Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AP Psychology Brain Imaging Techniques N
AP Psychology Brain Imaging Techniques N
Uploaded by
이정은0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageThis document provides an overview of several brain imaging techniques including their descriptions, purposes, and typical patient procedures. EEG records electrical brain activity through electrodes on the scalp and is widely used in sleep research. CT and MRI produce detailed 3D images of brain structure, with MRI providing additional information on brain activity and density. PET scans track radioactive tracers to create maps of active brain regions. fMRI combines MRI and PET techniques to link brain structure with activity during tasks. MEG and DTI are newer techniques, with MEG measuring magnetic fields and DTI examining white matter connections between brain areas.
Original Description:
Original Title
AP Psychology Brain Imaging Techniques n
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of several brain imaging techniques including their descriptions, purposes, and typical patient procedures. EEG records electrical brain activity through electrodes on the scalp and is widely used in sleep research. CT and MRI produce detailed 3D images of brain structure, with MRI providing additional information on brain activity and density. PET scans track radioactive tracers to create maps of active brain regions. fMRI combines MRI and PET techniques to link brain structure with activity during tasks. MEG and DTI are newer techniques, with MEG measuring magnetic fields and DTI examining white matter connections between brain areas.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageAP Psychology Brain Imaging Techniques N
AP Psychology Brain Imaging Techniques N
Uploaded by
이정은This document provides an overview of several brain imaging techniques including their descriptions, purposes, and typical patient procedures. EEG records electrical brain activity through electrodes on the scalp and is widely used in sleep research. CT and MRI produce detailed 3D images of brain structure, with MRI providing additional information on brain activity and density. PET scans track radioactive tracers to create maps of active brain regions. fMRI combines MRI and PET techniques to link brain structure with activity during tasks. MEG and DTI are newer techniques, with MEG measuring magnetic fields and DTI examining white matter connections between brain areas.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
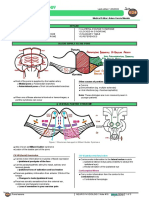
AP Psychology
AVHS/Emerson
BRAIN IMAGING TECHNIQUES
Name Description Purpose Patient Info
• records electrical
Produces amplified activity of brain • patient lying down;
EEG tracings of waves of electrodes placed on
Electroencephalograph • widely used in sleep
electrical activity in brain research scalp
CT A sophisticated x-ray; • can only show • patient lies down as
Computerized uses several x-ray structure of brain platform moves slowly
Tomography cameras to rotate through scanning ring
around the brain and • able to detect tumors
CAT form a detailed 3D • exposure to
Computerized Axial picture of carcinogenic radiation
Tomography brain structure
Uses magnetic fields • provides detailed • patient secured to
and radio waves to make picture of brain structure platform in scanner
MRI computer-generated
Magnetic Resonance images; • measures density and • must remain
Imaging produces visual “slices” location of brain material motionless during
of brain procedure
• enables researchers to • patient injected with
Produces visual display see what areas of brain radioactive tracer;
PET of brain activity are most active during detectors track release
Positron Emission certain tasks of gamma rays around
Tomography Computer translates • different scans used for patient’s head
signals into map of brain different chemicals such • patient may be asked
at work as neurotransmitters, to respond to stimuli or
drugs, & oxygen flow perform simple tasks
• shows details of brain • patient secured to
fMRI Combines elements of structure with info about platform in scanner
MRI and PET scans blood flow in the brain,
Functional Magnetic linking brain structure • patient may be asked
Resonance Imaging with brain activity during to respond to stimuli or
cognitive tasks perform simple tasks
• uses a device that
Study of the magnetic • used primarily for looks like a large
MEG fields generated by the research on brain helmet; placed over the
Magnetoencephalography brain through neural activity patient's head in a
activity specially shielded room
• fast, non-invasive
DTI • used to uncover minute
Variation of MRI structural aberrations in • uses fMRI scanner; pt
Diffusion Tensor scannner; uses specific brain; esp useful for secured to platform;
Imaging radio-frequency and examining the neurology takes about 15 minutes
magnetic field-gradient of psychological longer than MRI
pulses to track disorders & producing
movement of water more-targeted
molecules in brain, treatments
enabling scientists to • examines complex
create pictures of axons network of nerve fibers
(white matter) connecting the different
brain areas
You might also like
- Barr's The Human Nervous System: An Anatomical Viewpoint: Kiernan, J. A Rajakumar, NagalingamDocument4 pagesBarr's The Human Nervous System: An Anatomical Viewpoint: Kiernan, J. A Rajakumar, NagalingamSaras Agrawal0% (1)
- Hart ChartDocument3 pagesHart ChartbarukiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Neuroscience - LATEST (PART2)Document54 pagesUnit 3 - Neuroscience - LATEST (PART2)farah nabihahNo ratings yet
- 01-A-Single & Multi-Unit Electrophysiology-Grp14Document17 pages01-A-Single & Multi-Unit Electrophysiology-Grp14burnerbharadwajNo ratings yet
- Sanger 2024 J. Neural Eng. 21 012001Document15 pagesSanger 2024 J. Neural Eng. 21 012001RenanzinhooNo ratings yet
- Braingate SystemDocument7 pagesBraingate SystemAdithi StarNo ratings yet
- Brain ImagingDocument14 pagesBrain ImagingSenal Malaka PremarathnaNo ratings yet
- Brain Computer Interface (BCI)Document28 pagesBrain Computer Interface (BCI)nikhil kumarNo ratings yet
- Bci IeeeDocument6 pagesBci Ieeedesai.achyutakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Department of Instrumentation EngineeringDocument28 pagesDepartment of Instrumentation EngineeringMahi KatreNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER IN Physiological PsychDocument11 pagesREVIEWER IN Physiological PsychSaera VixoNo ratings yet
- EEG - Feature ExtractionDocument5 pagesEEG - Feature Extractiondumperacct123No ratings yet
- FullSlides Ch7 Imaging Brain ActivityDocument64 pagesFullSlides Ch7 Imaging Brain ActivityShusmita DiptiNo ratings yet
- Artificial Neural NetworksDocument25 pagesArtificial Neural NetworksSabri ALtmemiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 AI - Neural NetworksDocument11 pagesUnit 3 AI - Neural Networksharrshanrmt20No ratings yet
- Brain Computer Interface (BCI) : Visit To DownloadDocument28 pagesBrain Computer Interface (BCI) : Visit To Downloadnikhil RathiNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiological Brain Connectivity Theory andDocument25 pagesElectrophysiological Brain Connectivity Theory andl.fernandezNo ratings yet
- Neuralink PosterDocument1 pageNeuralink PosterDarshan JainNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document33 pagesUnit 2SasikumarNo ratings yet
- Cognitivepsych-Ch 3Document31 pagesCognitivepsych-Ch 3mylene davidNo ratings yet
- Bio Psy 5Document21 pagesBio Psy 5ayşe tankırNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computational NeuroscienceDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Computational NeuroscienceNotes SekarNo ratings yet
- M Ashford 2017Document6 pagesM Ashford 2017M Junaid SultanNo ratings yet
- PSYC 2410 DE S12 Textbook Notes Chapter 05 PDFDocument17 pagesPSYC 2410 DE S12 Textbook Notes Chapter 05 PDFKatarina GruborovićNo ratings yet
- Neurosky TechnologyDocument23 pagesNeurosky TechnologyTejasriVarma100% (2)
- Module2 4Document8 pagesModule2 4joan1239gabbyNo ratings yet
- Visit To DownloadDocument28 pagesVisit To DownloadSara WadeNo ratings yet
- Visit To DownloadDocument28 pagesVisit To DownloadSumanta BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Module 19Document135 pagesModule 19leomillmendiolaNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of A Wireless Multi-Channel EEG RecordingDocument6 pagesDesign and Implementation of A Wireless Multi-Channel EEG RecordingmasilelakbNo ratings yet
- Outline: - Brief Overview of Neuroimaging ModalitiesDocument62 pagesOutline: - Brief Overview of Neuroimaging ModalitiesMeric OzcanNo ratings yet
- Cureus 0014 00000021982 PDFDocument9 pagesCureus 0014 00000021982 PDFHafizhah Al HusnaNo ratings yet
- Core Studies - Canli Et Al 2000Document51 pagesCore Studies - Canli Et Al 2000Arundhati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Methods and Strategies of ResearchDocument6 pagesChapter 5 - Methods and Strategies of Researchmanilyn dacoNo ratings yet
- Brain Gate System1Document10 pagesBrain Gate System1helloNo ratings yet
- 03a ApplicationsDocument49 pages03a ApplicationsdagushNo ratings yet
- Diorio 2003Document7 pagesDiorio 2003diliplokande46No ratings yet
- Deep Learning Algorithm For Brain-Computer InterfaDocument12 pagesDeep Learning Algorithm For Brain-Computer InterfaRabah AlobaidyNo ratings yet
- HP1000 - AY23-24S2 - Biopsychology and NeuroscienceDocument47 pagesHP1000 - AY23-24S2 - Biopsychology and NeurosciencedelaninjonNo ratings yet
- 11 NeuralNetsDocument51 pages11 NeuralNetsxenef14809No ratings yet
- Electroencephalography: Source of EEG ActivityDocument16 pagesElectroencephalography: Source of EEG ActivityEmonNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument2 pagesSeminar ReportSathvick BatchuNo ratings yet
- Brain Gate: Name:Tejas .P.Bhandari Seat No:77 T.Y.B.C.A Sem-6Document24 pagesBrain Gate: Name:Tejas .P.Bhandari Seat No:77 T.Y.B.C.A Sem-6Khushboo Kirtikumar DesaiNo ratings yet
- Brain Machine Interface: Vidya R. ADocument6 pagesBrain Machine Interface: Vidya R. ANaveen NarayanNo ratings yet
- 6-Neural NTDocument44 pages6-Neural NTSAMRIDDHI JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Eeg CT Mri EtcDocument17 pagesEeg CT Mri EtcSana chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Biopsychology Chapter 1.5Document22 pagesBiopsychology Chapter 1.5Hannah DiñosoNo ratings yet
- EEG - Brainbit-SpecificationDocument2 pagesEEG - Brainbit-SpecificationSergio OlivieriNo ratings yet
- Artificial Neural Networks and Deep LearningDocument372 pagesArtificial Neural Networks and Deep LearningMostafa Hazem Mostafa attiaNo ratings yet
- Sample - Seminar ppt1Document14 pagesSample - Seminar ppt1PoojaNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Study of EEG Based Brain Computer InterDocument8 pagesA Detailed Study of EEG Based Brain Computer InterRishi CRMNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document17 pagesLecture 4Mujeeb khanNo ratings yet
- Classification of MRI Brain Images Using Neuro Fuzzy Model: Mr. Lalit P. Bhaiya, Ms. Suchita GoswamiDocument5 pagesClassification of MRI Brain Images Using Neuro Fuzzy Model: Mr. Lalit P. Bhaiya, Ms. Suchita GoswamiSamson LinusNo ratings yet
- 1 - IntroductionDocument34 pages1 - IntroductionRaj SahaNo ratings yet
- Stimulation of Neuronal Activity With LightDocument29 pagesStimulation of Neuronal Activity With LightThe Panda EntertainerNo ratings yet
- Seminar PPT - Swasti AggarwalDocument10 pagesSeminar PPT - Swasti AggarwalnipakforeverNo ratings yet
- An Augmented-Reality fNIRS-Based Brain-Computer Interface - A Proof-of-Concept StudyDocument25 pagesAn Augmented-Reality fNIRS-Based Brain-Computer Interface - A Proof-of-Concept StudyQBod27No ratings yet
- The-BrainDocument49 pagesThe-BrainBaciu Florina GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Lecture SlidesDocument51 pagesChapter 5 Lecture SlidesJosh SauverwaldNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: EEG Basics: Introduction To Modern Brain-Computer Interface Design Christian A. Kothe SCCN, UcsdDocument54 pagesLecture 2: EEG Basics: Introduction To Modern Brain-Computer Interface Design Christian A. Kothe SCCN, UcsdGilberto PerpiñanNo ratings yet
- How Your Brain and Nervous System WorksDocument14 pagesHow Your Brain and Nervous System WorksgkshishirNo ratings yet
- Memory Review SheetDocument2 pagesMemory Review Sheet이정은No ratings yet
- Mini AP Practice ExamDocument4 pagesMini AP Practice Exam이정은No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Tutorial: Consumer Choice and DemandDocument41 pagesMultiple Choice Tutorial: Consumer Choice and Demand이정은No ratings yet
- History and Approaches (2-4%) : IntrospectionDocument11 pagesHistory and Approaches (2-4%) : Introspection이정은No ratings yet
- Diagnosis BandingDocument19 pagesDiagnosis BandingoliviaNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument17 pagesStrokeSathias SundariNo ratings yet
- 134 - Neurology Pathology) Pons LesionsDocument5 pages134 - Neurology Pathology) Pons LesionsTamaraNo ratings yet
- DAFTARPUSTAKADocument2 pagesDAFTARPUSTAKARiri Angga NingrumNo ratings yet
- Lower Back Pain: A Need For Thorough Assessment: Practice Nursing September 2011Document6 pagesLower Back Pain: A Need For Thorough Assessment: Practice Nursing September 2011gursangeetNo ratings yet
- Dose-Response Study of N, N-Dimethyltryptamine in HumansDocument11 pagesDose-Response Study of N, N-Dimethyltryptamine in HumansAnonymous zxTFUoqzklNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar Pustakachica_asNo ratings yet
- Neuro HistologyDocument52 pagesNeuro HistologyZhiev Owen SullivanNo ratings yet
- Emergency Neurological Life Support: Intracranial Hypertension and HerniationDocument7 pagesEmergency Neurological Life Support: Intracranial Hypertension and HerniationPablo IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord InjuriesDocument51 pagesSpinal Cord Injurieswanglee2000No ratings yet
- POSTUROLOGIE PPSXDocument187 pagesPOSTUROLOGIE PPSXmihael26100% (9)
- Brain Gate Neural Interface Sysytem: by Lakshmi I V Btech Clg-HydDocument23 pagesBrain Gate Neural Interface Sysytem: by Lakshmi I V Btech Clg-Hydshaik nazneenNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology Chapter 2Document28 pagesAP Psychology Chapter 2Phil JacksonNo ratings yet
- CP PPT 10-11-11Document49 pagesCP PPT 10-11-11Eaht QuirongNo ratings yet
- Electric Shock/Lightning Injury: Key QuestionsDocument2 pagesElectric Shock/Lightning Injury: Key QuestionsarniwiantiNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide Unit 5: Unit 5: The Adolescent Brain and NeuroscienceDocument5 pagesLearning Guide Unit 5: Unit 5: The Adolescent Brain and Neurosciencemaconny20No ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W4Document6 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W4Racquel NerosaNo ratings yet
- BehaviourismDocument9 pagesBehaviourismVijeyachandhar DorairajNo ratings yet
- Nervous System-Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument64 pagesNervous System-Anatomy & PhysiologyDeshi SportsNo ratings yet
- ISNCSCI ASIA Spanish TranslationDocument5 pagesISNCSCI ASIA Spanish TranslationElsaPepperNo ratings yet
- General Psychology Prelim ExamDocument11 pagesGeneral Psychology Prelim ExamSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- CatatoniaDocument74 pagesCatatoniadrkadiyala2100% (1)
- Pain Management in The Emergency: Dr. Prathiba Prasad Emergency Physician Masafi HospitalDocument50 pagesPain Management in The Emergency: Dr. Prathiba Prasad Emergency Physician Masafi HospitalPrathiba PrassaddNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and BooksDocument41 pagesPhilosophy and BooksVandana Kannan100% (1)
- Unit 7 Study GuideDocument4 pagesUnit 7 Study GuideIan StantonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of CNS and PNSDocument72 pagesAnatomy of CNS and PNSTony Hermawan100% (1)
- Lesson 22 ECG TracesDocument13 pagesLesson 22 ECG TracesGemma WrigleyNo ratings yet
- Polygraphy ReviewDocument129 pagesPolygraphy ReviewKAPITAN TUMBA100% (1)