Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antonne Van Leeuwenhoek Discovered The Bacteria by Microscope
Uploaded by
hfjsdhfOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antonne Van Leeuwenhoek Discovered The Bacteria by Microscope
Uploaded by
hfjsdhfCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSIGNMENT
BACTERIA
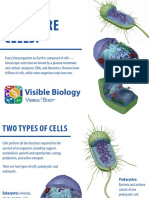
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Prokaryotes Eukaryotes
They do not have true nucleus. They have true nucleus.
They do not have membrane bounded organelles. They have membrane bounded organelles.
They are simple. They are complex.
e.g Bacteria e.g Animals, plants
Bacteria
Bacterial cell is different from plant and animal cell in many ways. They do not have true nucleus and
membrane bounded organelles. That why they are known as “prokaryotes”. They are the tiny organisms which
can’t be seen with the naked eye. They can only be observed under microscope.
Discovery of bacteria: Antonne Van Leeuwenhoek discovered the bacteria by microscope.
Occurrence: They are found in all environments. They are found in air, water, soil and also in or on the bodies
of plants and animals.
Structure: Bacterial cell includes following structures:
Capsule: It is a layer outside the cell wall. Most but not all bacteria have capsule.
Cell wall: A thin membrane located outside the plasma membrane and within the capsule. It protect the
cell and give shape to the cell.
Plasma membrane: It is a semi permeable membrane that helps in transport of chemicals and energy
generation.
Cytoplasm: The jelly like material located inside the plasma membrane in which genetic material and
ribosomes are located.
DNA: It is the genetic material of the bacteria, located within the cytoplasm in a region called nucleoid
region.
Ribosomes: These are small organelles located in the cytoplasm that are sites of protein synthesis.
Plasmid: A plasmid is a short, circular and double stranded segment of DNA that is found in cytoplasm,
separate from the main bacterial chromosomes. The term plasmid was first introduced by American
molecular biologist Joshua Lederberg in 1952.
Pilus: They are hair like and help a bacteria to stick to a surface.
Flagellum: A long whip like structure used for locomotion. Some bacteria have
more than one flagellum.
Different species of bacteria have different numbers and arrangements of flagella.
Monotrichous bacteria have a single flagellum at one end.
Amphitrichous bacteria have single flagellum on both sides.
Lophotrichous bacteria have cluster of flagella at one end.
Amphilophotrichous bacteria have cluster of flagella at both ends.
Peritrichous bacteria have many flagella distributed on entire body.
Shapes of bacteria: Bacteria are classified into 3 groups on the basis of their shape.
Cocci: They are of round/circular shape.
Bacilli: They are of rod shape.
Spirilla: They are of spiral shape.
Endospore: During unfavorable conditions, certain bacteria form resistant cells celled endospores, to
overcome the harsh environment. These endospore remain dormant for longer period of time and germinate,
when the environmental conditions become favorable.
Reproduction: Bacteria grows in colonies and reproduce both asexually and sexually.
Asexual reproduction: Bacteria increase in size, duplicate its DNA and split into two.
Sexual reproduction: Two separate bacteria exchange their piece of DNA.
You might also like
- Module 3-P. E. CellsDocument4 pagesModule 3-P. E. CellsRylle SimonNo ratings yet
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- All About CellsDocument49 pagesAll About CellsJeanine CristobalNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsDocument8 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsMarcy BoralNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument53 pagesCell and Cell OrganellesShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- 20160624120627topic 2 - CellsDocument30 pages20160624120627topic 2 - CellshilmanNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument41 pagesLESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Microbiology UNIT 1Document43 pagesEnvironmental Microbiology UNIT 1Esai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes: NucleoidDocument3 pagesProkaryotes: NucleoidHubdar Ali KolachiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellKylie VillafloresNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions What Are Monerans? How Does Monera Feed? Where Is Monera Found? How Are Monerans Classified? How Does Monera Reproduce?Document31 pagesFrequently Asked Questions What Are Monerans? How Does Monera Feed? Where Is Monera Found? How Are Monerans Classified? How Does Monera Reproduce?thayaNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument16 pagesCell BiologyKlint Rodney Mark Lule100% (1)
- Prokaryotic CellDocument4 pagesProkaryotic Cellkrista mae logronoNo ratings yet
- CellDocument6 pagesCellHONEYLYN CASINGNo ratings yet
- Yel's ReportDocument25 pagesYel's ReportMarc De JoyaNo ratings yet
- ProkaryotesDocument15 pagesProkaryotesVISHNU E SNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument103 pagesBIOLOGYKamesh RamamoorthyNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument3 pagesThe CellMary Ann FriasNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cells. BacteriaDocument6 pagesProkaryotic Cells. BacteriaAndreea VrabieNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes vs. EukaryotesChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Summaries 1-30 Microbiology Summaries 1-30Document53 pagesMicrobiology Summaries 1-30 Microbiology Summaries 1-30yepNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CELL BIO - 2014 FinalDocument17 pagesUnit 4 CELL BIO - 2014 FinalTizita EmanaNo ratings yet
- Biology 2Document3 pagesBiology 2Karriel AguilarNo ratings yet
- Pro Kary OtesDocument2 pagesPro Kary OteshomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Cell: Prepared By: Asley Raven MacatiagDocument29 pagesLesson 2 The Cell: Prepared By: Asley Raven MacatiagescribdeeNo ratings yet
- Form 4Hk/Year 10 Biology Characteristics and Diagrams of Bacteria, Viruses and FungiDocument12 pagesForm 4Hk/Year 10 Biology Characteristics and Diagrams of Bacteria, Viruses and FungiShadreck MagangaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Assignment Gr. 3Document26 pagesCell Biology Assignment Gr. 3Lamin N CeesayNo ratings yet
- Micro 1st ProkaryotesDocument16 pagesMicro 1st ProkaryotesMatahari SempurnaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Unit of LifeDocument17 pagesThe Cell Unit of LifeRitikNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Notes Final-2Document58 pagesMicrobiology Notes Final-2arvindk962706No ratings yet
- Unit-I Basic Cell BiologyDocument116 pagesUnit-I Basic Cell Biologyvishav sharmaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and OrganizationDocument13 pagesCell Structure and Organizationomololabalogun676No ratings yet
- VisibleBody Cell ComparisonDocument10 pagesVisibleBody Cell ComparisonAnjarika TripathyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 3Document32 pagesUnit 1 - 3Sunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument19 pagesProkaryote Vs EukaryotehamnaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument21 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellskenNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 DraftDocument136 pagesGeneral Biology 1 DraftReiggie Resurreccion100% (1)
- GB1 Module 1.2Document4 pagesGB1 Module 1.2beatriz OndilloNo ratings yet
- Prokaryoticandeukaryotic Cells Close ReadingDocument4 pagesProkaryoticandeukaryotic Cells Close Readingapi-165869000No ratings yet
- Lesson 2.3 General BiologyDocument15 pagesLesson 2.3 General BiologyMeiko DesantoresNo ratings yet
- Environment MicrobiologyDocument16 pagesEnvironment Microbiologymohamed ishaqNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology:: Mycoplasmas Are The Smallest Known Bacteria. They Are Cell Wall DeficientDocument8 pagesCell Biology:: Mycoplasmas Are The Smallest Known Bacteria. They Are Cell Wall DeficientMark Dave Benito TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Botany Full PDF EMDocument72 pagesBotany Full PDF EMAbinaya PalaniNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Bacteria and VirusesDocument51 pagesAP Biology Bacteria and VirusesMichael TsaiNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes VS EukaryotesDocument15 pagesProkaryotes VS EukaryotesChool Cydrick B. BascosNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes VS EukaryotesDocument15 pagesProkaryotes VS EukaryotesGamu GamuNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology and Virology by KaziDocument35 pagesBacteriology and Virology by KaziMohibNo ratings yet
- in Micro para Lecture Chapter 2Document21 pagesin Micro para Lecture Chapter 2Mica-Ella CasasolaNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines Quiapo, ManilaDocument4 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines Quiapo, ManilaKrystel LahomNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.1 CellDocument9 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.1 CellJosebeth CairoNo ratings yet
- Science of Living Systems: Dr. Prakhar TiwariDocument64 pagesScience of Living Systems: Dr. Prakhar TiwariAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheeetDocument3 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryote Worksheeetsomeone swagNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument10 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Endoplasmic ReticulumChristopher PhilipNo ratings yet
- Introd UctionDocument19 pagesIntrod UctiontusharNo ratings yet
- Biol 1017-Cell Biology: Prokaryotes & MicrosDocument50 pagesBiol 1017-Cell Biology: Prokaryotes & MicrosJoshua HarveyNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Notes Cell Basic Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCH 1 Notes Cell Basic Unit of LifetsudheraNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument6 pagesBiologyBlue TechNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Bacterial Structure and FunctionsDocument7 pagesThe Cell: Bacterial Structure and FunctionsMargarette DayohaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT (Cell The Unit of Life)Document27 pagesBIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT (Cell The Unit of Life)Ashay Kumar0% (1)
- (Language and Literacy Series) Carol Brennan Jenkins, Alice Altfillische Earle, George Kamberelis - Once Upon A Fact - Helping Children Write Nonfiction-Teachers College Press (2006)Document193 pages(Language and Literacy Series) Carol Brennan Jenkins, Alice Altfillische Earle, George Kamberelis - Once Upon A Fact - Helping Children Write Nonfiction-Teachers College Press (2006)hfjsdhfNo ratings yet
- Richard Johnston - Evolution - Fact or Fable (2002)Document94 pagesRichard Johnston - Evolution - Fact or Fable (2002)hfjsdhfNo ratings yet
- Introduction of BiologyDocument1 pageIntroduction of BiologyhfjsdhfNo ratings yet
- Fan R. - Linkage and Association Studies of QTL For Nuclear Families by Mixed Models (2003)Document21 pagesFan R. - Linkage and Association Studies of QTL For Nuclear Families by Mixed Models (2003)hfjsdhfNo ratings yet
- FDFDocument1 pageFDFhfjsdhfNo ratings yet
- Week 1-Introduction of BioindustryDocument31 pagesWeek 1-Introduction of BioindustryFery HaidirNo ratings yet
- General AnatomiDocument28 pagesGeneral Anatomid25No ratings yet
- 3d Cell RubricDocument1 page3d Cell RubricVina Rose Francisco AlomeaNo ratings yet
- PNU Final Coaching Gen - EdDocument15 pagesPNU Final Coaching Gen - EdTatinNo ratings yet
- Lactic Acid Production From Cane MolassesDocument4 pagesLactic Acid Production From Cane MolassesSenkatuuka LukeNo ratings yet
- Diresul Navy RDT-GF LiqDocument18 pagesDiresul Navy RDT-GF Liqabdlahmid_bahriNo ratings yet
- Chatgpt Handbook For TeachersDocument23 pagesChatgpt Handbook For TeachersŠadi Fadda100% (1)
- Upcoming Predicted Material For PTE-A Exam Feb-2019Document123 pagesUpcoming Predicted Material For PTE-A Exam Feb-2019GauravNo ratings yet
- Immune Response in The Human BodyDocument30 pagesImmune Response in The Human BodyjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Activity 2. Plant Cell Vs Animal CellDocument5 pagesActivity 2. Plant Cell Vs Animal CellMary Joyce BonayonNo ratings yet
- Blue BrainDocument20 pagesBlue BrainAnkitaPatel009No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document61 pagesUnit 3JessicaHaeNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Tingkat Pengetahuan Dan Dukungan Keluarga Terhadap Kepatuhan Ibu Hamil Mengkonsumsi Tablet Zat BesiDocument13 pagesHubungan Tingkat Pengetahuan Dan Dukungan Keluarga Terhadap Kepatuhan Ibu Hamil Mengkonsumsi Tablet Zat Besinovilia eka sariNo ratings yet
- Kak UkkDocument4 pagesKak UkksantiNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument21 pagesMitosisChristine PiedadNo ratings yet
- Ahmad Faizal Bin Ahmad Zahari (Resume)Document15 pagesAhmad Faizal Bin Ahmad Zahari (Resume)ahmad faizalNo ratings yet
- MFK-Drug Management CycleDocument32 pagesMFK-Drug Management CycleLhynda Priarti Latif100% (1)
- DNA Isolation From Cheek CellsDocument2 pagesDNA Isolation From Cheek CellsJed TuazonNo ratings yet
- Q1 Module 3 Science 9Document32 pagesQ1 Module 3 Science 9リリスセレインNo ratings yet
- Kroll Expert Report Avitabile V BeachDocument43 pagesKroll Expert Report Avitabile V Beachwolf woodNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ 43Document10 pagesĐỀ 43Le QuocNo ratings yet
- MCQ of Diagnosis BacterialDocument11 pagesMCQ of Diagnosis Bacterialمحمد اللاميNo ratings yet
- The Biology of Social Adversity Applied To Oral Health: N. Gomaa, H. Tenenbaum, M. Glogauer, and C. QuiñonezDocument9 pagesThe Biology of Social Adversity Applied To Oral Health: N. Gomaa, H. Tenenbaum, M. Glogauer, and C. QuiñonezFabricio LafebreNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab ReportDocument13 pagesBiology Lab Reportapi-390838152No ratings yet
- Lab 3: The Mechanical and Electrical Activity of The HeartDocument26 pagesLab 3: The Mechanical and Electrical Activity of The HeartfuarudinrNo ratings yet
- Effect of PH On Enzyme ActivityDocument12 pagesEffect of PH On Enzyme ActivityAb AbNo ratings yet
- Dolly The SheepDocument7 pagesDolly The SheepRhan AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- 24 5 2022 Ac01.0003860148 Csp-Ics-21254 91-9962016683Document8 pages24 5 2022 Ac01.0003860148 Csp-Ics-21254 91-9962016683Manikandan Ayyasamy100% (1)
- Paired Passages - PresentationDocument17 pagesPaired Passages - Presentationsuchi ravaliaNo ratings yet
- SH Libro CompletoDocument80 pagesSH Libro CompletoMickel Caballero100% (1)