Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Paging in Operating System: Example
Uploaded by
Aastha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views4 pagesPaging is a memory management scheme that allows non-contiguous allocation of physical memory. It divides both logical and physical address spaces into fixed-size blocks called pages and frames respectively. The memory management unit maps virtual to physical addresses using a page table, which can be stored in registers for small tables or cached using a translation lookaside buffer for larger tables.
Original Description:
Original Title
Page Table Concepts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPaging is a memory management scheme that allows non-contiguous allocation of physical memory. It divides both logical and physical address spaces into fixed-size blocks called pages and frames respectively. The memory management unit maps virtual to physical addresses using a page table, which can be stored in registers for small tables or cached using a translation lookaside buffer for larger tables.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views4 pagesPaging in Operating System: Example
Uploaded by
AasthaPaging is a memory management scheme that allows non-contiguous allocation of physical memory. It divides both logical and physical address spaces into fixed-size blocks called pages and frames respectively. The memory management unit maps virtual to physical addresses using a page table, which can be stored in registers for small tables or cached using a translation lookaside buffer for larger tables.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Paging in Operating System
Paging is a memory management scheme that eliminates the need for contiguous
allocation of physical memory. This scheme permits the physical address space of
a process to be non – contiguous.
Logical Address or Virtual Address (represented in bits): An address
generated by the CPU
Logical Address Space or Virtual Address Space( represented in words or
bytes): The set of all logical addresses generated by a program
Physical Address (represented in bits): An address actually available on
memory unit
Physical Address Space (represented in words or bytes): The set of all physical
addresses corresponding to the logical addresses
Example:
If Logical Address = 31 bit, then Logical Address Space = 231 words = 2 G
words (1 G = 230)
If Logical Address Space = 128 M words = 27 * 220 words, then Logical
Address = log2 227 = 27 bits
If Physical Address = 22 bit, then Physical Address Space = 222 words = 4 M
words (1 M = 220)
If Physical Address Space = 16 M words = 24 * 220 words, then Physical
Address = log2 224 = 24 bits
The mapping from virtual to physical address is done by the memory management
unit (MMU) which is a hardware device and this mapping is known as paging
technique.
The Physical Address Space is conceptually divided into a number of fixed-size
blocks, called frames.
The Logical address Space is also splitted into fixed-size blocks, called pages.
Page Size = Frame Size
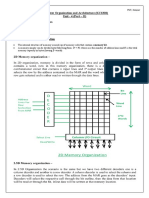
Let us consider an example:
Physical Address = 12 bits, then Physical Address Space = 4 K words
Logical Address = 13 bits, then Logical Address Space = 8 K words
Page size = frame size = 1 K words (assumption)
Address generated by CPU is divided into
Page number(p): Number of bits required to represent the pages in Logical
Address Space or Page number
Page offset(d): Number of bits required to represent particular word in a page or
page size of Logical Address Space or word number of a page or page offset.
Physical Address is divided into
Frame number(f): Number of bits required to represent the frame of Physical
Address Space or Frame number.
Frame offset(d): Number of bits required to represent particular word in a frame
or frame size of Physical Address Space or word number of a frame or frame
offset.
The hardware implementation of page table can be done by using dedicated
registers. But the usage of register for the page table is satisfactory only if page
table is small. If page table contain large number of entries then we can use
TLB(translation Look-aside buffer), a special, small, fast look up hardware cache.
The TLB is associative, high speed memory.
Each entry in TLB consists of two parts: a tag and a value.
When this memory is used, then an item is compared with all tags
simultaneously.If the item is found, then corresponding value is returned.
You might also like
- Language and The Pursuit of Hap - Chalmers BrothersDocument1,184 pagesLanguage and The Pursuit of Hap - Chalmers BrothersGeorge Adrian Oprea100% (2)
- Rough Translation of Emil Stejnar's Schutzengel BookDocument119 pagesRough Translation of Emil Stejnar's Schutzengel BookJustA Dummy100% (1)
- Assembly Programming:Simple, Short, And Straightforward Way Of Learning Assembly LanguageFrom EverandAssembly Programming:Simple, Short, And Straightforward Way Of Learning Assembly LanguageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Anatomy of A Program in MemoryDocument5 pagesAnatomy of A Program in Memorythong_bvtNo ratings yet
- Assignment / Tugasan HBEF3703 Introduction To Guidance and Counselling / May 2021 SemesterDocument8 pagesAssignment / Tugasan HBEF3703 Introduction To Guidance and Counselling / May 2021 SemesterTHURGANo ratings yet
- Nielsen Millennial Traveler Study Jan 2017Document11 pagesNielsen Millennial Traveler Study Jan 2017nhocti1610No ratings yet
- Paging in Operating SystemDocument1 pagePaging in Operating SystemMuhammad Usman NasirNo ratings yet
- Lec 22-24 Paging + TLBDocument31 pagesLec 22-24 Paging + TLBRIYANo ratings yet
- Name:M Faizan CH ID#S2016266035 Resource Person: Sir Owais Hakeem Assignmnet#3Document5 pagesName:M Faizan CH ID#S2016266035 Resource Person: Sir Owais Hakeem Assignmnet#3faizanNo ratings yet
- PagingDocument76 pagesPagingAnonymous RuslwNZZlNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Memory Management: June 03, 2013Document62 pagesOperating Systems Memory Management: June 03, 2013Zafar DarNo ratings yet
- Memorymanagement 160901110114Document56 pagesMemorymanagement 160901110114Quốc TrưởngNo ratings yet
- Unit 5memory ManagementDocument59 pagesUnit 5memory Managementtamannayadav741No ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 SolutionDocument8 pagesTutorial 7 Solution21803013No ratings yet
- Midterm PracticeDocument7 pagesMidterm PracticeZhang YoudanNo ratings yet
- CS401 Glossary CS401Document7 pagesCS401 Glossary CS401hassan_m2222No ratings yet
- PagingDocument45 pagesPagingManalAmerNo ratings yet
- Virtual Memory and Address Translation: ReviewDocument15 pagesVirtual Memory and Address Translation: Reviewarsi_marsNo ratings yet
- Memory Management UpdatedDocument115 pagesMemory Management UpdatedAbhinay YadavNo ratings yet
- Memory Management OverviewDocument9 pagesMemory Management OverviewbernardoakoNo ratings yet
- Windows Memory Management: Page Directory Page Tables Physical AddressDocument5 pagesWindows Memory Management: Page Directory Page Tables Physical Addressjesusda91No ratings yet
- MCS 012Document65 pagesMCS 012Vishal ThakorNo ratings yet
- MCS12Document65 pagesMCS12manigandankindlyNo ratings yet
- PagingDocument5 pagesPagingJACOB RACHUONYONo ratings yet
- Unit-3 (OS)Document36 pagesUnit-3 (OS)rishi reddyNo ratings yet
- SegmentationDocument10 pagesSegmentationRavindra MoteNo ratings yet
- Paging ND SegDocument38 pagesPaging ND Segcrishna411No ratings yet
- CS330 Operating System Part VDocument13 pagesCS330 Operating System Part VHarsh BihanyNo ratings yet
- Memory Management1Document58 pagesMemory Management1Manoj YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 5memory ManagementDocument61 pagesUnit 5memory Managementharshkumarbalaji117No ratings yet
- NumericalDocument9 pagesNumericalSK ANARULNo ratings yet
- MIC Ut1Document6 pagesMIC Ut1Prathamesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Data and Program RepresentationDocument7 pagesData and Program RepresentationkarkarpatiatNo ratings yet
- ExampleDocument9 pagesExamplesubash1111@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Logical AddressDocument5 pagesLogical Addressanjali gautamNo ratings yet
- Cache Memory in Computer OrganizatinDocument12 pagesCache Memory in Computer OrganizatinJohn Vincent BaylonNo ratings yet
- Chariya Assignment 5Document12 pagesChariya Assignment 5ravindu_rathnayakaNo ratings yet
- Memory Management: Background Swapping Contiguous AllocationDocument51 pagesMemory Management: Background Swapping Contiguous AllocationFazrul RosliNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document48 pagesModule 5Maheshvar ChandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Memory Management - IIDocument14 pagesMemory Management - II2200031111csehNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7: Ee15B124: H.Sahithya Kavya Ee15B127: Shyam Shankar H R November 6, 2017Document5 pagesAssignment 7: Ee15B124: H.Sahithya Kavya Ee15B127: Shyam Shankar H R November 6, 2017Shyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- T1Ch4Document53 pagesT1Ch4one09moreNo ratings yet
- Unit III Lecture 6 Memory Allocation Techniques Part IIIDocument5 pagesUnit III Lecture 6 Memory Allocation Techniques Part III964swati.thakurNo ratings yet
- S3-Lesson IIIDocument26 pagesS3-Lesson IIIEdouard Mvogo BilegueNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A Program in MemoryDocument19 pagesAnatomy of A Program in MemoryVictor J. PerniaNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and Architecture: Ashok Kumar TurukDocument54 pagesComputer Organization and Architecture: Ashok Kumar TurukSatya DasNo ratings yet
- NumericalupDocument9 pagesNumericalupSK ANARULNo ratings yet
- Data AnaDocument12 pagesData AnaranjithkumargruNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 PartDocument6 pagesUnit 4 PartArnav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 8086 ProcessorDocument49 pages8086 ProcessorLolllNo ratings yet
- STUDY OF 8086/8088: Assembler Is An Intermediate Program, Which Converts AssemblyDocument15 pagesSTUDY OF 8086/8088: Assembler Is An Intermediate Program, Which Converts AssemblyShashank SoodNo ratings yet
- Direct Mapping: Each Word in Cache Consists of The Data Word and It Associated TagDocument11 pagesDirect Mapping: Each Word in Cache Consists of The Data Word and It Associated TagAkshat KeshariNo ratings yet
- LEC78 Mem MGTDocument32 pagesLEC78 Mem MGTpaul mulwaNo ratings yet
- Mmu - Intel PentiumVsLinuxDocument5 pagesMmu - Intel PentiumVsLinuxMarilisaNo ratings yet
- Computer OrganizationDocument8 pagesComputer Organizationmeenakshimeenu480No ratings yet
- Lecture (Chapter 9)Document55 pagesLecture (Chapter 9)ekiholoNo ratings yet
- CSC 5sem CS2304NOLDocument60 pagesCSC 5sem CS2304NOLVinay Kshatriya HalNo ratings yet
- 602Document9 pages602Jas LimNo ratings yet
- Virtual Memory Address TranslationDocument4 pagesVirtual Memory Address TranslationNitin SoniNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 05 - Memory ManagementDocument57 pagesChapter - 05 - Memory ManagementDuy Bùi LêNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization & Assembly Languages: (After Mid 1)Document52 pagesComputer Organization & Assembly Languages: (After Mid 1)Ahmed RaoNo ratings yet
- AMP Module VDocument30 pagesAMP Module Vselva33No ratings yet
- Modern Introduction to Object Oriented Programming for Prospective DevelopersFrom EverandModern Introduction to Object Oriented Programming for Prospective DevelopersNo ratings yet
- Phe Manual 1000e GB tcm11-7539Document36 pagesPhe Manual 1000e GB tcm11-7539iwan kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Prasna Marga Part I, NotesDocument8 pagesPrasna Marga Part I, NotesSaurav ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Device ManagementDocument72 pagesIntroduction To Device ManagementMOHAMMED SHEHBAAZNo ratings yet
- Rwanda National Examinations Council Organisational Chart DeputyDocument1 pageRwanda National Examinations Council Organisational Chart DeputymugobokaNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual - Chain Link FenceDocument2 pagesInstallation Manual - Chain Link FenceChase GietterNo ratings yet
- Aras Jung Curriculum IndividualDocument72 pagesAras Jung Curriculum IndividualdianavaleriaalvarezNo ratings yet
- Ind As 108Document6 pagesInd As 108Khushi SoniNo ratings yet
- Improving Orientation With Yoked PrismDocument2 pagesImproving Orientation With Yoked PrismAlexsandro HelenoNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Training Improves Erectile Dysfunction and Premature EjaculationDocument9 pagesPelvic Floor Muscle Training Improves Erectile Dysfunction and Premature EjaculationGe NomNo ratings yet
- Using GPS, GIS, and Accelerometer Data To Predict Transportation ModesDocument7 pagesUsing GPS, GIS, and Accelerometer Data To Predict Transportation ModesAdanely Escudero BarrenecheaNo ratings yet
- Final CDP MuzaffarpurDocument224 pagesFinal CDP MuzaffarpurVivek Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Why Are You Applying For Financial AidDocument2 pagesWhy Are You Applying For Financial AidqwertyNo ratings yet
- 15 TribonDocument10 pages15 Tribonlequanghung98No ratings yet
- Physics Notes AJk 9th Class Chap6Document3 pagesPhysics Notes AJk 9th Class Chap6Khizer Tariq QureshiNo ratings yet
- HFAss 6Document1 pageHFAss 6Taieb Ben ThabetNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering NotesDocument120 pagesAutomobile Engineering Notesakshay2992No ratings yet
- Honeywell S4565 CVI Ignition ControlDocument66 pagesHoneywell S4565 CVI Ignition ControlcarlosNo ratings yet
- C Band Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar Observations During An Extreme Precipitation Event and Associated Dynamics Over Peninsular IndiaDocument16 pagesC Band Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar Observations During An Extreme Precipitation Event and Associated Dynamics Over Peninsular Indiamann singh100% (1)
- Numerical Study of Depressurization Rate During Blowdown Based On Lumped Model AnalysisDocument11 pagesNumerical Study of Depressurization Rate During Blowdown Based On Lumped Model AnalysisamitNo ratings yet
- Professional Education LET Reviewer 150 Items With Answer KeyDocument14 pagesProfessional Education LET Reviewer 150 Items With Answer KeyAngel Salinas100% (1)
- Contoh Implementasi QMSDocument8 pagesContoh Implementasi QMSIINNo ratings yet
- Weekly Science Report 29th July 2022Document12 pagesWeekly Science Report 29th July 2022John SmithNo ratings yet
- BDC Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesBDC Questions and AnswerssatishNo ratings yet
- ECE - 1551 Digital Logic Lecture 15: Combinational Circuits: Assistant Prof. Fareena SaqibDocument19 pagesECE - 1551 Digital Logic Lecture 15: Combinational Circuits: Assistant Prof. Fareena SaqibAll aboutNo ratings yet
- Data Center Cooling SolutionsDocument24 pagesData Center Cooling SolutionsGemelita Ortiz100% (1)
- GRFU Description: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocument9 pagesGRFU Description: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDJamal HagiNo ratings yet