Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Uploaded by
Jessareth Atilano CapacioCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Uploaded by
Jessareth Atilano CapacioCopyright:
Available Formats
What should I monitor at home?
It is important that you monitor your
dog’s overall attitude and any change in
appearance. It may be helpful to keep a
record of your pet’s breathing rate so
that you will notice increases or
changes from normal breathing. If you
notice any of the following, please call
us immediately:
Understanding
▪ heavy or labored breathing
Canine Dilated
▪ coughing
What are the goals of treatment?
Treatment of DCM is aimed at both
▪ fainting spells
Cardiomyopathy
▪ severe exercise intolerance
improving the heart’s function and
controlling the signs of congestive ▪ restlessness
heart failure.
▪ lethargy
Drugs such as digoxin are used to help Thank you for visiting the cardiology
the heart contract better and to slow service at the Ryan Veterinary
the heart rate if indicated. Diuretics Hospital. If you have any further
such as lasix are used to help control questions, please do not hesitate to
and prevent accumulation of fluid in or contact us.
around the lungs. ACE inhibitors, such
as enalapril, are prescribed to reduce
the cardiac workload by dilating
arteries. They can therefore
occasionally affect the kidneys and will
require regular kidney evaluation with
blood chemistry analysis.
Matthew J. Ryan Veterinary Hospital
Additional drugs may be prescribed to University of Pennsylvania Many Species. One Medicine.
control cardiac arrythmias (electrical School of Veterinary Medicine
disturbances in the heart) or to address 3900 Spruce Street
any other special needs your pet may Philadelphia, PA 19104
have. Phone: 215-898-8889
Emergency: 215-898-4685
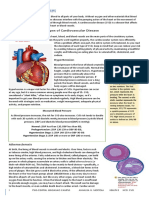
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
How does the heart work? What is Dilated Cardiomyopathy? Who is commonly affected by DCM?
The heart is the organ responsible for The disease usually afflicts large breed
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a disease dogs such as the Doberman pinscher,
maintaining the circulation of blood
of the heart muscle which causes the heart Boxer, Newfoundland, Great Dane,
within the body. It is a four-chambered
to weaken and enlarge. DCM usually affects Golden retriever, Labrador retriever, and
organ containing right and left atria both the left and right sides of the heart.
(upper chambers) and ventricles (lower the Irish wolfhound. DCM can also affect
Typically, both the ventricles and the atria English and American cocker spaniels,
chambers). The right side pumps are enlarged and often the muscular walls of
deoxygenated blood returning from the and rarely, other small breed dogs. In
the heart are much thinner than normal. American cocker spaniels, the disease
venous system in the body into the The end result is an impairment in the
lungs. From the lungs, oxygenated may be related to a deficiency in taurine
ventricle’s ability to pump blood out to the and/ or L-carnitine (amino acids).
blood enters the left side of the heart body and lungs. When the ventricles fail to
where it is pumped out into the tissues pump effectively, a backup of blood results The occurrence of DCM increases with age
of the body through the arteries. in the systemic circulation. If the left heart and typically has an age of onset between
fails, fluid backs up into the lungs causing 4 and 10 years. However, DCM occurs in
coughing and/or difficulty breathing. If the young Portuguese water dogs as an
right heart fails, fluid backs up into the inherited disease.
abdomen causing abdominal distension or
pleural effusion (fluid in the space
surrounding the lungs).
Left atrium
Right
What is the long term prognosis for
DCM?
Left ventricle
Long term prognosis for DCM varies
Right considerably. Unfortunately, most dogs
with signs of congestive heart failure at
Normal Heart with
the time of diagnosis die as a result of the
Heart DCM disease within 6 months. In the most
severe cases, some dogs may survive only
weeks to a few months. Occasionally,
dogs may do well clinically for 1-2 years.
You might also like
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument47 pagesCongestive Heart FailureRajesh Sharma100% (1)
- Campbell Chapter 18: The Genetic of Viruses and BacteriaDocument69 pagesCampbell Chapter 18: The Genetic of Viruses and BacteriaRafika Nur Handayani100% (1)
- Nclex Study 1Document11 pagesNclex Study 1Katie Shortt100% (4)
- Whybatsflyonlyatnight CLRDocument7 pagesWhybatsflyonlyatnight CLRRaj ManoNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy: Mrs. D. Melba Sahaya Sweety M.SC Nursing GimsarDocument55 pagesCardiomyopathy: Mrs. D. Melba Sahaya Sweety M.SC Nursing GimsarD. Melba S.S ChinnaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Laman Collection and Other Materials FinalDocument96 pagesIntroduction To Laman Collection and Other Materials FinalJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument12 pagesCongestive Heart FailureNader Smadi83% (6)
- Ba Duan JinDocument58 pagesBa Duan JinpositivamenteNo ratings yet
- Administering EnemaDocument35 pagesAdministering Enemabajaoc100% (1)
- Dressler’s Syndrome, (Postpericardiotomy Syndrome) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDressler’s Syndrome, (Postpericardiotomy Syndrome) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Ese OkanranDocument48 pagesEse OkanranJoão Toji50% (2)
- Cardiomyopathy: Leonard Shaju Joisy AloorDocument34 pagesCardiomyopathy: Leonard Shaju Joisy AloorJoisy AloorNo ratings yet
- Compositae FamilyDocument23 pagesCompositae FamilyA.H. Lammert Holdijk100% (1)
- Therapeutics - Gastrointestinal Tract: Heart FailureDocument5 pagesTherapeutics - Gastrointestinal Tract: Heart FailureDarnell DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Preventing and Treating Heart DiseaseDocument17 pagesPreventing and Treating Heart DiseaseVegan FutureNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in Science 4: San Carlos Elementary SchoolDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test in Science 4: San Carlos Elementary SchoolJohn Nomel B. Dominguez100% (1)
- A Survey of AI Risk Assessment Methodologies Full ReportDocument47 pagesA Survey of AI Risk Assessment Methodologies Full ReportJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- What Is Dilated Cardiomyopathy?Document4 pagesWhat Is Dilated Cardiomyopathy?pilipNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure in Dogs: 6 Practical Tips From CardiologistsDocument6 pagesHeart Failure in Dogs: 6 Practical Tips From CardiologistsJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy H.OsmanDocument12 pagesCardiomyopathy H.OsmanHassan osmanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Feline CardiomyopathyDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Feline CardiomyopathyDBCGNo ratings yet
- What Are Heart Disease and Stroke?Document2 pagesWhat Are Heart Disease and Stroke?ZenithaMeidaNo ratings yet
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy TherapyDocument7 pagesDilated Cardiomyopathy Therapyedrash85No ratings yet
- What Is Heart FailureDocument2 pagesWhat Is Heart FailureK Praful KumarNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: 1. Why Did The Hemoglobin Decreased? Anemia in ASD/VSD?Document11 pagesLearning Objectives: 1. Why Did The Hemoglobin Decreased? Anemia in ASD/VSD?DiedreNo ratings yet
- The Feline Cardiomyopathies: 3. Cardiomyopathies Other Than HCMDocument15 pagesThe Feline Cardiomyopathies: 3. Cardiomyopathies Other Than HCMAna AldazNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Week 2Document12 pagesScience 9 Week 2lenNo ratings yet
- Cayotopabocanegra, Josue Ipanaqueestrella, Adriana Lisalvador, Cristina Morantemontenegro, Maribel Yoverabravo, ChristianDocument18 pagesCayotopabocanegra, Josue Ipanaqueestrella, Adriana Lisalvador, Cristina Morantemontenegro, Maribel Yoverabravo, ChristianDoris BocanegraNo ratings yet
- MT23 3rd CHFDocument6 pagesMT23 3rd CHFKenneth OliverNo ratings yet
- Semana 4 Cardiac and Urinary System Disease 2022 PDFDocument21 pagesSemana 4 Cardiac and Urinary System Disease 2022 PDFJose Luis BustamanteNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument28 pagesCardioJuliana BusuegoNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy, Dilated Cardiomyopathy, Restrictive Cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic CardiomyopathyDocument5 pagesCardiomyopathy, Dilated Cardiomyopathy, Restrictive Cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic CardiomyopathypilipNo ratings yet
- CardiomyopathyDocument7 pagesCardiomyopathyAussie TechNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Andi Wahjono Adi, MD, FIHADocument46 pagesHeart Failure: Andi Wahjono Adi, MD, FIHAYuanita WahyuningsihNo ratings yet
- PDF Pad Screening PDFDocument16 pagesPDF Pad Screening PDFalb 348No ratings yet
- Inherited Heart DiseasesDocument8 pagesInherited Heart DiseasesAlec Palcon JovenNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument6 pagesCardiovascular DiseasesArli MiscalaNo ratings yet
- Left Ventricular Aneurysm Is14Document2 pagesLeft Ventricular Aneurysm Is14iqbalNo ratings yet
- CardiomyopathyDocument8 pagesCardiomyopathyapi-439576124No ratings yet
- ClientHandout MitralRegurgitationDocument5 pagesClientHandout MitralRegurgitationYanNo ratings yet
- Causes, Diagnosis, Signs and Symptoms: Heart FailureDocument13 pagesCauses, Diagnosis, Signs and Symptoms: Heart FailuremanatailsNo ratings yet
- Cardiomegaly: Submitted By, Sheela M John 2 Year MSC NursingDocument23 pagesCardiomegaly: Submitted By, Sheela M John 2 Year MSC NursingMaulana AkbarNo ratings yet
- Pdii Bipedal EdemaDocument5 pagesPdii Bipedal EdemacarlosNo ratings yet
- Cardivascular Deseases and Diabetes MellitusDocument38 pagesCardivascular Deseases and Diabetes MellitusYu QingNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Do You Experience Chest Pain?Document9 pagesSubjective Data: Do You Experience Chest Pain?Ellias RoseNo ratings yet
- Complication Diabetes Mellitus: Klinik Diabetes Terpadu Rs Islam KlatenDocument53 pagesComplication Diabetes Mellitus: Klinik Diabetes Terpadu Rs Islam KlatenAdam HartonoNo ratings yet
- Enlarged Heart (Cardiomegaly) : TypesDocument3 pagesEnlarged Heart (Cardiomegaly) : Typesadauto8979No ratings yet
- MS Quiz ReviewerDocument6 pagesMS Quiz ReviewerAndrea PayumoNo ratings yet
- Case 27 (LC Fix)Document14 pagesCase 27 (LC Fix)galih suharno0% (1)
- Tutorial KMB1 - 3C5 - Senin 18 Oktober 2021.id - enDocument8 pagesTutorial KMB1 - 3C5 - Senin 18 Oktober 2021.id - enNamulondo Mwajib BogereNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System ArticleDocument16 pagesCirculatory System ArticlemisssepatutinggiNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Heart Failure & Angina: Department of Pharmacology Liming Zhou 2010,3Document47 pagesDrugs For Heart Failure & Angina: Department of Pharmacology Liming Zhou 2010,3DR Muhammad Abdul BasitNo ratings yet
- Cardivascular Deseases and Diabetes MellitusDocument38 pagesCardivascular Deseases and Diabetes MellitusSyafiqah SabriNo ratings yet
- Mitral Valve Disease Information Sheet-1Document6 pagesMitral Valve Disease Information Sheet-1Ionela OprescuNo ratings yet
- Non-Communicable Diseases and Physical InactivityDocument37 pagesNon-Communicable Diseases and Physical InactivityMiles MontinolaNo ratings yet
- 수의생리학실습 1강 강의자료Document24 pages수의생리학실습 1강 강의자료Flasks AhnNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial FlutterDocument4 pagesAtrial Fibrillation and Atrial FlutterROHITNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Congestive Heart Failure By: Daniel Angelo E. ArangoDocument7 pagesCase Study: Congestive Heart Failure By: Daniel Angelo E. ArangoDaniel Angelo ArangoNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy A Heart DiseaseDocument37 pagesCardiomyopathy A Heart DiseaseCarl Justin BingayanNo ratings yet
- AERACardio - Client Brochure - Heart Disease and Congestive HeartDocument2 pagesAERACardio - Client Brochure - Heart Disease and Congestive HeartANo ratings yet
- CHF Handbook: Knowledge Is PowerDocument31 pagesCHF Handbook: Knowledge Is PowerChristian JodyNo ratings yet
- 5,6.heart FailureDocument12 pages5,6.heart FailureKUMUTHA MALAR A/P PARMESWARANNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disorders 2Document78 pagesCardiovascular Disorders 2Erlinda SagadsadNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Congestive Heart FailureDocument4 pagesThesis On Congestive Heart FailureHelpWritingACollegePaperCanada100% (2)
- Cad - AcsDocument40 pagesCad - Acssmart reyNo ratings yet
- Ncmaternity Lecture - Prelim Reviewer PDFDocument29 pagesNcmaternity Lecture - Prelim Reviewer PDFChskNo ratings yet
- HF Congestive Heart Failure 2Document3 pagesHF Congestive Heart Failure 2Yuppie RajNo ratings yet
- CardiomyopathyDocument13 pagesCardiomyopathyRaprnaNo ratings yet
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Dayra Monserrat Bernal GarcíaDocument7 pagesDilated Cardiomyopathy: Dayra Monserrat Bernal GarcíaDayra BernalNo ratings yet
- Teri 5 KangarooDocument20 pagesTeri 5 KangarooJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Ferma ActDocument21 pagesFerma ActJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Kangaroos 789Document2 pagesKangaroos 789Jessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- 2020 Eurogroup For Animals Kangaroo ReportDocument20 pages2020 Eurogroup For Animals Kangaroo ReportJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Primordial Soup - Origin Early Life - F2017Document46 pagesLecture 9 Primordial Soup - Origin Early Life - F2017Jessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Benchmarking Survey 2012 BrochureDocument16 pagesBenchmarking Survey 2012 BrochureJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- PBAAH925Document9 pagesPBAAH925Jessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Xs 55 MQ 137Document160 pagesXs 55 MQ 137Jessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- ELTI Catalogue General DataDocument16 pagesELTI Catalogue General DataJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Dilated Cardiomyopathies in Dogs: Prevalence %Document10 pagesDilated Cardiomyopathies in Dogs: Prevalence %Jessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Improving Mathematics Achievement in The New Normal Education System Using Genyo E-LearningDocument15 pagesImproving Mathematics Achievement in The New Normal Education System Using Genyo E-LearningJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Journal of Bacteriology-1990-Abeles-4386.fullDocument6 pagesJournal of Bacteriology-1990-Abeles-4386.fullJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Familial Dilated Cardiomyopathy of Young Portuguese Water DogsDocument9 pagesFamilial Dilated Cardiomyopathy of Young Portuguese Water DogsJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- E Book20GiraffeDocument16 pagesE Book20GiraffeJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Dilated CardiomyopathyDocument7 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Dilated CardiomyopathyJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy: A Paradigm of Revolution in MedicineDocument3 pagesDilated Cardiomyopathy: A Paradigm of Revolution in MedicineJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Factors Affecting Pupils' Science Achievement in ItalyDocument9 pagesAn Analysis of Factors Affecting Pupils' Science Achievement in ItalyJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Liberation Psychology and Pragmatic Solidarity: North-South Collaborations Through The Ignacio Martín-Baró FundDocument45 pagesLiberation Psychology and Pragmatic Solidarity: North-South Collaborations Through The Ignacio Martín-Baró FundJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Millennial Generation: Financial ServicesDocument5 pagesUnderstanding The Millennial Generation: Financial ServicesJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- PBL Report Traumatology: Group 6Document42 pagesPBL Report Traumatology: Group 6anthy putrisriyantiNo ratings yet
- National O.O. Bohomolets Medical University: Orthodontics and Prosthodontics Propedeutics DepartmentDocument63 pagesNational O.O. Bohomolets Medical University: Orthodontics and Prosthodontics Propedeutics Departmentسینا ایرانیNo ratings yet
- Bites and Stings - Dermatology - MKSAP 17Document4 pagesBites and Stings - Dermatology - MKSAP 17Ciara Marjorie HannaNo ratings yet
- Keperawatan Medikal Bedah Ii Skenario 2Document19 pagesKeperawatan Medikal Bedah Ii Skenario 2Nastiti DamayantiNo ratings yet
- No Wonder They Call Me A Bitch-1Document3 pagesNo Wonder They Call Me A Bitch-1PaulinaOdeth RothNo ratings yet
- Theory Spleen and LiverDocument65 pagesTheory Spleen and LiverMiddioPNo ratings yet
- Cat PDFDocument6 pagesCat PDFAnonymous GxMazRCNo ratings yet
- First Intro Video PDFDocument10 pagesFirst Intro Video PDFmohamedNo ratings yet
- Animales en Peligro de Extinción en InglesDocument7 pagesAnimales en Peligro de Extinción en InglesDarl GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Components of Removable ApplianceDocument140 pagesComponents of Removable Appliancenikitha100% (1)
- Biomentors (MCDB 1B) - Immunology Quiz (ANSWERS)Document2 pagesBiomentors (MCDB 1B) - Immunology Quiz (ANSWERS)Tiff VoNo ratings yet
- Development of VeinsDocument37 pagesDevelopment of Veinsokolodivine334No ratings yet
- The Soul According To The Ethnolinguistic Groups of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesThe Soul According To The Ethnolinguistic Groups of The PhilippinesEarl SantosNo ratings yet
- Clinical Study: Overjet and Overbite Influence On Cyclic Masticatory Movements: A CT StudyDocument7 pagesClinical Study: Overjet and Overbite Influence On Cyclic Masticatory Movements: A CT Studyarya091193No ratings yet
- Grappling With The Monster The Curse and The Cure of Strong Drink by Arthur, T. S. (Timothy Shay), 1809-1885Document131 pagesGrappling With The Monster The Curse and The Cure of Strong Drink by Arthur, T. S. (Timothy Shay), 1809-1885Gutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic MassDocument124 pagesPancreatic MassKMNo ratings yet
- Spoof TextDocument9 pagesSpoof TextHeather LeeNo ratings yet
- It Is Often Said That Government Spend Too Much Money On Projects To Protect WildlifeDocument1 pageIt Is Often Said That Government Spend Too Much Money On Projects To Protect WildlifeKaungPyae SoneNo ratings yet
- 15-10-2019, Mr. Jamal, 50 Yo, V.Laceratum Cruris Dextra + Skin Loss + Fraktur Os Fibula, Dr. Moh. Rizal Alizi, M.Kes, Sp. OT-1Document15 pages15-10-2019, Mr. Jamal, 50 Yo, V.Laceratum Cruris Dextra + Skin Loss + Fraktur Os Fibula, Dr. Moh. Rizal Alizi, M.Kes, Sp. OT-1anon_893244902No ratings yet
- NERVOUS SYSTEM (IB-DP BIOLOGY) - Multiple Choice Type QuestionsDocument5 pagesNERVOUS SYSTEM (IB-DP BIOLOGY) - Multiple Choice Type QuestionsVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Male Reproductive OrgansDocument18 pagesAnatomy of Male Reproductive OrgansPutri HolmesNo ratings yet
- Case Study DengueDocument11 pagesCase Study DengueCarl Julienne MasangcayNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 4Document5 pagesJurnal 4Nindita RahmaNo ratings yet