Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic Use
Uploaded by
AA DDOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic Use
Uploaded by
AA DDCopyright:
Available Formats
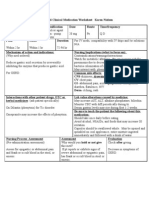
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: Medication
STUDENT NAME______________________________________
Zyloprim (Allopurinol)
MEDICATION___________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER____________
CATEGORY CLASS__C
_____________________________________________________________________
PURPOSE OF MEDICATION
Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic Use
Reduces uric acid production by inhibiting Gout, hyperuricemia, uric acid nephropathy
xanthine oxidase. preventionReccurent calcium oxalate calculi
Complications Medication Administration
Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, renal failure, acute 200-800 mg P.O daily Max 800
gout attack, rash, maculopapular rash mg daily Peak—1 1/2
hr200-400 mg/m^2 daily I.V as
a single infusion or in equally
divided doses q6,8,12 hrs
Peak—30 mins 1/2 life—1-2 hrs
Contraindications/Precautions
Hypersensitivity to Zyloprim and its components. HTN
(uncontrolled)
Nursing Interventions
Obtain baseline CBC and uric
acid level, as ordered, and
review results of renal and liver
function tests before and during
Zyloprim therapy.
Interactions Reconstitute and dilute I.V.
CNS: confusion, dizziness, headache, hemiplegia, preparation to a concentration
hypothesia, malaise, parethesia, restlessness, seizures,
seretonin syndrome CV: angina pectoris, coronary artery
vasospasm, htn, ischemia, MI GI: Abdominal pain or
discomfort, colitis, nausea
Client Education
Do not take to treat nonmigraine
headache. Drug may cause
Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness adverse CNS reactions. Notify
Decreased number of gout attacks. Decreased pain from prescriber if pregnancy is
gout. Decreased uric acid level suspected or occurs
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES
You might also like
- Toprol XLDocument2 pagesToprol XLKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- PLASILDocument2 pagesPLASILmilesmin100% (1)
- A Practical Guide to Insulin Pump Therapy for PregnancyFrom EverandA Practical Guide to Insulin Pump Therapy for PregnancyNo ratings yet
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocument1 pageNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsCassieNo ratings yet
- Drug OmeprazoleDocument1 pageDrug OmeprazoleSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Complementary and Alternative Medical Lab Testing Part 18: PsychiatryFrom EverandComplementary and Alternative Medical Lab Testing Part 18: PsychiatryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Drug Study CVA, DM, CKDDocument11 pagesDrug Study CVA, DM, CKDDylan Angelo AndresNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyComia AltheiaNo ratings yet
- Oral RevalidaDocument39 pagesOral Revalidajunathancortez123No ratings yet
- Practical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersFrom EverandPractical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Carbonic Anhydrase InhibitorDocument2 pagesCarbonic Anhydrase InhibitorBrandy RectoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes for Primary Care: A Step By Step ApproachFrom EverandDiabetes for Primary Care: A Step By Step ApproachNo ratings yet
- Example of Drug StudyDocument2 pagesExample of Drug Studydonna mae junioNo ratings yet
- Fix Your Genes to Fit Your Jeans: Optimizing Diet, Health and Weight Through Personal GeneticsFrom EverandFix Your Genes to Fit Your Jeans: Optimizing Diet, Health and Weight Through Personal GeneticsNo ratings yet
- Drug NeurontinDocument1 pageDrug NeurontinSrkocher100% (2)
- Avandia RosiglitazoneDocument1 pageAvandia RosiglitazoneCassieNo ratings yet
- Annexure 10 BDocument15 pagesAnnexure 10 Baqeel1970No ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Keppra (Levetiracetam)Document2 pagesKeppra (Levetiracetam)E100% (1)
- The Ideal Insulin Resistance Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Manage PCOS, Lose Weight And Prevent Diabetes With Nutritious RecipesFrom EverandThe Ideal Insulin Resistance Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Manage PCOS, Lose Weight And Prevent Diabetes With Nutritious RecipesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyJibran Jones GarciaNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- PacuancuanDocument5 pagesPacuancuanSaito SanNo ratings yet
- Baclofen (Drug Study)Document2 pagesBaclofen (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Famotidine (Pepcid)Document1 pageFamotidine (Pepcid)Cassie100% (1)
- Myasthenia Gravis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMyasthenia Gravis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- ZofranDocument1 pageZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- The Chronic Disease of Obesity: How Sponge Syndrome Causes Repeated Weight GainFrom EverandThe Chronic Disease of Obesity: How Sponge Syndrome Causes Repeated Weight GainNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis DrugsDocument6 pagesAppendicitis DrugsCross0No ratings yet
- Valproic Acid Drug CardDocument2 pagesValproic Acid Drug CardLiza Marie IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Drug TylenolDocument1 pageDrug TylenolSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studykarenkaren09No ratings yet
- LantusDocument1 pageLantusCassie100% (4)
- Kristinelou Marie N. Reyna December 29, 2020 BSN 2-6 PharmacologyDocument6 pagesKristinelou Marie N. Reyna December 29, 2020 BSN 2-6 PharmacologyKristinelou Marie ReynaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicDocument37 pagesTherapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicApple MaeNo ratings yet
- LisinoprilDocument1 pageLisinoprilKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Ezetimibe (Zetia)Document1 pageEzetimibe (Zetia)E100% (1)
- Lo Press orDocument1 pageLo Press orKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Tamoxifen NolvadexDocument1 pageTamoxifen NolvadexAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Aricept Donepezil Drug CardDocument1 pageAricept Donepezil Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Catapres Clonidine Drug CardDocument1 pageCatapres Clonidine Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Zaroxolyn MetolazoneDocument1 pageZaroxolyn MetolazoneCassieNo ratings yet
- Lorazapam (Ativan) PODocument1 pageLorazapam (Ativan) POAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document5 pagesDrug Study 2Bani Ann Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudySoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- Clonazepam Drug CardDocument1 pageClonazepam Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Zyloprim Drug CardDocument1 pageZyloprim Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Drug Card Motrin 800mgDocument2 pagesDrug Card Motrin 800mgAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesPrednisoloneKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Re Me RonDocument2 pagesRe Me RonKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain System - DisorderDocument1 pageChest Pain System - DisorderAA DDNo ratings yet
- Ostomy CareNursing - SkillDocument1 pageOstomy CareNursing - SkillAA DDNo ratings yet
- Rhogam Medication TemplateDocument1 pageRhogam Medication TemplateAA DDNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaSystem DisorderDocument1 pagePneumoniaSystem DisorderAA DDNo ratings yet
- DKASystem DisorderDocument1 pageDKASystem DisorderAA DDNo ratings yet
- Amenore Galactorea Hyperprolactinemia Adenoma HypophysisDocument24 pagesAmenore Galactorea Hyperprolactinemia Adenoma HypophysisShabrina Sari MedinaNo ratings yet
- EHRASurvey ManagementofAFinCKDPatients FinalManuscriptDocument10 pagesEHRASurvey ManagementofAFinCKDPatients FinalManuscriptLabontu IustinaNo ratings yet
- Use E-MANIC' For Secondary Mania Workup: Dowden Health MediaDocument2 pagesUse E-MANIC' For Secondary Mania Workup: Dowden Health MediaJagdishVankarNo ratings yet
- Homeopathic Materia Medica by Dunham Sulphur (Sulph) : Aloes GraphitesDocument17 pagesHomeopathic Materia Medica by Dunham Sulphur (Sulph) : Aloes GraphiteskivuNo ratings yet
- Uro Spots SummaryDocument25 pagesUro Spots Summarynthabiseng maboganaNo ratings yet
- Interpretations: How To Use Faecal Elastase TestingDocument6 pagesInterpretations: How To Use Faecal Elastase TestingguschinNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine InjuriesDocument18 pagesCervical Spine InjuriesAnnapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Examination Obstetrics Gynaecology - 3E (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFDocument325 pagesExamination Obstetrics Gynaecology - 3E (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFBernardo Fernandez SalazarNo ratings yet
- Arab Board Exam 2008Document7 pagesArab Board Exam 2008alaaNo ratings yet
- Exciplex® 308 NM Phototherapy: Autoimmune Disease?Document28 pagesExciplex® 308 NM Phototherapy: Autoimmune Disease?Band CafeNo ratings yet
- Newborn AssessmentDocument24 pagesNewborn Assessmentvincentsharon100% (2)
- Psycho Pharmacology: by Dr. Alit Aryani SPKJDocument28 pagesPsycho Pharmacology: by Dr. Alit Aryani SPKJMienaNo ratings yet
- Sample of NCP and Drug Study EPO FINAL DRUG STUDYDocument8 pagesSample of NCP and Drug Study EPO FINAL DRUG STUDYSherina BolosNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis - Fatin AinaDocument14 pagesUrinalysis - Fatin AinaAl- ImanuddinNo ratings yet
- Gastritis Englis 2018Document115 pagesGastritis Englis 2018irinaNo ratings yet
- STM MCQDocument4 pagesSTM MCQapi-233655790No ratings yet
- Paper AnalysisDocument4 pagesPaper AnalysisLayali MassisNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease and Stroke BrochureDocument3 pagesHeart Disease and Stroke Brochureapi-461951012No ratings yet
- Widiger 1991Document7 pagesWidiger 1991Ekatterina DavilaNo ratings yet
- Breastcancer Predisposition Syndromes: Deborah Hemel,, Susan M. DomchekDocument16 pagesBreastcancer Predisposition Syndromes: Deborah Hemel,, Susan M. DomchekPietro PeraldoNo ratings yet
- Medicine - Lesson NotesDocument12 pagesMedicine - Lesson NotesIuaena UlNo ratings yet
- Materi Onkologi DasarDocument27 pagesMateri Onkologi DasarMfahrul RoziNo ratings yet
- Lewy Body DementiaDocument20 pagesLewy Body DementiaAbdul SadiqNo ratings yet
- Stanford Hospital & Clinics Antimicrobial Dosing Reference Guide 2013Document3 pagesStanford Hospital & Clinics Antimicrobial Dosing Reference Guide 2013SANCHOSKYNo ratings yet
- Dehydration: Paul R. EarlDocument31 pagesDehydration: Paul R. EarlJaya Prabha100% (1)
- Alumno: Andrei Espinal BarretoDocument39 pagesAlumno: Andrei Espinal BarretoAndrei Espinal BarretoNo ratings yet
- Stanford Health Care Antimicrobial Dosing Reference GuideDocument6 pagesStanford Health Care Antimicrobial Dosing Reference GuidePaan SuthahathaiNo ratings yet
- Faktor Risiko Tuberkulosis Pada Anak: Muhammad S. D. Wijaya, Max F. J. Mantik, Novie H. RampenganDocument10 pagesFaktor Risiko Tuberkulosis Pada Anak: Muhammad S. D. Wijaya, Max F. J. Mantik, Novie H. RampenganMasithaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Cholestasis: Priyanka VishwakarmaDocument38 pagesNeonatal Cholestasis: Priyanka VishwakarmaAlex100% (1)