Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jalon China Molecular Sieves How-To-Choose-Molecular-Sieve
Uploaded by
Bhushan PatilOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jalon China Molecular Sieves How-To-Choose-Molecular-Sieve
Uploaded by
Bhushan PatilCopyright:
Available Formats
How to Choose Oxygen Molecular Sieve for Small Oxygen Concentrator
At present, there are two main types of molecular sieves used by oxygen concentrator in market, sodium type and
lithium type molecular sieve. The lithium type molecular sieves are more efficient than sodium type molecular
sieves that can greatly reduce the volume of oxygen generators that makes the oxygen concentrator smaller and
easier to carry around. Since the lithium molecular sieve is much more expensive than sodium type, sodium
oxygen molecular sieve is also very popular in market for most cases.
Among our products, JLOX-501A is sodium type molecular sieve and JLOX-101A is lithium molecular sieve. The
comparison of the application parameters of sodium molecular sieve and lithium molecular sieve is as follows:
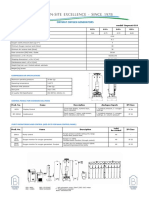
Parameters JLOX-101A JLOX-501A
Applicable Machines 1-20 L/min 1-5L/min
Oxygen Concentration 93±3% 93±3%
Air/Oxygen Ratio 10-14 10-14
Adsorption Cycle < 12 s < 12 s
Adsorption Pressure 1.0-2.0 bar 1.4-2.0 bar
Molecular sieve JLOX-101A and JLOX-501A adsorbents are patented products specially designed for use in
medical oxygen concentrators that employ a pressure swing cycle to generate high purity oxygen. JLOX-501A is
recommended to use in portable oxygen concentrators of 1-5/L min and JLOX-101A is recommended to use in
potable oxygen concentrator that required of with smaller size, JLOX-101A has the N2/O2 selectivity around 2
times higher and 2.75 times higher of static N2 adsorption capacity than JLOX-1501A. Both JLOX-101A and
JLOX-501A has a high nitrogen capacity and superior nitrogen/oxygen selectivity compared to equivalent
products in market that results in the use of significantly less material relative to other molecular sieve adsorbents
without sacrificing oxygen through put or purity.
Oxygen Flow Rate Loading Weight (g)
JLOX-101A 3L 500-600
5L 900-1200
10 L 2200-2400
3L 1600-1800
JLOX-501A 5L 2000-2400
10 L 5000-5500
Storage and Handling
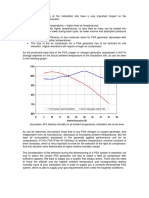
Both JLOX-101A and JLOX-501A will preferentially adsorb water over all other airborne molecules. To ensure
maximum nitrogen capacity, moisture pick-up from air exposure should be minimized. Adsorbed water can not be
readily removed via pressure or vacuum swing purging.
You might also like
- How Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisFrom EverandHow Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Jalon - Luoyang Jianlong Molecular Sieve TDS-MS-JLOX-100-SeriesDocument1 pageJalon - Luoyang Jianlong Molecular Sieve TDS-MS-JLOX-100-SeriesBhushan PatilNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionFrom EverandIon Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ozone Generators and Water Purification-2017 - PDF RoomDocument5 pagesOzone Generators and Water Purification-2017 - PDF RoomamacmanNo ratings yet
- NEW - IONPRO - VWS BRASIL (Modo de Compatibilidade)Document19 pagesNEW - IONPRO - VWS BRASIL (Modo de Compatibilidade)Alon CarlosNo ratings yet
- Water Quality GuidelineDocument2 pagesWater Quality GuidelinetehtehtehNo ratings yet
- Drinking Water Treatment138 28742Document7 pagesDrinking Water Treatment138 28742vaglohrdNo ratings yet
- Design Advantages For SWRO Using Advanced Membrane TechnologyDocument12 pagesDesign Advantages For SWRO Using Advanced Membrane TechnologyJestin RajNo ratings yet
- Jalon - Luoyang Jianlong Molecular SieveTDS-JLOX500Document1 pageJalon - Luoyang Jianlong Molecular SieveTDS-JLOX500Bhushan PatilNo ratings yet
- How Oxygen and Acids in Uence The Aging of TransformersDocument12 pagesHow Oxygen and Acids in Uence The Aging of TransformersRajesh MadapatiNo ratings yet
- About Reverse Osmosis What Is Reverse OsmosisDocument4 pagesAbout Reverse Osmosis What Is Reverse OsmosismateenNo ratings yet
- Axens AdsorbentsDocument19 pagesAxens AdsorbentsfloretotesoroNo ratings yet
- Indion 850 Resin Engg Data SheetDocument6 pagesIndion 850 Resin Engg Data SheetsoumitrabanNo ratings yet
- FILMTEC Membranes Nanofiltration Produces Sparkling Clean Water For Swedish Resort CommunityDocument3 pagesFILMTEC Membranes Nanofiltration Produces Sparkling Clean Water For Swedish Resort Communityvinay1999No ratings yet
- Anion Resin Spec SheetDocument12 pagesAnion Resin Spec SheetarufatoNo ratings yet
- gdwq4 With Add1 Annex5Document19 pagesgdwq4 With Add1 Annex5Keile Brugés PinedaNo ratings yet
- Technical Service Data Sheet for ECT Luminous 333 Nickel ProcessDocument8 pagesTechnical Service Data Sheet for ECT Luminous 333 Nickel ProcessKodagnanaso kodag100% (1)
- Best Home Oxygen Concentrators-Lowest Prices & Fast Shipping (Oxygen Machines) - 2021 - YuwellDocument1 pageBest Home Oxygen Concentrators-Lowest Prices & Fast Shipping (Oxygen Machines) - 2021 - YuwellPelayanan ResusitasiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Assignment 1: Aeration and Ion Exchange ExperimentsDocument23 pagesLab Report Assignment 1: Aeration and Ion Exchange ExperimentsAli Raza MeharNo ratings yet
- Treating Water: Methods for Disinfection and FiltrationDocument19 pagesTreating Water: Methods for Disinfection and FiltrationMichael Huisa TaipeNo ratings yet
- PSA Oxygen Cone ManufacturerDocument2 pagesPSA Oxygen Cone ManufacturerddadaraNo ratings yet
- Aeration SystemsDocument12 pagesAeration SystemsSaikat MajiNo ratings yet
- Brochure-Chlorine Di-Oxide Generation and Dosing SystemDocument4 pagesBrochure-Chlorine Di-Oxide Generation and Dosing SystemsamirNo ratings yet
- Importance of Water Treatment ProcessesDocument18 pagesImportance of Water Treatment ProcessesHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment ProcessesDocument9 pagesWater Treatment ProcessesMildred GwasiraNo ratings yet
- Arsenic Removal Research IHE Delft TMT Argentina 2018Document61 pagesArsenic Removal Research IHE Delft TMT Argentina 2018Area Tecnica Dpto calidadNo ratings yet
- 160 0004 Ozone NewDocument4 pages160 0004 Ozone NewRafael Lino De SousaNo ratings yet
- FILMTEC Membranes: Tech Manual ExcerptsDocument5 pagesFILMTEC Membranes: Tech Manual ExcerptsgsaviNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Treatment Methodselec3Document4 pagesMiscellaneous Treatment Methodselec3Edgelle Ejercito100% (2)
- A Fundamental Guide To Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Membrane SystemsDocument37 pagesA Fundamental Guide To Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Membrane SystemsJean RechellNo ratings yet
- Molecular SieveDocument4 pagesMolecular SieveAl AkilNo ratings yet
- Improvement of TEG Regeneration in Natural Gas Dehydration Using A Hydrocarbon SolventDocument7 pagesImprovement of TEG Regeneration in Natural Gas Dehydration Using A Hydrocarbon SolventAhmed ShaepNo ratings yet
- RotoCloneLVN Brochure US - 2022Document8 pagesRotoCloneLVN Brochure US - 2022FabianNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report 123 (Reference Copy) 123Document22 pagesSeminar Report 123 (Reference Copy) 123Ajith RajagopalanNo ratings yet
- Purified Water Methods and UsesDocument38 pagesPurified Water Methods and UsesRudi PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Air Seperation LoresDocument1 pageAir Seperation LoresrolwinNo ratings yet
- Nanofiltration Membrane Softening: Reverse OsmosisDocument2 pagesNanofiltration Membrane Softening: Reverse OsmosisHardik KhetaniNo ratings yet
- Rocor NB Liquid 25 LTRDocument3 pagesRocor NB Liquid 25 LTRGregory7778No ratings yet
- System OperationsDocument4 pagesSystem OperationsRicardo Alberto AhrensNo ratings yet
- Role of Condensate Polishing in Power PlantsDocument26 pagesRole of Condensate Polishing in Power PlantsmkgchemNo ratings yet
- Green Solvents For Petroleum and Hydrocarbon IndustriesDocument6 pagesGreen Solvents For Petroleum and Hydrocarbon IndustriesMădălina GrigorescuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Env - Eng. & Science, Sawyer, Mccarty, ParkinDocument22 pagesChemistry For Env - Eng. & Science, Sawyer, Mccarty, ParkinaseptinNo ratings yet
- Molecular Sieves PresentationDocument19 pagesMolecular Sieves PresentationVasant Kumar Varma100% (1)
- Chloride RemovalDocument12 pagesChloride Removaldilshad kapoor100% (1)
- IX News: Water Demineralisation. Ion Exchange and Reverse Osmosis: Competitors or Associates ?Document8 pagesIX News: Water Demineralisation. Ion Exchange and Reverse Osmosis: Competitors or Associates ?nermeen ahmed100% (1)
- Alkali Metal Cations Na, K, Li 7405: NIOSH Manual of Analytical Methods (NMAM), Fifth EditionDocument5 pagesAlkali Metal Cations Na, K, Li 7405: NIOSH Manual of Analytical Methods (NMAM), Fifth EditionLINDA IVON PARRADO SÁNCHEZNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment PlantDocument28 pagesWater Treatment PlantVuthpalachaitanya Krishna0% (1)
- Journal of Semipermeable Membrane andDocument8 pagesJournal of Semipermeable Membrane andMichael Bryan PrajogoNo ratings yet
- Ozone PDFDocument4 pagesOzone PDFShesharam ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Fluxes For Soldering: What Is A Flux?Document11 pagesFluxes For Soldering: What Is A Flux?Tanishq DwivediNo ratings yet
- Demineralization of Water: Dilip Kumar NTPC LTDDocument46 pagesDemineralization of Water: Dilip Kumar NTPC LTDDinesh VermaNo ratings yet
- Simulation Using COCODocument9 pagesSimulation Using COCORj JunsayNo ratings yet
- Oxiperm ISIA: Chlorine Dioxide Production of 0.5 To 20 KG/HDocument2 pagesOxiperm ISIA: Chlorine Dioxide Production of 0.5 To 20 KG/Hprabal rayNo ratings yet
- Design and modeling of ozone gas-liquid reactorsDocument31 pagesDesign and modeling of ozone gas-liquid reactorsNOURANo ratings yet
- Advances in Wastewater Treatment TechnologyDocument41 pagesAdvances in Wastewater Treatment TechnologyPonipolNo ratings yet
- Advances in Wastewater Treatment Technology Using Reverse Osmosis MembranesDocument41 pagesAdvances in Wastewater Treatment Technology Using Reverse Osmosis MembranesDnyaneshwar ManalNo ratings yet
- Kuntia 2012Document10 pagesKuntia 2012maher mzoughiNo ratings yet
- Surface Prep BrochDocument6 pagesSurface Prep BrochYohanes RezaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Sieve Desiccant Dehydrator For Natural Gas: Bettis Model DD (Standard Service) Bettis Model DD-S (Sour Service)Document4 pagesMolecular Sieve Desiccant Dehydrator For Natural Gas: Bettis Model DD (Standard Service) Bettis Model DD-S (Sour Service)Alina SmochinaNo ratings yet
- LB 2006 Bentivoglio 20 Ev PDFDocument8 pagesLB 2006 Bentivoglio 20 Ev PDFRahman ArifNo ratings yet
- Technical Datasheet - OxymatDocument26 pagesTechnical Datasheet - OxymatBhushan PatilNo ratings yet
- Brochure Ms Adsorbents PDFDocument8 pagesBrochure Ms Adsorbents PDFHaggy Prabu MargandhiNo ratings yet
- Jalon - Luoyang Jianlong Molecular SieveTDS-13XDocument1 pageJalon - Luoyang Jianlong Molecular SieveTDS-13XBhushan PatilNo ratings yet
- Jalon - Luoyang Jianlong Molecular SieveTDS-JLOX500Document1 pageJalon - Luoyang Jianlong Molecular SieveTDS-JLOX500Bhushan PatilNo ratings yet
- Impact of Ambient Air On PSA Design and Compressor Size SelectionDocument3 pagesImpact of Ambient Air On PSA Design and Compressor Size SelectionBhushan PatilNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications For Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) Oxygen PlantsDocument5 pagesTechnical Specifications For Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) Oxygen Plantszee khanNo ratings yet
- IWA Publishing - Biological Wastewater Treatment - 2nd Edition - 2020-07-17Document1 pageIWA Publishing - Biological Wastewater Treatment - 2nd Edition - 2020-07-17Bhushan PatilNo ratings yet
- Work Completion Report for Solar InstallationDocument3 pagesWork Completion Report for Solar Installationsingla.nishant1245No ratings yet
- Solar PST Ficha - 200v-250v - ENDocument2 pagesSolar PST Ficha - 200v-250v - ENmihaiNo ratings yet
- Solar IrradiationDocument4 pagesSolar IrradiationL CHNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification - Mangalore Station PipingDocument21 pagesTechnical Specification - Mangalore Station PipingbecpavanNo ratings yet
- Performance Assessment and Mass Energy Balance For Regenerative Type Air HeatersDocument98 pagesPerformance Assessment and Mass Energy Balance For Regenerative Type Air HeatersAnonymous knICaxNo ratings yet
- Marina Square Fire Water TankDocument1 pageMarina Square Fire Water TankMalaka KumaraNo ratings yet
- SUNPOWER Sp-Oasis-Datasheet-Rv2 - 0Document2 pagesSUNPOWER Sp-Oasis-Datasheet-Rv2 - 0ER BEN SAIDNo ratings yet
- DPR-CNG StationsDocument10 pagesDPR-CNG StationsMohsin MansooriNo ratings yet
- Aspirated Sampling SystemsDocument24 pagesAspirated Sampling Systemsstevef2100% (1)
- 9780L12 Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Maintenance and TroubleshootingDocument29 pages9780L12 Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Maintenance and Troubleshootingمعلومة على الماشىNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents (Centrifugal Pumps)Document4 pagesTable of Contents (Centrifugal Pumps)Ton BlokNo ratings yet
- Neraca Massa AmmoniakDocument10 pagesNeraca Massa AmmoniakMuhammad FadilNo ratings yet
- 150 EnglischDocument4 pages150 EnglischGat SolzaimaNo ratings yet
- Weichai Diesel GeneratorDocument2 pagesWeichai Diesel GeneratorIbrahim YunusNo ratings yet
- Pg-Gmaw-Xi TPLDocument30 pagesPg-Gmaw-Xi TPLmjsolihinNo ratings yet
- Workshop On New Cross-Cutting Technologies For Nuclear Power PlantsDocument25 pagesWorkshop On New Cross-Cutting Technologies For Nuclear Power PlantsMuhammadEhtishamSiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Marine Notes - MMD Exams India and Baiscs - MEO Class 4 Oral QuestionsDocument6 pagesMarine Notes - MMD Exams India and Baiscs - MEO Class 4 Oral QuestionsPuloma PramanickNo ratings yet
- Abbtc Bro1180 TPLC PDFDocument8 pagesAbbtc Bro1180 TPLC PDFLahiru Prabhatha Amarasena100% (1)
- Project Intro Internal Combustion EngineDocument4 pagesProject Intro Internal Combustion EngineAmit Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- 2nd Control of BoilerDocument14 pages2nd Control of BoilerMuanifNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Power at HPCL: Electrical Maintenance TechniquesDocument44 pagesMaintaining Power at HPCL: Electrical Maintenance TechniquessjillelamoodiNo ratings yet
- AE 1356 Propulsion Lab ManualDocument22 pagesAE 1356 Propulsion Lab ManualVasthadu Vasu KannahNo ratings yet
- Boiler maintenance typesDocument9 pagesBoiler maintenance typesMd Aamir ImamNo ratings yet
- 31369093Document2 pages31369093mohammed8051No ratings yet
- Mardiansyah Final ProjectDocument5 pagesMardiansyah Final ProjectMardiNo ratings yet
- Internship Report Dakhni Gas ProcessingDocument16 pagesInternship Report Dakhni Gas ProcessingTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Presentation DG SetsDocument52 pagesPresentation DG SetsNageswar Makala100% (5)
- Big M Pumps For Hot Oil Application-June 2013Document3 pagesBig M Pumps For Hot Oil Application-June 2013DelfinshNo ratings yet
- 750-237 Profire V-1Document110 pages750-237 Profire V-1Homer SilvaNo ratings yet
- Power-To-X Pespectivas 2022Document21 pagesPower-To-X Pespectivas 2022joao.santosNo ratings yet