Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Industrial Water Pollution Control Terms
Uploaded by
Apna VeerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Industrial Water Pollution Control Terms
Uploaded by
Apna VeerCopyright:
Available Formats
Industrial water pollution control terms
Activated carbon : carbon which is treated by high temprature heating with
steam or carbon dioxide producing an internal porous structre .
Absorption : the adhesion of an extremly thin layer of molecules to a surface of
solid or liquids with which they come in contact.
Aerobic : living or active only on presence of oxygen.
Aerobic biological oxidation : Any treatment utilizing aerobic organism as a agent
to reduce pollution load.
Anaerobic : living or active only in the absence of oxygen
Anerobic biological oxidation : Any method utlizing anaerobic organism to reduce
pollution load.
BOD : The Ampont of oxygen required for biological oxidation of organice matter
in a liquid.
Chemisorption : Adsorption where force holding the adsorbale to adsorbent is
chemical .
COD : The amount of oxygen required for chemical oxidation of matter in liquid.
Chlororination : Application of using chlorine to water or sewage for the purpose
of disinfection but frequenty for acomplishing other biological or chemical results.
Chalarifation : process of removing turbitidy & suspended solids by setting.
Chemicals can be added to improve and speedup setting process.
Coagulation : The process of adding a coagulent or other chemical materials for
treatment of water.
Colloids : A finely divided dispersion of one material in other material is called
colloids .
Dissolved oxygen : Amount of oxygen dissolved in water or sewage or any other
liquid. It is expressed in milligram per liter.
Effluent : A liquid which flows out of a containing space.
Filter tricking : Filter consisting of a artifical bed of coarse over which sewage
material is distributed.
Grease : grease includes fats, waxes,free fatty acids,soaps other nonfatty acid
materials .
Grit : The heavy minerals of matter in water sewage such as sand .
Hardness : A measure of capacity of water for precipitating soap.
Incrination : Combsution of waste water organic solid after water in evaported
from sludge .
Ozone : oxygen is molecular form with three atoms of oxygenin each molecule.
PH : a symbol denoting the negative logrithm of hydrogen ion concentration in a
solution.
Water Pollution : The introduction into a body of water of substances of such
characters and such quantity that its natural quality is so Altered as to impare its
usefulness or render its sense of taste and sight.
Pretreatment : any process used to reduce waste load partially before the water
waste is introduced into a main sewer system diliver to water treatment plant.
Primary Treatment : a process of removing sunbstainly floating and settleable
solid in waste water.
Secondary Treatment : Process to reduce the amount of dissolved organic matter
& further reduce the amount of suspended solid in waste water.
Tertiary Treatment : Process to remove all solids & organic matter from waste
water. Granula activated carbon method is a tertiay treatment.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Pakistan Chemical Manufacturers Association 3Document2 pagesPakistan Chemical Manufacturers Association 3Apna VeerNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Application Noteink Pump 170125111444Document1 pageApplication Noteink Pump 170125111444Apna VeerNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- CARSDocument15 pagesCARSApna VeerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Induction Motor: Experiment 11Document4 pagesIntroduction To Induction Motor: Experiment 11Apna VeerNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Introduction To Transformer: Experiment 8Document3 pagesIntroduction To Transformer: Experiment 8Apna VeerNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Introduction To DC Motors: Experiment 13Document4 pagesIntroduction To DC Motors: Experiment 13Apna VeerNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- icimodHimalicaPP PakistanDocument4 pagesicimodHimalicaPP PakistanApna VeerNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Fia Inspector and CustomDocument73 pagesFia Inspector and CustomApna VeerNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Study of Step Up & Step Down Transformer: Experiment 9Document3 pagesStudy of Step Up & Step Down Transformer: Experiment 9Apna Veer100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Worlds Currents AffairsDocument46 pagesWorlds Currents AffairsApna VeerNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
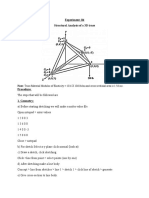
- Experiment: 04 Structural Analysis of A 3D Truss: and Cross Sectional Area Is 1.56 inDocument3 pagesExperiment: 04 Structural Analysis of A 3D Truss: and Cross Sectional Area Is 1.56 inApna VeerNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- New Statics Numericals With SolutionDocument15 pagesNew Statics Numericals With SolutionApna VeerNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Workshop Lec4Document16 pagesWorkshop Lec4Apna VeerNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
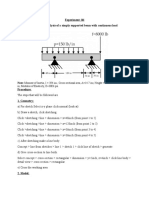
- Experiment: 06 Structural Analysis of A Simply Supported Beam With Continuous LoadDocument3 pagesExperiment: 06 Structural Analysis of A Simply Supported Beam With Continuous LoadApna VeerNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Payment Infrastructure in Pakistan: White Paper OnDocument30 pagesE-Commerce Payment Infrastructure in Pakistan: White Paper OnApna VeerNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Experiment: 01: Introduction To AnsysDocument21 pagesExperiment: 01: Introduction To AnsysApna VeerNo ratings yet
- Tobacco Industry Activities in Pakistan: WHO-EM/TFI/055/EDocument44 pagesTobacco Industry Activities in Pakistan: WHO-EM/TFI/055/EApna VeerNo ratings yet
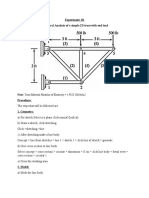
- Experiment: 03 Structural Analysis of 2D Truss With Load at CenterDocument2 pagesExperiment: 03 Structural Analysis of 2D Truss With Load at CenterApna VeerNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Defence Industry The Options For Pakistan: NDU Journal 2012Document20 pagesDefence Industry The Options For Pakistan: NDU Journal 2012Apna VeerNo ratings yet
- Experiment: 02 Structural Analysis of A Simple 2D Truss With End LoadDocument3 pagesExperiment: 02 Structural Analysis of A Simple 2D Truss With End LoadApna VeerNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Final List Voter C-15 of 2010Document4 pagesFinal List Voter C-15 of 2010Apna VeerNo ratings yet
- List of Hospitals: AIL Dedicated Help Line For Group Health Insurance Available 24/7 (0305-4449090)Document4 pagesList of Hospitals: AIL Dedicated Help Line For Group Health Insurance Available 24/7 (0305-4449090)Apna VeerNo ratings yet
- Anglais - Cies Assurances Agréées Schengen À IslamabadDocument1 pageAnglais - Cies Assurances Agréées Schengen À IslamabadApna VeerNo ratings yet
- Amazon VA NotesDocument101 pagesAmazon VA NotesApna Veer100% (2)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- CIVICUS Project Collaboration ProposalDocument12 pagesCIVICUS Project Collaboration ProposalApna VeerNo ratings yet
- Tag-Generator-Youtube-khadim Hussain-GlobalDocument28 pagesTag-Generator-Youtube-khadim Hussain-GlobalApna VeerNo ratings yet
- ADppt-S ADocument39 pagesADppt-S AApna VeerNo ratings yet
- Ad BLUEDocument61 pagesAd BLUEFrancisco Santiago Gallardo100% (3)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Ocr Gateways c1c2c3Document36 pagesOcr Gateways c1c2c3Jatinder BathNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil: Bangladesh Power Management Institute (BPMI) 2019Document34 pagesTransformer Oil: Bangladesh Power Management Institute (BPMI) 2019Farhan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Plug and Abandonment of Subsea WellsDocument23 pagesChapter 5 - Plug and Abandonment of Subsea WellsSalvador Morales LeónNo ratings yet
- Expansion Vessels enDocument32 pagesExpansion Vessels enahmed100% (1)
- Workplace HazardsDocument26 pagesWorkplace HazardsPageduesca RouelNo ratings yet
- MCAT Topic Focus Biology Electrophoresis and Blotting FSQ DrillDocument1 pageMCAT Topic Focus Biology Electrophoresis and Blotting FSQ DrillAnjalie GulatiNo ratings yet
- VBF 21Document6 pagesVBF 21harishupretiNo ratings yet
- BOQ Fountain Water Body (1) .XLSXBDocument6 pagesBOQ Fountain Water Body (1) .XLSXBPrashant Singh Chauhan60% (5)
- Ammonia Based Refrigeration SystemsDocument19 pagesAmmonia Based Refrigeration SystemsHoainam NguyenNo ratings yet
- Yokohama Conveyor BeltsDocument87 pagesYokohama Conveyor BeltsU Thaung Myint100% (12)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Petrogenesis of Metamorphic Rocks (Helmut G. F. Winkler)Document359 pagesPetrogenesis of Metamorphic Rocks (Helmut G. F. Winkler)Larissa Coelho100% (6)
- Post Weld Heat TreatmentDocument3 pagesPost Weld Heat TreatmentpvdrameshNo ratings yet
- Method Statement - Cementitious GroutingDocument8 pagesMethod Statement - Cementitious GroutingDimitris DountsisNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical Methods: Presented ToDocument36 pagesElectroanalytical Methods: Presented ToSyed UmairNo ratings yet
- Ex 3 - Reacting Masses, Solutions & ConcentrationsDocument4 pagesEx 3 - Reacting Masses, Solutions & ConcentrationsLeon Lim Teck ShernNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base WorksheetDocument4 pagesAcid and Base Worksheetapi-270967967No ratings yet
- Epn008msds N1250 - en - SDSDocument9 pagesEpn008msds N1250 - en - SDSSANI RIZKINo ratings yet
- Valorizacion Del Desecho de Aguas Residuales Del Prosamiento de AceitunasDocument11 pagesValorizacion Del Desecho de Aguas Residuales Del Prosamiento de AceitunasJalcamNo ratings yet
- Research Article Removal of 3-MCPD Esters and Related Substances After Refining by Adsorbent MaterialDocument6 pagesResearch Article Removal of 3-MCPD Esters and Related Substances After Refining by Adsorbent MaterialAlexNo ratings yet
- January - February 2013 - International Aquafeed Magazine - Full EditionDocument68 pagesJanuary - February 2013 - International Aquafeed Magazine - Full EditionInternational Aquafeed magazineNo ratings yet
- Basic Food Chemistry Guided NotesDocument3 pagesBasic Food Chemistry Guided NotesJBE legendsNo ratings yet
- PHYSIO ReviewerDocument3 pagesPHYSIO ReviewerPHILYP EPHRAIM PARANGALANNo ratings yet
- Braskem Braskem PP PCD 0140BR Polypropylene Impact CopolymerDocument2 pagesBraskem Braskem PP PCD 0140BR Polypropylene Impact CopolymerBFCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1 - CoagulationDocument51 pagesChapter 3.1 - CoagulationHanif NifNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Trihalomethanes: and Related Pentane-Extractable Organic HalidesDocument33 pagesAnalysis of Trihalomethanes: and Related Pentane-Extractable Organic HalidesaviantaraNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id4492574Document16 pagesSSRN Id4492574Sai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument23 pages6.1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsShadow MartinNo ratings yet
- Soil Color and Texture MeaningDocument9 pagesSoil Color and Texture MeaningTinashe KatsuroNo ratings yet
- Power Required For Mixing Power Required For MixingDocument5 pagesPower Required For Mixing Power Required For MixingSudiv GullaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tFrom EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosFrom EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonFrom EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Retro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsFrom EverandRetro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsNo ratings yet