Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Trends in Periods and Groups
Uploaded by
Teejay MakazhuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Trends in Periods and Groups
Uploaded by
Teejay MakazhuCopyright:
Available Formats
NOCKHARDY
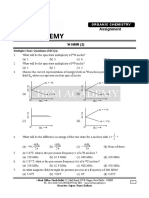
PERIODIC TRENDS
K NOTES PERIODICITY ALL TRENDS REFER TO GOING DOWN A GROUP AND ACROSS A PERIOD
AT A G L AN CE
A LEVEL CHEMISTRY ATOMIC RADIUS
Groups INCREASES • more electrons going into shells further from nucleus
TRENDS ➀ ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION Periods DECREASES • increased nuclear charge attracts electrons
➁ ATOMIC RADIUS
➂ IONISATION ENERGY
➃ ELECTRON AFFINITY IONISATION ENERGY
➄ ELECTRONEGATIVITY Groups DECREASES • electrons further from nucleus
• more shielding
➅ MELTING POINT • electrons held less strongly - easier to remove
Most trends can be explained by considering the attraction between the Periods INCREASES • increased nuclear charge attracts electrons
protons in the nucleus and the electrons in the outer shell or energy level • electrons become harder to remove
• IRREGULARITIES due to the way orbitals are filled
DOWN
GROUPS • atomic number increases
• atoms have more protons - increased nuclear charge ELECTRONEGATIVITY
• atoms get bigger - electrons occupy more shells Groups DECREASES • electrons further from nucleus
• more shielding
• outer electrons are shielded by filled inner shells • electron pair in covalent bond is attracted less strongly
• outer electrons are further from nucleus
• the pulling power of the nucleus gets less Periods INCREASES • increased nuclear charge attracts electron pair in bond
• outer electrons are held less strongly
ELECTRON AFFINITY
ACROSS Groups LESS NEGATIVE • electrons further from nucleus + more shielding
PERIODS • atomic number increases by one each time • electron are attracted less strongly
• atoms have one more proton and electron
• slight increase in nuclear charge Periods MORE NEGATIVE • increased nuclear charge attracts electrons
• electron is easier to pull in
• electrons occupy the same shell - no increase in shielding
• outer electrons are no further from nucleus
• the pulling power of the nucleus gets a little greater MELTING POINT - dependant on structure and bond type
• outer electrons are held more strongly Groups DECREASES • metallic bonding decreases as size increases
• electron cloud isn’t as effective at holding ions together
Nuclear Charge The charge due to the protons in the nucleus Periods VARIABLE • depends on structure and bonding - rises then falls
• rises as metals contribute more electrons to the cloud
Effective nuclear The effectiveness of the nuclear charge after • big rise for giant molecules in Group IV
Charge passing through any filled inner shells • drops for simple molecules with weak intermolecular forces
© J. L. HOPTON 1999
You might also like
- Chem NotesDocument300 pagesChem NotesTeejay MakazhuNo ratings yet
- A' Level Inorganic Chemistry: by Mukanda S.MDocument51 pagesA' Level Inorganic Chemistry: by Mukanda S.MTeejay Makazhu100% (4)
- Chem NotesDocument300 pagesChem NotesTeejay MakazhuNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: Alkanes Alkanes Alkenes Hydrocarbons As Fuels ArenesDocument23 pagesAlkanes: Alkanes Alkanes Alkenes Hydrocarbons As Fuels ArenesTeejay MakazhuNo ratings yet
- Electrode Potential QuestionsDocument2 pagesElectrode Potential QuestionsTeejay MakazhuNo ratings yet
- A Level Organic Chemistry NotesDocument68 pagesA Level Organic Chemistry NotesTeejay Makazhu100% (11)
- Electrode Potential QuestionsDocument2 pagesElectrode Potential QuestionsTeejay MakazhuNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal ComplexesDocument52 pagesTransition Metal ComplexesTeejay MakazhuNo ratings yet
- B CyclesDocument21 pagesB CyclesTeejay MakazhuNo ratings yet
- Copper Sulphate TitrationDocument29 pagesCopper Sulphate TitrationTeejay Makazhu100% (1)
- ENTHALPYDocument38 pagesENTHALPYTeejay MakazhuNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Comparision of Piping CodeDocument14 pagesComparision of Piping CodeAnonymous J1vjrU2No ratings yet
- Omega Air: B-DRY 110-1000 f-DRY 1200-6500Document2 pagesOmega Air: B-DRY 110-1000 f-DRY 1200-6500Junaid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Aspen AdsimDocument307 pagesAspen Adsimkiny81100% (3)
- Jones Classical Aerodynamic TheoryDocument320 pagesJones Classical Aerodynamic TheoryJohn ClistenesNo ratings yet
- Boiler Book PDFDocument44 pagesBoiler Book PDFmpgzyah100% (5)
- Pressure Relief ValveDocument24 pagesPressure Relief Valvevinoth.kumarNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@978 94 024 0867 6 PDFDocument735 pages10.1007@978 94 024 0867 6 PDFutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Flash Distillation - Che 411-27-01-2021Document18 pagesFlash Distillation - Che 411-27-01-2021Hannah CokerNo ratings yet
- 2 - 1H NMRDocument3 pages2 - 1H NMRAbhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- Extra High Strength Steels - Strenx vs. HardoxDocument1 pageExtra High Strength Steels - Strenx vs. Hardoxdavid blecicNo ratings yet
- Catalase InvestigationDocument5 pagesCatalase Investigation9름No ratings yet
- Hydrological Fluvial Coastal Limestone EnvironmentsDocument52 pagesHydrological Fluvial Coastal Limestone EnvironmentsDharam Jagroop100% (1)
- For Finals Practice ProblemsDocument13 pagesFor Finals Practice Problemsengr marcialawNo ratings yet
- PricelistDocument136 pagesPricelistCervantesquijoteNo ratings yet
- 3 Periodical Examination S.Y. 2018-2019 Science VI: Umingan Central Elementary SchoolDocument4 pages3 Periodical Examination S.Y. 2018-2019 Science VI: Umingan Central Elementary SchoolPrincis CianoNo ratings yet
- TUBE Bending FormulasDocument3 pagesTUBE Bending FormulasPavan BhadarkaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science FinalDocument19 pagesGrade 7 Science FinalHazel Escobio Justol CahucomNo ratings yet
- Nikon ECLIPSE LV100N POLCi-POLDocument8 pagesNikon ECLIPSE LV100N POLCi-POLvictorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - 12Document192 pagesChemistry - 12Gurusaran KalraNo ratings yet
- 3..oil Field TubularsDocument32 pages3..oil Field TubularsDarshan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Design of A Three-Storey Commercial Building: I. Description of The StructureDocument8 pagesDesign of A Three-Storey Commercial Building: I. Description of The StructureShōya Ishida100% (1)
- Kishen Hydormechanics in Dentine Role of Dentinal Tubules and Hydrostatic Pressure On Mechanical Stress-Strain DistributionDocument11 pagesKishen Hydormechanics in Dentine Role of Dentinal Tubules and Hydrostatic Pressure On Mechanical Stress-Strain DistributionОлександр БайдоNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document35 pagesChapter 07Hassan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual of RH 143Document7 pagesInstruction Manual of RH 143minhankyaw75% (4)
- Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesSeminar ReportAjit8675100% (7)
- Processing of Bopp FilmDocument49 pagesProcessing of Bopp FilmHassan Ali Khan75% (8)
- Ultrasonic Testing - Wikipedia PDFDocument26 pagesUltrasonic Testing - Wikipedia PDFKarthicWaitingNo ratings yet
- Grand Viva QuestionsDocument9 pagesGrand Viva Questionsbaniya is hereNo ratings yet
- Determination of Hydrocarbon Dew Point Using A Gas ChromatographDocument11 pagesDetermination of Hydrocarbon Dew Point Using A Gas Chromatographmajid maheriNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Physics Test On Fluid QuestionsDocument2 pagesForm 5 Physics Test On Fluid QuestionsThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet