Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Congenital Syphilis - Algorithm-110919-1
Uploaded by
Kamrul Ahsan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageThis document provides guidelines for evaluating and treating infants born to women with syphilis during pregnancy. It outlines 4 scenarios based on the infant and maternal criteria. Scenario 1 indicates proven or highly probable congenital syphilis and recommends a CSF analysis and treatment with aqueous crystalline penicillin. Scenario 2 indicates possible congenital syphilis and also recommends a CSF analysis. Scenario 3 indicates congenital syphilis is less likely, and no additional evaluation is needed but maternal titers should be reviewed. Scenario 4 is not included but refers the reader to CDC guidelines for more information.
Original Description:
Original Title
Congenital Syphilis_Algorithm-110919-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides guidelines for evaluating and treating infants born to women with syphilis during pregnancy. It outlines 4 scenarios based on the infant and maternal criteria. Scenario 1 indicates proven or highly probable congenital syphilis and recommends a CSF analysis and treatment with aqueous crystalline penicillin. Scenario 2 indicates possible congenital syphilis and also recommends a CSF analysis. Scenario 3 indicates congenital syphilis is less likely, and no additional evaluation is needed but maternal titers should be reviewed. Scenario 4 is not included but refers the reader to CDC guidelines for more information.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageCongenital Syphilis - Algorithm-110919-1
Uploaded by
Kamrul AhsanThis document provides guidelines for evaluating and treating infants born to women with syphilis during pregnancy. It outlines 4 scenarios based on the infant and maternal criteria. Scenario 1 indicates proven or highly probable congenital syphilis and recommends a CSF analysis and treatment with aqueous crystalline penicillin. Scenario 2 indicates possible congenital syphilis and also recommends a CSF analysis. Scenario 3 indicates congenital syphilis is less likely, and no additional evaluation is needed but maternal titers should be reviewed. Scenario 4 is not included but refers the reader to CDC guidelines for more information.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
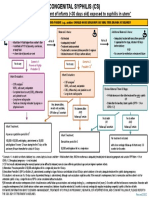
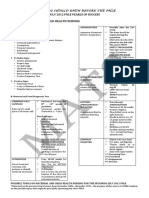
CONGENITAL SYPHILIS (CS)
Evaluation and treatment of infants (<30 days old) born to women with syphilis during pregnancy*
Start ALL INFANTS AND MOTHERS SHOULD HAVE SERUM RPR OR VDRL TITER DRAWN AT DELIVERY
Infant Criteria: Maternal Criteria: Additional Maternal Criteria:
• CS findings on physical exam • Not treated • Adequately treated with benza-
• Infant titer ≥4 fold higher than • Inadequately treated† thine penicillin G appropriate for
Infant and No to all No to all
mother’s titer • Treatment undocumented stage, ≥4 weeks before delivery
Maternal • + darkfield or PCR of lesion/body • Treated with a non-benzathine AND
Criteria fluid penicillin G regimen • No concern for reinfection or
• Received treatment <4 weeks treatment failure
before delivery
Scenario 1:
Yes to any Proven or Highly Scenario 2: Scenario 3:
Yes to any Yes to both
Probable CS Possible CS Less Likely CS
• CSF analysis§ No additional infant evaluation
• CSF analysis§
VDRL, cell count, and protein VDRL, cell count, and protein
• Complete blood count (CBC), • CBC, differential, and platelet count
differential and platelet count Review Maternal Titers & Stage:
• Long-bone radiographs
• Long-bone radiographs • ≥4 fold decrease in titer after
• Tests as clinically indicated treatment for early syphilis
Infant
OR
Evaluation by signs on physical exam. • Stable titer for low-titer, latent
syphilis (RPR < 1:4 or VDRL<1:2)
Any abnormalities, No abnormalities
results not available, AND
OR follow-upII uncertain follow-upII certain No to both Yes to either
OR AND
follow-upII uncertain follow-upII certain
Aqueous crystalline penicillin G‡
100,000–150,000 units/kg/day,
administered as 50,000 units/kg/dose
IV every 12 hours during the first 7 days Benzathine penicillin G No treatment indicated
of life and every 8 hours thereafter for 50,000 units/kg/dose IM in a single with close serologic follow-up of infant
Infant a total of 10 days dose every 2-3 months for 6 months
Treatment
* Scenario 4 – in which an infant at delivery has a normal physical exam and titer < 4 fold mother’s titer, AND the mother was adequately treated prior to becoming pregnant and sustains RPR titers <1:4 or VDRL<1:2 throughout pregnancy – is not included.
† Benzathine Penicillin G (BPG or Bicillin-LA), administered according to stage of disease and initiated at least 4 weeks prior to delivery is the only adequate treatment for syphilis during pregnancy.
‡ Alternative: Procaine penicillin G 50,000 units/kg/dose IM in a single daily dose for 10 days
§ CSF test results obtained during the neonatal period can be difficult to interpret; normal values differ by gestational age and are higher in preterm infants.
II All neonates with reactive nontreponemal tests should receive careful follow-up examinations and serologic testing (i.e., a nontreponemal test) every 2–3 months until the test becomes nonreactive. Neonates with a negative nontreponemal test at birth whose
mothers were seroreactive at delivery should be retested at 3 months to rule out serologically negative incubating congenital syphilis at the time of birth. Revised
FOR MORE INFORMATION ABOUT SCENARIO 4 MANAGEMENT, TREATMENT OF SYPHILIS IN PREGNANCY, NEONATAL CSF INTERPRETATION, AND CS INFANT FOLLOW-UP, PLEASE REFER TO THE 2015 CDC STD TREATMENT GUIDELINES. 6.17.19
You might also like
- CS AlgorithmDocument1 pageCS AlgorithmDraalexNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sepsis Algorithm2Document1 pageNeonatal Sepsis Algorithm2CHIERBEENo ratings yet
- Waqas Ahmed Usmani ROLL NO 17-78Document41 pagesWaqas Ahmed Usmani ROLL NO 17-78Waqas Ahmed UsmaniNo ratings yet
- F Psuneo NasDocument1 pageF Psuneo Nasalvin septianoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of A Pregnant FamilyDocument4 pagesAssessment of A Pregnant FamilyLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Case Study in ObwardDocument6 pagesCase Study in Obwardcharles_florendo25100% (3)
- Diabetes in PregnancyDocument1 pageDiabetes in Pregnancycatcat669111No ratings yet
- Eposter Infants of Mothers With Syphilis Glabela CPDocument1 pageEposter Infants of Mothers With Syphilis Glabela CPGlabela Christiana PandangoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Bacterial Meningitis Case PresentationDocument22 pagesPediatric Bacterial Meningitis Case Presentationapi-602288180No ratings yet
- Postterm PregnancyDocument2 pagesPostterm PregnancyicNo ratings yet
- Duty Report RIWDocument41 pagesDuty Report RIWRiyan W. PratamaNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip or PalateDocument19 pagesCleft Lip or PalateAnonymous LCLG7siTYnNo ratings yet
- Fetal MonitoringDocument6 pagesFetal MonitoringRraouzmaaliNo ratings yet
- Finals - MCN RLEDocument6 pagesFinals - MCN RLEKorean GirlNo ratings yet
- Post Term PregnancyDocument12 pagesPost Term PregnancyRizky Putra Ismeldi100% (1)
- Neonatal Jaundice PathwayDocument35 pagesNeonatal Jaundice Pathwaypragita ayu100% (1)
- Acute Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (Aub) : AlgorithmDocument8 pagesAcute Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (Aub) : AlgorithmPhiyaNo ratings yet
- 84 - UTI Ed and Uc Culture Results Decision TreeDocument1 page84 - UTI Ed and Uc Culture Results Decision TreeShimelis TadesseNo ratings yet
- CHN FinalsDocument15 pagesCHN FinalsLuna sibilityNo ratings yet
- Heartworm Disease: What To Do With Your SNAP ResultDocument1 pageHeartworm Disease: What To Do With Your SNAP ResultIantela AlexNo ratings yet
- Wilson Disease Testing AlgorithmDocument1 pageWilson Disease Testing Algorithmbassam alharaziNo ratings yet
- Outpatient Acute Pharyngitis For Adults and Pediatric Patients Algorithm - FinalDocument1 pageOutpatient Acute Pharyngitis For Adults and Pediatric Patients Algorithm - Finaljmor.3009No ratings yet
- Women's HealthDocument44 pagesWomen's HealthKylie ElaineNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdominal Pain Pathway: Management - Primary Care and Community SettingsDocument2 pagesAcute Abdominal Pain Pathway: Management - Primary Care and Community Settingsshella1selinaNo ratings yet
- CPG CroupDocument4 pagesCPG CroupMarvin M PulaoNo ratings yet
- ImmunoSeroLab M4Document3 pagesImmunoSeroLab M4ela kikayNo ratings yet
- ch2 fs1Document2 pagesch2 fs1ry beNo ratings yet
- Management of Normal LaborDocument98 pagesManagement of Normal LaborGoogle SecurityNo ratings yet
- 2nd Preceptorials FinalDocument14 pages2nd Preceptorials FinalGabriel MillaNo ratings yet
- $RQMTW24Document1 page$RQMTW24akxerox47No ratings yet
- F Seizures AssessDocument1 pageF Seizures Assessmahmudajannatul.7No ratings yet
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument23 pagesPulmonary EmbolismAkhilesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics PDFDocument14 pagesObstetrics PDFKatheryn100% (1)
- Acute Low Back Pain Flowchart January 2017Document1 pageAcute Low Back Pain Flowchart January 20171234chocoNo ratings yet
- Induction of Labour: Maternity and Neonatal Clinical GuidelineDocument30 pagesInduction of Labour: Maternity and Neonatal Clinical GuidelineFino GunnersNo ratings yet
- Bahan Tugas Tokolitik Ulfadiya Putri 1Document25 pagesBahan Tugas Tokolitik Ulfadiya Putri 1hopa shopNo ratings yet
- Syphilis Screening Testing and TreatmentDocument2 pagesSyphilis Screening Testing and TreatmentMoeed Iqbal100% (1)
- Late Preterm Early Term EOS - Neonatal ManualDocument2 pagesLate Preterm Early Term EOS - Neonatal ManualsumantamohammedNo ratings yet
- Care During 1st Stage of LabourDocument27 pagesCare During 1st Stage of LabourCHARLOTTE DU PREEZNo ratings yet
- PQCNC ASNS Learning Session - DataDocument28 pagesPQCNC ASNS Learning Session - DatakcochranNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and Diagnosis: New York State Department of HealthDocument2 pagesEvaluation and Diagnosis: New York State Department of HealthNisa Annisa ArfiyantiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Template: SBAR - Postpartum Care SDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Template: SBAR - Postpartum Care SAira Leigh MoralesNo ratings yet
- PromDocument1 pagePromwedishaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Placenta PreviaDocument3 pagesNCP - Placenta PreviaJulianna Alex ConopioNo ratings yet
- Perinatal SbarDocument1 pagePerinatal SbarGlendy DelrioNo ratings yet
- Cesarean Section Audit FormatDocument6 pagesCesarean Section Audit FormatRahul JalauniaNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk Factors: EtiologyDocument1 pageNon-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk Factors: EtiologyDenise FranciscoNo ratings yet
- PaedsDocument72 pagesPaedsOlivia Genevieve El JassarNo ratings yet
- Righ Choise TrialDocument17 pagesRigh Choise TrialOscar FloresNo ratings yet
- Pedia NCPDocument8 pagesPedia NCPFrancheska Nicole Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Neurodevelopmental Assessments For Prediction of Cerebral Palsy - From Brazelton, Hine To General Movements: The EvidenceDocument39 pagesNeurodevelopmental Assessments For Prediction of Cerebral Palsy - From Brazelton, Hine To General Movements: The Evidencekawaljit000No ratings yet
- MODULE 2.3 Antepartum - Pregnancy Module NURSING NOTESDocument11 pagesMODULE 2.3 Antepartum - Pregnancy Module NURSING NOTESQwer TyNo ratings yet
- G JaundiceDocument40 pagesG JaundiceRedina Tuya RamirezNo ratings yet
- Gynae SNI Final Print VersionDocument34 pagesGynae SNI Final Print VersionMr Soman Nadim IqbalNo ratings yet
- G NewexamDocument25 pagesG NewexamvineelainjetyNo ratings yet
- What You Should Know Before The PnleDocument6 pagesWhat You Should Know Before The PnleNicole OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Management of Covid HRPB - 22 March 2020Document1 pageManagement of Covid HRPB - 22 March 2020Kok Hui DiongNo ratings yet
- Newborn AssessmentDocument3 pagesNewborn AssessmentMimie CaliNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Chromosomal Microarray Nov2015-3Document34 pagesPrenatal Chromosomal Microarray Nov2015-3suryasivNo ratings yet
- 5 Facts You Should Know About The Green MarchDocument7 pages5 Facts You Should Know About The Green MarchDriss Baouche100% (1)
- Annual 2005Document128 pagesAnnual 2005KarredeLeonNo ratings yet
- Doanh Nghiep Viet Nam Quang CaoDocument1 pageDoanh Nghiep Viet Nam Quang Caodoanhnghiep100% (1)
- Effects of Monetory PolicyDocument5 pagesEffects of Monetory PolicyMoniya SinghNo ratings yet
- Out To Lunch: © This Worksheet Is FromDocument1 pageOut To Lunch: © This Worksheet Is FromResian Garalde BiscoNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Soal UPDocument16 pagesKumpulan Soal UPTriono SusantoNo ratings yet
- MSPM Clark UniversityDocument27 pagesMSPM Clark Universitytushar gargNo ratings yet
- Manual GPS Trimble Portugues CFX-750 / FM-750Document246 pagesManual GPS Trimble Portugues CFX-750 / FM-750José Luis Mailkut Pires100% (5)
- Theories of EmotionDocument11 pagesTheories of EmotionNoman ANo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networks Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesData Communication and Networks Syllabus PDFgearlaluNo ratings yet
- Emilio Aguinaldo: The First Philippine Republic The Malolos CongressDocument3 pagesEmilio Aguinaldo: The First Philippine Republic The Malolos CongressLIEZLE ANN EROYNo ratings yet
- Rationale of Labour Welfare To Employers and EmployeesDocument20 pagesRationale of Labour Welfare To Employers and Employeesajit yadav100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Design: Ccss - Ela-Literacy - Rf.2.3Document6 pagesLesson Plan Design: Ccss - Ela-Literacy - Rf.2.3api-323520361No ratings yet
- Week 1Document34 pagesWeek 1Mitchie Faustino100% (1)
- Friday Night Mishaps, Listening Plus TasksDocument3 pagesFriday Night Mishaps, Listening Plus TasksCristina Stoian100% (1)
- QinQ Configuration PDFDocument76 pagesQinQ Configuration PDF_kochalo_100% (1)
- Short Question: Computer Science For 9 Class (Unit # 3)Document5 pagesShort Question: Computer Science For 9 Class (Unit # 3)Yasir MehmoodNo ratings yet
- We Don't Need No MBADocument9 pagesWe Don't Need No MBAsharad_khandelwal_2No ratings yet
- Brochure For New HiresDocument11 pagesBrochure For New HiresroseNo ratings yet
- Canada Immigration Forms: E33106Document6 pagesCanada Immigration Forms: E33106Oleksiy Kovyrin100% (1)
- The Board-Management RelationshipDocument32 pagesThe Board-Management RelationshipAlisha SthapitNo ratings yet
- Karbohidrat: Gula, Pati & SeratDocument20 pagesKarbohidrat: Gula, Pati & SeratAlfi Syahrin SiregarNo ratings yet
- List of Mines in IndiaDocument4 pagesList of Mines in IndiaNAMISH MAHAKULNo ratings yet
- HOPE 2A MODULE 1 Introduction To SportsDocument11 pagesHOPE 2A MODULE 1 Introduction To SportsChristian Ray Lucnagan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Kuis 4Document10 pagesKuis 4Deri AntoNo ratings yet
- Machine Tools Design: InstructorsDocument31 pagesMachine Tools Design: InstructorsAladdin AdelNo ratings yet
- All This Comand Use To Type in NotepadDocument9 pagesAll This Comand Use To Type in NotepadBiloul ShirazNo ratings yet
- Broken Squares - Unfreezing Team Building ExerciseDocument4 pagesBroken Squares - Unfreezing Team Building Exerciselilywhite786No ratings yet
- Coles Stategic AssessmentDocument10 pagesColes Stategic AssessmentRichardNo ratings yet
- How To Perform A Financial Institution Risk Assessment: Quick Reference GuideDocument15 pagesHow To Perform A Financial Institution Risk Assessment: Quick Reference GuideYasmeen AbdelAleemNo ratings yet