Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ImmunoSeroLab M4
Uploaded by
ela kikayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ImmunoSeroLab M4
Uploaded by
ela kikayCopyright:
Available Formats
MODULE 4: SEROLOGIC TEST FOR SYPHILIS
• Test for Syphilis
OUTLINE
I Syphilis 1. Non-specific or non-treponemal serological tests
A Antigens ▪ For screening of syphilis
B Antibodies ▪ Serological tests that detect reagin
C Spinal Fluid Tests in Syphilis - Reagin: substance present in the serum of patients with certain diseases
i Biological False Positive Antibody (BFP) Reagin Antibody including syphilis
▪ Become positive 1-4 weeks after the appearance of initial symptoms
▪ Other Non-treponemal tests:
I. SYPHILIS - Toluidine Red Unheated Serum Test (TRUST)
• Causative agent: Treponema pallidum - Unheated Serum Reagin (USR)
• Gram (-) negative spirochetes, obligate intracellular parasite - Reagin Screen Test (RST)
• Venereal disease 2. Specific Treponemal antibody tests
• Two types of transmission: ▪ Do this after tested (+) positive in Non-specific or non-treponemal serological tests
1. Acquired: transmission through body fluids (VDRL or RPR)
▪ Sexual contact ▪ Confirmatory test
▪ Sharing of contaminated needles (skin lesion) ▪ Uses Treponema pallidum
▪ Direct contact - Antigen
2. Congenital: Mother to baby transmission - To detect specific antibodies produced by the patients suspected with syphilis
▪ Transplacental ▪ Other Serological Tests For Syphilis
▪ During Childbirth - Anti-Treponemal antibody (ATA)
• Stages of Syphilis - Anti-Treponemal ABs group detected by Reiter Protein Complement Fixation
1. Primary Stage: Hard Chancre/Hunterian Chancre Test (RPCFT)
2. Secondary Stage: Condylomata lata, may involve CNS, eyes, bones, liver ✓ Appears later than specific ABs
3. Latent Stage: No sign asymptomatic/non-reactive ✓ Some syphilis patient do not produce the form of ABs
4. Tertiary Stage: Gummas, involve deep organs ✓ Use is limited
Non-specific or Non-treponemal Serological Tests
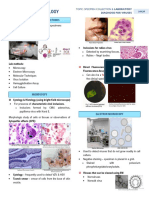
Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) Rapid Plasma Reagin (RPR)
Old method Modified version
• Read Microscopically using Microscope • Read Macroscopically
○ Cannot be read macroscopically because it will be hard to see the flocculation due o due to charcoal
to its color (White) o Clumping of cells is seen immediately Non-reactive Weakly reactive Strongly reactive
Non-reactive Reactive
Examination
From Left to Right: Reactive (with flocculation), non-reactive (without flocculation)
• Heated serum (common) - heated at 56C for 30 minutes • Unheated Serum
Specimen
• CSF (only if the baby is suspected with neurosyphilis) *Not recommended for CSF specimens
Method Microflocculation method Macroflocculation method
composed of rings which are 15mm in diameter and 1.75mm deep
Slide
• 0.03% Cardiolipin: serves as antigen • Original VDRL reagent • Phosphate: enhances solution
Reagent • 0.21% Lecithin: enhances sensitivity of the cardiolipin • Disodium EDTA: enhances the suspension • Thimerosal: preservative
• 0.90% Cholesterol: enhances the whole reaction • Charcoal: visualization • Choline Chloride: eliminates heating process
1. Add 1 drop of VDRL reagent using an
• Methods:
appropriate needle gauge depending on the
o Qualitative: 18-gauge needle • Add 1 drop of each reagent
Procedure method used (refer below)
o Quantitative: 19-gauge needle • Place in the ROTATOR at 100 rpm for 8 mins
2. Place it in ROTATOR at 180 rpm for 4 mins
o CSF: 22/23-gauge needle
o >4 mins = cannot be read
• Reactive (+): with flocculation • Reactive (+) o HIV • Weakly Reactive
Manner of Reporting/Result
• Non-Reactive (-): without flocculation o Syphilis: w/ warts o HPV: if w/ warts • Non-Reactive (-)
• False (+) positive result o Rheumatic fever o Malaria • False (+) positive result ▪ TB o Pregnancy
False result o SLE o Infectious Mononucleosis (IM) o Pregnancy o Collagen disease ▪ Chickenpox o Old age
▪ Arthritis ▪ Hepatitis • False (-) negative result
DARIO, GRANADA, LAGUD, PRIETO, TRESIANA 12
MODULE 4: SEROLOGIC TEST FOR SYPHILIS
▪ Lupus Erythematosus ▪ Measles o Technical errors
o Infections ▪ Leprosy ▪ wrong specs of agitation
▪ Infectious Mononucleosis (IM) o Autoimmune disease ▪ expired reagents
▪ Malaria ▪ Gonorrhea o Low antibody titer
▪ Prozone
Specific Treponemal Antibody Tests
Treponema Pallidum Immobilization Fluorescence Treponemal Antibody Absorption Treponema Pallidum Microhemagglutination T. Enzyme Linked
Test
Test (TPI) Test (FTA-ABS) Hemagglutination Test (TPHA) Pallidum Test (MHA-TP) Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
• In Other books: Most specific is FTA-ABS • Less sensitive
o If there are TPI and FTA-ABS in multiple choices, • Disadvantage: Less reliable in
Description Most specific test for syphilis
answer FTA-ABS diagnosing primary syphilis (causes
o UPDATED false (+) results)
• Neutralization
o Specific T. pallidum antibodies from • Indirect fluorescence
Principle Indirect agglutination Hemagglutination Indirect ELISA
the patient are mixed with actively o Increase the specificity of the reiter strain
motile T. pallidum (Nichols strain)
• T. pallidum reiter strain • T. pallidum antigen
• T. pallidum nio\chols strain • Glutaraldehyde stabilized either with • Enzyme-labeled antibodies
• Nichols strain: live actively motile T.
pallidum organism extracted from • Fluorescent-labeled antibodies animal RBC (refer below) coated with
Tanned formalin sheep RBC
o Enzyme-labeled used:
Reagent and Composition tissues/lesions of infected rabbits o Composition: Dead T. pallidum. Dried and fixed treponemal antigen
coated with treponemal
Alkaline phosphatase
o Absorbent: Reiter teponemes o Sheep RBC o Substrate used: Para-
• Complement: Guinea pig o Chicken RBC
antigen
o Conjugate: Fluorescent-labeled AHG nitrophenyl phosphate
complement
▪ Fluorescein isothiocyanate: Dye used • Turkey RBC ▪ White turns to yellow when
o Dilution: 1:15 alkaline PO is added
1. Patient serum is diluted and mixed with reiter strain 1. Tanned sheep RBCs are coated with
to remove nonspecific T. pallidum antibodies T. pallidum antigen from Nichol’s strain
Procedure 2. The absorbed serum is then added on a slide 2. If specific T. pallidum antigen is
x\containing nichols strain of T. pallidum present in the sample, agglutination
3. Fluorescent-labeled antibodies are then added will occur
(+) Positive: Fluorescence
• (+) Positive: immobilization of
treponemas
(+) Positive:
Result • Reactive (+): >50% (+) Positive: hemagglutination
hemagglutination
• Doubtful: 20-50%
• Negative: <20%
Antigens Antibodies Tests
Non-Treponemal or Non-specific Wasserman antigen (CARDIOLIPIN) REAGIN and anti-cardiolipin 1. VDRL 2. RPR
1. Treponemal group antigens - REITER CHON 1. Group Abs 2. Specific T. pallidum Abs 1. TPI 3. MHA-TP
Treponemal or Specific
2. Specific T. pallidum Antigens (pathogenic) ○ Anti-reiter CHON ○ Anti T. pallidum abs 2. FTA-ABS 4. TPHA
A. ANTIGENS • Treponemal Antibodies
• Wasserman Antigens o Directed against pathogenic T. pallidum and closely related strains
o Cardiolipin (Wasserman Ag) o Group Antibodies: directed group antigens
▪ A hapten and must be bound to a suitable carrier to be antigenic o Specific Treponemal Antibodies: specific for each treponemal antigen
▪ A phospholipid
▪ Microbial Cell Treponemes: serves as the foreign carrier C. SPINAL FLUID TESTS IN SYPHILIS
▪ Bound Phospholipid (cardiolipin): serves as the antigenic determinant
• Treponemal Antigens • Testing of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) is an important part of patient monitoring as well
o Reiter CHON as diagnostic test.
▪ A protein found in most treponemes (both in saprophytic and pathogenic • Neurosyphilis
treponemes) o Abnormally high WBC count
▪ Specific Treponemal Antigens: specific for each treponeme species o Elevated protein levels in the CSF
o (+) VDRL result
B. ANTIBODIES Note: FTA abs IgG and IgM detection continues to be a confirmatory test in diagnosis of
• Non-Treponemal Antibodies syphilis
o Reagin: an anti-cardiolipin Ags o Currently, most hospitals use ELISA, Western blot and PCR
DARIO, GRANADA, LAGUD, PRIETO, TRESIANA 13
MODULE 4: SEROLOGIC TEST FOR SYPHILIS
▪ Methods that are being studied as an additional diagnostic test especially for o Pneumonia
congenital syphilis and neurosyphilis o Vaccination with live attenuated viruses
o Malaria
i. BIOLOGICAL FALSE POSITIVE ANTIBODY (BFP) REAGIN ANTIBODY o Pregnancy
• Chronic
• Associated with other diseases (BFP)
o Leprosy: reagin titer lowers immediately after treatment
• Acute
Comparison of Precipitation Techniques
Technique Application Principle
Nephelometry Igs, Complement, CRP, other serum proteins Light that is scattered at an angle is measured, indicating the amount of antigen or antibody present
Antigen diffuses out into gel that is infused with antibody.
Radial Immunodiffusion Igs, Complement
Measurement of the radius indicates concentration of the antigen
Both antigen and antibody diffuse out from wells in a gel.
Diffusion Complex antigens such as fungal antigens
Lines of precipitate formed indicate the relationship of antigens
Immunoelectrophoresis Differentiation of serum proteins Electrophoresis of serum followed by diffusion of antibody from wells
Immunofixation Electrophoresis Over – or – under production of antibody Electrophoresis of serum followed by direct application of antibody to the gel
Comparison of Agglutination Reactions
Type Of Reaction Principle Results
Direct Agglutination Antigen is naturally found on a particle
Indirect (Passive) Agglutination Particles coated with antigens not normally found on their surfaces Agglutination indicates the presence of patient antibody
Reverse-Passive Particles are coated with reagent antibody
Haptens attached to carrier particle.
Agglutination Inhibition Lack of agglutination is a positive test, indicating the presence of
Particles compete with patient antigens for a limited number of antibody sites
patient antigen
Hemagglutination Inhibition Red blood cells spontaneously agglutinate if viral particles are present
Comparison of Tests Used for the Diagnosis of Syphilis
Type of Reaction Principle Results Comments
Direct Agglutination Antigen is naturally found on a particle
MICROSCOPY
Indirect (Passive)
Particles coated with antigens not normally found on their surfaces Agglutination indicates the Requires active lesion. Must have good specimen, experienced technologist;
Agglutination
presence of patient antibody inexpensive
Requires active lesion.
Reverse-Passive Particles are coated with reagent antibody
More specific than darkfield; specimen does not have to be live
Haptens attached to carrier particle.
Agglutination Inhibition
Particles compete with patient antigens for a limited number of antibody sites Lack of agglutination is a positive test,
indicating the presence of patient antigen Flocculation; good for screening tests, treatment monitoring, spinal fluid testing;
Hemagglutination Inhibition Red blood cells spontaneously agglutinate if viral particles are present
false positives
RPR Modified VDRL with charcoal particles, more sensitive than VDRL in primary SY
Cardiolipin Reagin
TRUST Uses red particles to visualize the reaction; similar to RPR
Treponemal
FTA-ABS Nichol’s strain of T. pallidum Confirmatory; specific, sensitive, may be negative in primary stage
EIA Treponemal or recombinant Anti-treponemal Simple to perform; can be automated; not as sensitive as FTA-ABS
MHA-TP or SERODIA TP-PA Sheep’s RBCs or gel particles sensitized with T. pallidum sonicate Anti-treponemal Not as sensitive as FTA-ABS
PCR Non-treponemal DNA in patient sample is amplified None Highest sensitivity is in primary stage of SY; availability is limited
Characteristics of Acute Phase Reactants
Protein Response Time (hr) Normal Conc. (mg/dl) Increase Function
CRP 6-10 0.5 1000x Opsonization, complement activation
Serum Amyloid A 24 3.0 1000x Removal of cholesterol
Alpha-Antitrypsin 24 200-400 2-5x Protease inhibitor
Fibrinogen 24 110-400 2-5x Clot formation
Haptoglobin 24 40-200 2-10x Binds hemoglobin
Ceruloplasmin 48-72 20-40 2x Binds copper, oxidizes iron
C3 48-72 60-140 2x Opsonization, lysis
Mannose-Binding Protein 0.15-1.0 Complement activation
• CRP, Serum Amyloid: 1000x increase in inflammation
REFERENCES
• Procalcitonin: biomarker of sepsis Notes from the discussion by Mrs. Maria Redora R. Esteban, RMT
• Albumin, Transferrin, Prealbumin: negative acute-phase reactants CANVAS Notes
DARIO, GRANADA, LAGUD, PRIETO, TRESIANA 14
You might also like
- 2-Syphilis congenital PKEL finalDocument24 pages2-Syphilis congenital PKEL finalGilang KusdinarNo ratings yet
- Syphilis Part 2 (2023) - 1Document31 pagesSyphilis Part 2 (2023) - 1PrakritiNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument10 pagesConcept MapStephen YorNo ratings yet
- 5th Rotation - IsBB (Tour)Document2 pages5th Rotation - IsBB (Tour)loona oneNo ratings yet
- Sti Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesSti Lecture NotesSTACEY SALVILLANo ratings yet
- Serological TestsDocument2 pagesSerological TestsKimberly EspaldonNo ratings yet
- Publicationsohpsyphilis Testing and Lab InterpretationDocument4 pagesPublicationsohpsyphilis Testing and Lab InterpretationQusai & MOHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- H008019 Resolving ABO Discrepancies E 2017 01Document2 pagesH008019 Resolving ABO Discrepancies E 2017 01Wei Leng OngNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument10 pagesConcept MapStephen Yor100% (1)
- MLS-115-LEC-COMPILEDDocument46 pagesMLS-115-LEC-COMPILEDJohanna MarieNo ratings yet
- Is Lab WeekDocument3 pagesIs Lab Weekkimmynemil80No ratings yet
- Test Information TPPADocument6 pagesTest Information TPPAebustillobxuNo ratings yet
- Syphilis Screening Testing and TreatmentDocument2 pagesSyphilis Screening Testing and TreatmentMoeed Iqbal100% (1)
- Serology Tests for Syphilis DiagnosisDocument7 pagesSerology Tests for Syphilis DiagnosisCarlo PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Antibody Screening and Identification ObjectivesDocument3 pagesAntibody Screening and Identification ObjectivesApril SudarioNo ratings yet
- Pmls MidtermsDocument11 pagesPmls MidtermsErnest VincentNo ratings yet
- Renal function and urinalysis evaluationDocument4 pagesRenal function and urinalysis evaluationSheriffCaitlynNo ratings yet
- Immunohematology Handouts UpdatedDocument15 pagesImmunohematology Handouts UpdateddmclmllNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Antiboby Detection 1Document5 pages7.0 Antiboby Detection 1Sherwin BumanglagNo ratings yet
- Eposter Infants of Mothers With Syphilis Glabela CPDocument1 pageEposter Infants of Mothers With Syphilis Glabela CPGlabela Christiana PandangoNo ratings yet
- VDRL/RPR: Dominic Edward Z. TomasDocument26 pagesVDRL/RPR: Dominic Edward Z. TomasDominic TomasNo ratings yet
- Specimen Collection Errors and FactorsDocument11 pagesSpecimen Collection Errors and FactorsApril Lady Faith P. PaundogNo ratings yet
- Syphilis Testing, New and Old, Rapid and Not So RapidDocument47 pagesSyphilis Testing, New and Old, Rapid and Not So RapidRima Carolina Bahsas ZakyNo ratings yet
- Acute Tick-Borne Disease Testing AlgorithmDocument1 pageAcute Tick-Borne Disease Testing AlgorithmSimon WHookNo ratings yet
- Reyes Solangoy IS Lab NotesDocument9 pagesReyes Solangoy IS Lab NotesRyhanna Lou ReyesNo ratings yet
- Mtap - Immunohema Transfusion MedicineDocument9 pagesMtap - Immunohema Transfusion MedicineMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- Antibody PanelDocument5 pagesAntibody PanelCarl Dominic GasconNo ratings yet
- Serology of Bacteria, Viruses and ParasitesDocument128 pagesSerology of Bacteria, Viruses and Parasitesreginarosesalazar0127No ratings yet
- Part Ii Specimen Collection & Laboratory Diagnosis For VirusesDocument6 pagesPart Ii Specimen Collection & Laboratory Diagnosis For VirusesBONNA FAYE CHRISZEL HUI YING TANNo ratings yet
- Organisms Specimen Isolation Serological Tests Legionella/ LegionellaDocument3 pagesOrganisms Specimen Isolation Serological Tests Legionella/ Legionellasana khanNo ratings yet
- Rapid test detects cardiac Troponin IDocument1 pageRapid test detects cardiac Troponin IPABRIK SEPULUHNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Guidelines For Acute Diarrhea: For Educational Purposes OnlyDocument1 pageLaboratory Guidelines For Acute Diarrhea: For Educational Purposes OnlyAnonymous ZbhBxeEVNo ratings yet
- Period of Communicability: ChloramphenicolDocument10 pagesPeriod of Communicability: ChloramphenicolDona Mae TaberaNo ratings yet
- Pedia: Hepatic Dysfunction: Fcnlxa - St. Luke's College of NursingDocument3 pagesPedia: Hepatic Dysfunction: Fcnlxa - St. Luke's College of NursingLAXA FRANCINENo ratings yet
- Finals - MCN RLEDocument6 pagesFinals - MCN RLEKorean GirlNo ratings yet
- MUS Tutorial IMLTD SF HomeWorkDocument22 pagesMUS Tutorial IMLTD SF HomeWorkMustofa AididNo ratings yet
- Serological Diagnosis of Bacterial InfectionsDocument81 pagesSerological Diagnosis of Bacterial InfectionsAffie SaikolNo ratings yet
- Seizure New Onset Clinical PathwayDocument17 pagesSeizure New Onset Clinical PathwayKim Shyen BontuyanNo ratings yet
- 11december2020 20201211 Clinical Management Guidelines For COVID-19 Infection 1204Document14 pages11december2020 20201211 Clinical Management Guidelines For COVID-19 Infection 1204Jawariya ZiaNo ratings yet
- A Novel Nested Real Time Polymerase ChainDocument6 pagesA Novel Nested Real Time Polymerase ChainSadiya RhasyaNo ratings yet
- Complete Urine Analysis 07-03-2022Document1 pageComplete Urine Analysis 07-03-2022RB STNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Dengue: Dr.M.sravana Durga, 1 Year Junior Resident MD PaediatricsDocument24 pagesDiagnosis of Dengue: Dr.M.sravana Durga, 1 Year Junior Resident MD PaediatricsAneesh MyneniNo ratings yet
- Is FinalsDocument78 pagesIs FinalsMarissa CordovaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Syphilis - Algorithm-110919-1Document1 pageCongenital Syphilis - Algorithm-110919-1Kamrul AhsanNo ratings yet
- 4 - Chemical Examination of UrineDocument14 pages4 - Chemical Examination of UrineKunware TropaNo ratings yet
- Is 6Document8 pagesIs 6Danna Angelick ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anti-Nmda Receptor (Nr1) Igg Antibodies: Indications For OrderingDocument3 pagesAnti-Nmda Receptor (Nr1) Igg Antibodies: Indications For OrderingLis SetiyoriniNo ratings yet
- CS AlgorithmDocument1 pageCS AlgorithmDraalexNo ratings yet
- Serological Diagnosis of SyphilisDocument81 pagesSerological Diagnosis of Syphilistummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Tests in SyphilisDocument9 pagesTests in SyphilisaditiNo ratings yet
- 28 Eastick PDFDocument33 pages28 Eastick PDFEgi PatnialdiNo ratings yet
- Principles of serodiagnosis techniquesDocument26 pagesPrinciples of serodiagnosis techniquesNipun ShamikaNo ratings yet
- Ag Ab DetectionDocument43 pagesAg Ab DetectionMaaz AlwaliNo ratings yet
- Poster Final 1Document1 pagePoster Final 1Montana McLeanNo ratings yet
- Tes Lab Penyakit Infeksi Dan Tropis (April 2011)Document143 pagesTes Lab Penyakit Infeksi Dan Tropis (April 2011)Fajrul AnsarNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends in The Serologic Diagnosis of Syphilis: Muhammad G. Morshed, Ameeta E. SinghDocument21 pagesRecent Trends in The Serologic Diagnosis of Syphilis: Muhammad G. Morshed, Ameeta E. SinghNana ArthetaNo ratings yet
- Lupus AnticoagulantDocument27 pagesLupus AnticoagulantAndrew Arnold David Villanueva100% (1)
- Serological Investigation of InfectionsDocument18 pagesSerological Investigation of InfectionsAsd AsdNo ratings yet
- MLSP: Nature of The Clinical LaboratoryDocument4 pagesMLSP: Nature of The Clinical LaboratorythisbusinesstobusyNo ratings yet
- Lincoln Penned Numerous Speeches Cooper Union AddressDocument1 pageLincoln Penned Numerous Speeches Cooper Union Addressela kikayNo ratings yet
- Imse Trans Lab 8Document7 pagesImse Trans Lab 8ela kikayNo ratings yet
- ImmunoSeroLab M1 M4 MergedDocument14 pagesImmunoSeroLab M1 M4 Mergedela kikayNo ratings yet
- Module 4 PDFDocument15 pagesModule 4 PDFela kikayNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Antigen and Antibody RecognitionDocument10 pagesModule 2: Antigen and Antibody Recognitionela kikayNo ratings yet
- My Article On Character TraitsDocument1 pageMy Article On Character Traitsela kikayNo ratings yet
- Capstone 90Document1 pageCapstone 90ela kikayNo ratings yet
- ImmunoSeroLab M2Document4 pagesImmunoSeroLab M2ela kikayNo ratings yet
- American Bar AssociationDocument1 pageAmerican Bar Associationela kikayNo ratings yet
- Dropping Food Coloring Into Milk Rube Goldberg Rocket Balloon CarDocument1 pageDropping Food Coloring Into Milk Rube Goldberg Rocket Balloon Carela kikayNo ratings yet
- Capstone 86Document1 pageCapstone 86ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Ethics Vs MoralityDocument1 pageEthics Vs MoralitySiddharth soniNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Ash Dangerous To InhaleDocument1 pageVolcanic Ash Dangerous To Inhaleela kikayNo ratings yet
- 1815 Explosion of Mount Tabora CalderaDocument1 page1815 Explosion of Mount Tabora Calderaela kikayNo ratings yet
- Capstone 72Document1 pageCapstone 72ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Capstone 71Document1 pageCapstone 71ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Capstone 73Document1 pageCapstone 73ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Capstone 47Document1 pageCapstone 47ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Capstone 58Document1 pageCapstone 58ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Dost-Phivolcs Alert Level 3Document1 pageDost-Phivolcs Alert Level 3ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Capstone 68Document1 pageCapstone 68ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Bean in A Clear CupDocument1 pageBean in A Clear Cupela kikayNo ratings yet
- Capstone 46Document1 pageCapstone 46ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Capstone 62Document1 pageCapstone 62ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Part B PUBLIC PRACTICE DIFFERENT TYPES OF THREATS UPDATE 1Document3 pagesPart B PUBLIC PRACTICE DIFFERENT TYPES OF THREATS UPDATE 1ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Indonesia's Mount Semeru Eruption Triggered by Heavy Rain and Lava Dome CollapseDocument1 pageIndonesia's Mount Semeru Eruption Triggered by Heavy Rain and Lava Dome Collapseela kikayNo ratings yet
- Capstone 40Document1 pageCapstone 40ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Capstone 37Document1 pageCapstone 37ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Capstone 38Document1 pageCapstone 38ela kikayNo ratings yet
- Fcps 1 FAQDocument9 pagesFcps 1 FAQarslanNo ratings yet
- Classification of Infectious Diseases by The Mechanism of TransmissionDocument17 pagesClassification of Infectious Diseases by The Mechanism of TransmissionAyomide AlayandeNo ratings yet
- B-Cell LymphomaDocument77 pagesB-Cell LymphomaH.B.ANo ratings yet
- Signs and SymptomsDocument6 pagesSigns and Symptomsdareine22No ratings yet
- Eruptive Fever DiseaseDocument61 pagesEruptive Fever DiseasePearl DiBerardino100% (2)
- Tiruneh 2020Document5 pagesTiruneh 2020Shafici CqadirNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Control of Malaria (With A Focus On Sub-Saharan Africa)Document30 pagesEpidemiology and Control of Malaria (With A Focus On Sub-Saharan Africa)Suchie ILyasNo ratings yet
- MEMO - RV RTPCR - MergedDocument5 pagesMEMO - RV RTPCR - MergedMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Selected Differential Diagnosis of Red Eye: Table 1Document3 pagesSelected Differential Diagnosis of Red Eye: Table 1Rian DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Microbial Pathogens and Strategies For Combating Them - Science, Technology and Education (Table of Contents)Document17 pagesMicrobial Pathogens and Strategies For Combating Them - Science, Technology and Education (Table of Contents)Tahmina MonowarNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Fundamentals Nursing ExamDocument7 pagesNCM 103 Fundamentals Nursing ExamJEREMY MAKALINTALNo ratings yet
- Prisons and Health, 9 Infectious Diseases in PrisonDocument8 pagesPrisons and Health, 9 Infectious Diseases in PrisonBam ManNo ratings yet
- COVID-19: Further Evidence That The Virus Originated in The USDocument3 pagesCOVID-19: Further Evidence That The Virus Originated in The USRodolfoANo ratings yet
- Psychoneuroimmunology: From Philosophy, Intuition, and Folklore To A Recognized ScienceDocument6 pagesPsychoneuroimmunology: From Philosophy, Intuition, and Folklore To A Recognized ScienceMita MiftaNo ratings yet
- DR - Vinay PhagocytosisDocument62 pagesDR - Vinay PhagocytosisVinaykumar HallurNo ratings yet
- Salmonella Infections: (Salmonelloses)Document56 pagesSalmonella Infections: (Salmonelloses)andualemNo ratings yet
- Dry Skin Behind Ear Causes and TreatmentsDocument4 pagesDry Skin Behind Ear Causes and Treatmentssunziv19No ratings yet
- Rapid Anti-HIV (1&2) Test: Reagents and Materials SuppliedDocument4 pagesRapid Anti-HIV (1&2) Test: Reagents and Materials Suppliedweli81_131308225No ratings yet
- Verify Urine & Blood Test Reports OnlineDocument9 pagesVerify Urine & Blood Test Reports OnlineRajat singhNo ratings yet
- HEMATOPOIESISDocument65 pagesHEMATOPOIESISDian Artileristiana50% (2)
- Understanding the Immune SystemDocument18 pagesUnderstanding the Immune SystemPrajjwal ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Imhm321 Week 3 Lecture - Abo Blood Group SystemDocument39 pagesImhm321 Week 3 Lecture - Abo Blood Group SystemConsigliereNo ratings yet
- Inflammation: Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DDocument70 pagesInflammation: Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- FOURTH MEETING RickyDocument3 pagesFOURTH MEETING RickyQhie'yPhie ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument3 pagesDaftar PustakamemeeeyyyNo ratings yet
- Kunj. Sakit Se (T 2019Document30 pagesKunj. Sakit Se (T 2019IKBAL HARUNNo ratings yet
- POGI Infection in Pregnancy 2022Document93 pagesPOGI Infection in Pregnancy 2022SDM RSTINo ratings yet
- AIIMS CAPSULE AtfDocument70 pagesAIIMS CAPSULE Atfsimrankaur2003studNo ratings yet
- Tuberculin Skin TestDocument14 pagesTuberculin Skin TestKaioNo ratings yet