Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Finding The Expected Value: HSIEH: Probability and Statistics 4
Uploaded by
tahermoh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views20 pagesOriginal Title
pdf (5)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views20 pagesFinding The Expected Value: HSIEH: Probability and Statistics 4
Uploaded by
tahermohCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
Finding
the Expected Value
4 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Example 2.33
n The problem of data calls
n W = h(R) = R2
n What is E[W]?
5 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Example 2.30
n Random variable V is the amplitude of a signal
n Y=V2/2 is the average power of the signal
n What is PY(y)?
11 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
The Case of Scaling What if a < 0?
13 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Examples of Scaling
What if X is a discrete random
variable like Poisson (α)?
14 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
The Case of Shifting
15 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Linear Transformation
17 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Example of Linear Transformation
18 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
A More General Transformation
chain rule for differentiation
F Note the range of Y (for which the formula applies)
19 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Proof
20 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Example
n X is a uniform (0, 1) random variable, and
n Find the PDF of Y
21 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Another Example
n X is a uniform (0, 1) random variable, and
n Find the PDF of Y
22 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
General Transformation Revisited
F Note the range of Y (for which the formula applies)
23 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Sketch of Proof
24 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Example
n X is a standard normal random variable, and
n Find the PDF of Y
25 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Example 3.26
n X is uniformly distributed over [-1, 3]
n Find FY(y) and fY(y) if Y=X2
26 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Example 3.25
n Output signal of a microphone is Gaussian (0, 5)
n The signal is then sent to the input of a limiter circuit
n Find the CDF and PDF of the output W
27 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Discretization (Uniform)
How about the floor function?
28 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Discretization (Exponential)
How about the floor function?
29 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
Example 3.14
n Two charge plan of telephone calls
n Common rate is $0.15 per minute
n Plan A rounds up the last minute and Plan B counts the
exact duration (fractional minute for calculation)
n Duration of a phone call in minutes is an exponential
random variable with λ = 1/3
n What is the expected cost per call for each plan?
30 HSIEH: Probability and Statistics
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Dimensional Analysis and SimilarityDocument9 pagesDimensional Analysis and SimilarityaeroacademicNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
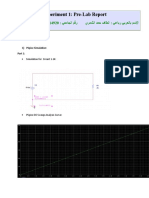
- Experiment 1: Pre-Lab Report: 1) Pspice SimulationDocument3 pagesExperiment 1: Pre-Lab Report: 1) Pspice SimulationtahermohNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 1.objectives:: Experiment # 2Document7 pages1.objectives:: Experiment # 2tahermohNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- 207 Lab Report Fall 2017-2018 Experiment No.: TitleDocument3 pages207 Lab Report Fall 2017-2018 Experiment No.: TitletahermohNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- © 1 Least-Squares of LN Versus: - (#2) T - QDocument1 page© 1 Least-Squares of LN Versus: - (#2) T - QtahermohNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Fluid Mech - 1.38Document1 pageFluid Mech - 1.38tahermohNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 Problems PDFDocument1 pageAssignment1 Problems PDFtahermohNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Archimedes and The Kings CrownDocument1 pageArchimedes and The Kings CrowntahermohNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Problem 1: (5 Points) : (0.75 Point) (0.75 Point)Document4 pagesProblem 1: (5 Points) : (0.75 Point) (0.75 Point)tahermohNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- ENSC-283 Assignment #2 Hydrostatic ForcesDocument2 pagesENSC-283 Assignment #2 Hydrostatic ForcesEddie TanNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Assignment1 Problems PDFDocument1 pageAssignment1 Problems PDFtahermohNo ratings yet
- ENSC-283 Assignment #2: Hydrostatic Forces on Circular Gate and Pressurized Tank PlateDocument6 pagesENSC-283 Assignment #2: Hydrostatic Forces on Circular Gate and Pressurized Tank PlateOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Finding The Expected Value: HSIEH: Probability and Statistics 4Document20 pagesFinding The Expected Value: HSIEH: Probability and Statistics 4tahermohNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
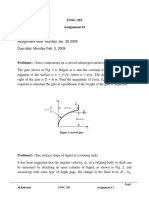
- ENSC-283 Assignment #3: Figure 1 Curved GateDocument2 pagesENSC-283 Assignment #3: Figure 1 Curved GatetahermohNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- PDFDocument321 pagesPDFtahermohNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Discrete Uniform Random VariablesDocument20 pagesDiscrete Uniform Random VariablestahermohNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Part 3: Regulatory ( Stabilizing ) Control: Inventory (Level) Control StructureDocument63 pagesPart 3: Regulatory ( Stabilizing ) Control: Inventory (Level) Control StructuretahermohNo ratings yet
- Example 4.8: Fax Transmissions in A CompanyDocument27 pagesExample 4.8: Fax Transmissions in A CompanytahermohNo ratings yet
- Example 4.8: Fax Transmissions in A CompanyDocument27 pagesExample 4.8: Fax Transmissions in A CompanytahermohNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Signals-And-Systems 9780471988007 30478Document592 pagesSignals-And-Systems 9780471988007 30478Michael Benhamou86% (7)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Example 4.23: Joint PDF of X and Y FollowsDocument19 pagesExample 4.23: Joint PDF of X and Y FollowstahermohNo ratings yet
- Course2 - SocDocument56 pagesCourse2 - SoctahermohNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Practical Plantwide Process Control: PID Tuning: Sigurd Skogestad, NTNUDocument66 pagesPractical Plantwide Process Control: PID Tuning: Sigurd Skogestad, NTNUtahermohNo ratings yet
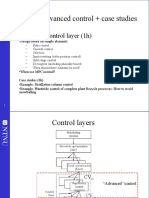
- Part 5: Advanced Control + Case StudiesDocument52 pagesPart 5: Advanced Control + Case StudiestahermohNo ratings yet
- Course Summary: (Economic Optimal Operation)Document58 pagesCourse Summary: (Economic Optimal Operation)tahermohNo ratings yet
- Course1 - PlantwideDocument58 pagesCourse1 - PlantwidetahermohNo ratings yet
- Course Summary: (Economic Optimal Operation)Document58 pagesCourse Summary: (Economic Optimal Operation)tahermohNo ratings yet
- Part 5: Advanced Control + Case StudiesDocument52 pagesPart 5: Advanced Control + Case StudiestahermohNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Industrial2 - PIDDocument66 pagesIndustrial2 - PIDCiubotaru Diana ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- DSP Lecture NotesDocument24 pagesDSP Lecture Notesvinothvin86No ratings yet
- Sol hmw3Document5 pagesSol hmw3Martín FigueroaNo ratings yet
- June 2017 QPDocument52 pagesJune 2017 QPEyad UsamaNo ratings yet
- 4431Document186 pages4431Muhammad Khurram Shehzad100% (1)
- Multiple-Choice Tests in Advanced MathematicsDocument78 pagesMultiple-Choice Tests in Advanced Mathematicsnararoberta100% (2)
- Equations and inequalities guideDocument4 pagesEquations and inequalities guideNar NarNo ratings yet
- Daa PBL 2.0Document17 pagesDaa PBL 2.0Ankush ChajgotraNo ratings yet
- Complex Number - Chapter NotesDocument17 pagesComplex Number - Chapter NotesDivyanshi VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Python Non-Uniform Fast Fourier Transform (Pynufft) : An Accelerated Non-Cartesian Mri Package On A Heterogeneous Platform (Cpu/Gpu)Document22 pagesPython Non-Uniform Fast Fourier Transform (Pynufft) : An Accelerated Non-Cartesian Mri Package On A Heterogeneous Platform (Cpu/Gpu)darlyNo ratings yet
- Journal of Physics A Mathematical and General 2002 Vol. 35 (14) p3245Document20 pagesJournal of Physics A Mathematical and General 2002 Vol. 35 (14) p3245Héctor F BonillaNo ratings yet
- SACE Stage 2 Math Methods - Surge and Logistic Functions InvestigationDocument13 pagesSACE Stage 2 Math Methods - Surge and Logistic Functions Investigationmaxwell-mearnsNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Mathematics P2 Nov 2012 Memo EngDocument29 pagesMathematics P2 Nov 2012 Memo EngedwardnephNo ratings yet
- Hkcee Mathematics - 13.2 Coordination Geometry - Circles - P.1Document7 pagesHkcee Mathematics - 13.2 Coordination Geometry - Circles - P.1Brian LiNo ratings yet
- Stiffness and Damage Identification With Model Reduction TechniqueDocument8 pagesStiffness and Damage Identification With Model Reduction Techniquegorot1No ratings yet
- Remedial Kls 12 EasyDocument16 pagesRemedial Kls 12 EasyDigilib Cambridge TazkiaNo ratings yet
- TSPSC SQT Notification for Technical Education Dept StaffDocument35 pagesTSPSC SQT Notification for Technical Education Dept StaffSrinath LadduNo ratings yet
- Cauchy-Riemann Equations: Simple Example Interpretation and ReformulationDocument11 pagesCauchy-Riemann Equations: Simple Example Interpretation and ReformulationMso1111No ratings yet
- Mechanics of MaterialsDocument282 pagesMechanics of MaterialssydengineerNo ratings yet
- A2 12-1 Study Guide and Intervention AnswersDocument2 pagesA2 12-1 Study Guide and Intervention Answersjta86183No ratings yet
- Rise of ML and its Impact on StatisticsDocument12 pagesRise of ML and its Impact on StatisticsIsmael KaïssyNo ratings yet
- Mnlayer: High-Performance Layered Elastic Analysis ProgramDocument13 pagesMnlayer: High-Performance Layered Elastic Analysis Programnegar khakshurNo ratings yet
- Geometric Sequences and SeriesDocument20 pagesGeometric Sequences and Seriesjulius romanoNo ratings yet
- MB148 - SILABO Calculo VectorialDocument4 pagesMB148 - SILABO Calculo VectorialCésar Santisteban Tuñoque0% (1)
- STA102Document6 pagesSTA102oonodakpoyereNo ratings yet
- Penn Calc WikiDocument387 pagesPenn Calc WikiJohn Kaufman100% (3)
- Tendency: Measures of CentralDocument29 pagesTendency: Measures of CentralADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- CAT 2024 Batch 10 Complete ScheduleDocument9 pagesCAT 2024 Batch 10 Complete ScheduleShourya PanchalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18: Series Solution of Linear Differential Equations (Iii)Document3 pagesLecture 18: Series Solution of Linear Differential Equations (Iii)Patricio CisternasNo ratings yet
- 6 - Introduction To OptimizationDocument8 pages6 - Introduction To OptimizationDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Duality in Fundamentals of Operation ResearchDocument4 pagesDuality in Fundamentals of Operation ResearchVaraprasad ChakriNo ratings yet