Professional Documents
Culture Documents
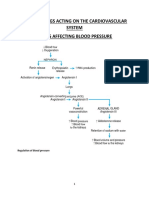
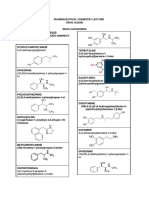
Thiazides:: Block Na/Cl Transporter in Renal Distal Convoluted Tubule
Uploaded by
LA Briguela0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageHypertension Drugs
Original Title
HTN DRUGS1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHypertension Drugs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageThiazides:: Block Na/Cl Transporter in Renal Distal Convoluted Tubule
Uploaded by
LA BriguelaHypertension Drugs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Hypertension Drugs
Sympathoplegics, Sympathetic Nerve α blockers β blockers
Diuretics Centrally Acting Terminal Blockers
Prazosin, Terazosin, Metoprolol,
Reserpine Doxazosin Carvedilol, Nebivolol
Clonidine & Blocks vesicular amine Selectively block α1 Block β1 receptors;
THIAZIDES: Block Na/Cl
transporter in renal distal Methyldopa transporter in adrenoceptors carvedilol also blocks
convoluted tubule Activates Alpha-2 noradrenergic nerves α receptors; nebivolol
-Hydrochlorothiazide also releases nitric
-Metolazone (Popular for use with adrenoceptors and depletes
loop agents for synergistic effects) transmitter stores oxide
-Chlorothiazide (Only parenteral
thiazide available (IV))
-Chlorthalidone (Long half-life
(50–60 h) due to binding to red
blood cells)
LOOP DIURETICS: Block Propanolol
Na/K/2Cl transporter in Guanethidine Nonselective
renal loop of Henle prototype β blocker
-Furosemide Interferes with amine
-Bumetanide and Torsemide
(sulphonamide loop agent similar
release and replaces
to Furosemide) norepinephrine in
-Ethacrynic acid (Not a vesicles
sulfonamide but has typical loop
activity and some uricosuric
action)
Metoprolol, Atenolol
SPIRONOLACTONE: Block Very widely used as
aldosterone receptor in
renal collecting tubule β1-selective blockers
-Eplerenone (Like spironolactone,
more selective for aldosterone
receptor)
You might also like
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Drug Class Mechanism of Action Example: ThiazideDocument2 pagesDrug Class Mechanism of Action Example: ThiazideLyod BalagasayNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Antagonist: PharmacologyDocument3 pagesAdrenergic Antagonist: PharmacologyJB RSNJNNo ratings yet
- Anti Adrenergic Drug1Document13 pagesAnti Adrenergic Drug1Ravi KaushikNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agents SeminarDocument48 pagesAdrenergic Agents SeminarTheBoss 20No ratings yet
- Drug ClassesDocument5 pagesDrug ClassesZaira Clarisse de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agents: University of Negros Occidental-RecoletosDocument66 pagesAdrenergic Agents: University of Negros Occidental-Recoletosmary grace trinidadNo ratings yet
- Pharmacodynamics How Drugs WorkDocument21 pagesPharmacodynamics How Drugs WorkWen SilverNo ratings yet
- Pharma 2Document6 pagesPharma 2Mohammad ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 31: Adrenergic Antagonists: Drug ListDocument7 pagesChapter 31: Adrenergic Antagonists: Drug ListMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- 2015 Psych DrugsDocument1 page2015 Psych DrugsmounicapaturuNo ratings yet
- 3 Treatment of HypertensionDocument7 pages3 Treatment of HypertensiontiaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Adrenoceptor Antagonist DrugsDocument7 pagesChapter 10 Adrenoceptor Antagonist DrugsChristine Annmarie TapawanNo ratings yet
- Ans NursingDocument15 pagesAns Nursingwww.nikhilbabu123No ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Movement Disorders: Christian WaeberDocument34 pagesPharmacology of Drugs Used in Movement Disorders: Christian WaeberciaranNo ratings yet
- Sedative Hypnotics - RAMELTEON: Not Metabolized by CYP3A4 MOA Pharmacokinetics Indications AE CI BenzodiazepinesDocument3 pagesSedative Hypnotics - RAMELTEON: Not Metabolized by CYP3A4 MOA Pharmacokinetics Indications AE CI BenzodiazepinesJOSLIN ROZ GALILEANo ratings yet
- PHARM Ven InjectableAnestheticsDocument28 pagesPHARM Ven InjectableAnestheticsDhaif dhaifNo ratings yet
- The Hitchhiker's Guide To Clinical Pharmacology: Pharmacodynamics: How Drugs WorkDocument23 pagesThe Hitchhiker's Guide To Clinical Pharmacology: Pharmacodynamics: How Drugs WorkMylz MendozaNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument29 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistsBenedict Brashi100% (1)
- Unit 03: Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular System Drugs Affecting Blood PressureDocument12 pagesUnit 03: Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular System Drugs Affecting Blood PressureDental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument236 pagesPharmacologynbde2100% (5)
- List of Drugs Pharmacology 2Document13 pagesList of Drugs Pharmacology 2Maisarah Ab SamadNo ratings yet
- The Sedative/Hypnotics: Durmishkhan Akhsabadze, MDDocument79 pagesThe Sedative/Hypnotics: Durmishkhan Akhsabadze, MDminakshi bossNo ratings yet
- Right-Hand Tremor at Rest, WhichDocument47 pagesRight-Hand Tremor at Rest, WhichsyarintaadeninaNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument18 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistsKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- 03 Sympathomimetics-And-Blockers NCM206Document9 pages03 Sympathomimetics-And-Blockers NCM206julinka beyla yansonNo ratings yet
- SY - Medichem I - Adrenergic BlockersDocument38 pagesSY - Medichem I - Adrenergic BlockersKevalNo ratings yet
- Alpha Blockers PharmacologyDocument23 pagesAlpha Blockers PharmacologyHesbon MomanyiNo ratings yet
- General PharmacologyDocument136 pagesGeneral Pharmacologyyayooo2004No ratings yet
- Adrenergic Antagonists EditedDocument60 pagesAdrenergic Antagonists EditedJohn Benedict VocalesNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistDocument30 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistOmar AlaamNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Cardiovascular DrugsDocument27 pagesPharmacology Cardiovascular DrugsMitzel AlvaranNo ratings yet
- NAPLEX Mechanisms of ActionsDocument10 pagesNAPLEX Mechanisms of ActionsVerinice Nañasca67% (3)
- Anti ConvulsantsDocument23 pagesAnti ConvulsantsRaman Kumar0% (1)
- Benzo ChartDocument1 pageBenzo Chartnateman216No ratings yet
- 277 761972 UnitIIDocument31 pages277 761972 UnitIIASMITNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Concept MapDocument1 pageHypertension Concept MapmetNo ratings yet
- Kimia Medisinal Antiadrenergic 4BDocument46 pagesKimia Medisinal Antiadrenergic 4BDina Sulastiyo MurtiNo ratings yet
- Pharm 3 BDocument3 pagesPharm 3 Bravi2likeNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Antagonists - Alpha BlockersDocument13 pagesAdrenergic Antagonists - Alpha BlockersLaiba IkramNo ratings yet
- Sympatholytics Alpha BlockersDocument22 pagesSympatholytics Alpha BlockersbetacancrisNo ratings yet
- 5 Adrenoceptor BlockersDocument52 pages5 Adrenoceptor BlockersHamid Hussain HamidNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology IV L5Document4 pagesPharmacology IV L5سلطان القلحNo ratings yet
- TMC Intravenous Anaesthetic AgentsDocument15 pagesTMC Intravenous Anaesthetic AgentsJey RajNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Drugs 2015Document48 pagesAdrenergic Drugs 2015Rizki SariWahyuniNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotics: There Is No Cure For Schizophrenia Just Symptomatic Control Is DoneDocument48 pagesAntipsychotics: There Is No Cure For Schizophrenia Just Symptomatic Control Is Donevarsham2No ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Parkinsonism: Functional Circuitry Between The Cortex, Basal Ganglia, and ThalamusDocument5 pagesDrugs Used in Parkinsonism: Functional Circuitry Between The Cortex, Basal Ganglia, and ThalamusHamad AlshabiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs TaskDocument2 pagesCardiovascular Drugs TaskMaily OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFDocument21 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFAndres F. TorresNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology HandoutDocument5 pagesPharmacology HandoutMark Elben Teodoro100% (1)
- College of Nursing: 1 Semester (S.Y. 2019-2020)Document87 pagesCollege of Nursing: 1 Semester (S.Y. 2019-2020)Francis PeterosNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System Pharmacology: Elly Nurus SakinahDocument64 pagesCentral Nervous System Pharmacology: Elly Nurus Sakinahkareem92No ratings yet
- Tufts Med ListDocument5 pagesTufts Med ListMarisa Deana Pontrelli100% (1)
- Sistem Saraf Otonom PPT Fartoks Sabtu PagiDocument27 pagesSistem Saraf Otonom PPT Fartoks Sabtu PagiNur HafidahNo ratings yet
- Untitlednf Fli DJ Ig Tu JDocument30 pagesUntitlednf Fli DJ Ig Tu JBEST OF BESTNo ratings yet
- PR STEPLADDER CTS AmmaliaDocument27 pagesPR STEPLADDER CTS AmmaliaAmmalia RachmiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument14 pagesPharmacology SummaryteddyjolinNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System Drugs: Endogenous AdrenergicsDocument23 pagesAutonomic Nervous System Drugs: Endogenous AdrenergicsGrace HernandezNo ratings yet
- 3B Ids 2Document32 pages3B Ids 2LA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- RAD Radiographic Features of Common ArthritidesDocument7 pagesRAD Radiographic Features of Common ArthritidesLA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- 18.8 ENT I Head and Neck 2Document23 pages18.8 ENT I Head and Neck 2LA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- PHARCHEM2 LIST Hormones To Cardiovascular DrugsDocument7 pagesPHARCHEM2 LIST Hormones To Cardiovascular DrugsLA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- PHARCHEM2 List AntimicrobialsDocument14 pagesPHARCHEM2 List AntimicrobialsLA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- Leaves: Ma. Lourdes Angela V. Briguela - 1B-PH - 2014-2015Document16 pagesLeaves: Ma. Lourdes Angela V. Briguela - 1B-PH - 2014-2015LA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- Fruits: Ma. Lourdes Angela V. Briguela - 1B-PH - 2014-2015Document16 pagesFruits: Ma. Lourdes Angela V. Briguela - 1B-PH - 2014-2015LA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- Flowers: Ma. Lourdes Angela V. Briguela - 1B-PH - 2014-2015Document9 pagesFlowers: Ma. Lourdes Angela V. Briguela - 1B-PH - 2014-2015LA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicDocument2 pagesAnalgesicLA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- Pharchem2 Drug AlbumDocument40 pagesPharchem2 Drug AlbumLA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- Management of Ascites in Children Lane2015Document13 pagesManagement of Ascites in Children Lane2015Henry BarberenaNo ratings yet
- A Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument8 pagesA Fluids and ElectrolytesAnastasiafynnNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument37 pagesCase StudyAnonymous t78m8ku100% (1)
- Plabable-Gems-28. Pharmacology Plabable GemsDocument60 pagesPlabable-Gems-28. Pharmacology Plabable GemsHabo HaboNo ratings yet
- Obat-Obat KardiovaskulerDocument50 pagesObat-Obat KardiovaskulerMuhammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Diuretic DrugsDocument16 pagesDiuretic DrugslabillabooNo ratings yet
- 05-Physical Examination of UrineDocument7 pages05-Physical Examination of Urinekalantan23No ratings yet
- Teaching PlanDocument14 pagesTeaching Planapi-620190735No ratings yet
- 6.1. AntihipertensiDocument52 pages6.1. AntihipertensiDada DoniNo ratings yet
- Fluid Balance Case StudyDocument9 pagesFluid Balance Case StudyAna BienneNo ratings yet
- Module 8 PharmaDocument34 pagesModule 8 PharmaGin MananganNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument27 pagesHypertensionAnamika ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument9 pagesAcknowledgementjhzenNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 3 Blok KV: Casey Vira AprilleaDocument70 pagesPemicu 3 Blok KV: Casey Vira AprilleaCASEY VIRA APRILLEANo ratings yet
- SCIT 1408 Applied Human Anatomy and Physiology II - Urinary System Chapter 25 BDocument50 pagesSCIT 1408 Applied Human Anatomy and Physiology II - Urinary System Chapter 25 BChuongNo ratings yet
- K Disorders CCN PDFDocument14 pagesK Disorders CCN PDFLuis CuestaNo ratings yet
- N E D L G National Essential Drug List &guidelinesDocument32 pagesN E D L G National Essential Drug List &guidelinesportosinNo ratings yet
- Prof. Mark Jheran Alvarez, USRN, MAN-MSDocument52 pagesProf. Mark Jheran Alvarez, USRN, MAN-MSMark Jheran AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi Sistem RenalDocument89 pagesFarmakoterapi Sistem RenalNhovieNhowaaNo ratings yet
- Mannitol and PhenytoinDocument15 pagesMannitol and PhenytoinirmaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics - AMBOSS PDFDocument9 pagesDiuretics - AMBOSS PDFOpio Isaac100% (1)
- Pharmacology MCQS WITH ANS (1) - CompressedDocument289 pagesPharmacology MCQS WITH ANS (1) - Compressed09Dhawal PatilNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes (ClinchemDocument5 pagesElectrolytes (ClinchemGail IbanezNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Pediatric CardiologyDocument425 pagesEssentials of Pediatric CardiologySyed Alam100% (2)
- The Turkey Book - An Introductory Manual For The WardsDocument147 pagesThe Turkey Book - An Introductory Manual For The WardsThe Physician Assistant LifeNo ratings yet
- El Mal Día de Harry MannDocument5 pagesEl Mal Día de Harry MannAdriana Plata BecerrilNo ratings yet
- Nle Pentagon Reviewer For Nclex Answer QuestionsDocument30 pagesNle Pentagon Reviewer For Nclex Answer QuestionsSpoonNo ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive Drugs - DiureticsDocument49 pagesAnti Hypertensive Drugs - DiureticsApurba Sarker Apu100% (1)
- NCP For CHFDocument11 pagesNCP For CHFqingwen100% (5)
- Furosemide in Infant and XhildrenDocument5 pagesFurosemide in Infant and XhildrenAbdi KebedeNo ratings yet