Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Question & Answer Welding
Question & Answer Welding
Uploaded by
Sherif Yehia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views90 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views90 pagesQuestion & Answer Welding
Question & Answer Welding
Uploaded by
Sherif YehiaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 90
»
6)
)
8)
9)
toy
i)
12)
ARAMCO VENDOR INSPECTION EXAMINATION
MECHANICAL
What is a WPS, PQR, WPQ?
als variables?
‘What are the definitions of essentials and non-essen
What is the definition of pre-heating?
Why is inter-pass temperature control required when welding of austenitic stainless
steel?
List five items that you would expect to find in a Materials Test Repon?
Answers
a) Purchase Order Number
b) Lot
©) Heat Number
4) Chemical Analy:
©) Mechanical Test Results
) Specification (mat , grade, type/class)
9) Manufacturer's Name
‘What is Carbon Equivalent and what is its importance in regards to weldi
Low Hydrogen electrodes are to be maintained in
a ~ their re-sealed containers
b~ electrode holders with an open lid
€~ electrode oven
IF the root gap have been found too small before welding, a proper comective action
would be
a increase the welding heat,
b- open a wider gap by gouging or grinding J
€~none of the above
iroular welds should always be done before longitudinal ones
TRUE / FALSE
What the acronyms GTAW/FCAW/SMAWIGMAW/SAW. stands. for? Explain the
basic process
Name the three basic steps to be checked prior 10 welding
What is the most important 1a be checked before start Welding of clad materials?
13) What would be the most appropriate welding process be when welding full penetration
joints from only one side?
a-FCAW
b-GTAW
c~SAW
d-GMAW
14) What is “Interpass Temperature”
15) Why is pre-heating important for welding alloy steels?
16) What is the purpose of PWHT?
17) What extra attention is payed for Low Hydrowen Electrodes?
18) What is “P-No" for SA 16 Gr. 70, according to ASME IX?
19) What is Thermal Expansion”
20) Why the cracks appear: a) Because of Heat
after welding, c) ..
21) How welding stresses are relieved: a) Heating and quenching the welds. b) Heating at a
designed temperature and controlled cooling: c) Drilling holes in weld seam: d)
22) What is difference between DCRS and DCES
23) Which are the three main attribute mentioned on a Tensile Test Report?
24) RT is the most suitable NDT method for detecting the edge wall lack of fusion,
‘TRUE/FALSE
25) Why are the bevel edges controlled before welding?
26) Which is the most appropriate method for detecting laminations on bevel edge? a) RT;
b) PT; c) both; d) NONE
27) Name three (3) methods for the transfer of filler material for GMAW.
28) Describe the position “3G"
29) When a welder is qualified for position SG. in which position can he weld?
30) What is Joint Efficiency?
31) Name four (4) types of joints
32) Which are the most three (3) suitable groove geometries for SAW?
33) For PT fluorescent, MT fluorescent and Leak Test is used ultraviolet light
TRUE/FALSE
34) For inspection of stainless steels strip lining is used: a) RT; b) MT; c) both; d) None
while welding, b) because of cooling
Aramco Vender Inspection E; amination
Mechanical
1) What is a wps, pqr. and wps?
WPS: welding procedure specification This is a written Procedure, which states essential
and some non- essential variables on a spcefic job
POR: this is the record of mechanical and other {esting conducted on the test coupon toa
given wps
WPQ: this isthe test under taken by the welder to Prove his ability to be certified
To weld on a certain welding procedure
2) What is the defination ofthe essential and non-essen jal variables?
Essential variables: changes bey nd the limitation of the par are essential variables. shall
Fequire the requalification of procedure
Non: Essential variables: changes with inthe hmitation of PAF is not require
requalification of procedure.
3) What is the defination of the pre heating”
‘The application of the heat to the base metal immediately before the welding is pre
heating,
‘Why is inter pass temp control required when welding of austenitic stainless stec!?”
To prevent the hardening in the heat affected zones ‘rough the dendrite growth and
Prevent under bead cracking
*) His five tems that sou would expect o find ia materia tet centficate?
a) Manufactures name,
b) Purchase order no
©) Specification ( niater. typeiclass)
4) Mechanical test
©) Chemical test
A) Heat no.
8) Lot no.
5) What is carbon equivalent and what its important in regards to welding?
CE=C+ (Mn 4Si) +(CreMotvy + (Nit Cu
6 ¥ 1
Chemical analysis may be obtained trom
| Mill est certiicate 2 tspieat production chomisin
Ae aS
7) Low Hydrogen electrodes are to be maintained in
a) = their rescaled container
by ~ Electrode holder with an open tid
@ -electrode oven
8) If the root gap have been found to small before welding a proper corrective action
would be,
A= increase the welding heat
B- open a wider gap by gauging or grinding.
€ ~non of the above
°) Circular welds should always be done before longitudinal ones?
TRUEIFALSE _
10) What the acronyms GTAW/ECAW/SMAW/GMAW/SAW. ‘Stand for?
GTAW: Gas tungsten are welding
FCAW: Flux cored are welding
SMAW: shielded metal arc welding,
SAW: submerged arc welding,
GMAW: gas metal are welding
11) Name the three basie steps to be checked before stant welding?”
|) Edge preparation and cleanness.
2) Consumables
3). Welder quatification
4) Pre heat GF required)
« 12) What is most important to check before stato clding of clad material?
Weathax Condiken
Preheating,
13) What would the most appropriate welding processes be when welding full penetration
Joint from one side”
NFCAW 2GTAW SAW yomaw
14) What is inter-pass temperature?
&
Ina multipass weld. the welding temperature of the weld area between weld passes is
known as interpass temp,
5) Why is pre heating important for welding alloy steels?
a) To reduce the cooling rate during the welding.
b) To prevent entrapment of hdrogen gas
©) To prevent formation of hardenable microstructures that will result in brittleness.
d) To eliminate the under bead crac!
16) What is the purpose of the PWHT?
Purpose of the PWHTT is to relieve the residual stress in the welding. PWHT of
ieldment is heating the weldment gradually to required sonk temperature and holding
for specific time and cool down to required cooling rate is PWHT.
17) What extra attention is paid for low hydrogen clectrodes?
Should be kept in the electrode oven. not to be exposed to open atmosphere.
20) Why the crack appears?
a) Because of heating while welding
b) Because of cooling after welding,
21) How welding stress is retieved?
a) Heating and quenching the weld
® Heating at a designed temperature and controtied cooling.
©) Drilling a hole in weld scams
22) What is the diff. Between DCRS and DCES”
23) Which are the 3 main attribute mentioned on a tensile test report?
1) elongation
2). ultimate stress
3) yield stress
4) gross section area
24) RT is the most suitable NDT method for detecting the edge wall lack of fusion?
TRUE /FALSE.
25) Why are the bevel edges controlled before welding”
To increase the joint efficiency and to eliminate the weld defects
mination on bevel edge’
26) Which 1s the most appropriate method for detecti
1) RT 2) PT 3) BOTH 4) NONE
27) Name three methods for the transfer of filler material for GMAN\"*
NGLOBULAR 2) SPRAY 3) DROPLET 4) DIP.
28) Describe the position “3G”
3G isthe position groove weld on the plate in \enicaldircetion: the arc is start at
{he root ofthe joint at lowest side of the groove and carried upwards
29) When a welder is qualified for position SG in which position can he weld?
1G. 26. & 5G
30) Name four types of joints?
1) Butt-joint 2yT-joimt 3)lap-joint 4) comer joint.
31) For PT fluorescont. MT fluorescent and leak test is used ultraviolet light?
TRUE / FALSE
32) Which are the most three suitable grooves geonictric for SAW welding, ?
single v- groove weld, 2ysingle berel groove 3)double \ groove,
QUESTION
1. What is the “Technical Definition” of
Zpiltoniag of valve stem below hordsontal te not preferred to prevent
Giposition of debris on the bonet which will prevest closure of the valve.
Corrosion 1g also reason,
3. What epecific areas do the following standards covers?
a). ANSI B31.1. Power Piping,
b). ANSIB31.3 ©; Process Piping.
. ANSIB32.4 ; Pipe Line Transportation Systems For ‘Uguid Hydrocarbons And Other Liquids
d). ANS! 31.8 Gas Distribution And Transportation For Piping System.
e). AWSD12; ‘Structural Welding Code-Steel.
fl. ASNTTC-1A, Training/ and certification; ifor NOT and Inspection.
g). ASME Il Part c: ‘Specification for Welding Rods, Electrodes, and Filler Metals,
h). ASMEV. : Nondestructive Examination.
. ASMEVM Rule for construction of Pressure Vessels,
J). ASMEIX 2 Welding ‘and Brazing Qualification.
k). SAEP : Saudi Aramco Engineering Procedures.
I). SAES : ‘Saudi Aramco Engineering Stondards,
im) SAIC : Saudi Aramco Inspection Checklist,
n)SATIP. : Saudi Aramco Typical Inspection Plans.
0) SATR : Saudi Aramco Test ‘Reports,
p) SAMSS. Z Saudi Aramco Mareiat System Specifications.
Pall [PGT
1. Joint No.
2. Welder No.
3. Dine no and drawing no.
5. What is 101 (penetrameter) sensitivity and what does it determine?
fOr determine the quality of the radiographic techniques used and
therefore, will help us in knowing as to what degree of defect can be
detected.
&. Whathass accurred if the light image of the letter *B* appears on your radiograph?
There is backscatter radiation exposed to the flim.
v{2. I it possible to locate defects by magnetic particle or Liquid penetrant examination which
can not be found by radiography ? Explain?
were phere near surface or susface that may be perpendicular with the ay
of radtation such ag internal lamination and cold lap.
13. What is the basic difference between a DIN and an ASME penetrameters?
PIN is wie type while ASME 4s hole type
+4, Denote the three (3) main reason to use preheats
1. To reduce the cooling rate duriag welding .
2. To prevententrapment of hydrogen gas.
eaeme Prevent formation of hardenable microstructures that will result in
brittlene!
“15. What are radiograpic film ARTIFACTS, Give 4 Examples?
1. Water Marks,”
2. crinps.
3. Scrathes on the fi1n,
4) Disbondnent of £41m enuleion,
3. Light tesle.
16. What does the term “ Holiday Detector * mean?
This is a test performed to locate a bre:
coating
oF discontinuity ona protective
VA7. What is the purpose of a QC Plan vs QA/QC Manual?
oc plan is a list of Quality Control activities to be performed in
Secording with the approved QA/QC manual on certain project.
‘18, What position is the gate to be in during a “shell” test? Explain why.
Partially opened position so that any cavity on the valve hody can be
subjected to the testpressure.
19, What is the ultimate purpose of the backseat test for a gate valve?
Fe ensure that there 4a no leakagé through the bonnet and aten packing.
20. Is the packing gland to be tight during the backseat test of a gate valve?
xo
21, Name at least 6(six} area that should be checked during the dimensions! inspection of a
ised face welding neck flange?
a) Rating.
b) No. Of bolt hole.
V30. What is UG?
- Geometrical Unshazpneze,
V1. Whea shooting an ellipse, where will the penetrameter go?
+ Sourse side.
52. What 4 (four) parameters do we get from Tensile Test?
Hlongation, Ultinate Stress, Yield stress, Cross Section ‘A rea,
1733, Which section of ASME Vil are scatter/distibution dlagrams for Radiography interpretation?
+ Section 4
34. Inwhat section oF ASME Vill re the other defect?
- was
VAS. What properties have the 3 sub-are faxes?
+ Inert; chemical change Active; Alloys
AS. Why do we maintain the iterpess temperature hen welding stanlse Steel?
70 Prevent hardening in the Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) through denditric
growth and to prevent under bead craking
¥37. What material do we use when welding dissimilar material?
308° Inconel for greater ware resistance,
38. What is Dwell ime?
The time for the penetrant to soak into any surface opening and the time
for the developer to draw out an indication .
$9. What is the defference between stress relieving and normalizing?
Rormalizing tenperature is above upper critical temperature, Normalizing
cool at control rate
Stress relieving temperature is below upper critical temperature.
~40. What are the three(3) types'of hardness?
- Rockwell, Vickezz, Brinnel .
Al. When is peening allowed to ANSVASME B31.3?
- Not allowed
2
>
3
753. When a contractor supplies «part ofa vessel What is required?
PARTIAL MASTER DATA REPORT
54. Whatis a WES, PQR and WPQ?
58. Whats he defisation ofthe estential end non-esrential variables:
Essential variables isa change welding condon whick wil affect of mechanical properties(other then notch
‘oughness) of weldments (e.g, change in P-number, ‘welding process, Filler metal, electrode, preheat or
‘Post heat treatment),
‘Non-essential vara henge eng condom isl tty of welder to deposit sound weld
metal (such as change'velding process, deletion of ing, elecwOde, F-Number, technigue, etc)
56. What i the defination of the preheat?
‘the application of the heat Go base metal immediately before welding,
$7. Whatis Carbon Equivatent (CE) and whet i its important in regards to welding?
GES Ct(Na +-92)/6 + (ce + No + vI/5 + (mt 4 cuy/is
Chemical analysis may be obtained from:
2) Mi22 test certificate 2) typical Production chentetey
38. Low hydrogen electrodes are tobe maintained in
(a) -Their resealed container.
(®) -Blectrode holder with an open 1id,
fc) -Blectrode oven,
$9: Ifthe root gap have been found to small before ‘Welding a proper corrective action would be:
A- increase the welding heat,
3 7 Open a wider gap by gauging or grinding.
C—non of the above,
60. Circular welds should always be done before longitudinal ones?
TRUE / Fanse
69. How welding stress i relieved?
4. Heating and quenching the weld,
2. Heating at a designed temperature and controlled cooling.
© Drilling a bole in weld seam,
70. Whats the diffrence between DCRS and DCES?
n ‘Which ae the main atibute mentioned ons tensile tet report:
1, Blongation.
2." Ultinate stre,
3. Yield atze:
4. Cross Section Area,
73. What ita purpose of Destructive and Mechanical test?
we ensure that the required level of certain mechanicalproperties have been
achieved
74. ‘What are amecahanical tests carried out to check (ho mechanical properties? (Quantity)
Zr Rares test. (Vickers, Brinel, Rockwel1) .
3: Toughness test (charpy v, z20d, crop /orak TP Opening Displacement Test )
3 Tensiie Test. (Tranaverse/tongitudine? wei metal)
75. Wea kinds of test to evaluate the quality of welds? (Qualityy
J. Macro test,
+ Bending Test (side, face; root)
3+ Fillet veld fracture testing.
4) BULE weld nick -braak testing.
76. Whats the purpose/ntended of “Positive Mateel Identification” (PMI)?
‘Ated welds have been correctly supplied and installed as specified,
77. Why are the bevel edges controlled before welding? ~
To increase the joint efficiency and to eliminate the weld
defect.
78, Which isthe most appropriate method for detecting lamination on bevel edge?
1) RT 2) PT 3) BOTH 4) NONE
SPECIMEN WRITTEN EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
CSWIP 3.1
Ll Part A and Part A2
Candidates are required to tick, or otherwise indicate, the corrective answer in the
section provided. There is only one correct answer for each question.
1 Applying preheat when welding carbon manganese steel is normally done
to avoid:
a) Slag inclusions
b) Hydrogen cracking
©) Lack of sidewall fusion
d) Porosity
2 Which of following mechanical properties of a weld in carbon manganese
steel is most affected if the heat input per unit length of weld is
excessively high?
a) Elongation
b) Tensile strength
c) Hardness
d) Toughness
3 You observe centerline cracking a weld that as been made one of five
work stations each making similar components. The first action to tak
a) Impound all welding consumables
b) Report the occurrence to high authority
©) Stop all welding
4) Call for full NDT checks
4 Which of the following defects is unlikely to be found by visual
inspection.
a) Linear misalignment
b) Undereut
©) Overlap
) Linear slag inclusion
5 Which of the following welding processes uses a resisitive heating system
to achieve weld metal deposition.
a) Manual metal arc welding
b) — Submerged-are welding
c) Electro slag welding
d) Resistance spot welding
Page |of 32
10
"
Which of the following units could Charpy V notch energy be measured
in?
a) Pounds per square inch
b) Joules
) Newtons per square millimeter
4) None of the above
‘The usual method of assessing the sensitivity of radiograph is by means of
a
a) Dosimeter
b) —_Fluoroscope
©) 1Q1( Penetrameter)
4) Clinometer
Under normal contract conditions, weld procedure approval tests for pipe
work are:
a) Mandatory
b) Depend upon site and weather conditions
©) Dependent upon the contractor's confidence in his procedures
4) Only required when CO2 welding is to be used.
Which of the following destructive tests is not normally required for
welder approval test for mild steel?
a) Bend test
b) Macro examination
c) _ Impact tests
4) Fracture tests
Hydrogen controlled electrodes were developed principally for:
a) The prevention of porosity
b) The prevention of cracking
c) The enhancement of arc voltage
4) Their ease of are starting
For which of the following is pre-heating most likely to be required?
a) Austenitic stainless steels
b) High strength alloy steels
©) Lowand medium strength steels
4) Lowcarbon steels
Poge 20/32
12
13
4
15
16
Manual metal arc welding of low alloy steels is more likely to be
performed with:
a) Rutile electrodes.
b) Cellulosic Electrodes
¢) Iron powder electrodes
4) Basic hydrogen controlled electrodes
which of the following defects is more common to weld deposited by the
CO-2 welding process than weld deposited by manual metal arc?
a)
b)
°)
4d)
Slag inclusion
Excess penetration
Lack of side fusion
‘Tungsten inclusions
Which defect would you expect to obtain in TIG welds in non-deoxidized
steel?
a)
b)
°)
a
Under cut
Porosity
‘Tungsten inclusions
Linear misalignment
Which of the following can arise from copper inclusions is a ferrite steel
weld?
a)
b)
°)
d)
Weld metal cracks
HAZ cracks
Lamellar tearing
Porosity
Which of the following is likely to give the highest impact strength in
ferritic weld metal?
a)
b)
°)
a
Cellulosic electrodes
Submerged are with acid flux
Spray transfer Co-2-welding
Basic coated normal metal are electrodes
Page 3of32
17
19
20
21
22
Which of the following methods of NDT would be most likely to detect
lack of side fusion in ferritic steel welds?
a) Penetrants
b) Magnetic particles
©) Radiography
4) Ultrasonic flaw detector
‘You suspected that ferritic steel plates, which have been edge, prepared
contain crack in the prepared edges, Which NDT method would you use to
check this?
a) Radiography
b) Magnetic particle
°) Penetrants
d) Ultrasonic flaw detector
Which of the following defects do you not expect to find by visual
examination of completed welds?
a) Linear slag inclusions
b) Under cuts
c) Overlap
4) Linear misalignment
Stress relief is not helpful in one of the following cases. Which one?
a) _ In improving resistance to stress corrosion cracking
b) _Indimensional stability after machining improving
c) _ In lowering the peak residual stress
4) Insoftening the stee!
‘What is the maximum hardness usually recommended for the HAZ of a
medium strength ferritic steel weld?
a) 100 DP Hv
b) 350 DP HV
©) 500 DP Hv
d) 750 DP Hv
‘What effect to midthickess lamination in steel plate normaly have when
they are located within a weld HAZ?
a) Cause lamellar tearing
b) Fuse together to form a bond
©) Affect the weld metal composition
4) Cause internal tearing on a micro-scale
Page 4 of 32
23
4
25
26
27
When hydrogen control is specified for a manual metal arc-welding
project the electrode would normally be:
a) Cellulosic
b) Iron oxide
©) Acid
4) Basic
You would with certainty recognize a hydrogen controlled flux covered
electrode from its:
a) Color
b) Length
©) Trade name
d) AWS/BS639 Code Letter
When manual metal are welding is being carried out on an open
construction site, which groups of welder are most likely to require
continuous monitoring?
a) Concrete shuttering welding team
b) Pipe welders
c) Plate welders
4) Plant maintenance welders
You noticed manual metal arc welding electrodes, stripe of flux, are being
used as filler wire, for TIG welding. You would object because:
a) tis too expensive
b) The wire would be too thick
©) The weld metal composition may be wrong,
d) ‘The wire is too short
When open site working, serious porosity in manual metal arc welding is
brought to your attention. What would you investigate?
a) Electrode type
b) Power plant type
¢) Electrode storage
4) Day temperature
Page $ of 32
29
30
31
32
33
The steel composition in structural contract is changed form 0.15%
carbon, 0.6% manganese, to 0.2% carbon, 1.2% manganese. Might this
influence the incidence of?
a) Porosity
b) Cracking in the weld area
ce) Under cut for fillet welds
d) Lack of root fusion defects
One of the following alloys is non-magnetic, Which?
a) 4.0% Chromium molybdenum
b) 12.0% Chromium
c) Austenitic Stainless Steel
d) 9.0% Nickel Steel
When the TIG welding Austenitic Stainless Steel pipe. Argon gas backing
is called for, This is to:
a) Prevent oxidation
b) Prevent under bead cracking
©) Prevent porosity
4) Control the penetration bead shape
Pre-heating a carbon steel manual metal are welding is carried out to
inimize the risk of
a) Scattered porosity
b) Worm hole porosity
c) Parent metal cracking
4) Lack of penetration
IN UK practice, BS 499 Part2 specifies that the drawing dimension quoted
fora fillet weld is the:
a) Leg length
b) Actual throat thickness
°) Weld width:
For open site manual metal are welding the following equipment is
available. Which would you choose for safe working?
a) Single operator transformer
b) Multi operator transformers
©) AC/DC composite power unit
4) Diesel engine driven motor generator
Page 60f32
34
35
36
36
37
38
If submerged welding to be used to make butt welds, which would you be
most critical of:
a) The root gap tolerance
b) The angle of penetration
©) The root face width
4) The gas cut finish
During CO-2 welding, the arc length is most likely to be affected by:
a) The wire diameter
b) The current return connections
) The gas flow rate
d) The torch to work angle
Pre heating for arc welding applies to:
a) Assembly welding only
b) Assembly and tack welding
) Joint over 25 mm thick only
4) Cruciform welds only
You see a welder using oxy-acetylene flame with along feathered inner
cone. What would be the effect of this on carbon steel?
a) ‘The weld could be hard and brittle
b) The weld metal could be too soft
c) There will be no effect on the weld
d) The weld have under cut
‘A welder qualification test is 0 verify:
a) The skill of the welder
b) The quality of the materials
©) The non-destructive procedures
4) The manufacturing methods
A fabricating procedure calls for fillet welds to be blended in by grinding,
This is to influence:
a) HAZ cracking
b) Fatigue life
c) Residual stresses
4) Yield strength
Poge 70f 32
39
41
43
Bend test specimens have been taken from a 25 mm thick carbon steel butt
weld. Which would show lack of inter-run fusion:
a)
b)
©)
d)
Side bend
Root bend
Face bend
Guided bend
Lamellar tearing has been occurred in steel fabrication. BEFORE welding
could it have been found by?
a)
b)
°)
4d
X-ray examination
Dye penetrant
Ultrasonic inspection
It would not have been found by any inspection method
You are to over see are welding of some machine fittings and find they are
cadmium plated. What you:
a)
b)
°)
d)
Permit it to proceed
Permit it to proceed with fume extraction
Stop the operation at once
Advise the welder to drink milk and proceed
What two functions in are welding must be in equilibrium to enable a
stable arc to be established?
a) Are voltage
b) Current
©) Wire/electrode feed rate
4) Metal burn-off rate
In MMA welding, what parameter is used for the control penetration into
the base material?
a) Voltage
b) Welding speed
©) Iron powders in the coating
¢) Current
Page 8 of 32
44
45
46
47
48
49
In the welding of butt joint from one side, which of the following controls
the profile of the root bead?
a) Root Face
b) Bevel Angle
©) Root Gap
d) One of the above
‘What type of power source characteristic is required for manual welding?
a) Constant voltage
b) Flat Characteristic
©) Drooping Characteristic
4) Motor Generator
Which of the following destructive tests would indicate the toughness of
weld metal/parent metal ~ HAZ.
a) Macro
b) Nick break
©) Hardness
4) Charpy vee noteh
Degreasing components are essential for quality welding but some agents
may:
a) Cause corrosion Problems
b) Give off Phosgene Gas
c) Leave Residues
a) Allof the Above
Which of the following chemical elements has the greater effect on the
harden ability of a steel plate?
a) Molybdenum
b) Chromium
ce) Titanium
d) Carbon
In MAG/CO2 welding, which parameters give the greatest control of weld
appearance during dip transfers or short-circuiting welding?
a) Wire sick-out length
b) Amperage
c) Wire feed speed
4) Inductance
Page 9of 32
50
52.
53
34
55
In MMA welding, the slag produced can be varied to suit the welding
position; which type of slag would be required for welding in the HV
position?
a) Fluid
b) Viscous
©) None of the above
4) Semi fluid
The weld metal deposits of manual metal are electrode achieve its
mechanical strength through?
a) The core wire
b) The flux coating
©) Iron powder with the flux coating
What constituent is needed in coat
prevent formation of porosity in wel
of electrode of an electrode to
ig of rimming steel?
a) Tron powder
b) Calcium fluoride
©) Silicon
4) Calcium carbonate
Welds made with high heat inputs show a reduction in one of the
following properties?
a) Duetility
b) Toughness
©) Fatigue strength
4) Mechanical strength
In the welding of Austenitic pipe work, the borer is usually purged with Ar
to?
a) Prevent formation of porosity in the weld
b) Prevent burn-through in the root run
¢) Prevent oxidation of the rood bead
4) Eliminate the formation of H2
In X-ray the quality of the radiograph negative is assessed by the?
a) Density of the Film
b) Il indicator
°) KVA available
4) Stand-off distance
Page 10 of32
56
57
58
59
60
61
A steel described, as QT will have improved tensile properties it has?
a) Had control of chemical composition
b) Been heat treated
©) Been quality tested
4) Been vacuum melted
Which one o the following steels would give rise to the formation of
porosity when autogenously welded with an are process?
a) Fully killed steel
b) Semi killed steel
c) Rimming steel
4) Fine grained steel
In submerged are welding, the use of excessively high voltage would
result in?
a) Insufficient flux melting
b) Excessive flux melting
©) Slag removal difficulties
d) — Spaiter
The use of cellulosic electrode is often made when welding the root pass
of pipes in the field, This is because?
a) Hydrogen control is needed
b) Iron powder in the electrode
©) Higher are voltage can be obtained
4) Shorter are length can be achieved
In the welding of Austenitic stainless steels, the electrode and plate
material can be purchased with low carbon contents. The reason for this is
to prevent?
a) Cracking I the HAZ
b) The formation of chromium carbides
©) Cracking in the weld metal
4) Distortion
‘Submerged are fluxes can be supplied in two forms; thses are?
a) Sintered and agitated
b) Agitated and fused
) Crushed and agglomerated
4) Fused and agglomerated
Page 11 of 32
63
65
66
67
In a steel, which has improved creep properties at elevated temperature,
which one of the following elements helps in this improvement?
a) Tungsten
b) Manganese
©) Molybdenum
d) Carbon
‘Welding a steel plate of CE of 0.45 would require preheating to?
a) Prevent the formation of sulphides
b) Prevent hardening in the HAZ
©) Prevent the formation of carbides
4) To improve mechanical properties in the weld
Which of the following processes uses. the “Keyholing”
system of fusion?
a) Friction welding
b) Diffusion bonding
¢) Electron beam welding
4) Autogenous TIG welding
In friction welding, is the metal at the interface in the?
a) Liquid state
b) Solid state
©) Plastic state
4) Blastie state
Welding procedures may require welds to be deposited at a controlled rate
heat input. High heat inputs would?
a) Have poor profile
b) Have larger grain size
) Have high hardness in the HAZ
) Have low elongation properties
In a tensile test, a brittle material would be indicated if the fracture
surface?
a) Shows reduction in size
b) Is flat and featureless
©) Breaks in the weld metal
) Breaks in the parent material
Page 12 of32
68
69
70
1
B
What destructive test would be required to ascertain the likelihood of
cracking in the HAZ of a weld?
a) Nick break
b) Side bend test
©) Charpy input
4) Macto test
In submerged are welding, excessive are voltage may cause?
a) Excessive penetration
b) Change in weld metal composition
°) ‘Narrow weld width
d) Excessive bead profile
The British code for visual inspection requirements is:
a) BS4872
b) —-BS499
c) —_BS4870
d) None of the above
A code of practice for visual inspection should cover the following:
a) Before, during and after welding activities
b) Before welding activities only
©) After welding activities only
4) None of the above
Incomplete penetration in a butt joint could be caused by:
a) Excessive root face width
b) Excessive root gap size
©) —_ Lowcurrent setting
4) Botha&c
Incomplete root fusion weld certainly be caused by:
2) Linear misalignment
b) Incorrect tilt angle
3) Differing root face widths
d) All of the above
Page 13 of 32
14
75
76
7
8
799
When visually inspecting a completed single vee butt weld cap you would
certainly assess:
a) Cap height
b) Toe blend
©) Weld width
d) AB&C
You notice a very “ved” ripple shape. This is most likely caused by:
a) Poor consumable choice
b) Welding position
¢) Excessive travel speed
4) Allofthe above
“Toe blending” is important as it may affect:
a) Corrosion
b) Fatigue life
c) Overlap type defects
4) Allofthe above
Slag inclusion would occur with:
2) Manual metal are
b) Metal inert gas
¢) Submerged are welding
4) BothaA&C
Undercut principally caused by:
a) Excessive amps
b) Excessive volts
©) Excessive travel speed
d) All of the above
Undereut normally assessed by:
a) Its depth
b) Its length
ce) Its blending
d) All of the above
Page Hof 32
80
81
82
82
83
A welding procedure is useful to:
a) Give information to the welder
b) Give information to the inspector
©) Give “Confidence” to a product
4) Allofthe above
An essential variable may:
a) Change the properties of the weld
b) Influence the visual acceptability
©) Require re-approval of a weld procedure
4) Allof the above
‘A magnifying glass may be used during visual inspection but BS 5289
states that its magnification should be:
a) Uptos¢
by) 2-256
oc) 5-109
d) None of the above
When visually inspecting a fillet weld, it would normally be “sized” by:
a) The leg lengths
b) The actual throat thickness
c) The design throat thickness
4d Botha&C
The planar defect is:
a) Incomplete fusion defects
b) Slag inclusion
©) Incomplete penetration
4) Botha&C
Penetrant and Magnetic particle inspection are mainly used to:
a) Aid visual inspection
b) Because application standard says so
¢) To confirm “visual uncertainties”
4) Allofthe above
Page 15 of 32
85
86
87
88
89
90
Defects outside of the limits specified in a standard should always be:
a) Repaired
b) Reported to “a senior person”
©) Assessed along with other defects
d) All of the above
MIG welding tends to be susceptible to lack of fusion problems. This is
because of:
a) Poor maintenance of equipment
b) Incorrect setting
©) Poor inter run cleaning
4) Allof the above
Manual metal arc electrodes can be grouped into three main types. Thses
are:
a) Basic cellulosic and rutile
b) Neutral cellulosic and rutile
©) Basic cellulosic and neutral
d) None of the above
The main causes of porosity in welded joints are:
a) Poor access
b) Loss of gas shield
c) “Dirty” materials
d) All of the above
“Weave technique” may give rise to:
a) Better profiles
b) Improved toe blending
©) Improved ripple shape
4) Allof the above
Cracks in welds may be due to:
a) Solidification problems
b) Hydrogen problems
c) —_ Excessive stresses
d) — Allof the above
Page 16 of 32
1
92
93
94
95
97
With reference to a root penetration bead, you could certainly assess:
a) Root fusion and penetration
b) Root concavity
©) Burn-through
4) Allofthe above
A fatigue failure characteristic by the appearance of the fracture surface. It
would be:
a) Rough and tom
b) — “Cheveron” - like
c) Smooth
4) None of the above
“Stray arcing” may be regarded as a serious defect. This is because:
a) _ It may reduce the thickness dimension of a component
b) It may cause liquation cracks
¢) __Itmay cause hard zones
4) Allof the above
Overlap in welds could be influenced by:
a) Poor welding technique
b) Welding process
©) Welding position
d)— Allofthe above
Flame cut preparations may, during welding, increase the likelihood of:
a) Cracking
b) Misalignment problems
©) Inclusions
4) Allof the above
Macroscopic examination requires any specimen to be inspected:
a) Once, after etching
b) Twice, before and after etching
©) Using a microscope
a) None of the above
Which of the following may be classes as a “more serious defect”:
a) Slag inclusions
b) Fusion defects (interun)
©) Fusion defects (surface)
Poge 17 of 32
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
Code of practice is:
a) A standard for workmanship only
b) Asset of rules for manufacturing a specific product
©) Levels of acceptability of a weldment
4) None of the above
Movement of the arc by magnetic forces in-MMA welding is termed:
a) Are deviation
b) Are misalignment
©) Arc blow
d) Arceye
A metallurgical problem most associated with submerged arc welding is:
8) Hydrogen cracking in HAZ
b) Solidification cracking in the weld metal
©) Hydrogen cracking in the weld metal
Lamellar tearing in the weld metal
Oxy pressure and nozzle size would influence what in flame cutting:
a) The temperature required for cut initiation
b) The ability to cut stainless steels
©) The depth of cut obtainable
d) None of the above
The main uses of arc cutting/gouging processes is in:
a) The cutting of single bevel preparations
b) ‘The removal of deposited welds
©) The cutting of single U-type preparations
Which of the following processes joins metals plastically:
a) Friction welding
b) Resistance welding
ce) Plasma welding
4) Allof the above
Which electrode classification would be relevant AWS A 5.1-81:
a) E6013
b) E5133
c) E7018-G
d) Fleet weld 5
Page 18 of 32
105
106
107
108
109
110
Which of the following coating is associated with “Stove” welding;
a) Rutile
b) Cellulosic
°) Basic
d) Oxidizing
‘A common gas mixture used in MIG welding nickel alloys to combine
00d levels of penetration with good are stability would be:
a) 100% Co2
b) 100% argon
©) 80% argon 20% CO2
d) 98% argon 2% oxygen
‘The type of SAW flux is more resistance to moisture absorption:
a) Fused
b) — Agglomerated
©) Basic
d) All of about the same resistance
The flame temperature of oxy/acetylene mixture gas is given as:
a) 3200°C
by 2300°C
°) 5000° C
d) None of the above
A large grain structure in steels is said to produce:
a) Low ductility values
b) —_Low fracture toughness values
©) High fracture toughness values
4) High tensile strength
The likelihood of brittle fracture in steels will increase with:
a) A large grain formation
b) A reduction of in service temperature to sub zero levels
©) Fervitic rather than austenitic steels
4) Allofthe above
Page 19 of 52
12
113
114
Ms
116
Repair welding is often more difficult than production due to:
a) The material being ingrained with in-service contaminates
b) Restricted access with the repair area
©) The possible position of the weld
d) Any of the above
Hydrogen cracking in the weld metal is likely when:
a) Carbon manganese steels
b) Stainless steels
©) Micro alloyed steels (HSLA)
4) Lowcarbon steels
EN standard 288 would refer to which of the following:
a) Welder approval testing
b) Welding equipment
©) Welding procedure approval
4) Consumables for submerged are welding
Porosity is caused by:
a) Entrapped slag in the solidifying weld
b) _Entrapped gas in the solidifying weld
c) Entrapped metallic inclusions in the solidifying weld
d) None of the above
In bend test, the face of the specimen is in tension and root is
compression; the type of test being carried out would be:
a) A root bend test
b) Aside bend test
©) A face bend test
4) None of the above
Ultrasonic testing is of advantage in detecting which of the following weld
‘imperfections over other NDT methods:
2) Lack of side wall fusion
b) Surface undercut
©) Incompletely filled groove
4) Overlap
Poge 20 of 2
7
118
119
120
121
122
The process of tempering is often carried out to regain toughness after
which of the following processes:
a) Annealing
b) Normalizing
©) Hardening
4) Stress relieving
The presence of iron sulphide in the weld metal is most likely to produce
which of the following upon contraction of the weld:
a) Solidification cracking
b) Hydrogen cracking
©) Intergranular corrosion
4) Stress corrosion cracking
Generally the most suitable method of detecting lack of sidewall fusion
would be:
a) Ultrasonic
b) MPI
©) Radiography
4) Penetrants
Hot shortness term is used to indicate:
a) Lamellar tearing
b) Solidification cracking
©) Hydrogen cracking
4) None of the above
The use of cobalt as an isotope would generally be used on:
a) Thin materials
b) Tee joints
©) Plate thickness greater than 25mm
d) None of the above
In welding procedure term, a change in essential variable means
a) —_Re-qualification of the welding procedure
») Possible change in the weld’s microstructure
©) Possible change in t he mechanical properties
4) Allofthe above
Poge 21 of 2
123
124
125
126
127
128
‘Weld symbol placed on a dotted line in accordance with ISO requirements
means:
a) Weld on “arrow” side
b) Weld on “other” side
c) Weld on site
4) Full penetration required
A welding inspector's main attribute includes:
a) Knowledge and experience
b) Literacy
©) Honesty and integrity
d) All of the above
The correct term for a joint prepared on one component only is:
a) A bevel butt
b) AJ butt
c) A*K” butt
4) Allof the above
Technically a code of practice is:
2) A standard
b) A “set of rules” for the manufacture of a product
¢) Related to welder and weld procedure approval
4) Allof the above
‘The correct term for cap height is:
a) Reinforcement
b) Cap profile height
c) Excessive weld metal
4) Allof the above
A tensile test will assess
a) Impact values
b) Stress
c) Strain
d) Both a) & c)
Page 22 0f 32
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
The important point if high temperature stcel is that:
a) They can withstand creep failure
b) They may suffer re-heat cracking problems
©) They may suffer loss of toughness
4) Alllof the above
An austenitic stainless steel may suffer:
a) Weld decay
b) Sensitization
©) Solidification cracking
4) Alllof the above
Carbon equivalent values are useful to determine:
a) Weld ability aspects
b) Crack sensitivity aspects
©) Typical mechanical properties
4) Allof the above
A basic electrode would normally:
a) Have superior mechanical properties
b) Require baking before use
©) Not be used on low carbon steels
4) Botha) and b)
When referring to TIG welding, the shielding gas could be:
a) Argon + Hydrogen
b) Argon + Helium
©) Argon-+ Nitrogen
4) Allof the above
When referring to MIG welding, the shielding gas could be:
a) Argon
b) Argon + 1% Oxygen
©) Argon +20% CO?
4) None of the above
Submerged arc utilities:
a) Deep penetration characteristic
b) High deposition rate on DC+
©) Flat (P.A.) welding only
Page 23 of 32
136
137
138
139
140
141
Ultrasonic would be prefer over radiography due to:
a) Ability to find more defects
b) Lowest skill requirements
©) Ability to detect laminations
4) Both a) and c)
The most serious defects
a) Planar
b) Cracks
©) Lack of fusion
d) All of the above
The weldability of a material may be affected by:
a) Temperature of the component
b) The C.E. % of the material
©) The elements in the material
4) Allof the above
Post heat treatment:
) Must be applied to welds if a crack free weld is required!
b) Should never exceed 300 dg C
©) May stress relieve
d) Must always be applied using gas flames
Which of the following welding processes may be described, as a low
hydrogen process in comparison with general MMA welding:
a) TIG
b) MIG
°) MAG
4) None of the above
e) All f the above
Which form of NDT could be used on a fillet weld on aluminum?
a) Dye penetrant testing
b) Ultrasonic testing
c) Radiography
d) MPI
©) abande
f) — Donly
2) Alllof the above
Page 24 of 2
142
143
144
145,
146
147
Which of the following NDT methods would not detect sub-surface
defects?
a) MPI
b) Dye penetrant testing
©) Ultrasonic testing
4) Radiography
©) All of the above would detect sub-surface defects
Why have a high 0.C.V. with MMA welding
a) Toiinitiate the are
b) To obiain penetration
¢) To avoid lack of fusion
d) MMA welding does not have a high O.C.V.
‘What is the purpose of a ‘rectifier’ in relation to welding plant?
a) Toadjust the voltage
b) To adjust the amperage
©) Toconvert A.C to D.C.
d) To prevent are strikes
Fish — eyes, chevron cracks and fissures are:
a) Not associated with welding
b) Types of cracks
©) Only encountered in MMA welds
d) Hydrogen related problems
Pre heating prior to welding:
a) Must always be carried out
b) Need not be carried out if post heat treatment is to follow welding
©) Is always carried out using gas flame
4) None of the above
2) All of the above
‘What does pre heat prior to welding have an affect on:
a) Hardenability
b) — Weldability
©) Cooling rate
4) Allof the above
©) None of the above
Page 25 of 32
148
149
150
151
152
153
The toes of the cap on a butt weld:
@) Must overlap on the external surface of a pipe or plate by at least
1.5mm
b) Must be grounded
c) Must never be grounded
d) None of the above
Which of the following butt-weld preparations is generally most
susceptible to ‘lack of side wall fusion’ during MMA welding?
a) A‘U’ preparation
b) —A‘V’ preparation
©) A ‘double V” preparation
4) Lack of side wall fusion does not exist with MMA
‘What is the leg length of a fillet weld?
a) ‘The distance from the toe to the face
b) The distance from the root and to the face center
c) The distance from the root to the toe
d) ‘The distance from toe to toe
What is ‘throat’ thickness of the fillet weld?
a) ‘The distance from toe to the face
b) ‘The distance from the root to face center
©) ‘The distance from the root to the toe
d) The distance from toe to toe
Quality assurance is:
8) The inspection of a product or service
b) A management system designed only to ensure material
compatibility
©) _Notssolely related to planning and inspection.
4) The implementation of quality contro!
Which welding process is considered the most versatile?
a) SAW
b) TIG
©) MIG/MAG
<) MMA
Page 26 of 32
154
155
156
157
158
159
Quality assurance:
a)
b)
)
@)
Is an other term for inspection
Related to all activities and functions concemed with the
attainment of quality
Is the activity of ensuring documents relating to specific contracts
are in order
Is the activity of carrying out quality control
Which NDT method would never be use on a 6” aluminum pipe weld?
Radiography
Magnetic particle inspection
Ultrasonic testing
Dye penetrant testing
Why is hot ~ pass so-called?
a)
b)
°°
a)
Because it is applied at a high amperage
Because it is applied when the root is still hot
Because it could cause ‘hot - shortness”
Because it heat treats the root
Generally speaking a welding inspector, as a minimum requirement:
a)
b)
°)
da)
e)
Must have at a thorough knowledge of NDT
Must know how to interpret radiographs
‘Must have a thorough knowledge of welding metallurgy
None of the above
All of the above
Which of the following is not an inert gas?
a)
b)
©)
d)
Argon
Xenon
Carbon dioxide
Helium.
Why is welding is shielded?
a)
b)
°)
d)
To eliminate hydrogen
To retard the cooling rate of the weld
To eliminate the atmosphere
To ensure maximum heat input
Page 27 of 2
160
161
162
163
164
The primary duty of welding inspector:
a) _ Isensure welds are defect free
b) Isto ensure the weld is free from residual stresses
©) Isto write job specifications
4) Is to ensure all welding and associated activities are carried out in
accordance with the procedure(s)
Which of the following welding processes is most susceptible to lack of
fusion?
a) Submerged are
b) CO» (metal active gas)
c) Manual metal are
d) Tungsten inert gas
Fillet welds are
a) Preferable to butt welds due to high strength
b) Difficult to assess with Non Destructive Testing in comparison
with butt (grove) welds
©) Used only for ‘appearance’ purposes
4) Only feasible on steels
©) Alllof the above
API stands for
a) Associated Pipeline Industries
b) American Pipe Institute
c) American Pipeline Institute
d) American Petroleum Institute
When welding using the MMA process, varying the arc length
the most variation of:
Il give
a) Voltage
b) Amperage
©) Polarity
4) None of the above
Page 28 of 32
165
166
167
168
169
170
Lap joints contain:
a) Fillet welds
b) Corner joints
°) Butt welds
d) Single bevel butt welds
Which are welding process utilizes a non-consumable electrode?
a) MIG
b) TIG
ce) = MMA
d) SAW
2) Allofthe above
A welding Inspector:
a) Must know how to interpret radiographs
b) May be required to interpret radiographs on certain contracts,
©) Should be able to weld
4) Both bande
) — Alllof the above
Which electrodes are very susceptible to causing porosity in the deposited
welds if long arc employed?
a) Basic
b) Cellulosic
©) Ratile
d) None of the above
What do you understand by the term ‘minimum interpass temperature”
a) Minimum pre heat temperature
b) Minimum siress relieve temperature
©) The lowest temperature to be used when normalizing
d) The lowest temperature allowed during welding and between
passes
Is it permissible to allow a single ‘V’ butt weld to cool down passes?
a) Itis solely the decision of the welder
b) It depends on the requirement of the procedure and specifications
©) __ Itis solely the decision of the welding inspector
d) No, all welds should be completed before dropping the temperature
to ambient
Page 29 of 32
im
172
173
174
175
176
‘What is the problem with ‘restraint’ during welding?
a) It does not cause a problem
b) It may lead to cracking, especially with small welds between large
components,
c) It causes distortion
@) Restraint is term not used in relation to welding
Which mechanical test (s) can b e used to make an assessment of surfacing
breaking defects?
a) Bend test
b) Nick - break test
©) Macro test
d) ‘None of the above
e) —Allof the above
What is the purpose of a tensile test?
a) To assess tensile strength
b) To assess ductility
©) Toassess yield strength
d) All of the above could be assessed
When a metal returns to its original shape after an applied load has been
removed, the metal is said to have:
b) —_Ductility
©) Elasticity
d) — Malleability
Fluctuating load is: cyclic stresses, below the UTS on a weld component
may lead to:
a) Tensile failure
b) Yield failure
©) Fatigue failure
4) Shear failure
Stress is equal to:
a) Stress
b) Load divided by cross ~ sectional area
©) Extension of gauge length divided by original gauge length
4) Toughness
Page 30 0f 32
177
178
179
180
181
182
Strain is equal to:
a) Stress
b) Load divide by cross ~ sectional are
©) Extension of gauge length divided by the original gauge length
d) Toughness
Stress can be measured in:
a) N/mm?
b) PSI
©) mm
¢)— Bothaandb
What is a crater pipe?
a) Anoval tube
©) Another term for burn through
©) A type of porosity
4) A shrinkage defect
Which British standard relates to welding term and symbols
a) BS 639
b) —-BS638
©) BSI8
4) BS 499
How could you accurately measure the root radius of a charpy or Izod
specimen?
a) With a machine called shadowgraph
b) With arule
©) With a vernier caliper
4) With a densitometry
Herringbone porosity is:
2) A particular pattem of porosity
b) Made up of wormholes
©) Made up of piping
4) All the above are correct
) None of the above
Page 31 0f 32
183
184
185
186
187
A crack is a weld zone:
a) Is repairable
b) Always results in s cut ~ out and complete reweld
©) Is acceptable up to 2mm in length
4) May be repaired or cut - out depending on specification
requirements,
If the amperage were too low during the welding of a root bead the
possible result would be:
a) Lack of penetration
b) Lack of fusion
c) The freezing of the electrode
4) Allofthe above
Stress acting in the opposite direction of compressive stress is known as:
a) Residual stress
b) Shear stress
©) Hoop stress
d) Tensile stress
Distortion may be affected by:
a) Restraint
b) Heat — input
©) Material properties
4) Material thickness
) — Allof the above
Distortion:
a) Is plastic deformation
b) _ Is elastic deformation
©) Is another term for stress
d) May be elastic or plastic deformation
e) All of the above
Page 32 of 2
SATORP/TR INTERVIEW QUESTIONNARE (WELDING)
f 1) What is the package number and explain?
* Package one stands for Distilation & Hydro treating unit.
Different units are
& 91/92- High Pressure Hydro Desulphurization
> 101/102- Low Pressure Hydro Desulphurization
> 114/112-Naphtha Hydrotreater Unit
> 151/152- Distillation and Hydro treating Hydrogen Unit
> 155- Off Gas PSA Unit
> 150-Hydrogen storage unit
> 011/012- Crude Distilation Unity Vacuum Distillation Unit
2) What are the duties & responsibilities of a welding inspector?
‘* Perform material inspection.
* Perform consumable inspection.
‘* Application of inspection gauges, instruments and tools.
Check equipment and accessories.
Witness procedure qualification test.
Witness welder qualification test.
Perform visual inspection.
Review / witness NDT
Witness mechanical test.
Monitor heat treatment
Observe production and fabrication welding.
Interpret and assure compliance to Code / Standard / Specification.
Review technical drawing.
Witness weld repair.
Prepare and compile inspection records.
ee ee ee
3) What is the formula for heat input?
2. Heat Input (j/cm)= Voltage x Amperage x 60 / Travel Speed(cm/min)
4) What are welder qualification limits?
© Base metal qualification limits. (P no. and Thickness)
© Filler material qualification li .(F No.)
¢ Pipe diameter and position qualification limits.
© Weld metal thickness qualification limits.
5) What is WPS?
« The WPS is a written document that provides direction to the welder
for making production welds in accordance with Code/Standard
requirements.
6) How is the Procedure Qualification Record (PQR) different from the WPS?
* Procedure Qualification Record certifies that test welds performed in
accordance with the WPS meet Code requirements and summarizes
the specific test results.
7) What is POR?
* Arecord of welding variables used to produce an acceptable test
weldment and the results of tests conducted on the weldment to qualify a
welding procedure specification
8) What are essential variables?
a. Essential Variable (Procedure) ~ A change in a welding condition
which will affect the mechanical properties (other than notch
toughness) of the weldment. E.g. — change in P Number, welding
process, F number, electrode, preheat or postweld heat treatment.
b. Essential Variable (Performance) ~ A change in a welding condition
which will affect the ability of a welder to deposit sound weld metal.
E.g- change in welding process, deletion of backing, electrode, F
number, technique etc.
9) What are supplementary essential variables?
a. The change in a welding condition which will affect the notch
toughness properties of a weldment is known as supplementary
essential variable.
10) Can we use two welding process in a WPS?
* Yes (Eg: GTAW + SMAW)
11) What is PWHT?
* Postweld heat treatment (PWHT),defined as any heat treatment after
welding, is often used to improve the properties of a weldment.
@
a
12)Why we are using PWHT?
* To increase the resistance to brittle fracture and relaxing residual
stresses.
13) Mention the drying temperatures for low hydrogen SMAW electrodes?
> 260-430°C for 2 hrs min (A5.1)
> 370-430°C for 2 hrs min(AS.5)
> 120-250°C for 2 hours minimum. (SS and Non-Ferrous
electrodes)
14) What do you meant by low hydrogen consumables?
> Low hydrogen consumables are defined as less than or equal to 8 ml
of hydrogen per 100 g of deposited weld metal.
15) What are dissimilar metal welds?
> Any weld joint (excluding weld overlays or strip lining) between
ferritic steel and either austenitic stainless steel, duplex stainless
steel, or nickel-based alloys, or Use of stainless steel or nickel-based
filler metals on ferritic steels.
16) Explain about 31.37
* The piping which is generally found in petroleum refineries, chemical,
pharmaceutical, textile, paper, semi conductor and cryogenic plants, and
related processing plants.
* This section includes
a) Acceptable material specifications and component standards, including
dimensional requirements & pressure temperature ratings.
b) Requirements for design of components and assemblies, including
piping supports.
©) Requirements and data for evaluation and limitation of stresses,
reactions, and movements associated with pressure, temperature
changes, and other forces.
d) Guidance and limitations on the selection and application of materials,
components, and joining methods.
e) Requirements for the fabrication, assembly, and erection of piping.
f) Requirements for examination, inspection, and testing of piping.
19)What are the types of Mechanical tests?
> Tension Tests
@
Guided Bend Tests
Fillet Weld Tests
Notch Toughness Test
Stud Weld Test
vvvv
20)The term used to describe delay in the production schedule to permit inspection
is
* Hold Point
21) Equation for Heat Input?
> H=60EI/ 1000S
Where,
© H- Heat Input (KJ/mm)
* E-- Arc Voltage (volts)
© | —Current (Amps)
© S-Travel Speed (in/min)
22)What is the Procedure Qualification Thickness Limits?
ASME SEC IX QW- 452
i) It is the test coupon < 1” - Size welded (Dia)
ii) Thickness always 2T — T - Thickness of Test Coupon
iii) Minimum Thickness Qualified - 1.5mm
23)What are the essential variables for PWHT?
© Heating rate
‘+ Temperature attained
* Choking temperature and
* Cooling rate.
24)What is the gap of socket weld?
* 1.5mm to3mm
25)Formulae for carbon equivalent?
© CE=C+(Mn)/6 +(Cr+Motv)/5 + (Ni+Cu)/15
26)What do you mean by ITP?
+ Itis a mandatory item in the Quality Plan to guide and assure quality in a
specific type of work in a specific sequence of QC activity steps.
27) What is NCR?
* NCR: (Non Conformity report): A record reporting the variation from the
specified requirements.
28) How do you calculate the weld repair percentage?
> % RR = (Lr/Lw) X 100
Where, %RR— Percent repair rate
Lr ~ Total length of repair in one week
Lw ~Total length of weld radiographed in one week
29) RT % of M, D, Normal and Sever cyclic service?
> D Service : a) ifrating is 2 1500 Ib, 100 % RT
b) If MDT -29°C, 5% RT
¢) Hydrocarbon service, 100%
> Mservice : a) ifrating is 2 600 Ib, 100 % RT
b) If MDT s -29°C, 20% RT
¢) Hydrocarbon service, 100%
> HP Service : 100% RT
» SC Service : 100% RT
30) What should be the distance b/w two parallel welds?
> 20mm or three times the wall thickness of the joint, whichever is
greater.
31)What factors (give at least four) are taken into account when selecting and
designing a joint for a welding application?
> Strength
> Accessibility for welding
> Minimize distortion
> Cost of welding
> Accessibility for inspection
32)What is the difference b/w stud bolt and machine bolt?
> Machine bolt has a head on one side and nut on other side but stud bolt
have nuts on both sides.
33)Which standard do you refer for the welding equipment calibration?
> BS 7570.
34)What are the tests required for verifying supplementary essential variables?
Notch toughness tests-
> Charpy V- Notch test
> Drop weight.
35) What is the chemical composition of a low hydrogen electrode — E7018?
> £7018-C0.15, Mn 1.60, Si 0.75, P 0.035, $ 0.035, Ni 0.30, Cr 0.20,
Mo 0.3, V 0.08.
36) What does L stands for 3161 and the composition?
> Low Carbon.
37) Mention the drying temperatures for low hydrogen SMAW electrodes?
> 260-430°C for 2 hrs min (A5.1)
> 370-430°C for 2 hrs min(A5.5)
> 120-250°C for 2 hours minimum. (SS and Non-Ferrous
electrodes)
37) What are the different factors that cause HIC?
> Asensitive microstructure
> Asufficient level of hydrogen
> Ahigh level of stress
38)What is the minimum thickness of pipe that requires stress relieving to be
done as per B31.37
> 19mm
39) What is the function of shielding gas?
> Stabilises the arc roots on the material surfaces.
> Ensures smooth transfer of the molten metal from the wire to weld
pool.
> Forms the arc plasma.
40)|f welder is qualified in 3G position in pipes, he can weld all position?
3G position in pipe not mentioned in ASME Sec IX,
The pipe positions are 1G, 2G, 5G and 6G as per ASME Sec IX.
41)If Mechanical damage occurred on base metals what will be your course of
action?
\f any Mechanical damage found on the base metal, conduct the thickness
measurement and Magnetic Particle Test or Penetrant Test to be conducted, if
it is within tolerance accept it otherwise submit the report to higher authority for
further action.
42)You have observed in the specimen certain defects, why do you consider it as
important and do the report of it, state two planar defects? What are causes for
the occurrence of it and how will you avoid it?
Defects: Is a rejectable one i.e., a discontinuity which exceeds the code limits is
defects. Depending up on the conditions and severity it has to be repaired.
The two planar defects are i) Lack of side wall fusion ii) Undercut.
i) Lack of side wall fusion: Contaminated surface may due to oil, grease, and
rust ete., and too narrow gap, current very low and improper manipulation of
electrodes.
Prevention: Bevel ends shall be thoroughly cleaned and free from detrimental
contaminants, appropriate root gap, welding parameter within the WPS range
and right manipulation of electrodes.
ii) Undercut : Due to excessive current, travel speed too high.
Prevention: Appropriate travel speed, welding parameters under control and.
shall be within the WPS range.
43)What is the P No; for CS & SS?
« CS-P1
* SS-P8
44)Buttering or weld build up on the prepared surface shall not exceed
+ Exceed the lesser of 1/3" of base metal thickness or 10mm without the
prior approval of the company.
45) Internal misalignment of Butt joints shall not exceed
2 1.5mm
46) Fillet Weld Profiles
* Convex, Concave, Mitre
47)Explain E 8018
E- Electrode
80 Tensile Strength
1 for all Position
8 Coating
48)The preheat shall be established over a minimum distance of
* 75mm on each side of the weld.
49)Electrodes, filler wires, flux which standards to be used?
* ASME SEC IC
50)What equipment will use to determine oxygen level?
* Oxygen Scavenger
51)What is the surface temperature of PT?
© SC to 52°C
52)What is the F number for the filler wire ER70S?
* 6
53)What are the duties of a QC Inspector for Consumable receiving inspection?
Check the Test Certificates (T.C.) of each batch of electrodes for the
conformance of parameters with respect to project requirements.
Check the availability of labels on each package units (Pack or Box) and
completeness of the information in them.
Check the condition of the package and electrode / filler wire. If any
damage found, it is reported for the corrective action.
Check the correctness of the batch No.; Electrode/Filler wire diameter and
other data with respect to the Test Certificate.
a. After inspection, the welding materials are stored in the warehouse or in
the welding consumables control room under ambient temperature.
b. All welding consumables shall be stored in racks, off the floor, in such a
way as to prevent any physical damage or contamination. Consumables
for the use on various types and grades of material shall be clearly
segregated by type and size to minimize possibility of error in distribution.
54) What is the exposure time for low hydrogen electrode?
* The electrodes may not be exceeded more than four hours, the exposure
may be extended to 8 hours if the electrodes are continuously stored in a
portable oven upto 65°C minimum.
55)What are the things to be checked in sockolets?
* All fitting bores are to be concentric within 0.76mm for all sizes.
* To prevent cracking of a fillet weld install a 1.5 cardboard washer or
withdraw the pipe 1.5 mm from bottom of the socket before welding.
56)Why post heating is done on some pipe after the welding is over?
+ To maintain uniform homogeneous structure.
57)What are weldolets and sockolets? And where they are generally used?
* Weldolets and sockolets are self reinforced fittings.
* Weldolets are used for butt welded branch connections where standard
tee is not available due to size restrictions and the piping is at a
criticalyhigh pressure service.
* Sockolets are used to socket welding branch connection which requires
reinforcing pads.
58)What is the density of steel?
+ 7.86 kgim?
59)In 316L, what is the L stands for?
* L stands for low carbon steel
60)If heat input increases what will happen?
© Yield strength decreases
Tensile strength decreases
Percent in elongation increases
Notch toughness siightly increases and then decreases
Hardness decreases
Cooling rate decreases ( R « 1/ TH) Where R is the cooling rate, To is
the preheat temperature, H is the heat input.
61) What is the cause of porosity?
* The presence of gas pores in a weld caused by entrapment of gas during
solidification is termed as porosity. The pores are in the form of small
spherical cavities either clustered locally or scattered throughout the weld
deposit. Sometimes entrapped gas give rise to a single large cavity called
Blowholes.
* Cause: -
A. Chemically imperfect welding consumables, for example, deficient
in deoxidiser.
B. Faulty composition of base material or electrode, for example, high
sulphur content.
@
2
Presence of oil, grease, moisture and mill scale on the weld
surface.
Excessive moisture in the electrode coating or submerged-arc flux.
Inadequate gas shielding or impure gas in a gas ~shielded process.
Low welding current or too long an arc.
Quick-freezing of weld deposit.
ormo
62) How do you calculate concave fillet weld?
Fillot wold leg
Fille
_7~Seribe lines
Fillot wold
fo
| - Fillot wold tog
(a) Concave Fillet Weld
© Calculated by throat
* Fillet weld size is the leg length of the largest isosceles right triangle which
can be inscribed within the fillet weld cross section.
63)How do you calculate the convex fillet weld?
Fillet weld lag ‘Scribe tines
/—Convaxity
/
‘Weld too
Fillet wold
sae op
(b) Convex Fillet Wald
Fillet weld leg
* Calculated by Leg size
+ Convexity is the maximum distance from the face of convex fillet weld
perpendicular to line joining the weld toes.
64)What is annealing and normalizing process?
Annealing process is a heat treatment in which a sold state is heated and then
cooled at a slow rate.
The annealing temperature and the rate of cooling depend on the material and
the purpose of the treatment. Annealing is used to effect any of the following
changes in metal:
> To relieve stress
> Induce softness
> Alter mechanical properties, electrical, magnetic or physical properties.
> Refine crystalline structure
> Remove gases
> Produce a definite microstructure.
Normalizing process is a process in which a ferrous metal is heated to a suitable
temperature above the transformation range and is subsequently cooled in still
air at room temperature.
65)What are the characteristics of good welding cable?
Wear and abrasion resistant
High electrical resistance
Good heat resistance
The size of the cable required for a particular application depends on the
maximum amperage to be used for welding, the length of the welding circuit
(welding and work cables combined), and the duty cycle of the welding machine.
66)What are the tests required for analysis of consumables?
Chemical Analysis (ASME SEC II C )
PMI (JERES-A-206)
67)What are the tests required for verifying supplementary essential variables?
Notch toughness
68)What is an isotope? Different types of isotope? Explain the characteristics of
isotope?
Atoms of the same element which are identical in their chemical behavior but
different from one another in the number of neutrons contained in their nuclei, and
thus have different atomic weights.
Isotopes also act as flow tracers for detecting leaks in buried or inaccessible
equipment.
* Isotopes such as cobalt-60, cesium-137, and iridium-192
69)Name the instrument used for measuring density of photographic or
radiographic film?
» Densitometre
70)What are the factors on which the density of radiographic film depends?
The density of radiographic films depends upon the following: -
A. Total amount of radiation emitted by X-ray or gamma ray.
B, Amount of radiation reaching the specimen.
C. The amount of radiation passing through the specimen.
D. Intensifying action of the screen if used.
74) How will you calculate the geometric unsharpness in radiographic film?
Geometric unsharpness of the radiograph shall be determined in accordance
with:
Ug = Fa/D
where
Ug = geometric unsharpness
F = source size: the maximum projected dimension of the radiating source
(or effective focal spot) in the plane perpendicular to the distance D from
the weld or object being radiographed, in.
D = distance from source of radiation to weld or object being
radiographed, in.
d= distance from source side of weld or object being radigraphed to film.
72)What is the welder qualification based on f number?
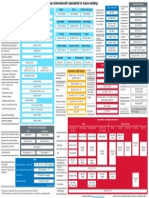
Semen] OTR [Fam [FF] aS Rk] St FS ra
etch || ts || re] | oe | a [wee | a? [ono
nats For |e | Sei | | a | eb |i |g [ te || Ha,
Fv
bs
Fo. We ‘
ia
fz xf«felelele
Fa 1 we
wa
5 »]xlxle
Fe oes 7
eis
face wioan x
is
fo so
Baxting x
Fa 3 Woon
eS
xf etx fx fe fe] x]x fx] x
73)Which markers are used on SS materials?
* Low halogens and Low sulfur less than 200 ppm
74)Define Arc blow?
* The deflection of an arc from its normal path because of magnetic
forces.
oes are the standards for welding as JER Standard?
JERES-W-011-Welding Requirements for On-Plot Piping
» JERES-W-010-Welding Requirements for Pressure Vessels
* JERES-W-012-Welding Requirements for Pipelines
» JERES-W-014-Weld Overlays and Welding of Clad Materials
« JERES-W-016-Welding of Special Corrosion-Resistant Materials
76)Write the weld layers?
1. Root
Il. Hot Pass
Fill
IV. Cap
77)What are the Weldment Terms?
i. Weld Face
ii, Weld Root
|. Fusion Zone
iv. Fusion Boundary
v. Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
vi. Weld Toes
vii. Weld Width
78)Write Small Bore Fittings?
Weldolet
Sockolet
Threadolet
Elbolet
Nippolet
79)Dry developers?
* Can be applied by spraying, flowing pricy solvent can be applied by
electrostatic spray particle should be (-) and high voltage shock all to be
done in a log chamber so we can sauce the 80% of the material
80)Principle of UT.
* Reflection of Sound
81)What is the use of Couplant?
+ To remove the air gap between the transducer and object.
82)What is the Welding Process?
a) GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding)
b) SMAW (Shielded Metal Arc Welding)
c) SAW (Submerged Arc Welding)
d) FCAW (Flux Coated Arc Welding)
e) GMAW (Gas Metal Arc Welding)
f) PAW (Plasma Arc Welding)
83)Welding Position
Pipe - 1GR, 2G, 5G, 6G,
Plate — 1G, 2G, 3G, 46
PIPE:-
1G: - A Pipe is Horizontal Position and weld beed is a vertical position. The
Pipe will be rotated.
2G: - A Pipe is Vertical Position and weld bed is Horizontal Position
5G: - A Pipe is Horizontal Position and weld beed is Vertical Position
6G: - A Pipe is a 45° Position
PLATE:
1G: - Plate is Horizontal and weld is Horizontal
2G: - Plate is Vertical and weld is Horizontal
3G: - Plate is Vertical and weld is Vertical
4G: - A Plate is in Overhead Position weld is Horizontal Position
84) What are the preheat requirements as per JERES?
PREHEAT REQUIREMENTS
MATERIAL WALL THICKNESS _| MIN PREHEAT
Upto 30mm 20°
csaLtcs 30-50 mm 20"
> 50mm ~ 100
P 4(P11) ALL 150
P5B( P5, PS) ALL 250
SS L ALL “| 10
* If ambient temp. is below 5°C, preheat to 40°C is mandatory.
** 80°C min, if specified UTS= 490 Mpa & heat ip < 20 KJ
@ Max interpass temp. for SS(P8): 1770
~ [Max interpass temp. for CS, alloy (P5,P9,P11) 315°C _
85)Why we maintain the interpass temperature?
« The yield and ultimate tensile strengths of the weld metal are both a
function of the interpass temperature.
* High values of interpass temperature tend to reduce the weld metal
strength. Additionally, higher interpass temperatures will generally provide
a finer grain structure and improved Charpy V notch toughness transition
temperatures.
86)What is the difference b/w tensile test & yield test?
* A tensile test is a test to obtain an accurate assessment of the strength and
ductility of a material or a weld, or in an all-weld-metal test, to determine
¢ mechanical properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, elongation,
and reduction in area,
* Ayield test is to obtain the strength at some arbitrary amount of extension
under load or a permanent plastic strain (offset).
STRENGTH, MPa
0
“| 02% oF sreomen ance vena
— WoneAsina ExaINEERNa STAAIN(ELAETIC® PLASTIC) —e
87)Low hydrogen electrode handling and ovens?
* When containers of low hydrogen electrodes are opened, they will be
immediately placed in an electrode baking oven. The welding material
store shall be a controlled access area. Unauthorized personal
including welder & welding operated shall be prohibited consumables
from out it,
* The maximum electrodes issued shall be for about 5 hours. From
heating oven, as a good practice, electrodes to be placed below the
electrode still into the holding oven.
* Baking will be done for low hydrogen electrodes e.g. 7018 at
temperature 350°C in accordance with the manufacturer
recommendation.
88)While welding of pipe trunion to pipe/reinforcement pad you have to put a hole
or leave some portion of welding why?
* For venting of hot gas which may get generated due to welding.
89)What is the affect if the quantity of hydrogen induced in weld metal is more?
* When hydrogen is more in weld metal, it tends to make the material
brittle & subsequently leads to cracking. These cracks are called
hydrogen induced cracking or delayed crack. To avoid this the electrode
before using is backed at 250°C to 300°C for one hour in mother oven &
then cooled down to 100°C in the same oven & finally transferred to
portable oven for use where temperature is maintained at 60’to 70°C
90)List 3 disadvantages of RT over other NDT Methods.
+ Radiation Safety Precautions, Planar defects not readily detectable,
heavy equipment.
‘91)Why don't we take a branch for Cryogenic Service from bottom side though
the fluid is in liquid state?
¢ There is the chance of Ice formation during normal operation and since
ice flows from the bottom of the pipe it will block the branch pipe
connection.
92)From which side of pipe will you take a branch connection?
© When Fluid is Gas, Air or Steam and Cryogenic Service — Topside.
When Fluid is Liquid - Bottom Side.
93)What are the different types of hardness tests carried out?
* Brinell hardness Test.
Rockwell Hardness Test.
Vicker Hardness Test.
94)What is a theoretical throat?
The distance from the beginning of the joint root perpendicular to the
hypotenuse of the largest right triangle that can be inscribed within the
cross section of a fillet weld. This dimension is based on the
assumption that the root opening is equal to zero.
95)What is the procedure for application of wrapping and coating?
* Procedure for application of Coating and wrapping: -
A. Prior to application of wrapping & coating, the surface of pipe should be made
free from all loose Mill scale, dirt, rust, grease, moisture and other foreign
material. This is achieved by blast cleaning to grade Sa 2%.
B. The pipe exterior surface or blast surface shall be coated with primer within
four hours of shot blasting. The primer shall not be applied when the pipe surface
temperature is below 7°C and above 70°C. When moisture is present on the
surface, the same is heated for sufficient time to dry the surface.
©. The pipe after priming shall be coated with two-flood coat of hot enamel
incorporating the simultaneous application of inner & outer wrapping,
96) How you will measure linear indications and acceptance?
' Material thickness size
thks1émm : <1.6mm_—
LE 46mm 2 thk < 50mm $3.2mm _|
thk= 50mm. sémm |
97)What is a duplex stainless stee!?
* The term duplex stainless steel describes steel with microstructure
containing austenite and ferrite in which the lesser phase is at least 30%
by volume. First generation duplex stainless steels (typically 26% Cr, 4.5%
Ni, and 1.5% Mo) were about 5 to 80% ferrite.
98) What is DIRECT CURRENT ELECTRODE POSITIVE (DCEP)?
* The arrangement of direct current arc welding leads in which the electrode
is the positive pole and the work piece is the negative pole of the welding
are.
99)What is DIRECT CURRENT ELECTRODE NEGATIVE (DCEN)?
* The arrangement of direct current arc welding leads in which the electrode
is the negative pole and workpiece is the positive pole of the welding arc.
100) What are grains?
© Groups of erystals presenting metal after it have solidified.
101) What are the types of gasket?
* Based on construction
A. Full face.
B. Spiral wound metallic.
C. Ring type.
D. Metal jacketed
E. Inside bolt circle.
* Based on material
@
A. Synthetic rubber
B. Solid Teflon
C. Compressed Asbestos
D.CS (High pressure fluid)
E, SS (High fluid corrosive)
F. Spiral Wound a) Teflon b) CS c) SS
1) What are the types of flanges?
Based on pipe attachment
Slip — on. - The Slip-on type flanges are attached by welding inside as
well as outside. These flanges are of forged construction.
Socket Weld. : - The Socket Weld flanges are welded on one side only.
These are used for small bore lines only.
Screwed: - The Screwed-on flanges are used on pipe lines where
welding cannot be carried out.
Lap Joint. : - The Lap Joint flanges are used with stub ends. The stub
ends are welded with pipes & flanges are kept loose over the same.
Welding Neck. : - The Welding neck flanges are attached by butt welding
to the pipe. These are used mainly for critical services where the weld
joints need radiographic inspection.
Blind. : - The Blind flanges are used to close the ends which need to be
reopened.
Reducing. : - The reducing flanges are used to connect between larger
and smaller sizes without using a reducer. In case of reducing flanges,
the thickness of flange should be that of the higher diameter.
Integral. :- Integral flanges are those, which are cast along with the
piping component or equipment.
Flanges are classified based on pressure temperature ratings as: -
A, 150,
B. 300,
C. 400
D. 600,
E, 900,
F. 1500,
G. 2500
Flanges are classified based on facing as: -
A. Flat face. (FF)
B. Raised face. (R/F)
C. Tongue and groove. (T/G)
D. Male and female. (M/F)
E. Ring type joint. (RTJ)
* based on face finish as: -
A. Smooth finish.
B. Serrated finish.
102) What is tack weld?
* Tack weld is the temporary weld to maintain joint alignment. All tack welds
shall be made by qualified welders. Recommended tack thickness is 3.2 —
4.8mm & length is 12.5 - 25.4 mm. the minimum number of tack welds for
3.5 inch and below are 3 equally spaced tacks. Above 3.5 inch 4 equally
spaced tacks.
103) What is Schedule ‘Q'?
* Schedule Q stands for Owner's minimum quality requirements for
Contractor/Subcontractor quality system.
104) What type of cutting used is SS? Types of Grinding wheel and how to
identify them?
* Plasma are cutting and grinding wheel
+ Types for grinding wheel are: Iron oxide, zirconium, Aluminum oxide.
* Identification by color coding.( blue)
105) What are the common welding defects?
A. Lack of penetration
B. Lack of fusion.
C. Undereut.
D. Slag inclusion.
E, Porosity.
F. Crack.
G. Faulty weld size & profile.
H. Distortion
106) Types of Orifice Plates
Concentric Orifice
Electric Orifice
Segmetal Orifice
107) What is the Profile Imperfection?
') Spatter
ii) In Completely filled Groove
ili) Lack of Root Fusion
iv) Incomplete Root Penetration
v) Shrinkage Grooves
vi) Root Concaring
vii) Crater Pipe
vili) Excess Penetration
ix) Burn Through
108) What does sensitivity depends on?
Definition and Control
109) Types of Probe in UT?
Normal probe, Angular probe, triangular probe (45°, 60°, 70°).
110) Hydrophilic emulsifies are?
Water miscible liquids used to emulsify the excess oil fluorescent
penetrant
111) The discontinuities would be impossible to detect using PT?
Internal inclusions
112) What is an alloy steel?
Iron based alloy- c < 2%, Mn >.25 %, min qualtities of one or more
alloying elements other than Mn, silicon and Cu, that does not specify Cr
content = 10%
Candidate’s Name: Nationality/Location:
Interview Date
Interviewer(s):
‘Competency Evaluation & Interview Tool for GC 12+
With Specific Evaluations for Mechanical Candidates
Use for all fulure interviews of Inspection Department Personnel for GC-12+
Skoy f VITAL fe i 12 & GC
PARTS
4. Rate Intelligence (Pose 2 specific problem, Candidate to provide solution)
2. Rate Personality (Questions)
3. Rate Motivation & Drive (Questions)
NOTE: SEE QUESTIONS 1-10!
‘These first three ites are the basic foundation for Candidate Competency. Without these, the candidate
cannot be reasonably expected to achieve success for COMPANY.
4, Rate Knowledge (Technical Questions)
5. Rate Experience (Specific Questions)
NOTE: SEE ATTACHMENT QUESTIONS!
‘These questions can be given to the employee just prior to the job interview and answers can be quickly
reviewed with the Candidate to minimize time spent on the teleconference or phone interview. The
‘Candidate's response to his Performance during the test can be also be evaluated
‘Caution: Care should be taken to see that COMPANY does not lose control of these interview questions.
CV Review, Company Concerns/Questions (However many arose on CV Reviews)
1. Company concem questions from e-mails on review (examples shown below)
‘A)_ Your resume showed many short-lerm jobs over the past 10 years, what could you say that will
‘convince us thal you have plans for longer-term employment at Saudi Aramco.
B)_ Your resume showed that you have an 11-year-old daughter. Will there be a problem with her
having to leave Country by age 14 to attend boarding school?
©) Your resume shows limited overseas experience and no Middle East work experience. .etc
Rate Basic Competency by Intelligence/Personality/Motivational Drivers (Questions)
2, Can you tell me about your (PARTICULAR JOB REQUIREMENT SKILLS) and why you would be the right
‘choice for this position?
3. In your opinion, what has been your greatest accomplishment as a professional/inspector?
4. What have you done in the area of Teamwork to upgrade skills of those working forfwith you during your
career?
5. Can you give me an example of a confic that you may have had with an employee under your
‘supervision and how you handled it?
6. What do you consider to be your key strengths as a parson?
7. What has been the most dificult situation you have had to deal with and how did you handle it?
‘8, Why would you be an asset as an employee of Saudi Aramco?
‘9. What do you consider your strengths as an Inspector to be? As @ person?
410, What is your chief motivation as a Professional Inspector? As @ person?
Candidate’s Name: Nationality/Locatio
Interview Date: Interviewer(s):
INTERVIEW ATTACHMENT (FAX TO RECRUITER FOR CANDIDATE TO FILL OUT) WANSWER KEY
Rate Technical Knowledge (Mechanical, GC-12)
‘Quality Systems
1, Describe the dlference between QA & QC?
‘Answer:
What do quality system audits evaluate?
‘Answer:
3, Saudi Arameo has adopted the basic framework and definitions of the International Quality System
Standards ISO-9000 Series. This has been done fo provide universal understanding and improve
‘communication between the COMPANY and prospective CONTRACTORS whose Quality System is
‘congruent with the [S0-£000 Series. Describe the basic elements of an ISO 9000 Series Quality Program?
Answer:
Mechanical/Welding
4, What is an essential variable as related to a Weld Procedure Specification (WPS)?
‘Answer
5, Qualification Record (POR) and a WPS?
Answer
6. Heat input (SMAW per ASME IX) is @ combination of what two electrical characteristics & travel speed?
Answer:
7. Excessive heat input is mainly attrbuted fo what poor welding techniques during SMAW process?
Answer:
8. What
8 potential sources of Hydrogen encountered during SMAW process?
Answer:
‘9. What are several likely causes of porosity in carbon steel welds using the SMAW process?
Answer:
40, What dimension is measured to determine the size of a concave fillet weld?
Answer:
+12, What cimension is measured to determine the size of a corwvex filet weld?
Answer:
Candidate’s Name: __ Nationality/Location:
Interview Date: Interviewer(s):
13, Where would cracking most ikely occur from excessive current input in a single pass weld?
Answer:
144. Using GTAW process, describe what happens lo a weld without proper purging/back gessing on SS
material?
Answer:
15, Name 3 of the 5 mechanical tests in ASME IX employed for procedure & performance quelificalions?
Answer:
MechanicallNDT (assume SMAW process used for all questions)
46. How is Magnetic Particle inspection of a weld using the wet continuous test method performed?
Answer:
117. Indications with Liquid Penetrant Testing are easily seen ifthe surface has been prepared by grinding
prior to testing? Truelfalse? Why?
Answer:
48, Name an NOT method and technique that employs a reflected sound beam that can be used for the
volumetric examination of welds?
Answer:
19. List 3 disadvantages of RT over ather NDT Methods.
Answer:
20. Ifa product is to be stress relieved, why is It important to use exactly the same RT procedure before and
after stress relieving?
Answer:
21. A dark narrow area 2-3mm wide appears on a radiograph all along the edae of the area representing the
‘weld, The joint has @ 60-Degree double-vee groove. What is the indication most likely to be?
Answer:
22. A localized darker density Radiographic image with fuzzy edges in the center of the width of the weld
image that may or may not be wider than the width of the root pass image Is most likely what?
Answer:
23. Name 5 common film artifacts that may be cause for rejection of Radiographic Film?
Answer:
Candidate's Name: Nationality/Location:
Interview Date: Interviewer(s):
24. When the radiation source is located inside piping with the film located outside, single-wall exposure and
‘single-wall view, name this type of exposure?
Answer:
25, How do gamma rays compare with X-rays when applied to RT of welds?
Answer.
Rate Specific Knowledge (Experience)
26. Per ASME B31.3 (assume latest ecition), name three of the four Categories of Fluid Service?
Answer:
27. Per ASME 831.3, who Is responsible for classification of service lo a given category?
Answer:
28, Par ASME 891.9 assume latest ein) what are the RT requrementsfor Socket welds sever cycle
service’
Answer:
28, Relating lo the above question, Give good reasons why random RT of socket welds is recommended?
Answer
30. Briefly describe good QC practice relating 10 the instalation & bolting of flanges?
‘Answer
31. What is an often-overlooked Inspection/NDT requirement on the installation of an orifice flange?
‘Angwer
32, Per ASME Section VIII, Dv. 1, can a nozzle to be altached to the exterior surface of a pressure vessel
‘without any portion of the nczzle projecting into the shell?
Answer
33, Explain the difference between a 2:1 Elipsoidal head and a hemispherical head?
Answer:
34, Which of the above two heeds given equal thickness can withstand greater intemal pressure?
Answer:
36, In ASME Section Vill Division 1, Parts UW and UCS cover what scope of work?
Answer
Candidate's Name: Nationality/Location:
Interview Date: Interviewer(s):
36, Name several Inspection items on internal componentitray installation for new columns?
Answer:
37. What API documents apply to the replacement of an existing flocr for an Aboveground Oil Storege tank?
‘Answer:
38, What are two key items to be resolved prior to addition of new nozzles to older tanks per API 6537
Answer
39, Briefly describe an area impressed Cathodic Protection System?
Answer:
40, Relating to Contractor Weld Shop evaluation prior to the beginning of pipe welding for a major project,
what are several key items you would look for as the Inspector assigned to approve the shop for Company?
Answer:
1
2
Candidate’s Name: Nationality/Location:
Interview Dat Interviewer(s)
Competency Evaluation & intorview Too! for GC 12+
With Specific Evaluations for Mechanical Candidates
Use forall (ulure interviews of Inspection Department Personnel for GC-12+
FORMAT FOR INTERVIEW
are vit nt of ani 6-42 & GC-19 Co
PART
1, Rate Intelligence (Pose a specific problem, Candidate to provide solution)
2. Rate Personality (Questions)
3, Rate Motivation & Drive (Questions)
NOTE: SEE QUESTIONS 1-10!
‘These first three items are the basic foundation for Candidate Competency. Without these, the candidate
‘cannot be reasonably expected to achieve success for COMPANY.
“This will be covered during the interview and will provide invaluabl
4, Rate Knowledge (Technical Questions)
5. Rate Experience (Specific Questions)
NOTE: SEE ATTACHMENT QUESTIONS!
‘These questions can be given to the employee just prior to the job interview and answers can be quickly
reviewed with the Candidate to minimize time spent on the teleconference or phone interview. The
Candidate's response to his Performance during the test can be also be evaluated.
Caution: Care should be taken to see that COMPANY does not lose control of these interview questions.
CV Review, Company Concerns/Questions (However many arose on CV Reviews)
1. Company concem questions from e-mails on review (examples shown below)
A) Your resume showed many short-term jobs over the past 10 years, what could you say that will
‘convince us that you have plans for longer-term employment at Saudi Aramco.
8) Your resume showed thal you have an 11-year-old daughter. Will here be a problem with her
having to leave Country by age 14 to attend boarding school?
©) Your resume shows limited overseas experience and no Middle East work experience...elc
Rate Basic Competency by Intelligence/Personality/Motivational Drivers (Questions)
2. Can you tell me about your (PARTICULAR JOB REQUIREMENT SKILLS) and why you would be the right
Cchoiee for this position?
3, In your opinion, what hes been your greatest accomplishment as a professionallinspector?
4, What have you done in the area of Teamwork to upgrade skils of those working forfwith you during your
career?
'5. Can you give me an example of a conflict thal you may have had with an employee under your
‘supervision and how you handied it?
6. What do you consider to be your key strengths as a person?
7. What has been the most diffcul situation you have had to deal with and how did you handle it?
8, Why would you be an asset as an employee of Saudi Aramco?
9. What do you consider your strengths as an Inspector to be? As a person?
10. What is your chief motivation as a Professional Inspector? As a person?
Candidate's Name: Nationality/Location:
Interview Date: Interviewer(s):
INTERVIEW ATTACHMENT (FAX TO RECRUITER FOR CANDIDATE TO FILL OUT) wANSWER KEY
Rate Technical Knowledge (Mechanical, GC-12)
Quality Systems
1. Describe the difference between QA & QC?
Answer: Qually Contols the operational techniques (Inspection, Examination & Testing) thal
tised fo ful requirements for quality. Gually Assurance i the system of action and planning
needed {0 provide confianco that a Product or Service wl satisfy qualy requirements
2. What do quality system audits evaluate?
Answer: The degree of quality system conformanes to established requirements.
3. Saudi Aramco has adopted the basic framework and definitions of the International Quality System
Siandards 1SO-9000 Series. This has been done to provide universal understanding ana improve
‘communication between the COMPANY and prospective CONTRACTORS whose Qualiy System is
congruent with the ISO-9000 Series. Describe the basic elements of an ISO 9000 Series Quality Program?
Answer:
Assurance per 1S0-9000
‘Quali Systems per 1SO-9001, 9002, 9003
‘Qually Plan Guidelines per ISO 10005,
MechanicalfWelding
4, What is an essential variable as related to a Weld Procedure Specification (WPS)?
‘Answer: A change in a welding condition that will affect the weld’s mechanical properties.
‘5, Whal is the relationship between a Procedure Qualification Record (PAR) and a WPS?
‘Answer: The PR documents what occurred during the welding and testing of the test coupon.
6. Heat input (SMAW per ASME IX) is a combination of what two electrical characteristics & travel speed?
Answer: Voltage and Amperage
7. Excessive heat input is mainly attributed to what poor welding techniques during SMAW process?
Answer: Excessively wide weaving and slow travel speed.
8, Whal are 3 potential sources of Hydrogen encountered during SMAW process?
Answer: Moisture in the metal and electrode coating, ol, elemental Hydrogen in the base metal
‘9, What are several likely causes of porosity in carbon steel welds using the SMAW process?
‘Answer: Poor welding technique and equipment, excessive wind, moisture & weld contaminants.
+10, Whal dimension is measured to determine the size of a concave filet weld?
‘Answer: Throat
+12, What dimension is measured lo determine the size of a convex filet weld?
Answer: Leg
113. Where would cracking most Ikely occur from excessive current input in a single pass weld?
Answer: Centerline of the weld
14, Using GTAW process, describe what happens to a weld without proper purging/back gassing on SS
material?
‘Answer: Oxidation at the ID (Sugaring)
18, Name 3 of the 5 mechanical tests in ASME IX employed for procedure & performance qualifications?
‘Answer: Tension, Guided Bend, Fillet-weld, Notch-toughness & Stud-weld tests
Candidate's Nami Nationality/Location:
Interview Date: Interviewer(s):
INTERVIEW ATTACHMENT wANSWER KEY
Rate Technical Knowledge (Mechanical, GC-12)
MechanicalNDT (assume SMAW process used for all questions)
16. How is Magnetic Particle inspection of a weld using the wet continuous test method performed?
‘Answer: The particles (usually Ruorescen\) are sprayed, poured on or applied by immersion and
the magnetizing currents applied while the particles are sti owing.
17. indications with Liguld Penetrant Testing are easily seen ifthe surface has been prepared by grinding
prior o testing? Trueffalse? Why?
Anewer: False, becouse grinding can smear metal and mask/cover discontinuities.
418. Name an NDT method and technique that employs a reflected sound beam that can be used for the
volumetric examination of welds?
Answer: Ultrasonic Testing using Shear Wave Technique provides good volumetric exam coverage.
19, List 3 disadvantages of RT over other NDT Methods.
‘Answer: Radiation Safely Precautions, Planar defects not readily detectable, Heavy equipment
20. Ifa product is {o be stress relieved, why is it important fo use exactly the same RT procedure before and
after stress relieving?
‘Answer: So that a baseline evaluation is performed to ensure that borderline indications are not
misinterpreted after siress rele.
21. A dark narrow area 2.3mm wide appears on a radiograph all along the edge of the area representing the
‘eld, The joint has @ 60-Degree double-vee groove. What s the indication most likely 1o be?
‘Answer: External Undercut
22. A localized darker density Radiographic image with fuzzy edges in
image that may or may not be wider than the width of the root pass image is most likely what?
‘Answer: Burn-through
23. Name 8 common film artifacts thal may be cause for rejection of Radiographic Film?
‘Answer: Film Scratches, light leaks, chemical stains, fogged film, static marks, water marks,
streaks, crimp marks, finger marks, lint, crt
24. When the radiation source is located inside piping with the film located outside, single-wall exposure and
‘single-wall view, name this type of exposure?
‘Answer: Panoramic
25. How do gamma rays compare with X-rays when applied to RT of welds?
‘Answer: Gamma rays have greater penetration ability, but give poorer contrast.
Rate Specific Knowledge (Experience)
26. Per ASME 831.3 (assume latest edition), name three of the four Categories of Fluid Service?
‘Answer: Categories D, M, High Pressure & Normal
27. Per ASME B31.3, who is responsible for classification of service to a given category?
Answer: The Owner
28. Per ASME B31.3 (assume latest edition), what are the RT requirements for Socket welds in severe cycle
service?
‘Answer: None
29, Relating to the above question, Give good reasons why random RT of socket welds is recommended?
‘Answer: Both gross welding defects & poor quality welders can be identified, with repairs and
corrective action taken, & Gap can be verified.
30. Briefly describe good QC practice relating to the installation & bolting of flanges?
Answer: Verily Materials (ype, size and rating) are acceptable, gasket verification & good bolting
practices (torque value requirements mel) in accordance with approved procedures.
Candidate's Name: Nationality/Location:
Interview Dati Interviewer(s):
‘31, What is an often-overlooked Inspection/NDT requirement on the installation of an orifice flange?
‘Answer: Visual weld inspection of the seal weld & NDT has been missed prior to bolting of flanges
32, Per ASME Section VIII, Div. 1, can a nozzle to be altached to the exterior surface of a pressure vessel
without any portion of the nczzle projecting into the shel?
‘Answer: Yes, with many restrictions
33. Explain the ditference between a 2:1 Ellpsoidal head and a hemispherical head?
‘Answer: A hemispherical head has no flange and knuckle region and holds greater volume.
34. Which of the above two heads given equal thickness can withstand greater internal pressure?
Answer: The 2:1 elliptical head can withstand much more internal pressure given equal thickness.
36. In ASME Section Vil, Division 1, Parts UW and UCS cover what scope of work?
‘Answer: UW designates requirements for pressure vessels and vessel parts fabricated by
welding, and UCS designates requirements for pressure vessels and vessel parts constructed of,
carbon and low alloy steels.
38, Name several Inspection items on intemal componentitray installation for new columns?
Answer:
1. Drawings, Cales & Data review
2. Verification of Material Construction of Internal components (Iray assemblies & systems,
‘hardware, packing medium)
3. Location, levelness and orientation of internal components per Mfg. Drawings/tolerances.
4, Seams, holes, gaps, missing items, looseness of hardware in trays
5. Leakage Tests as needed for rays, troughs, weirs, etc.
6. Final Cleanliness of Tray Assemblies
37, What API documents apply to the replacement of an existing floor for an Aboveground Oil Storage tank?
Answer: API 653 & API 650
38. What are two key items to be resolved prior to addition of new nazzles to older tanks per API 653?
Azmror Tonk Mona Hentcaton, Metal Design Considerations & selection (need for shell
inser
39. Briefly describe an area impressed Cathodic Protection System?
Answer: Electrical current & use of selectively placed sacrificial anodes is employed to stop/siow
the electrochemical reaction that occurs during the corrosion pracess.
40, Relating to Contractor Weld Shop evaluation prior to the beginning of pipe welding for a major project,
‘what are several key items you would look for as the Inspector assigned lo approve the shop for Company?
Answer: 5M-+ € formula = Manpower, Methods, Materials, Machines, Measurement, Environment
1. ManpowerEnsure adequate Personnel that are trained, qualified, certified & approved
2. Methods=Ensure that standards are followed and that weiding procedures, special processes
(PMI, PWHT, etc) are acceptable and thal there is a good quality system (paper trail) in place.
3. Materials=Ensure Materials are approved, certified, documented (traceable), stored corectly
with area for deficient items (quarantined), and segregation of dissimilar metals,
4, Machines=Ensure Equipment is adequate for the intended work and in good working condition,
5. Measurement=Ensure Contractor QC Program & testing/calibration program is in place for
‘equipment and work.
6. Environment=Ensure that the working environment (building) is safe, sheltered from the
‘elements and adequate to ensure quality work,
‘Questions Related to pipe under stress:-
1
What are Primary loads? Mention some of Primary Loads?
Answer:
These ae typically stoady or sustained types of loads. These loads have their origin in some force
acting on the pipe causing tension, compression, torsion etc leading to normal and shear stress.
Primary loads are not self limiting, Some ofthe primary loads are a
‘A. Iniomal fd pressure
B. External pressure.
. Gravitational forces acting on the pipe such as weight ofthe pipe & fluid.
D. Forces dus to relief or blow down,
E. Pressure waves generaied due lo water hammer effecs.
2, What do you mean by self limiting?
Answer:
it means that the stresses continue to exist as long as long the load persists and deformation does
rot stop because the system has deformed into a no-stress condition but because strain hardening
has come into play.
3. Whatare secondary loads? Mention some of the secondary loads?
Answer:
‘Secondary loads are caused by displacement of some kind. Some of the secondary loads are as:-
‘A. Force on piping due to tank settlement.
BB. Vessel nozzle moving up due to expansion of vessel.
C. Pipe expansion or contraction.
. Vibration due to rotational equipment.
4. Whatis the most used choice of co-ordinate system for defining the stresses?
Answer: -
ina pipe subjected to intemal pressure or any other load, the most used choice of co-ordinate system
s
‘Axial or Longitudinal direction.
B. Circumferential or Hoope's direction.
©. Radial direction.
‘The stresses in the pipe wall are expressed as axial(S,), Hope's (Sy) and Radial (Sq).These
siresses which stretch or compress a grain’ crystal are called normal stress because they are normal
to the surface of the crystal
5 What do you mean by Hoop Stresses and how sate it?
Angwer: - -
Stresses which are generated circ =
Hoop Sires. Itis calculated by;-
Hoop Stress (S.) = Pdy/ 2t
Where? = Foto
d=0D | Ud oe
far oY
How does Hoop Str
Page 26 of 63
What are the other stresses against which the design of piping is safe guarded?
‘A. Principal stress.
B. Shear stress.
‘Apart from the siress which is normal to the surface of the crystal as mentioned in question No. 4, the
grains would have been oriented in the pipe wall in all possible orientations. The above stresses
(Axial, Circumferential and Radial stress) have stress component in direction normal to faces of
randomly oriented crystal. Each crystal thus faces normal stresses. One of these orientations must be
such that it maximizes one of the normal stresses. Normal stresses for such orientation (maximum
normal stress orientation) are called principal stresses and are designated as Sy (maximum), S2and
'S,(mninimum).
Principal stresses are way of defining the worst case scenario as far as the normal stresses
are concerned.
In addition to the normel stresses, a grain can be subjected to shear stresses as well. These stress
‘act parallel to the crystal surface. The shear stresses occur if the pipe is subjected to torsion, bending
‘ete. Just as there is an orientation for which normal stresses are maximum, there is an orientation
‘which maximizes shear stress. The maximum shear stress in a 3-D stale of stress can be shown to
be as:
Fear = (Sr SZ
12. hall of the difference between the maximum and minimum principal stresses.
What does the solid mechanics states regarding the Normal stresses?
Anewer:-
‘Solid mechanic states that the sum of the three normal stresses for all orientation is always the same
for any given external load
Which component of normal stress is considered negligible?
Answer:
10.
In most pipe design cases, the radial component of normal stresses (Sx) is negligible as compare to
the other two component (Sand §}).
How the two principal stresses and maximum shear stress are calculated?
Answer:
Use of Mohr’ circie allows calculating the two principal stresses and maximum shear sess as:-
Sr= (Si + SW/2 + [(GL- Sw2 }?+ 1%
Sa OS + SWZ -(H- Sz P47]
Sam = 0.6 ((81 ~ Sy)?# 4 241 °F
“The third principal stress (minimum Le. $:) is zero.
What are the potential loads faced by pipes during normal operation? Write their relationship
to the stresses developed?
I loads faced by a pipe are:-
“temal pressure load.
*Y SINGH Approved by KENGAM VL. Revo
age 37 of
‘A. Axiat Load:
‘A pipe may face an axial force (F,) as shown in figure. The load may be tensile or compressive. In
figure only tensile load acting on pipe is shown. The load (F,) leads to normal stress in axial direction
(G). The load bearing cross-section is the cross-sectional area of the pipe wall normal to the load
direction, Ay. The stress developed is given by:~
Sus Fil Aw
‘The load bearing cross- section is calculated as:-
‘Aea= 1 (do? d7)/4 (rigorous)
(Ga +0) 2_ (based on average Diameter.)
dat (based on outer Diameter.)
‘Some examples of cause of axial load are as
4. The metal cross- section at the base of the column is under the weight of the column section
above it including the weight of other column accessories such as insulation, trays, ladders etc.
2, Sometimes the pipe is intentionally cut a litle short than the end- to- end length required. It is
than connected fo the nozzle by forcibly stretching it. The pipe as assembied is under axial
fension. When the hot fluids starts moving through the pipe, the plpe expands and the
‘compressive stresses are generated, The cold tensile stresses are thus nullified.
B, Internal / External pressure Load:-
A pipe used for transporting fluid is subjected to the intemal pressure load. This internal or
external pressure induces siresses in the axial as well circumferential (Hoope’s) directions. The
pressure also induces stresses in the radial direction but is offen neglected.
‘Axial Stress.
‘The internal pressure exerts an axial force equal (o pressure times the internal cross-section of
pipe as-
Fein ds)
' then induces axial stress calculated as:
lating metal cross-section as well as pipe cross-section )
‘Approved by KENGAM VL Revo
: = = Page 38 of 6
‘Hoope’s or Circumferential Stress
“The internal pressure also induces stresses in the circumferential direction as shown in figure.
Hope's Stross Due to internal Pressure.
‘The stresses are maximum for grains situated at the inner radius and minimum for those situated
althe outer radius. The Hope's sIress at any point in between radial poston (0 is given as-
Syate= PEP+ Rr?) ———— (Lame's equation)
From membrane theory, Sy is calculated as
Su=Pdl2t or Pal Zt
‘Badial Stress,
For thin walled pipes, the radial siress variation can be neglected.
Radial stresses are dso induced due to intemal pressure as shown in figure.
Radial Stresses Due to Internal Pressure.
At the outer skin, the radial stress is compressive and equal to the atmospheric pressure (Pyrx) oF
‘extemal pressure (Pex) on the pipe. At the Inner radius, it is also compressive but equal to
‘absolute fluid pressure (Py.). In between it varies. But itis often neglected.
C. Bending Loat
Pipe bending is caused mainly due to two reasons:
A. Uniform weight load
B. Concentrated weight load.
‘Mini THAKURY Checked bySANJAY SINGH! Approved by KENGAM VL. Rev
vat)
14, What i the relation between Milliamperage (source strength) and film distance?
Answer:
‘The Milliamperage (M) is directly proportional to the square of the focus to film distance (D). The
‘equation is expressed as: -
M.D?
Me DP
+ Where, Mi and M2 are the Milliamperage.
Di and D2 are the distance from focus to film,
12, Whats the relation between exposure time & film distance?
Answer:
‘The exposure time (T) is directly proportional to the square of the focus {o film distances (D)..
‘The equation is expressed as :
Th -_p?
Te De
43. Whatis the rolation between Source strength & exposure time?
Answer: -
‘The Milliamperage (M) is inversely proportional to the time of exposure (7). The equation is
expressedas: -
M12 or MiTh -M2T2
Mz Tt
«+ Where, Mi and M2 are the Milliamperage.
Trand T2are the time of exposure,
Note: The above relation is also called Reciprocity law and is true for direct X-ray or gamma ray with
lead screen exposure. The above relation is not quit accurate for exposure to light
14, How the source strength of radiographic isotopes expressed?
Answar: -
‘The source strength of radiographic isotopes expressed in terms of Curie.
15, What do you mean by exposure?
Answer: -
itis defined as the quantity of X or gamma radiation that produces in alr, ions carrying 1 coulomb (C)
‘of charge ( of either sign) per Kg of air, The unit of exposure is C/K.
1
‘What do you mean by Roentgen?
Answer: -
Roentgen is the old unit for exposure. It is defined as the amount of X or gamma radiation which
liberates te s u of charge of elther sign in 1 C. C of air at ST P.
AR = 1esu/CCofairat STP.
= 2.68 X 10" C/Kg air.
‘created by MIMIR THAKUR/ Checked bySANJAY SINGH! Approved by KENGAM VL Revo
Sn ee AS
Page 23 of 8
47. What is Dose equivalent?
Answer: -
Dose Equivalent = Quality factor X absorbed dase.
Quality factor generally considered as:
AO1 forX.yorB.
B. 3 for Thermal neutrons.
C. 20 for a- particles.
The unit of dase equivalent is Sievert (SV).
Formerly, the unit of dose equivalent was 1 rem.
1 Sievert = 100rem ( Roentgen).
18, What is the function of radiographic screens?
Answer: -
Itintensifies the radiographic Images on the film,
19. Whatare the types of radiographic screens generally used?
Answer: -
‘Types of radiographic screens generally used are:
‘A. Lead screen.
B. Fluorescent screen or salt screens.
20. What are the types of Lead screens?
Answer: -
‘Types of Lead screens are:
A. Lead foll screen.
B. Lead oxide screen,
21, What do you mean by intensification factor (IF)?
Answer: -
Exposure time required to produce required film density without screen.
Intensification factor = —— <<<
Exposure lime for same density using screen.
{In the above definition it is assumed that same film and radiation source used for the both the
exposure,
22, Whatare the factors upon which the intensification factor depends?
‘Answer: -
Intensification factor due to metallic screens depends on the following: -
A. Metal of foil.
B. Thickness of fil
C. Energy of radiation.
1D. Specimen thickness.
23. How the intensification factor depends on metal of foil?
Answer: -
For a given radiation source, the number of electrons produced depends on the nature of the metal
foil, Intensification factor increases with atomic number of the metal. For gamma ray radiography
‘generally Lead screen are used.
‘Created by MIMIR THAKUR/ Checked bySANJAY SINGH! Approved by KENGAM VL Rove
aot 63
24. How the intensification factor depends on thickness of fol?
Answer: -
‘The intensification factor increases with the increase in the thickness of the foil. Intensification
increases maximum corresponding {o the range of photoelectron in that metal. After further increase it
temains practically constant. I the thickness further increased, grealer number of gamma photons will
be attenuated and this will reduce the produce of photosiectrons.
25. How the intensification factor depends on energy of radiation?
nergy of radiation, more is the intensifying action.
26. How the intensification factor depends on thickness of the specimen?
Answer: -
‘4 specimen placed in between the source and film performs following two functions: -
‘A. Iiters the primary radiation.
1B. Gives low energy scattered radiation.
‘The radiographic screen can have different sensitivities for primary radiation and the radiation given
by the above two effects. Hence the change in intensification factor with object thickness is expected.
‘The intensification of low energy scattered radiation is more than the intensification of high energy
filtered radiation.
27. Where the fluorescent screen finds its use?
Anower: -
‘The fluorescent screens are widely used for medical purpose to reduce the exposure time.
28. What are the main constituents of a radiographic film?
Answer: =
‘The radiographic films consist ofthe folowing: -
A. Base material
B. Subbing layer.
C. Emulsion and
D. Protective layer! Super coat.
29, Whatiis the differont base material tried so far for radiographic film?
Anawer: -
‘The materials so far tried for base is:
A. Glass.
B. Cellulose Nitrate.
C. Cellulose Acetate.
D. Cellulose Triacetale.
E. Polyester ( Most suilable material to be used as base material).
30. What is the function of Subbing material, Emulsion & protective layer in radiographic film?
Answer: -
‘Subbing material Itprovides the sticky action to the emulsion, as the emulsion does not
‘adhere directly on the base material.
Emulsion contains silver bromide gelatin ( Generally animal bone marrow)
Protective Layer It is coated on emulsion in order to protect the same from physical
‘damage, abrasion and stress mark.
‘Created by MIMIR THAKUR/ Checked bySANJAY SINGH! Approved by KENGAM VL Revo
Page 25 0f63
31. How the Radiographic films are classified?
Answer:
‘The Radiographic films are classified as:
A. Class~| :~Highest contrast, Lowest speed.
B. Class—Il_ :-High contrast, Low speed.
C. Class—Ill_ :-Medium contrast, Medium speed.
1D. Class—IV :-Low contrast, High speed.
32, Whatis the basis of classification of radiographic film?
Answer:
Classification of Radiographic film is done on the basis of grain size of Silver Bromide (Silver Bromide
Crystals). Finer the grain size of Silver Bromide in emulsion, slower will be the speed. Generally used
crystal size is 0.22, 0.52, 0.68, 0.80 and 1 micron.
33. What is speed with reference to Radiography film?
Answer: -
it can be defined as the density records on the film resulting {rom a given exposure. It is inverse of
exposure required to produce on radiograph of particular density under the specified conditions. A
exposure to achieve particular density is called fast flm and more exposure called
58 ~ IIltype ( 05,07 ~ Agfa make) film is generally used for radiography.
36. What type of film Is not used for industrial purpose (Used for Medical purpose]?
Class ~ IV type ( 010 — Agfa make) film is not used for industrial purpose.
36. What do you mean by film processing?
Answer: -
‘When the film is exposed to the radiation, creates latent image or invisible image by converting the
silver bromide present in the emulsion into metallic silver. The exposed film when processed converts
latent image into visible image.
37. Whatare the main steps in film processing?
Answer:
Main steps in film processing are: -
A. Developing
B. Stop bath,
C. Fixture,
D. Washing
E Drying
38. What aro the ingredients of Developer?
Answer: -
A. Developing Agent ‘Metol, Hydroquinone and Pencilone.
B. Accelerator Sodium carbonate.
CC. Restrainer Potassium Bromate.
©. Preservative Sodium Sulphate.
‘Created by MIHIR THAKUR/ Checked bySANJAY SINGH! Approved by KENGAM VL revo
Page 26 of 62
38. Whatis the function of Accelerator present in Developer?
Answer: -
itencourages the developer to supply more electrons.
40. What is the function of Restrainer present in Developer?
Answer: -
Il opposes to reduce the unexposed silver bromide. It acts as antifogging agent.
What is the function of Preservative present in Developer?
Itprevents oxidation.
42. What Is the affect of temperature on Developer?
Answer: -
‘The Developer supplies more electrons at high temperature and reduces the developing time,
‘Opposite is the case when the temperature is lower.
43, What is the ideal developing temperature?
‘Answer:
Below 18°C and above 24°C, developing is not recommended.
44, Whatiis the developing time generally recommended?
Answer: -
5 lo 8 minutes. Larger developing time increases the fog density. The developing time below 3
minutes is not recommended as the required density shail not be achieved and may miss minor
discontinuities.
45. What is the ingredient of Stop Bath?
Answer: -
2% Acetic Acid.
48. What is the function of Stop Bath?
Answer: -
‘Stops the Developing action by neutralising the alkaline developer.
47. What are the ingredients of Fixer?
Answer: =
Fixing Agent A, Sodium thiosulphate commonly known as Hypo. Commonly used fixing agent.
B, Ammonium thiosulphate. Used as rapid fixing agent.
48. Whatis the function of Fixer?
Answer: -
itremoves all unexposed siver grains and clouded film starts to become clear.
49. Whatis the recommended time for Fixer?
Answer: «
General recommendation Is 5 to 15 minutes.
60. What is Radiographic sensitivity?
Answer: -
It is the combination of Radiographic contrast and Radiographic definition. The Radiographic
sensitivity is judged by Image qualily Indicator (IQl), also known as penetrametre. Judging the
{qualitative & quantitative quality of radiograph, a penetrametre is required. The image of IAI on the
radiograph is the evidence thal the radiographic inspection was conducted under proper condition
and achieved the required sensitivity.
wire diameter.
x 100
‘Thickness of the job.
‘Created by MIKIR THAKURY Checked bySANJAY SINGH! Approved by KENGAM VL. ovo
Page 27 of 63
51, Whatis the general requirement of Radiographic Sensitivity?
Answer: =
‘General requirement of Radiographic sensitivity are: -
> 2% (Less then two percent) ~ Good.
<< 2% (More ten two percent) ~ Not acceptable.
52. Whatare the commonly used IQ?
Answer: -
‘Commonly used 101 are: -
A. Wire type Penetrametre.
B. Plate type Penetrametre.
©. Step type Penetrametre.
D. Step- Hole type Penetrametre.
53. What are the eriteria for selection of 10i or Penetrametre?
Answer:
Penetrametre should be made of same material as that of the specimen.
‘The selection of !Q! should be made as:
A. For carbon Steel & Low Alloy Steel :~ Carbon Stee! IQ.
B. For High Alloy Steel & Stainless Steel :- Stainless Steel IOI.
C. For Aluminum & Aluminum Alloy ‘Aluminum 11,
. Copper & copper Alloy ‘Copper IA,
54, Name some IQ?
Answer: -
‘Wire types IQ! :- 1480-7, 6180-12,10-IS0-46
55, What do you mean by Radiographic contrast?
Answer: =
Density difference between the two adjacent areas of the radiograph is known as contrast
Radiographic contrast Is the combined effect of the following
A. Subject contrast.
‘8. Film contrast
56. Whatis subject contrast?
Answer: -
"The factor of the specimen, which affects the contrast, is known as subject contrast.
57, Whatis film contrast?
Answer: -
"The factor ofthe fim, which affects the contrast, is known as Film contrast.
58. What are the factors, which affects subject contrast?
Answer: -
‘Subject contrast affected by:~
A. Thickness difference in the specimen.
Uniform thickness of the specimen shows no contrast but thickness difference in the specimen
‘sows good contrast.
8. Badiation Quality.
Best contrast is achieved by ray of suitable low kilovoltage (Soft Radiation). By increasing the
kilovollage (Harder Radiation) penetration will increase but decrease the subject contrast.
‘Scattered Radiation.
By reducing the scattered radiation (internal, side and back scatters) using diaphragm, masks,
Filers, and lead screens increase the subject contrast.
c.
‘created by MIKIR THAKURY Checked bySANJAY SINGH! Approved by KENGAM VL. Revo
“he
Page 28 of 3
58. Whatare the factors, which affects the film contrast?
Answer: -
Film contrast affected by: -
A Type.of fim
Grain size of the film controls the film contrast. Finer the grains (lower speed ) of the film higher
the film contrast,
8. Film processing.
Inereasing the developing time increases the density as well as fog density and decreases the film
‘contrast. Processing of film in fresh developer gives higher contrast then the exhausted developer.
. EilmDansity.
‘At higher film density, the film contrasts is more and at low density the flm contrast is les
60. _ Where the IQ! (Ponetrametre) is placed?
Answer:
‘The IO! or penetrametre should be placed as possible on the source side of the radiation. When it's
not possible as in case of double wall single image radiography, it can be placed on the film side with
2 lead letler "F near the QI. The IQ should be placed in most unfavourable location with respect to
the radiation beam.
61. What are the different types of Radiography or Exposure technique?
Answer: -
Different types of Radiography techniques are: ~
‘A, Single wall single image (Panoramic Exposure).
B. Double wall single image.
C. Double wall double image.
‘Question related to Equioment and piping Layout:
4. Whatare the steps involve in Plant design?
Answer: -
‘The mechanical design and development of the plant has three major steps.
A. Conceptual layaut design.
B. Equipment layout design.
. Piping layout design.
2. What Is conceptual layout design?
itis the part of basic engineering package. It consists of following information: -
‘A. Essential process design requirement such as horizontal & vertical relationship of equipment.
BB. Space allocation for basic plant requirement (space required for laboratories, office, storage etc.)
CC. Planning for control room, motor control center room etc.
3. What is Equipment layout design?
‘Answer: -
itis the detailing of conceptual layout. It is the basic document of mechanical engineering design or in
‘other words this document is the basis for development of construction drawing by all disciplines. tis
‘sometimes also referred as plot plan for large outdoor plant.
{t consists of following information:
‘A. Floor space needed for the equipment and other facilities are shown.
B. Access, removal space, cleaning area, storage space and handling facilities are outlined.
4, What are the essential dataf documents required for preparation of equipment layout?
Answer: -
"The essential data or documents required for preparation of equipment layout is as: -
A. Process flow diagrams (PFO) and Piping & instrument Diagrams (P& ID).
PFD! P& ID indicates the interconnectivity of each equipment, information regarding solid
handing, gravity feed, line slopes, loop sizes, venting requirement, special piping materials ele.
which in turns governs the equipment location to a great extent.
Ccreaied by MIMIR THAKUR! Checked bySANJAY SINGH/ Approved by KENGAM VL. Rove
Page 28 of 63
B. Project design data.
‘This consists of following information as: ~
“Geographic location, proximily to roads and railway, topography and lecal codes and regulations,
weather conditions ‘such as rainfall records, seasonal temperature differences, wind direction,
‘outlet points for drains etc.
4 The above information such as wind direction influences the location of cooling towers, furnaces,
stacks etc. Similarly, the information regarding outlet drain points affects the design of storm water
rains and requirements of enclosures.
C. Equipment sizes and Building.
This includes fabricated equipment such as vessels, Heat Exchangers, Reactors, Tanks and
proprietary equipment like pumps, Compressors, Furnaces etc. Far locating the above, the
Equipment is grouped fo have optimum location for minimum pipe run as well as fallow the process
flow sequence.
5. What are the two basie configurations for the equipment layout (unit plot plan)?
Answer: -
“The equipment layout can basically be divided into two configurations:
|A. The Grade Mounted Horizontal arrangement as seen in the refineries and petrochemical plants.
B. The vertical Arrangement as seen in many chemical process industries.
6. What is Grade mounted Horizontal Arrangement of equipment layout?
Answer: =
in the Grade mounted Horizontal Arrangement, the equipment is placed on the either side of the
Central pipe rack wilh auxiliary roads. Advantage of this arrangement is that the equipment is located
at grade level, which makes it easier to construct, operate and maintain. Disadvantage is that i takes
lot of ground area,
I arrangement of equipment layout?
-
“The structure mounted vertical arrangement has equipment located at multilevel in steel or concrete
structure. This could be indoor or outdoor. Advantage is of small coverage area and ability to house
the facility to sull process requirement or climate conditions.
8. Whatare the basic principles of locating the Equipment irrespect of the type of arrangement?
Answer: -
‘The certain basic principles to be followed while locating the equipment is 2s:
A. Economic piping:
fh calor to minimize the cost of piping, the equipment should be located in process sequence and
‘close enough to suit safety needs, access requirements and flexibility. The equipments are identified
which forms the subsystem within the unit. The component within the subsystem to be arranged to
have most economical piping and the whole subsystem to be arranged within the unit to have most
‘economic interconnection.
B. Process Requiremer
‘The equipment layout should support requirement like minimum pressure drop, gravity feed and loop.
¢. Common operati
‘The equipment that requires common maintenance facilities, common utility and continuos operator
attention shall be located the same area
D. Underground Facilities:
Before deciding the equipment location, the facilities such as storm water drain, effluent drain, fre
water, cooling water to be placed underground.
9, Whatiis Line Routing Diagram?
Answer: -
‘A tine routing diagram is a schematic representation of all process and uliliy-piping system drawn on
'2 copy of plot plan. This diagram does nol show the exact locations, elevations or interference but it
locales the most congested area.
‘Grnated by MIHIR THAKUR/ Checked bySANJAY SINGH! Approved by KENGAM Vi. Revo
Page 20 0f 62
40. How do you ealculate the width of Pipe rack?
Answar
We(IXnXx s)+A+B.
Where, f Safety Factor
5 if pipes are counted from PFD.
2 if pipes are counted from P&ID.
rn: number of lines in the densest area up to size 450NB.
= 300 mm (Estimated average spacing)
25 mm (if lines are smaller than 250 NB)
+ Additional Width for:
‘Lines larger than 450 NB.
: For instrument cable tray / duct,
For Electrical cable tray.
's 300 mm (estimated average spacing)
225 mm (iffines are smaller than 250 NB)
+ future provision
= 20% of (FX NX 8) +A
41. Up to what limit the width of pipe Rack is restricted? What type of arrangement shall be done
If the width of rack calculated is more then the restricted limited?
Answer: -
‘Normally pipe Rack width is limited to 6.00 Mirs. If the width of rack caleulated Is more then the
‘arrangement shall be done in multiple layers. The arrangements adopted are: -
‘A, Single column Rack T" type.
B. Double column Rack with a single tir.
. Double column Rack with a double tie.
42. How much space is kept in between column of pipe rack?
Answer: -
‘Normally, 5 to 6 Mirs. spacing is kept in between the column of pipe rack
43, At which location the wide spacing (epacing more than the normal) in between the column Is
necessary?
Answer: -
Wide spacing is necessary at road crossing or where loading or access space is needed.
144, How much Headroom clearance is required under the following type of crossing?
A. Structures! pipe lines inside operating aroa.
B. From top of the Rail.
C. Above crest of road for crane movement.
D. Above crest of road for Truck movement.
E. Above crest of road between process units.
‘A. Structures/ pipe lines inside operating area. : 2200
B. From top of the Rail. 7000
C. Above crest of road for crane movement. : 7000
1D. Above crest of road for Truck movement. 6000
E. Above crest of road between process units. = 4500
45. What sort of drawing! layout is required for piping layout?
Answer:
‘The following Drawing Layout are required for piping layout.
A. Piping & instrumentation Diagram (P8 10).
B. Equipment Layout.
. Piping Specification,
. Equipment Drawing
E. Vendor Requirement for proprietary equipment.
‘Created by MIMIR THAKUR/ Checked bySANJAY SINGH! Approved by KENGAM VL Revo
Page 34 of 63
16. What care shall be takon while routing piping for instruments?
Answer: -
Following points shall be taken care of while routing piping for instruments.
‘A. Flow measuring instrument needs certain straight length on upstream & downstream of the
instruments. Normally, 15D on the upstream and 5D on the downstream is kept.
BB. The pipe line in which flow meters such as magnetic flow meters, vortex meters, turbinemeters etc
are located shal be routed in such a way that the line must be filed with liquid all the time. The
pipe line shall be supported with robust support on both side of the meter.
. Conttol valves are located at grade e.g. al about 500mm height from finished ground to provide
convenient access for operation and maintenance. Block and bypass valve shall be located to
have easy operation! access from the grade. Locating control valve on the vertical line shall be
avoided.
D, Isolation valves for level gauges and pressul
secondary indicators of pressure, temperatur
operating area.
E. Rotameter shail be placed on vertical line and the inlet shall be from the bottom of the instrument.
‘gauges shall be made accessible. All primary and
flow, level, positioners etc shall be visible from the
Question Related to Mechanical Design Fundamentals:-
4. What are the Failures with reference to the structural design?
Answer:
Failure of a structural part can occur by:
A. Excessive elastic deformation.
B. Excessive non-elastic deformation.
. Fracture.
‘Any design has to guard against these perceived failures.
2. What are the factors upon which the mechanical properties of material are dependent?
Answers
‘Mechanical properties of any material of construction are dependent on
‘A. Chemical composition of the material.
BB. Method by which the material is manufactured.
3. What Is stress?
Answer:
it is defined as the applied load per unil cross-section of the specimen. The common unit are psi
{pound per square inch), kpa, Mpa, kg/cm?
3. Whatis strain?
Answer:-
For tensile load, itis the ratio of increase in length of the specimen under constant sustained load to
the original length of the specimen before the load is applied. For compressive load, it the ratio of
decrease in length to the original length under sustained load. Strain is thus an observable and
measurable quantity as the extension or compression of the specimen can be directly measured. It is,
a dimensionless quantity.
4. Draw the Stress-Stain curve showing the Behavior ofthe specimen under stress?
Anewer
/—— vere its points
stress \ ane
‘Created by MIHIR THAKUR/ Checked bySANJAY SINGH! Approved by KENGAM Vi. Rove
Page 32 of 63
When there is no load, there are no stresses and no strain. When a smail tensile load is applied, the
strain can be moasured and stress derived. I the load is removed, the specimen returns to ils original
Shape. That is there is no residual or permanent strain in the specimen. This situation continues Up to
aeeetain level of stress. A stress strain curve in this region is a straight line Le. stress is proportional
{o strain, This region of curve is called the elastic region, as the MOC;s behavior is elastic lke &
rubber,
‘As the tensile load during the test is increased further, a situation arises when the specimen does not
‘ature to the original dimension even when the load is withdrawn, This is also the level or siress level
ca inich the stress strain curve begins to deviate from the elastic straight line behavior as shown in
the graph. Thus, the metal / specimen are undergoing plastic deformation in addition to elastic
Getormation. When the load is withdrawn, the elastic deformation is recovered but the plastic
deformation stays.
5. What is upper yield point with referonce to above stress-strain Graph (Ultimate Tensite
Strength)?
Answer:
“The highest stress that the metal can withstand under sustained load without continuing (0 elongate
under same load is called the upper yield point.
6. _ What is lower yield point with reference to above stress-strain Graph?
Answer:
7. What 18 the effect on the specimen when subjected to a sustained load with higher
tomporatures?
Answer:-
‘is the temperature ofthe test increases, specimen of the same material would elongate more forthe
‘Same load as compared to specimen tested at lower temperature. It means that the material becomes
Softer as itis subjected to higher and higher temperatures.
Strose-atrain curves are different for different materials and at different temperatures for the
‘same materials,
Stress
Increasing Temperature
Strain
‘stress-strain curves at iffrant Temperatures
8. Whatis Allowable Stress?
Answer:
It is defined as ulimate tensile strength divided by factor of safety. The safety factor ts obviously
(reater then 1. Design which ensure that the stress value anywhere inthe structure is less than this
Gilowable stress are considered safe as they do net allow the structure element to come anywhere
Glove to the point where plastic instablily leading fo disruption r disintegration of element would set
‘created by MIMIR THAKUR/ Checked bySANJAY SINGH! Approved by KENGAM VL Revo
@. What is the value of allowable stress if yield stress or 0.2% proof stress value is avaliable at
design temperature?
Answer:
tthe yield stress or 0.2% proof stress value is availabe at design lemperature, the same shall Be
divided by a safely factor of 1.5 to get allowable sires.
to. Tree ie Value of allowable atross ifthe yield stress is not available at design temperature
but is available at room temperature?
Answer:=
the yield stress © nol avaiable at design temperature but is availabe at room temperature, the
‘same shall be divided by safely factor of 3.0 to get allowable stress.
11. What is the value of allowable stress Ifthe stress value for rupture due to static fatigue oF
creep failure Is available at design temperature?
Answer
F tne strese volue for rupture due to static fatigue or creep failure is available at design temperature,
the same shall be divided by salely factor of 1.5 to get allowable stress.
Noto: The safety factor consldered above I recommended fr carbon stel and low alloy see
42, How much design temperature shall be considered for the structural parts which are heated
bby steam, thermic fluid ete?
Answer
esign temperature shall be the highest expected temperature of the healing media or highest
expected body part temperature plus 10° C. Here, 10° Cis the safety margin.
42. What shall be the safety margin (temperature related) considered for fired vessel ports which
are shielded (by Refractory) and the parts which are unshielded?
Answel
‘Safety margin for shielded parts 2 20°C,
Safely margin for unshielded parts 50°C.
Noe: The auove safety marge ae Jost guidelines, What ould be the safely maria would depends upon ihe
‘severity of operation
44, Define Proof Stress?
Answer:
Fog alo called 0.2% proof stress. It is the siress for 0.2% strain. In simpler terms, itis the siross
‘value for siram value of 0.002 on the stress strain curve.
45, How the proof stress in a material is altered (increased marginally)?
Answer:- .
Stres
= Strain
Increase in proof stress due to cold work.
concider @ stress stra curve 2s shown above. Let a fresh specimen be subjected lo gradoty
Consign tensile loads, A 0.2% proof siress can be marked on the curve 25 the stese value
reas ng io pont C on the culve. Let the load be increased beyond this point up fe Point Don
created by MIMIR THAKUR/ Checked bySANJAY SINGH/ Approved by KENGAM VL- Revo
Page 34 0f63
the curve. The specimen has surely passed the elastic range and crossed over (o plastic deformation,
(On withdrawal of the load, the specimen would relum back to point E with a residual permanent strain
as shown above. Tensile load test can now be conducted on this specimen which has seen plastic
deformation or cold work previously. The specimen would now follow a stress- strain curve with strain
zero at point E. Along this stress strain curve (EGF), 0.2% proof sttess corresponds to point G which
is higher than th proo stress forthe fresh specimen,
The material in the above case seems to have hardened with its experience of stress earlier,
Most material shows this marginal increase in their proof stress due to cold work.
46. Whatare the types of failures encountered in Piping?
Answer:
41. Catastrophic Failure. 2, Fatigue Failure,
417. _ Define catastrophic failure?
Anewer:-
The failures which occurs suddenly as soon as the load crosses the threshold (Ultimate tensile
strength). These failures take place on the first occurrence of the loads in excess of yield stress.
18. Whats fatigue failure?
Answer:
The failure which occurs due to damaging of the grain structure of the specimen subjected to
Prolonged application of sustained load and or tensile ~compressive load cycle.
18. Whatare the types of Fatigue failure?
Anewar
Types of fatigue failure are:~
A. Static Fatigue,
B. Cyclic Fatigue.
19. Whatis Static Fatigue?
Answer:
‘The specimen which fails under sustained load subjected to considerable length of time. The total
time for which the load was applied is important. Whether itis applied continuously or in installments
{is not important,
20. What is cyclic fatigue?
Answer:
‘The specimen which fails under a load cycle subjected lo considerable numbers of times. The total
‘numbers of cycles for which the load was applied is important. Whether the cycle was frequent or
infrequent is not important
21. Explain the failure of the specimen subjected to cyclic load?
Answer:-
Consider 2 specimen subjected to a tensile load increasing from zero to X and then this load is
gradually withdrawn til it is zero. Now compressive load applied gradually tl itis X and then it is
Grav til the load is zero. This comprises a cycle and is repeated again and again. With each cycle,
the grains in the material get displaced relative to each other and get more and more interlocked.
With each cycle, the material loses its ductity in small increments. A lime comes when the grains are
80 badly interlocked that they cannot allow deformation to withstand load and a small crack develops,
This crack grows with further cycles and failure occurs.
22, Whatis creep failure?
Answer:
Occurrence of static fatigue failure when the material is under prolonged sustained load coupled with
high temperature is called creep failure.
188 at fallures for solid rod, sphore and cylinders?
23. Write the sequence of stress
Answer:-
Atypical sequence of stress values at failure for solid rods and two most important shapes in process
industry namely, sphere and cylinder is Rod > Sphere > Cylinder.
‘Croated by MIHIR THAKURY Checked bySANJAY SINGH! Approved by KENGAM VL, Revo
You might also like
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- 04 - Product Traceability Procedure - Asf-Qc-Ptp-001Document5 pages04 - Product Traceability Procedure - Asf-Qc-Ptp-001Sherif Yehia0% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- (Iso/tr 17671-5) (Iso/tr 17671-6) (Iso/tr 17671-7) (Iso/tr 17671-8)Document1 page(Iso/tr 17671-5) (Iso/tr 17671-6) (Iso/tr 17671-7) (Iso/tr 17671-8)Ivan Briscoe100% (7)
- 02 - Calibration Procedure - Asf-Qc-Cal-001Document7 pages02 - Calibration Procedure - Asf-Qc-Cal-001Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- FPC AsfDocument24 pagesFPC AsfSherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- 02 - Calibration Procedure - Asf-Qc-Cal-001Document7 pages02 - Calibration Procedure - Asf-Qc-Cal-001Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (843)
- Punching Validation-FACTORY 1Document3 pagesPunching Validation-FACTORY 1Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- NCR RegistryDocument5 pagesNCR RegistrySherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledSherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1577218623250Document1 pageOrca Share Media1577218623250Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- 00 - 7563 SigmaTherm 450Document2 pages00 - 7563 SigmaTherm 450Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Asf-Qc-Itp-002Document4 pages01 - Asf-Qc-Itp-002Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- Iso 4624 2002 en FR PDFDocument6 pagesIso 4624 2002 en FR PDFSherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- 04 - Material Receiving Inspection Procedure - Asf-Qc-Mri-001Document8 pages04 - Material Receiving Inspection Procedure - Asf-Qc-Mri-001Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- 04 - Material Receiving Inspection Procedure - Asf-Qc-Mri-001Document8 pages04 - Material Receiving Inspection Procedure - Asf-Qc-Mri-001Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- BS en ISO 5817 2014 Acceptance For NDTDocument38 pagesBS en ISO 5817 2014 Acceptance For NDTSherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- ISO 2553 - Welding Symbols PDFDocument54 pagesISO 2553 - Welding Symbols PDFSherif YehiaNo ratings yet