pagesWith Notesent 1Kathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- ...Document1 page...Kathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Prayer To St. Joseph of CupertinDocument1 pagePrayer To St. Joseph of CupertinKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Q 1 - P, Then The Probability Distribution of A Binomial Random Variable X, The Number ofDocument3 pagesQ 1 - P, Then The Probability Distribution of A Binomial Random Variable X, The Number ofKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- A Part in Everything We Are in Our Heart... "Document2 pagesA Part in Everything We Are in Our Heart... "Kathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Musiiiic UploadsDocument1 pageMusiiiic UploadsKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Famtree RizalDocument2 pagesFamtree RizalKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- PrintDocument1 pagePrintKathleen Grace ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Conflit Israelo PalestinienDocument7 pagesDissertation Conflit Israelo PalestinienPaySomeoneToWriteAPaperForMeUK100% (2)
- Chapter 5 - Societies To Social NetworksDocument11 pagesChapter 5 - Societies To Social NetworksSumeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Math 7 LAS W1&W2Document9 pagesMath 7 LAS W1&W2Friendsly TamsonNo ratings yet
- Prologue: Managerial Accounting and The Business EnvironmentDocument156 pagesPrologue: Managerial Accounting and The Business EnvironmentMarcus MonocayNo ratings yet
- CostcoDocument12 pagesCostcoThảo Nguyên PhạmNo ratings yet
- Youth Worker Course Gold CoastDocument6 pagesYouth Worker Course Gold Coastf5dq3ch5100% (2)
- CH 7b - Shift InstructionsDocument20 pagesCH 7b - Shift Instructionsapi-237335979100% (1)
- Air Pollution Modelling With Deep Learning A ReviewDocument6 pagesAir Pollution Modelling With Deep Learning A ReviewliluNo ratings yet
- The Baldur's Gate Series 1 - Baldur GateDocument125 pagesThe Baldur's Gate Series 1 - Baldur GateJustin MooreNo ratings yet
- Graduate Study at KIMEPDocument20 pagesGraduate Study at KIMEPKIMEPNo ratings yet
- C Ce 200Document59 pagesC Ce 200hanieh rezapourNo ratings yet
- Multi-Purpose Three Phase Meter: CIRWATT SeriesDocument44 pagesMulti-Purpose Three Phase Meter: CIRWATT SeriesIsmail HussainNo ratings yet
- Eligibility Conditions: Advertisement For Regular Commission in Pakistan Army Through 136 Pma Long CourseDocument5 pagesEligibility Conditions: Advertisement For Regular Commission in Pakistan Army Through 136 Pma Long CourseHusnain IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Seven Elements of Effective NegotiationsDocument3 pagesSeven Elements of Effective NegotiationsKilik GantitNo ratings yet
- Gamla Stan PDFDocument4 pagesGamla Stan PDFAlexandra FricosuNo ratings yet
- Sales Marketing Director in Tampa FL Resume William RoelingDocument2 pagesSales Marketing Director in Tampa FL Resume William RoelingWilliamRoelingNo ratings yet
- Directorate of Pension, Provident Fund & Group Insurance: WWW - Wbepension.gov - inDocument37 pagesDirectorate of Pension, Provident Fund & Group Insurance: WWW - Wbepension.gov - inSandipan RoyNo ratings yet
- Sika Comfor PorefillerDocument5 pagesSika Comfor Porefillerrangarajan1989No ratings yet
- Unit-I Introduction To Compilers: CS6660-Compiler Design Department of CSE &IT 2016-2017Document95 pagesUnit-I Introduction To Compilers: CS6660-Compiler Design Department of CSE &IT 2016-2017amdevaNo ratings yet
- Past:: Simple Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect ContinuousDocument12 pagesPast:: Simple Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect ContinuousAhmed Abd El HafeezNo ratings yet
- 04.1 Foreign Graduates1Document30 pages04.1 Foreign Graduates1Frederico CavalcanteNo ratings yet
- Autodesk 2016 Product Keys 1Document3 pagesAutodesk 2016 Product Keys 1EfrEn QuingAtuñaNo ratings yet
- NEBULIZATIONDocument2 pagesNEBULIZATIONMae ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Wilkerson Case Study FinalDocument5 pagesWilkerson Case Study Finalmayer_oferNo ratings yet
- The Ghosts of 1898: Wilmington'S Race Riot and The Rise of White SupremacyDocument16 pagesThe Ghosts of 1898: Wilmington'S Race Riot and The Rise of White Supremacysherae9154532No ratings yet
- Social Change Theme in The Cherry Orchard - LitChartsDocument17 pagesSocial Change Theme in The Cherry Orchard - LitChartsShivashankar. DNo ratings yet
- Uv Mapping TutorialDocument5 pagesUv Mapping Tutorialbkb193No ratings yet
- Gas Pressure Reduction StationDocument2 pagesGas Pressure Reduction StationMathias OnosemuodeNo ratings yet
- The Impact On Digital Marketing During Pandemic Outbreak COVID-19 On Business DevelopmentDocument5 pagesThe Impact On Digital Marketing During Pandemic Outbreak COVID-19 On Business DevelopmentInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Coastal Boards Co Is A Merchandising Business The Account BalancesDocument1 pageCoastal Boards Co Is A Merchandising Business The Account BalancesFreelance WorkerNo ratings yet