Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GPOBA Fact Sheet 08-18-10 - English
Uploaded by
feriha_mugisha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesOutput-based aid (OBA) is an approach to increasing access to basic services for the poor by linking payment of aid to delivery of specific outputs that are verified. It contracts service delivery to third parties, who receive performance-based subsidies to complement user fees. To date, over 130 OBA projects totaling $3.5 billion have been identified, benefiting over 6.6 million people. The Global Partnership on Output-Based Aid (GPOBA) supports OBA through grants and technical assistance, with donor funding totaling $242.6 million as of June 2010.
Original Description:
Original Title
GPOBA fact sheet 08-18-10_english
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOutput-based aid (OBA) is an approach to increasing access to basic services for the poor by linking payment of aid to delivery of specific outputs that are verified. It contracts service delivery to third parties, who receive performance-based subsidies to complement user fees. To date, over 130 OBA projects totaling $3.5 billion have been identified, benefiting over 6.6 million people. The Global Partnership on Output-Based Aid (GPOBA) supports OBA through grants and technical assistance, with donor funding totaling $242.6 million as of June 2010.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesGPOBA Fact Sheet 08-18-10 - English
Uploaded by
feriha_mugishaOutput-based aid (OBA) is an approach to increasing access to basic services for the poor by linking payment of aid to delivery of specific outputs that are verified. It contracts service delivery to third parties, who receive performance-based subsidies to complement user fees. To date, over 130 OBA projects totaling $3.5 billion have been identified, benefiting over 6.6 million people. The Global Partnership on Output-Based Aid (GPOBA) supports OBA through grants and technical assistance, with donor funding totaling $242.6 million as of June 2010.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
OUTPUT-BASED AID – FACT SHEET
What is Output-Based Aid? How does OBA contribute to aid
• Output-based aid (OBA) is an innovative ap-
effectiveness?
proach to increasing access to basic services— • Knowing who will provide and who will receive the
such as infrastructure, healthcare, and educa- subsidy and what it’s for helps ensure transparency.
tion—for the poor in developing countries. • Payment on output delivery shifts performance risk
• OBA is used in cases where poor people are to the provider by making him accountable.
being excluded from basic services because they • Having a predetermined subsidy provides incentives
cannot afford to pay the full cost of user fees for innovation and efficiency.
such as connection fees. • The subsidy acts as an incentive to mobilize private
• OBA is one of a spectrum of results-based sector finance and expertise.
instruments. It is part of a broader donor effort • The focus on outputs means that OBA schemes
to ensure that aid is well spent and that the internalize tracking of results.
benefits go to the poor.
What makes a successful OBA
How does OBA work?
project?
• Unlike traditional approaches, OBA links the
payment of aid to the delivery of specific services The evidence on what makes a good OBA project is
or “outputs.” These can include connection of still coming in, but some key factors have already been
poor households to electricity grids or water and identified. These include:
sanitation systems, installation of solar heating • A sound regulatory environment.
systems, or delivery of basic healthcare services. • Finding a reliable and motivated service provider
• Under an OBA scheme, service delivery is (private or public).
contracted out to a third party, usually a private • Linking the payment of subsidies to appropriate
firm, which receives a subsidy to complement or outputs.
replace the user fees. • Setting tariffs that cover at least operation and
• The service provider is responsible for “pre- maintenance costs.
financing” the project until output delivery. • Targeting the subsidies effectively to the poor.
• The subsidy is performance-based, meaning • The availability of funds (either from the operators’
that most of it is paid only after the services or own resources or from banks) to “pre-finance” the
outputs have been delivered and verified by an outputs.
independent agent.
• The subsidy is explicitly targeted to the poor
(e.g., by focusing on areas in which poor people What has been the experience
live).
with OBA so far?
• So far, the Global Partnership on Output-Based Aid
has identified about 131 OBA projects with a total
value of about $3.5 billion in the World Bank Group
(WBG) and another 66 schemes outside the WBG.
Funding for OBA has come from the WBG, GPOBA,
Supporting the delivery of basic services in developing countries
other donors such as KfW, and governments. opment partners through its publications and out-
Most OBA projects are in infrastructure and reach activities.
health, with some in education.
• To date, GPOBA has signed 31 grant Contact us
agreements for OBA subsidy funding for If you are interested in pursuing OBA projects, have
a total of US$124.9 million, with the first experience in OBA that you would like to share, or wish
grant agreement signed in April 2006. to obtain more documentation, please visit the GPOBA
Nearly 6.6 million people are expected to website (www.gpoba.org) or contact:
benefit from these schemes in 23 coun- Cathy Russell
tries worldwide in both rural and urban Communications Officer
areas. The average subsidy per capita is GPOBA
US$18.8.
• As of June 30, 2010, GPOBA projects Tel.: (+1 202) 458 8124 | Fax: (+1 202) 522 0761
have disbursed US$15.1 million based Email: gpoba@worldbank.org
on independently verified outputs, directly
impacting more than 564,000 people. This
is encouraging as typically projects take at
least a year to implement before the first
outputs can be delivered and verified.
• Initial results from OBA pilots include
increased private investment in basic ser-
vices and efficiency gains due to competi-
tive bidding.
• As more project results come in, GPOBA
will continue to share them with the devel-
What is the Global Partnership on Output-Based Aid?
• The Global Partnership on Output- • As of June 30, 2010, donor funding
Based Aid (GPOBA) is a partnership for GPOBA totals US$242.6 million
of donors and international organi- (contributions and pledges).
zations working together to support • GPOBA provides three types of sup-
OBA approaches to improving service port: technical assistance for OBA
delivery for the poor. schemes, dissemination of experiences
• GPOBA was established in 2003 by and best practices in OBA, and grants
the UK (DFID) and the World Bank. Its for OBA subsidy funding.
other donors are the IFC, the Nether- • The program’s focus sectors are water
lands (DGIS), Australia (AusAID), and and sanitation, energy, telecommunica-
Sweden (Sida). tions, transport, health, and education.
World Bank | Mailstop: U3-306
Washington, DC 20433, USA
To find out more, visit www.gpoba.org August 2010
You might also like
- Getting A Grant For Your BusinessDocument4 pagesGetting A Grant For Your BusinessJohn-Marc CompératNo ratings yet
- Medical Marijuana RecommendationDocument1 pageMedical Marijuana Recommendationespinza1No ratings yet
- Chamish - Bye Bye Gaza (Globalist Plans For Destruction of Israel) (2006)Document413 pagesChamish - Bye Bye Gaza (Globalist Plans For Destruction of Israel) (2006)mika.100% (5)
- Mango - Financial Sustainability Types of Funding AnalysisDocument7 pagesMango - Financial Sustainability Types of Funding AnalysisGanga DharanNo ratings yet
- Soriano V Laguardia DigestDocument2 pagesSoriano V Laguardia DigestCfc-sfc Naic Chapter100% (2)
- Leaked Briefing Notes Obtained by Moms On The MoveDocument10 pagesLeaked Briefing Notes Obtained by Moms On The MoveSean HolmanNo ratings yet
- Britain's Black DebtDocument1 pageBritain's Black DebtLindaSpeth0% (2)
- Pangasinan Coop Masterlist 2013 PDFDocument43 pagesPangasinan Coop Masterlist 2013 PDFeslima5100% (2)
- Sayyid Qutb's MilestonesDocument48 pagesSayyid Qutb's MilestonesArdit KrajaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On The GCF Funding Priority Areas & Country ProgrammeDocument12 pagesPresentation On The GCF Funding Priority Areas & Country ProgrammeMunashe MukonoweshuroNo ratings yet
- Uwezo Uganda Policy For Resource Mobilisation - Partnerships2021 1Document7 pagesUwezo Uganda Policy For Resource Mobilisation - Partnerships2021 1Monydit SantinoNo ratings yet
- Blue Action Fund-Grant SynopsisDocument2 pagesBlue Action Fund-Grant SynopsisCarlos O. TulaliNo ratings yet
- BOF 2018 - Partnerships With Thinktanks - Galiya IsmakovaDocument19 pagesBOF 2018 - Partnerships With Thinktanks - Galiya IsmakovaWalter PoickNo ratings yet
- Workshop Dakar UNCDF LDUDocument59 pagesWorkshop Dakar UNCDF LDUabdikarim_omarNo ratings yet
- Community Support Fund Guidance Notes, July 2012Document15 pagesCommunity Support Fund Guidance Notes, July 2012Rich WattsNo ratings yet
- The European Innovation Partnership (EIP) Agricultural Productivity and Sustainability" Moving Innovation in Agriculture Ahead !Document42 pagesThe European Innovation Partnership (EIP) Agricultural Productivity and Sustainability" Moving Innovation in Agriculture Ahead !vaibhav0584No ratings yet
- Presentation BracDocument31 pagesPresentation BracSabah Sheesh AhmedNo ratings yet
- RFP Case StudyDocument4 pagesRFP Case StudyAnonymous LxsFkX1UNo ratings yet
- Asian Development BankDocument13 pagesAsian Development BankAngellene Magrare SalanatinNo ratings yet
- Day 2, 2 Presentation Ingrid Gardiner SerbiaDocument22 pagesDay 2, 2 Presentation Ingrid Gardiner SerbiaBalkan Civil Society Development NetworkNo ratings yet
- 2 Resource Mobilization - PDF StrategiesDocument13 pages2 Resource Mobilization - PDF StrategiesHasrat AliNo ratings yet
- A AD DB B T T: R RA Annssppa AR RE Ennc CYYDocument29 pagesA AD DB B T T: R RA Annssppa AR RE Ennc CYYatguintuNo ratings yet
- Project Āwhina Brief OverviewDocument3 pagesProject Āwhina Brief OverviewYvonne TuckerNo ratings yet
- Ndis Costs OverviewDocument69 pagesNdis Costs OverviewAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Phase 4 Information Book and Concept Proposal Form: Update: August 2018Document21 pagesPhase 4 Information Book and Concept Proposal Form: Update: August 2018Rimex DavaiNo ratings yet
- Sample RFP Client Management Software Document PDFDocument12 pagesSample RFP Client Management Software Document PDFAhmedManamaNo ratings yet
- Disease Prevention and Treatment Guidelines Global Grant Funding enDocument23 pagesDisease Prevention and Treatment Guidelines Global Grant Funding encwchiascribd99No ratings yet
- Meaney-Laverriere BudgetDocument6 pagesMeaney-Laverriere BudgetGtownVoiceNo ratings yet
- JD Project Manager 1 1Document7 pagesJD Project Manager 1 1BiniNo ratings yet
- SLP Activity TUDLAS GRICHENDocument7 pagesSLP Activity TUDLAS GRICHENGrichen TudlasNo ratings yet
- Sightfirst Grant ApplicationDocument13 pagesSightfirst Grant ApplicationGeorge SitanayaNo ratings yet
- Kabula 2013Document8 pagesKabula 2013MelikteNo ratings yet
- Day 1 ECCA TrainingDocument78 pagesDay 1 ECCA Trainingadinsmaradhana100% (1)
- Support To Ngo Initiatives For The Prevention of Hiv/Aids: Project GuidelinesDocument5 pagesSupport To Ngo Initiatives For The Prevention of Hiv/Aids: Project GuidelinesDebasish RoyNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Donor Funding On The Performance of Local Government in Wakiso District Local Government.Document13 pagesThe Effect of Donor Funding On The Performance of Local Government in Wakiso District Local Government.KIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Improving PerformancDocument6 pagesImproving PerformancImprovingSupportNo ratings yet
- BRAC Microfinance Program in Bangladesh and Its International ReplicationsDocument26 pagesBRAC Microfinance Program in Bangladesh and Its International ReplicationsRevamp TwentyoneNo ratings yet
- Asian Development BankDocument33 pagesAsian Development BankSohailNo ratings yet
- 2013 Dow Pittsburg Community Grants Program Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument3 pages2013 Dow Pittsburg Community Grants Program Frequently Asked QuestionsDecian1No ratings yet
- Investor Presentation 2023Document89 pagesInvestor Presentation 2023mukeshindpatiNo ratings yet
- Esg Reporting in Banks 1706981673Document4 pagesEsg Reporting in Banks 1706981673luiz f TubinoNo ratings yet
- 10 Region GuidelinesDocument2 pages10 Region GuidelinesSamwise158No ratings yet
- Grants Call 2021-2022: Information For Applicants 1. Introduction and OverviewDocument9 pagesGrants Call 2021-2022: Information For Applicants 1. Introduction and OverviewKashvi ChandokNo ratings yet
- Dalberg - 130214 ADB IB Workshop - Introduction To IB Models - VFDocument33 pagesDalberg - 130214 ADB IB Workshop - Introduction To IB Models - VFADBPovertyNo ratings yet
- Lge 2010sr Stakeholder CommunicationDocument6 pagesLge 2010sr Stakeholder CommunicationAnh Khoa PhạmNo ratings yet
- GTCO American Rescue Plan PlanDocument23 pagesGTCO American Rescue Plan PlanDevon Louise KesslerNo ratings yet
- Briefing20 Scie Personal Budgets Young PeopleDocument28 pagesBriefing20 Scie Personal Budgets Young PeopleONLINEACCOUNT7715No ratings yet
- Olivia Dickson NED Financial Reporting Council, Impact Investing Institute, Pontaq Innovation FundDocument14 pagesOlivia Dickson NED Financial Reporting Council, Impact Investing Institute, Pontaq Innovation FundSid KaulNo ratings yet
- Social Transfer For Social Protection Towards Poverty ReductionDocument28 pagesSocial Transfer For Social Protection Towards Poverty ReductionJayson De LemonNo ratings yet
- Does Upcoming Pictures Makes You Remember AnythingDocument49 pagesDoes Upcoming Pictures Makes You Remember AnythingpankajnbholeNo ratings yet
- Integrated OutreachDocument3 pagesIntegrated OutreachCherotichNo ratings yet
- 2024 Grant Application Guide Fondation NexansDocument6 pages2024 Grant Application Guide Fondation NexansChristian David Vasconez VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Incubadoras Sustentabilidad en El MundoDocument6 pagesIncubadoras Sustentabilidad en El MundoMill LetNo ratings yet
- Basic Education and Literacy Guidelines enDocument9 pagesBasic Education and Literacy Guidelines enjake_calderónNo ratings yet
- PPP AlternativesDocument27 pagesPPP AlternativesarshiahmedNo ratings yet
- Six Examples of Large-Scale ProgramsDocument7 pagesSix Examples of Large-Scale ProgramsPhilcas LiNo ratings yet
- IFAD Vietnam Country Programme Evaluation March 2011Document29 pagesIFAD Vietnam Country Programme Evaluation March 2011IFAD VietnamNo ratings yet
- Digicel Foundation Community Grants 2021 Funding Guideline - FINALDocument3 pagesDigicel Foundation Community Grants 2021 Funding Guideline - FINALMathew WengmokNo ratings yet
- Direct Aid Program Application-ApplicationDocument10 pagesDirect Aid Program Application-ApplicationJojit BalodNo ratings yet
- x5e8M1fMS7SXvDNXzEu0ow - Exercise - Getting Help in Microsoft Word 365Document3 pagesx5e8M1fMS7SXvDNXzEu0ow - Exercise - Getting Help in Microsoft Word 365Mohsin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Partnership Working in Public HealthDocument20 pagesPartnership Working in Public HealthRio ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Climate Justice Working Group 12.2.21Document15 pagesClimate Justice Working Group 12.2.21OANo ratings yet
- 5consul Book Ch3Document8 pages5consul Book Ch3itsmohanecomNo ratings yet
- PSI: Private Sector Investment Programme: Funding Opportunity by The Netherlands For Private SectorDocument14 pagesPSI: Private Sector Investment Programme: Funding Opportunity by The Netherlands For Private SectorAhmed Ammar YasserNo ratings yet
- A Governance Framework for Climate Relevant Public Investment ManagementFrom EverandA Governance Framework for Climate Relevant Public Investment ManagementNo ratings yet
- Gateway Framework: A Governance Approach for Infrastructure Investment SustainabilityFrom EverandGateway Framework: A Governance Approach for Infrastructure Investment SustainabilityNo ratings yet
- Sadia's EssayDocument8 pagesSadia's EssayAsha ElNo ratings yet
- Final Triangle BibliographyDocument6 pagesFinal Triangle Bibliographyapi-203561364No ratings yet
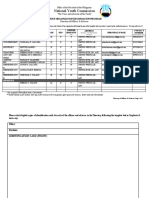
- National Youth Commission: Youth Organization Registration ProgramDocument2 pagesNational Youth Commission: Youth Organization Registration ProgramSun Shine OalnacarasNo ratings yet
- Onuf Making TerrorismDocument9 pagesOnuf Making TerrorismAna-Maria MoțocNo ratings yet
- Pollack, Mark A., Trump As A Change Agent in International Law - Ends, Means, and Legacies (June 15, 2022) PDFDocument36 pagesPollack, Mark A., Trump As A Change Agent in International Law - Ends, Means, and Legacies (June 15, 2022) PDFWilliam WulffNo ratings yet
- Breadwinner MomsDocument29 pagesBreadwinner MomsNewsday100% (1)
- Republic Act No 8042 Migrant Workers ActDocument13 pagesRepublic Act No 8042 Migrant Workers ActAdrianne BenignoNo ratings yet
- Week-11 Dualist and Monist TheoriesDocument5 pagesWeek-11 Dualist and Monist TheoriesApoorva YadavNo ratings yet
- St. Vincent Perez v. LPG Refillers Association of The Phils G.R. No. 159149 August 28, 2007Document3 pagesSt. Vincent Perez v. LPG Refillers Association of The Phils G.R. No. 159149 August 28, 2007jon_cpaNo ratings yet
- An Occasional Letter On The Female SexDocument4 pagesAn Occasional Letter On The Female SexErwinNicdaoNo ratings yet
- 53739-Article Text-156238-4-10-20220613Document13 pages53739-Article Text-156238-4-10-20220613Jafar UmarNo ratings yet
- BodethiguicosoDocument30 pagesBodethiguicosoKaiTrầnNo ratings yet
- Applying For Lic or ID SOS MichiganDocument1 pageApplying For Lic or ID SOS MichiganDolly PandyaNo ratings yet
- Executive Order No. 305Document52 pagesExecutive Order No. 305Dalton Chiong100% (1)
- 1946 ElectionDocument12 pages1946 Electionumer KhalidNo ratings yet
- 3.one of The Darkest Days of Philippine HistoryDocument51 pages3.one of The Darkest Days of Philippine HistoryAmakusa RyuNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1: How Do You See The Development of Two Nation Theory? Justify Your Answer WithDocument2 pagesAssignment No 1: How Do You See The Development of Two Nation Theory? Justify Your Answer WithSuleyman KhanNo ratings yet
- Progressive Movements in Pakistan CollectionDocument24 pagesProgressive Movements in Pakistan CollectionashrafkakkarNo ratings yet
- Maria Antoinette and Louis XviDocument3 pagesMaria Antoinette and Louis Xviapi-267173947No ratings yet
- Consti1 Outline ADBautista (1st Semester SY 2006 2007)Document16 pagesConsti1 Outline ADBautista (1st Semester SY 2006 2007)lex libertadore100% (1)
- 16th President of The Republic of The Philippines: Rodrigo "Digong" R. DuterteDocument6 pages16th President of The Republic of The Philippines: Rodrigo "Digong" R. DuterteJudith DelRosario De RoxasNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography SomaliaDocument9 pagesAnnotated Bibliography SomaliaDr. Abdurahman M. Abdullahi ( baadiyow)No ratings yet
- History of The USA - Reconstruction To New Age PoliticDocument3 pagesHistory of The USA - Reconstruction To New Age PoliticAnuj KumarNo ratings yet
- Summary All DTAs and Protocols 6 June 2012Document4 pagesSummary All DTAs and Protocols 6 June 2012sacripalNo ratings yet