Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermal Physics Heat Capacity and Latent Heat
Uploaded by
NadeenMohamedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermal Physics Heat Capacity and Latent Heat
Uploaded by
NadeenMohamedCopyright:
Available Formats
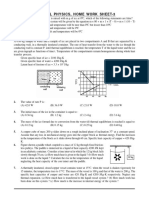
Theme 07: Thermal Physics
Heat Capacity and Latent Heat Worksheet
1 Normal body temperature for humans is 37℃. What is the corresponding temperature in Kelvin?
2 Explain briefly why Kelvin is a universal measure of temperature (unlike degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit).
3 If 2200 J of heat is added to a 190 g object, its temperature increases by 12 ℃. What is the heat
capacity of this object?
4 A student immerses a 2.0 kW electric heater in an insulated beaker of water at 20℃. The heater is
switched on and after 120 s the water reaches boiling point. Calculate the specific heat capacity of
water. The mass of the water is 1.2 kg.
5 Calculate the mass of water boiled away in a 3 kW electric kettle in 3 minutes. Note that the latent heat
of vaporisation for water is 2.26 × 106 J kg −1 .
6
(a) Calculate the energy needed to heat an aluminium pan of mass 0.4 kg from 20 ℃ to 100 ℃ given
that the specific heat capacity of aluminium is 900 𝐽 𝑘𝑔−1 𝐾 −1.
(b) Now if 1.6 kg of water is added to this pan and also heated from 20 ℃ to 100 ℃ calculate the total
energy required to heat both the pan and the water.
(c) If we are using a 2.0 kW electric heating plate to heat the pan and water then calculate the time it
takes to heat both the pan and the water.
7 A 65 kg cyclist expends 340 W whilst cycling. Assume that the cyclist loses no energy to the
surroundings and that the average specific heat capacity of her body is 3900 J kg −1 K −1
(a) Calculate the thermal energy generated in one minute.
(b) Calculate the temperature rise of the runner’s body in one minute.
The runner can reduce her temperature through evaporation of sweat.
(c) If the runner loses energy at a rate of 400 W then calculate the mass of sweat evaporated in
one minute. Note that the latent heat of vaporisation for water is 2.26 × 106 J kg −1.
8 A 0.22 kg steel pot on a stove contains 2.1 L of water at 22 °C. When the burner is turned on, the water
begins to boil after 8.5 minutes. (Note: 1 𝐿 = 10−3 𝑚3 and the specific heat capacity of steel is
448 𝐽 𝑘𝑔−1 𝐾 −1 )
(a) At what rate is heat being transferred from the burner to the pot of water?
(b) At this rate of heating, would it take more time or less time for the water to start to boil if the
pot were made of gold rather than steel? (heat capacity of gold is 150 𝐽 𝑘𝑔−1 𝐾 −1).
9 How much heat must be removed from 0.96 kg of water at 0 °C to make ice cubes at
0 °C? Latent heat of fusion for water, Lf = 33.5 104 J kg-1.
10 When you go out to your car one cold winter morning you discover a 0.57 cm thick layer of ice on the
windshield, which has an area of 1.6 m2. If the temperature of the ice is
−2 °C and its density is 917 kg m-3 find the heat required to melt all the ice. Latent heat of fusion for water,
Lf = 33.5 104 J kg-1, specific heat for ice, c = 2090 J kg-1 K-1.
| Kaplan International Pathways | 1 | kaplanpathways.com
You might also like
- Bsbsus401 Implement and Monitor Environmentally Sustainable Work Practices AssessmentDocument62 pagesBsbsus401 Implement and Monitor Environmentally Sustainable Work Practices Assessmentfaraz83% (6)
- BB101 Engineering Science Chapter 6 Temperature and HeatDocument7 pagesBB101 Engineering Science Chapter 6 Temperature and HeatAh Tiang100% (4)
- Physics Lesson Note SS2 2nd Term 2022 - 1Document103 pagesPhysics Lesson Note SS2 2nd Term 2022 - 1isaac bakare100% (7)
- Level Past Paper Questions - Hysics O P: TOPIC-8 Heat Capacity PAPER-1 Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesLevel Past Paper Questions - Hysics O P: TOPIC-8 Heat Capacity PAPER-1 Multiple Choiceelty Tan50% (2)
- Foundation Certificate FC312 Physics (B) End of Module Open Book Examination (Practice) Question Book Time Allowed: 120 MinutesDocument11 pagesFoundation Certificate FC312 Physics (B) End of Module Open Book Examination (Practice) Question Book Time Allowed: 120 MinutesNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- IAPWS95Document18 pagesIAPWS95mealtunNo ratings yet
- 7.2.3 - Heat Capacity Latent Heat WorksheetDocument2 pages7.2.3 - Heat Capacity Latent Heat WorksheetNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Specific Heat and Latent HeatDocument3 pagesTutorial 2 Specific Heat and Latent HeatYAN XIN TENGNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics Important NumericalsDocument1 pageThermal Physics Important NumericalsMehboob KhanNo ratings yet
- Latent Heat QuestionsDocument2 pagesLatent Heat QuestionsSatria HalimNo ratings yet
- Specific heat capacity and latent heat questionsDocument2 pagesSpecific heat capacity and latent heat questionsDhany HaryantoNo ratings yet
- Heat CapacitiesDocument9 pagesHeat Capacitiesanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Heat Energy problems - Level 1 problem setDocument3 pagesHeat Energy problems - Level 1 problem setbobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Tutorial: Heat EnergyDocument1 pageChapter 9 Tutorial: Heat EnergySahida IshakNo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity ExperimentsDocument18 pagesHeat Capacity ExperimentsKisaka GNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document14 pagesCH 11UbadahNo ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument2 pagesThermal PhysicsCarlos KasambiraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1_ch2035 (1)Document2 pagesTutorial 1_ch2035 (1)Thùy LinhNo ratings yet
- To Prepare Chinese TeaDocument4 pagesTo Prepare Chinese TeaKong MikeNo ratings yet
- Latent Heat 10Document2 pagesLatent Heat 10a.m782007No ratings yet
- Chapter 12a Specific Heat Capacities, Specific Latent HeatDocument4 pagesChapter 12a Specific Heat Capacities, Specific Latent HeatPathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- 12ns practice problemsDocument3 pages12ns practice problemsMwape KeXiana MukukaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Tutorial Problems and AnswersDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Tutorial Problems and AnswersShuhaila Hanis RosliNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL CH 1 - Part 2Document3 pagesTUTORIAL CH 1 - Part 2Adam MrsmNo ratings yet
- TB Chapter11 PDFDocument16 pagesTB Chapter11 PDFsmohanty20No ratings yet
- Physics Revision On Heat (Calculation) : Water Ice F 5 V 6 Absorbed ReleasedDocument1 pagePhysics Revision On Heat (Calculation) : Water Ice F 5 V 6 Absorbed ReleasedLim JingNo ratings yet
- Specific Heat CapacityDocument7 pagesSpecific Heat Capacitykeeesh4100% (1)
- SHC QUNDocument3 pagesSHC QUNYoviNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document2 pagesAssignment 5Shirish MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 30 Thermochemical Changes Practice 1Document9 pagesChemistry 30 Thermochemical Changes Practice 1Alaa mohamed Shaat BANo ratings yet
- Thermochem Solved Practice Problems PDFDocument9 pagesThermochem Solved Practice Problems PDFRez Balayo JanabanNo ratings yet
- Tuto PhysicsDocument3 pagesTuto PhysicsLia XeraNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsProblemsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsProblemsmachcar100% (1)
- Exercise 1 Heat & TemperatureDocument1 pageExercise 1 Heat & TemperatureSelwah Hj AkipNo ratings yet
- CalorimetryDocument5 pagesCalorimetryVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Temperature & Heat - Part 2Document4 pagesTutorial 2 Temperature & Heat - Part 2Yixiang TanNo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity and Latent Heat QuestionsDocument2 pagesHeat Capacity and Latent Heat QuestionstuvvacNo ratings yet
- Heat P1P2Document4 pagesHeat P1P2Sharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- RevisionWsheet 5054 ThermalPropertiesofMatterDocument4 pagesRevisionWsheet 5054 ThermalPropertiesofMatterHem HemNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Specific Heat Capacity ChartDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer Specific Heat Capacity Chartshahab waheedNo ratings yet
- NK C SI R: Thermal Physics, Home Work Sheet-3Document2 pagesNK C SI R: Thermal Physics, Home Work Sheet-3bhadrabijumohan2007No ratings yet
- Form 3 Holiday Assignment November December 2017Document14 pagesForm 3 Holiday Assignment November December 2017maxwel oboraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - GiancoliDocument4 pagesChapter 14 - GiancoliHectorCabzNo ratings yet
- Topik 6b - ExerciseDocument4 pagesTopik 6b - ExerciseMd KhairulNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics IIDocument8 pagesThermodynamics IIFauzan HantoroNo ratings yet
- Thermometry: T/s T/KDocument9 pagesThermometry: T/s T/KJing Yu VoonNo ratings yet
- Specific Heat Capacity Physics Form 4 TopicDocument7 pagesSpecific Heat Capacity Physics Form 4 TopicRusnizaARNo ratings yet
- QMCT WSDocument2 pagesQMCT WSJorge Montero VallejoNo ratings yet
- HK1MSW78Document6 pagesHK1MSW78Gkid GkidNo ratings yet
- SHCDocument6 pagesSHCAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - QuestionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 1 - Questions2200851No ratings yet
- 5th Form Assignment 2Document2 pages5th Form Assignment 2Philip MooreNo ratings yet
- Q MC Q ML Q ML: Original Temperature of The Water?Document2 pagesQ MC Q ML Q ML: Original Temperature of The Water?Muddamsetty ArunkalyanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy 1Document1 pageThermal Energy 1DhanBahadurNo ratings yet
- Answer Problem Sheet-06 Me201 EntropyDocument5 pagesAnswer Problem Sheet-06 Me201 EntropyAtif IrshadNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 (Thermal Problem) : Cu Water V 6Document2 pagesHomework 1 (Thermal Problem) : Cu Water V 6DepurpleeNo ratings yet
- 3.9 Quantity of HeatDocument38 pages3.9 Quantity of Heatcicilywairimu25No ratings yet
- B.E (IV SEM) MECH - ENGG / Tutorial - 4 B.E (IV SEM) MECH - ENGG / Tutorial - 4Document2 pagesB.E (IV SEM) MECH - ENGG / Tutorial - 4 B.E (IV SEM) MECH - ENGG / Tutorial - 4Kumaran RNo ratings yet
- How it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common useFrom EverandHow it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common useNo ratings yet
- 8.1.2 - Ideal Gases WorksheetDocument1 page8.1.2 - Ideal Gases WorksheetNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Practice Quiz Test 1 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesPractice Quiz Test 1 Answer KeyNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- FC312E Physics: Simple Harmonic MotionDocument38 pagesFC312E Physics: Simple Harmonic MotionNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- SHM Worksheet Solutions KaplanDocument3 pagesSHM Worksheet Solutions KaplanNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion Worksheet 2: Kaplan International Pathways 1Document1 pageSimple Harmonic Motion Worksheet 2: Kaplan International Pathways 1NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion Worksheet: x = (7.8 cm) cos (2πt/ (0.68 s) )Document1 pageSimple Harmonic Motion Worksheet: x = (7.8 cm) cos (2πt/ (0.68 s) )NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Practice Quiz Test 1 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesPractice Quiz Test 1 Answer KeyNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Volcano 2014 BBDocument11 pagesVolcano 2014 BBNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- 105 Eq Sheet 2Document1 page105 Eq Sheet 2NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Volcano Lecture2015Document28 pagesVolcano Lecture2015NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- 105 Eq Sheet 3Document2 pages105 Eq Sheet 3NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- 8.2.2 - Kinetic Theory WorksheetDocument1 page8.2.2 - Kinetic Theory WorksheetNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- E202 Sample Final Exam Fall 2012 Sept 12Document10 pagesE202 Sample Final Exam Fall 2012 Sept 12NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary 2015Document34 pagesSedimentary 2015NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Un ConformityDocument10 pagesUn ConformityNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Topic 4, Signal CoordinationDocument26 pagesTopic 4, Signal CoordinationNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Structure Geology2013Document15 pagesStructure Geology2013NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Rock Identification2015Document53 pagesRock Identification2015NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Structure Geology2015Document8 pagesStructure Geology2015NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary Rocks22015Document45 pagesSedimentary Rocks22015NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Minerals 2015Document35 pagesPhysical Properties of Minerals 2015NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Minerals 2015Document29 pagesMinerals 2015NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Igneous Rocks2015Document13 pagesIgneous Rocks2015NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Igneous Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rocks2015Document6 pagesIgneous Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rocks2015NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic Rock2015Document47 pagesMetamorphic Rock2015NadeenMohamed100% (1)
- PlateTectonics2015 ExtraDocument62 pagesPlateTectonics2015 ExtraNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Geology of Qatar 2015Document22 pagesGeology of Qatar 2015NadeenMohamed100% (3)
- Earthquakes 2015Document68 pagesEarthquakes 2015NadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument11 pagesEnergy ResourcesNadeenMohamedNo ratings yet
- Catalytic: Cracking Acetic Acid To AceticDocument6 pagesCatalytic: Cracking Acetic Acid To AceticPawan NagarNo ratings yet
- Starlette Plus: The Small Range of Refrigeration DryersDocument4 pagesStarlette Plus: The Small Range of Refrigeration DryersJas SumNo ratings yet
- Clamp Meters: Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pagesClamp Meters: Quick Reference GuideRaul InzunzaNo ratings yet
- Toyota Prius Timing Chain Service GuideDocument13 pagesToyota Prius Timing Chain Service Guidefernando ortizNo ratings yet
- Design and Optimization of Domestic Solar Dryer: Review ArticleDocument6 pagesDesign and Optimization of Domestic Solar Dryer: Review ArticleBahynorerama DpNo ratings yet
- Rab Jembatan Kaliwungu - Revisi-Penawara - Fik OkokDocument77 pagesRab Jembatan Kaliwungu - Revisi-Penawara - Fik Okoklerebulan udyNo ratings yet
- Features: Power Isolation TransformersDocument8 pagesFeatures: Power Isolation TransformersLKGNo ratings yet
- UGC NET Career ScopeDocument12 pagesUGC NET Career ScopeKadamb SachdevaNo ratings yet
- AUTOMOTIVE PASSENGER VEHICLES LUBRICANTS (English)Document24 pagesAUTOMOTIVE PASSENGER VEHICLES LUBRICANTS (English)darionestoroskiNo ratings yet
- ECBC Implementation Experience - A Case Study on UPERC BuildingDocument21 pagesECBC Implementation Experience - A Case Study on UPERC BuildingAanchal MishraNo ratings yet
- Election Manifesto of Bangladesh Awami League-2008Document15 pagesElection Manifesto of Bangladesh Awami League-2008api-3709098No ratings yet
- 132kV Cable & FO Cable Layout in CUP S/SDocument16 pages132kV Cable & FO Cable Layout in CUP S/SSuprodip Das100% (1)
- Method Statement - Underground Cable Laying Rev04Document26 pagesMethod Statement - Underground Cable Laying Rev04Ahamed UmarNo ratings yet
- Salivary AmylaseDocument43 pagesSalivary Amylasecountdracula9283% (6)
- Mil STD 3004 2Document70 pagesMil STD 3004 2Santosh IngoleNo ratings yet
- Lovibond PFX995/950 Series: Operators Instruction ManualDocument19 pagesLovibond PFX995/950 Series: Operators Instruction Manuallisda AsmidaNo ratings yet
- Vestas safety training introductionDocument8 pagesVestas safety training introductionadrianNo ratings yet
- Kwh Summary Report AnalysisDocument2 pagesKwh Summary Report AnalysisManoj TyagiNo ratings yet
- FF Notes PDFDocument81 pagesFF Notes PDFasim zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Professional Stepper-Motor Analogue Pressure Gauge: Caution!Document4 pagesProfessional Stepper-Motor Analogue Pressure Gauge: Caution!tito titoNo ratings yet
- Gear Drives Vs Belt DrivesDocument17 pagesGear Drives Vs Belt DrivesAaryan MahakalkarNo ratings yet
- Esp 2Document5 pagesEsp 2mahaveenNo ratings yet
- Engine Performance Data at 1800 RPM: X3.3 1 Cummins India Limited S3.8Document4 pagesEngine Performance Data at 1800 RPM: X3.3 1 Cummins India Limited S3.8Rasheed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Installing Takegawa Hyper Cam (KLX110/DRZ110)Document1 pageInstalling Takegawa Hyper Cam (KLX110/DRZ110)MinibikeTechNo ratings yet
- Worksheet#2 QuestionsDocument7 pagesWorksheet#2 QuestionsChua RhickNo ratings yet
- Flame retardant halogen-free power cableDocument5 pagesFlame retardant halogen-free power cableChand BashaNo ratings yet
- ISO 18436-2 CAT-III Certified Vibration Analyst Hamza AshrafDocument2 pagesISO 18436-2 CAT-III Certified Vibration Analyst Hamza AshrafHamza AshrafNo ratings yet
- Maximum Fuel: Franchise ProgramDocument17 pagesMaximum Fuel: Franchise ProgramAdlai CastroNo ratings yet