Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tugas Bahasa Ingris
Uploaded by
wa ode wulan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesTugas Bahasa Ingris
Uploaded by
wa ode wulanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
NAME : WA ODE WULAN
NIM : 124021 2018 094
CLASS : 2C
ABDOMINAL COLIC
A. DEFINATION OF ABDOMINAL COLIC
Abdominal colic is a disorder of the normal flow of intestinal ontents
along the intestinal track. Obstruction occurs when there is a distrubancee that.
Obstruction of the flow of intestinal contents forward but the peristaltis is normal.
B. CAUSES OF ABDOMINAL COLIC
1. Mechanical adhesions or adhesions after surgery (90% of mechanical
obstruction)
Carcinoma
Volvulus
Intussusception
Obstipation
Polyps
Stricture
2. Fuctional (non mechanical)
Paralytic ileus
Spin)al cord lesions
Regional enteritis
Electrolyte imbalance
Uremia
C. SYMPTOMS OF COLIC ABDOMEN
1. Simple mechanics – upper small intestine
Colic disease (cramps) in the mid to upper abdomen, distension, initial bile
vomiting, increased bowel sounds (high-pitched chirping sounds at short
intervals), minimal diffuse tenderness.
2. Simple mechanics – lower intestine
Significant midabdominal colic disease, severe distention, vomiting – little
or no – then have pulp, bowel sounds and ‘hush’ sounds increased, diffuse
tendernss is minimal.
3. Simple mechanics – colon
Cramps (middle to lower abdomen), distention that appears last then
vomiting (facular), increased bowel sounds, minimal diffuse tenderness.
4. Partical mechanical obstruction
Can occur with intestinal granulomatosa in crohn’s disease. Symptoms of
abdominal colic are cramping abdominal pain, mild distension and diarrhea.
5. Stragulation
Symptoms of abdominal colic develop quickly; severe continuous and
localized pain; moderate distension; persistent vomiting; usually bowel sounds
decrease and tenderness is localized violently. Stool or vomitus becomes dark or
bloody or contains faint blood.
D. ABDOMINAL COLIC TREATMENT
RL ifusion; if anuria -> infusion RL: D5= 1 : 1
If severe dehydration -> drips, a catheter is inserted
Give mild analgesics (xylomidone), Spasmolytic: baralgon, sulfas aliopin
(inj): if very painful -> give 1 ampid petidin, don’t give antibiotics if the
cause is unclear
If the patient is restless, give Diazpam 10 mg iv, can be repeated every 30
minutes
If it’s hot, give antipyretics (paracetamol)
If the general condition is bad, give supportive vitamin/alonamin F (inj),
cortison inj 3 cc or dexamethasone 2 amp
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 2012 NCCAOM Herbal Exam QuestionsDocument10 pages2012 NCCAOM Herbal Exam QuestionsElizabeth Durkee Neil100% (2)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Nursing Care Plan For "Lymphomas"Document9 pagesNursing Care Plan For "Lymphomas"jhonroks89% (9)
- Cardiovascular Physical TherapDocument7 pagesCardiovascular Physical TherapJadie Prenio100% (4)
- Nclex RN GI & Burns & FracturesDocument87 pagesNclex RN GI & Burns & Fracturesgraceface55100% (4)
- UIE Wells: JULY 2010Document42 pagesUIE Wells: JULY 2010Emenike Donald EjiejiNo ratings yet
- Journal ReviewDocument19 pagesJournal ReviewIvandy 99No ratings yet
- English Task: 4. Fill in The Blanks With The Correct Words From The Word BankDocument4 pagesEnglish Task: 4. Fill in The Blanks With The Correct Words From The Word Bankwa ode wulanNo ratings yet
- English TaskDocument10 pagesEnglish Taskwa ode wulan0% (1)
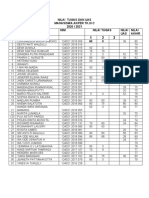
- Nilai Tugas Dan Uas TK Iii CDocument1 pageNilai Tugas Dan Uas TK Iii Cwa ode wulanNo ratings yet
- English TaskDocument6 pagesEnglish Taskwa ode wulanNo ratings yet
- English Task: 4. Fill in The Blanks With The Correct Words From The Word BankDocument4 pagesEnglish Task: 4. Fill in The Blanks With The Correct Words From The Word Bankwa ode wulanNo ratings yet
- QweqDocument18 pagesQweqakbarNo ratings yet
- English Task: 4. Fill in The Blanks With The Correct Words From The Word BankDocument4 pagesEnglish Task: 4. Fill in The Blanks With The Correct Words From The Word Bankwa ode wulanNo ratings yet
- P1 - Kamis, 02 Maret 2023Document1 pageP1 - Kamis, 02 Maret 2023josephNo ratings yet
- Rosuvastatin and AtorvastatinDocument11 pagesRosuvastatin and AtorvastatinNandan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Paediatrics Ii (A)Document1 pagePaediatrics Ii (A)AlolikaNo ratings yet
- 155 Latest Drugs - Neet PG Next PG Ini Cet FmgeDocument16 pages155 Latest Drugs - Neet PG Next PG Ini Cet FmgeSamikshya NayakNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Slide Presentation SET BDocument28 pagesParasitology Slide Presentation SET BNorjetalexis CabreraNo ratings yet
- 202004061939435276sptrivedi Fish DiseasesDocument19 pages202004061939435276sptrivedi Fish DiseasesSaravanan arnoldNo ratings yet
- ExplanationDocument8 pagesExplanationmarisa dwilestariNo ratings yet
- VP Shunt UrgencyDocument7 pagesVP Shunt UrgencyAollia GoodmaanNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic and NephriticDocument3 pagesNephrotic and Nephritickguzman92No ratings yet
- Hystrix Like Ichthyosis With DeafnessDocument3 pagesHystrix Like Ichthyosis With DeafnessjehzamudioNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Regarding Prevention of Helminthic Disease Among School ChildrenDocument5 pagesKnowledge Regarding Prevention of Helminthic Disease Among School ChildrenIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Blindness: Blindness Is The Condition of Poor Visual Perception. Various Scales Have BeenDocument5 pagesBlindness: Blindness Is The Condition of Poor Visual Perception. Various Scales Have BeenMonday VerdejoNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis:: Nontyphoidal Salmonella InfectionDocument2 pagesGastroenteritis:: Nontyphoidal Salmonella InfectionYana KostNo ratings yet
- Septick ShockDocument15 pagesSeptick ShockAnisa Dwi BudiartiNo ratings yet
- Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument41 pagesClick To Edit Master Subtitle StyleMahar NaveedNo ratings yet
- Accuracy of Lung UltrasoundDocument6 pagesAccuracy of Lung UltrasoundСергей КапустинNo ratings yet
- Committee Opinion: Endometrial Intraepithelial NeoplasiaDocument7 pagesCommittee Opinion: Endometrial Intraepithelial NeoplasiaRizkiNo ratings yet
- CBT For Tinnitus (20 Nov 2023)Document48 pagesCBT For Tinnitus (20 Nov 2023)agietz27No ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests - Purpose and ProcedureDocument12 pagesLiver Function Tests - Purpose and ProcedureJennifer CollinsNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Name of Procedure Indications Contraindications Articles Required Special Considerations and Precautions 1. Non-Stress Test MaternalDocument4 pagesS.NO. Name of Procedure Indications Contraindications Articles Required Special Considerations and Precautions 1. Non-Stress Test Maternaljyoti ranaNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Recovery After Cesarean Delivery Role.2Document6 pagesEnhanced Recovery After Cesarean Delivery Role.2Kirin PorNo ratings yet
- Giant Pulmonary Bullae in Children: Journal of Pediatric Surgery Case Reports July 2020Document7 pagesGiant Pulmonary Bullae in Children: Journal of Pediatric Surgery Case Reports July 2020SOPHIASTIA KUSBIANTI MHS 2017No ratings yet
- Stoma ExaminationDocument23 pagesStoma ExaminationHy1234No ratings yet
- Sci9 Q1 Mod2 Effects of Lifestyle On The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems.Document28 pagesSci9 Q1 Mod2 Effects of Lifestyle On The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems.Mary Grace UntalanNo ratings yet
- Common Sleep Problems in Children - Pediatrics in Review - 2011Document11 pagesCommon Sleep Problems in Children - Pediatrics in Review - 2011JanelleNo ratings yet
- Infection Control - NclexDocument4 pagesInfection Control - NclexTashaNo ratings yet