Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modular Coordination in Construction Industry
Modular Coordination in Construction Industry
Uploaded by
Arathi NittadukkamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modular Coordination in Construction Industry
Modular Coordination in Construction Industry
Uploaded by
Arathi NittadukkamCopyright:
Available Formats
Modular Coordination in Construction Industry
What is Standard MS 1064?
MS 1064 is a guide line towards the usage of Modular Coordination (MC) in building
constructions which consists of Part 1 to Part 10 under the general title, "Guide to Modular
Construction in Buildings". It provides the general principles, room and storey heights,
coordinating sizes and preferred sizes for various building components, dimensions of
elements, components and spaces in the planning and design of building.
Modular Coordination (MC) is a concept for coordinating dimension and space for which
buildings and components are dimensionalised and positioned in basic units or modules.
MS1064 introduces a certain geometric discipline using practical approaches which relate to
set-up coordination and measurement of components and spaces in the building design. The
standard specifies that the module basic M = 100mm as the basic unit to be used in a square
of M. The introduction of MC in the industry is to improve productivity and quality in
building construction construction as well as to act as a tool towards rationalisation and
industrialisation of the building industry.
MC has been introduced in Malaysia since 1986, but has not been widely implemented in the
building industry. The main factors limiting the uses of MC in building industries is lack of
knowledge on MC concept and it requires precision dimensioning and proper planning.
The characteristis of MC are:
- The basic module is small in terms of odd size in order to provide design flexibility, yet
large enough to promote simplification in the components' variation in sizes.
- Industry friendly features that not only cater for manufacturing but also the transportation
and assembly requirements.
- Ergonomically designed to promote efficiency
- Internationally accepted to support international market
MC Concept
MC may be applied to the design, manufacture and assembly of buildings, its components
and installations. It also affects the work positioning and dimensioning during construction.
At the work level, MC allows for relative independence in decision making with the common
dimensional language. The concept of MC is based on:
- The used of modules (basic modules and multi-modules)
- A reference system to define coordinating spaces and zones for building elements and for
the components which form them
- Rules for locating building elements within the reference system
- Rules for sizing building components in order to determine their work size
- Rules for defining preferred sizes for building components and coordinating dimensions for
building
The principal objective of implementing MC is to improve productivity through the reduction
of wastages in the production, installation process, to improve quality in the construction
industry and to encourage an open system. With Open System approach, building
components could combine in a variety of individual building projects while ensuring the
architect freedom in their designs.
MC is an important factor in application of Industrialised Building System by way of
standardization of components ad dimensions such as reduce time of production and
installation of components, achieving repeatability and able to construct building at lower
cost.
THE SCHOCKBETON CONSTRUCTION SYSTEM
The most popular wall, floor, and roof-systems in pre-fabricated concrete are used in
residential buildings. Pre-fabricated houses and apartment buildings are generally planned on
the basis of panel construction.
Certain panels are supporting; others are merely dividers. This system is widely used in
Europe. Facades comprise, as sandwich elements, an inner supporting panel, thermal
insulation varying in thickness from 50 mm to 150 mm and an outer, non-supporting panel in
architectural concrete.
This system allows for rapid construction, good sound insulation and fire resistance, plus a
smooth finish, ready to be painted or papered.
Walls made of pre-fabricated panels are usually in steel-reinforced concrete. Their height is
that of a building storey, and their length varies from 6 to 14 metres. Standard thickness is 80
mm for non-supporting , and 150 to 200 mm for supporting panels. Special applications may
require a thickness of up to 300 mm.
Advantages for the CONSTRUCTION MANAGER
- Wider spans
- Lower maintenance
- Resistance to corrosion and mildew
- Increased design possibilities
- Greater choice of finishes
- Faster construction
- Simpler building plans
- Better quality control
- Improved fire resistance
- Greater durability
Advantages for the ARCHITECT
- Closed system
- Diverse elements
You might also like
- Marketing EssentialsDocument545 pagesMarketing EssentialsĐông Đông100% (1)
- Autodesk AutoCAD Civil 3D 2018Document4 pagesAutodesk AutoCAD Civil 3D 201811 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Tata Cliq FinalDocument23 pagesTata Cliq FinalVanshika Kalra0% (1)
- Organisation Structure To Support Concurrent Engineering in ConstructionDocument11 pagesOrganisation Structure To Support Concurrent Engineering in ConstructionAhmed Adel MoemenNo ratings yet
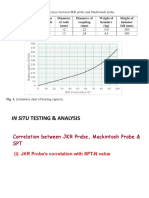
- Mackintoh Probe Test and Bearing CapacityDocument5 pagesMackintoh Probe Test and Bearing Capacity11 Sqn RER83% (6)
- The Bim and Level of BimDocument10 pagesThe Bim and Level of Bim11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Fencing British StandardsDocument2 pagesFencing British Standards11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Backgrounder: 1. SchlumbergerDocument5 pagesBackgrounder: 1. Schlumbergervikri rahmatNo ratings yet
- Category Management and Private LabelsDocument4 pagesCategory Management and Private LabelsAditi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Introduction To Modular CoordinationDocument3 pages3.0 Introduction To Modular Coordinationkhalid abdulazizNo ratings yet
- Modular Coordination in Construction IndustryDocument10 pagesModular Coordination in Construction IndustrysatrimsNo ratings yet
- BCT 563 - Lecture 1 (Introduction To MC)Document64 pagesBCT 563 - Lecture 1 (Introduction To MC)farahNo ratings yet
- Mordular CoordinationDocument1 pageMordular CoordinationKalpana GuptaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Open System in IBSDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Open System in IBSNg Chia ShenNo ratings yet
- Significance of Modular Coordination in Rehabilitation SheltersDocument3 pagesSignificance of Modular Coordination in Rehabilitation SheltersVaijayanti MundadaNo ratings yet
- Modular CVC - Aftamend - v4Document2 pagesModular CVC - Aftamend - v4Adron LimNo ratings yet
- Modular CoordinationDocument11 pagesModular CoordinationRahul NawaniNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Nur Helmi Bin Mohd Mislim 2020845232 BCT563 Assignment2 PDFDocument6 pagesMuhammad Nur Helmi Bin Mohd Mislim 2020845232 BCT563 Assignment2 PDFMAXSWELL MANGGIE ZAMRYNo ratings yet
- Unit I: The Process and Theory of PrefabricationDocument4 pagesUnit I: The Process and Theory of PrefabricationMuthu MariNo ratings yet
- BCT 563 - Lecture 3 (MC Dimension and Measurement)Document43 pagesBCT 563 - Lecture 3 (MC Dimension and Measurement)farahNo ratings yet
- Prefabrication IntroductionDocument3 pagesPrefabrication IntroductionGiri ThirthaNo ratings yet
- Module - Why ?: Modern Industrial Society Economic Growth Dynamic Development Rapid ExpansionDocument65 pagesModule - Why ?: Modern Industrial Society Economic Growth Dynamic Development Rapid ExpansionPrakriti GoelNo ratings yet
- DS84 418Document10 pagesDS84 418Chandni DayakarNo ratings yet
- Journal 563Document5 pagesJournal 563MAXSWELL MANGGIE ZAMRYNo ratings yet
- Cross Phase Product Configurator For Modular Buildin 2021 Automation in ConsDocument14 pagesCross Phase Product Configurator For Modular Buildin 2021 Automation in ConsJin Ho KoNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.omega.2017.08.008Document23 pagesAccepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.omega.2017.08.008Avinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document12 pagesModule 6joyelpaulNo ratings yet
- Modular Manufacturing in Garment Industries: September 2013Document13 pagesModular Manufacturing in Garment Industries: September 2013yuktiNo ratings yet
- Fin Irjmets1688455909Document5 pagesFin Irjmets1688455909Muhamad SafiqNo ratings yet
- Modern Methods of Construction Ijariie10601Document28 pagesModern Methods of Construction Ijariie10601Aanchal AroraNo ratings yet
- Modular Construction: Submitted To:-Mr. Sumit Phugat SirDocument18 pagesModular Construction: Submitted To:-Mr. Sumit Phugat SirAnkit YadawadNo ratings yet
- Modular Systems in Building Construction SAVEERAJA PDFDocument20 pagesModular Systems in Building Construction SAVEERAJA PDFHiral JainNo ratings yet
- Modular Coordination: Deeksha Mittal Pratiksha Aggarwal Shailja Kumari Vibha Kachroo (5 Year)Document51 pagesModular Coordination: Deeksha Mittal Pratiksha Aggarwal Shailja Kumari Vibha Kachroo (5 Year)Ilyas quraishiNo ratings yet
- Modular ConstrctnDocument4 pagesModular ConstrctnParvez Saif100% (1)
- Modular Manufacturing in Garment Industries: ISO 9001:2008 CertifiedDocument12 pagesModular Manufacturing in Garment Industries: ISO 9001:2008 CertifiedAnkur MakhijaNo ratings yet
- BCT 563 - Lecture 2 (Introduction To Standardisation)Document43 pagesBCT 563 - Lecture 2 (Introduction To Standardisation)farahNo ratings yet
- Design Review Information - CIMOSA Product Design and Development QFD FMEADocument19 pagesDesign Review Information - CIMOSA Product Design and Development QFD FMEApersischatzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Advanced Building Construction - Background & Purpose 10.26.21Document17 pagesLesson 1. Advanced Building Construction - Background & Purpose 10.26.21Jay-r MiñozaNo ratings yet
- DesinmodDocument15 pagesDesinmod9mhsphnfm9No ratings yet
- Knowledge Engineering: Knowledge Engineering (KE) Refers To All Technical, Scientific and SocialDocument2 pagesKnowledge Engineering: Knowledge Engineering (KE) Refers To All Technical, Scientific and SocialmuswarNo ratings yet
- Assignment IBSDocument13 pagesAssignment IBSEsya Iman0% (1)
- Syseng Product StructureDocument10 pagesSyseng Product StructureErdal TekinNo ratings yet
- 5 Modular CoordinationDocument69 pages5 Modular Coordinationpooja apteNo ratings yet
- Construction Cost ComparisionDocument7 pagesConstruction Cost ComparisionmrlobboNo ratings yet
- Session 2 - Modular PSDocument8 pagesSession 2 - Modular PSPuja PrasadNo ratings yet
- Categorizing Modularization Strategies To Achieve Various Objectives of Building InvestmentsDocument18 pagesCategorizing Modularization Strategies To Achieve Various Objectives of Building InvestmentsRubensBenbassatNo ratings yet
- Modular CoordinationDocument8 pagesModular CoordinationAditi Manoj.SNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 15 00910 v4Document29 pagesSustainability 15 00910 v4quetzal fiberalNo ratings yet
- Application of Modularmanufacturing System in Garment IndustriesDocument7 pagesApplication of Modularmanufacturing System in Garment Industrieskv100% (1)
- Assignment 1 MeasurementDocument8 pagesAssignment 1 Measurementashith.shajanNo ratings yet
- Modular CoordinationDocument107 pagesModular Coordinationchamil_dananjayaNo ratings yet
- IbsDocument4 pagesIbsMohd Fazli LajakNo ratings yet
- Modular Coordination IbsDocument5 pagesModular Coordination IbsCik Mia100% (1)
- Optimizing The Order Processing of Customized Products Using Product ConfigurationDocument9 pagesOptimizing The Order Processing of Customized Products Using Product Configurationhayat.koma.2023No ratings yet
- Modular Rules For 3D Wall Component Tolerances and ConclusionDocument5 pagesModular Rules For 3D Wall Component Tolerances and ConclusionMuhammad Zuhdi IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 8 ShimizuDocument10 pages8 ShimizuVikram PrasadNo ratings yet
- Near Optimum Selection of Module ConfiguDocument3 pagesNear Optimum Selection of Module ConfiguAndresSantanderHerediaNo ratings yet
- What Is Modular Construction - Types, Pros, Cons, and ApplicationsDocument9 pagesWhat Is Modular Construction - Types, Pros, Cons, and Applicationsmk harshaNo ratings yet
- Building Performance and Maintenance Information Model Based On IFCDocument17 pagesBuilding Performance and Maintenance Information Model Based On IFCrizkaNo ratings yet
- Breit Et Al. 2010 - Digital Simulation in Lean Project DevelopmentDocument11 pagesBreit Et Al. 2010 - Digital Simulation in Lean Project DevelopmentLisbeth Berrio AtapauccarNo ratings yet
- Resume Togaf 9.2Document7 pagesResume Togaf 9.2irham fuadiNo ratings yet
- Mass Customization, Postponement and Modularization Strategies: A Theoretical ConsiderationDocument7 pagesMass Customization, Postponement and Modularization Strategies: A Theoretical Considerationजयन्त पुरोहितNo ratings yet
- CEMDocument9 pagesCEMChristineNo ratings yet
- Planning and Coordination of Modular ConstructionDocument15 pagesPlanning and Coordination of Modular ConstructionOne God MiracleNo ratings yet
- Adjudication in Construction ContractsDocument4 pagesAdjudication in Construction Contracts11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Polyurethane Waterproofing TreatmentDocument2 pagesPolyurethane Waterproofing Treatment11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Team Delta Rovers Malaysia SDN BHDDocument1 pageTeam Delta Rovers Malaysia SDN BHD11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Steel MeshDocument12 pagesReinforcement Steel Mesh11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Nonwoven Fabric GeotextileDocument4 pagesNonwoven Fabric Geotextile11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Bolt Arrangement Edge Distance End DistanceDocument2 pagesBolt Arrangement Edge Distance End Distance11 Sqn RER100% (1)
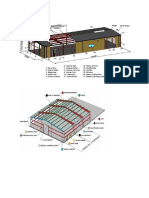
- Metal Building Parts NameDocument8 pagesMetal Building Parts Name11 Sqn RER100% (1)
- Side Reinforcement in BeamsDocument1 pageSide Reinforcement in Beams11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Pump Horse Power To Kilowatt ConversionDocument1 pagePump Horse Power To Kilowatt Conversion11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Gutter DetailsDocument4 pagesGutter Details11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Site InvestigationDocument8 pagesSite Investigation11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Lynda Autodesk Civil 3D Essential TrainingDocument1 pageLynda Autodesk Civil 3D Essential Training11 Sqn RER100% (1)
- Standard Penetration TestDocument4 pagesStandard Penetration Test11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Plaxis Professional v8Document1 pagePlaxis Professional v811 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Form QTDocument2 pagesForm QT11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- BS 1722 - FenceDocument2 pagesBS 1722 - Fence11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Voestalpine Metsec PLCDocument2 pagesVoestalpine Metsec PLC11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Types of Concrete Joints and Placing TipsDocument8 pagesTypes of Concrete Joints and Placing Tips11 Sqn RER100% (1)
- Types of Admixtures of ConcreteDocument8 pagesTypes of Admixtures of Concrete11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Football SubsoilDocument3 pagesFootball Subsoil11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- SAJ STD MPs 01 Marker PostDocument1 pageSAJ STD MPs 01 Marker Post11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- Syabas Strandard Spec For Pipe Laying WorksDocument26 pagesSyabas Strandard Spec For Pipe Laying WorksAmran HamdanNo ratings yet
- Sree Subha Sales-Ad - RRDocument8 pagesSree Subha Sales-Ad - RRANILNo ratings yet
- Agile Scrum Assessment Online ExamDocument7 pagesAgile Scrum Assessment Online ExamTasneem OsamaNo ratings yet
- Opening Remakrs MessageDocument1 pageOpening Remakrs MessageVicky G BontilaoNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing Trends 2020: Industry Highlights and Market TrendsDocument38 pages3D Printing Trends 2020: Industry Highlights and Market TrendsAlex BurdeNo ratings yet
- CH - 12 Building and Managing A Winning TeamDocument22 pagesCH - 12 Building and Managing A Winning TeamNorman Ocana JrNo ratings yet
- Most Active Investors in The Indian Startup EcosyDocument1 pageMost Active Investors in The Indian Startup EcosyShashank MishraNo ratings yet
- Sample Report On Facilitating Change in Health and Social Care by Instant Essay WritingDocument17 pagesSample Report On Facilitating Change in Health and Social Care by Instant Essay WritingInstant Essay WritingNo ratings yet
- IATF16949+Chapter+33 +Internal+AuditsDocument19 pagesIATF16949+Chapter+33 +Internal+AuditsSathish Kumar RockkzzNo ratings yet
- Case Application 2 Flight Plans Discussion Questions 1. The Four Functions of Managers AreDocument2 pagesCase Application 2 Flight Plans Discussion Questions 1. The Four Functions of Managers AreusamaNo ratings yet
- The Driver Business Plan2Document16 pagesThe Driver Business Plan2AhmedHassanSharkasNo ratings yet
- Homr Loan HDFC BankDocument73 pagesHomr Loan HDFC BankPRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BBA 6th SemDocument6 pagesSyllabus BBA 6th Semhimanshuagarwal27890% (2)
- Working Capital ReviewerDocument4 pagesWorking Capital Reviewerjennyxrous26No ratings yet
- ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURE OF MCLDocument65 pagesORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURE OF MCLSoumya Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Industrial RelationsDocument29 pagesIndustrial Relationstrendy FashionNo ratings yet
- Swot Analysis: Date: 03 Jan 2021Document2 pagesSwot Analysis: Date: 03 Jan 2021Binay ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 8 Edit Finance Corporate FinanceDocument101 pages8 Edit Finance Corporate FinanceKhail Gooding0% (2)
- ROI - PCE - SLB - Octli-2 - 01272020 PDFDocument19 pagesROI - PCE - SLB - Octli-2 - 01272020 PDFnadihe13No ratings yet
- The Competency Framework 1697547786Document13 pagesThe Competency Framework 1697547786montaserangirNo ratings yet
- Narayan Murthy LeadershipDocument3 pagesNarayan Murthy Leadershiprameshrangachari2008100% (5)
- WMS MSCA PresentationDocument53 pagesWMS MSCA PresentationJuNAiDSuAlEh100% (1)
- AFM - Corporate Debt RestructuringDocument1 pageAFM - Corporate Debt Restructuringnikesh25No ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy Comparison of Airtel and HutchDocument43 pagesMarketing Strategy Comparison of Airtel and HutchMOHD.ARISHNo ratings yet
- SSO Company ListDocument3 pagesSSO Company ListMohd AsrulNo ratings yet
- VIVADocument34 pagesVIVAnjhuyfytrdtNo ratings yet
- 2015 Cone Ebiquity Global CSR ReportDocument64 pages2015 Cone Ebiquity Global CSR ReportDuy NguyenNo ratings yet