Professional Documents
Culture Documents
REVIEW
Uploaded by
Maria Charis Anne IndananOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
REVIEW
Uploaded by
Maria Charis Anne IndananCopyright:
Available Formats
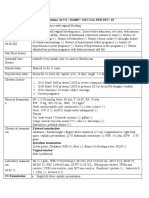
SIGNS
*presumptive - morning sickness [HCG from placenta (acidic) - provide crackers
(alkaline)]
*probable - pregnancy test
*positive - UTZ; quickening at 1st trime
->primi: 5th month
->multi: 4th month
Diagnostic Tests
*transvaginal utz - empty bladder
*abdominal utz - full bladder
Ultrasound: Volume of amniotic fluid; gender of the fetus
Fetal Cord: 50-60 (normal length)
Nuchal Cord/Cord Coil - Long
Abruptio placenta - Short
Nitrazine Test - amniotic fluid (pale yellow; urine-like)
*blue - alkaline - (+) rupture
*yellow - acidic - (-) rupture
OB Bag
*Benedicts Solution
*Gentian Violet - mouth sore (stomatitis)
*Acetic Acid - vinegar of the OB bag
Acetic Acid Test
- to determine proteinuria (sign of abnormality) -> PIH
*Procedure:
1. Fill the test tube with sample (2/3 maternal urine)
2. Put 1/3 acetic acid
3. When mixed, mixture should be clear.
4. Heat for 1-2 minutes only.
5. Clear (-)proteinuria; Cloudy (+)proteinuria
Benedicts Test - blue
- to determine glycosuria (sign of abnormality) -> GDM (common)
*Macrosomic - NSD (7 mos) -> premature -> betamethasone (steroids, promote fetal
lung maturation to prevent respiratory distress)
*Macrosomic - CS (9 mos)
*Procedure:
1. Put 5ml of benedicts solution in the test tube.
2. Heat the solution for 1-2 minutes.
3. Put 8-10 gtts of maternal urine.
4. Blue (-)glycosuria; Green (+1)glycosuria;
Yellow (+2)glycosuria; Orange (+3)glycosuria;
Red (+4)glycosuria
CS
*classis CS - vertical incision (injures muscle layer, causing impairment of
uterine contraction) - CS forever - same area always - up to 3
myometrium - muscle layer of the uterus (with horizontal patterns) - promote
uterine contraction
*bikini (transverse) - horizontal incision (causes minimal muscle injury only) -
able to deliver again via NSD (Viganal Birth After CS- VBAC)
-> MAS MAHAL
meconium staining - aspiration - emergency - classic
Alpha Feto Protein - blood exam for fetal abnormality
fetus -> alpha feto protein -> maternal blood (specimen)
- to determine Down Syndrome during fetal development
- to determine Neural Tube Defect
*Normal Level: 38-42 mg/dl
* <38 mg/dl: Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
Normal Chromosomes: 23 pairs; 46 chromosomes
Down Syndrome: excessive chromosomes (duplication of chromosome 21)
* >42 mg/dl: Neural Tube Defect (Spinal Cord Defect/Spina Bifida)
Cause: Folic Acid Deficiency (Foods to take: green leafy vegetables)
OBSTETRIC FORMULA
1. Naegel's Rule - Expected Date of Confinement (EDC) or Expected Date of Delivery
(EDB)
*ask for the mother's last menstrual period (LMP) - consider the first day of
the LMP
[-3, +7, +1 :April-Dec] [+9, +7, same year: Jan-Mar]
2. Haase's Rule - Fetal Length
1-5, mutiply by itself. 6-9, multiply by 5
1 - 1 cm 6 - 30 cm
2 - 4 cm 7 - 35 cm
3 - 9 cm 8 - 40 cm
4 - 16 cm 9 - 45 cm
5 - 25 cm
3. Johnson's Rule - Fetal Weight
1. Measure fundal height in cm (mother)
2. Check if floating or engaged (fetus) - Leopold's Maneuver
For engaged fetus: FH-12x155 grams
For floating fetus: FH-11x155 grams
4. Mc Donald's Rule - AOG
(FHx2)/7
5. Bartholomew's - AOG
1. Assess location of fundus.
Landmarks:
*Symphisis Pubis - 12 weeks/3mos
*Umbilicus - 20 weeks/5 mos
*Xyphoid Process - 8mos
*1-2cm below the xyphoid - 9 mos (lightening)
6. Maternal Weight Gain
Normal total weight gain during pregnancy: 25-35 lbs
>35 lbs: edema (PIH)
1st trime: 1 lb/month (total: 3 lbs)
2nd trime: 1 lb/week (total: 12 lbs)
3rd trime: 0.8-0.9 lbs/week (total: 8-11 lbs) - decreased production of
amniotic fluid
You might also like
- OBSTETRICS - NotesDocument16 pagesOBSTETRICS - NotesGabrielle Joyce TagalaNo ratings yet
- 5-Dx of PregnancyDocument46 pages5-Dx of PregnancybenNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument12 pagesAssessment of Fetal Growth and Developmentaracelisurat100% (1)
- HIDDENDocument12 pagesHIDDENEdvansHenryNo ratings yet
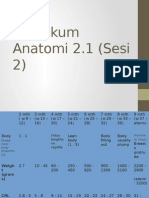
- Praktikum Anatomi 2.1 Sesi 2Document24 pagesPraktikum Anatomi 2.1 Sesi 2RizkiOktasariNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ExamsDocument15 pagesLaboratory ExamsJalil RegaroNo ratings yet
- Molar PregnancyDocument15 pagesMolar Pregnancyapi-3705046No ratings yet
- Antenatal AssessmentDocument46 pagesAntenatal AssessmentmariaNo ratings yet
- ObsGyn RR @academycerebellumDocument180 pagesObsGyn RR @academycerebellumNeeladri DawnNo ratings yet
- ObstetricsDocument6 pagesObstetricsanonymousNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument84 pagesAssessment of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentAlessandra Franchesca CortezNo ratings yet
- 4 ProcessDocument12 pages4 ProcessTel EscorialNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy (Y)Document64 pagesPregnancy (Y)Mohamed AbbasNo ratings yet
- NCM 209 Lesson 1 FinallDocument8 pagesNCM 209 Lesson 1 Finalldanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- Intra Uterine Fetal Death (IUFD) : Oleh: Dwi Yuliannisa AmriDocument24 pagesIntra Uterine Fetal Death (IUFD) : Oleh: Dwi Yuliannisa AmriagungwibowoNo ratings yet
- Intra Uterine Fetal Death (IUFD) : Oleh: Dwi Yuliannisa AmriDocument24 pagesIntra Uterine Fetal Death (IUFD) : Oleh: Dwi Yuliannisa AmriDwi Yuliannisa AmriNo ratings yet
- OB Nursing Ma'Am PacabisDocument16 pagesOB Nursing Ma'Am PacabisArgee AlonsabeNo ratings yet
- AntepartalDocument43 pagesAntepartalxing414No ratings yet
- Presumptive (Subjective Symptoms)Document5 pagesPresumptive (Subjective Symptoms)Rezza Gift K. GALLARDONo ratings yet
- Midterm FetalDocument4 pagesMidterm FetalRizalyn Padua ReyNo ratings yet
- SsssDocument25 pagesSsssDe Leon, Austine Sydney D.No ratings yet
- HY ObgynDocument52 pagesHY ObgynteapalmtreeNo ratings yet
- HY ObgynDocument32 pagesHY ObgynAndreiSaffiotiNo ratings yet
- Normal Uterine Size:: Proliferative Phase Secretory PhaseDocument4 pagesNormal Uterine Size:: Proliferative Phase Secretory PhaseLoricon OlivaNo ratings yet
- Turkey Book 04 Ob Gyn PDFDocument14 pagesTurkey Book 04 Ob Gyn PDFjay bristolNo ratings yet
- HY ObgynDocument29 pagesHY Obgynsaffet guleryuzNo ratings yet
- Bov Preg& Its Diagnosis-1Document24 pagesBov Preg& Its Diagnosis-1Mega KapitanNo ratings yet
- Mehlmanmedical Hy ObgynDocument30 pagesMehlmanmedical Hy ObgynJennifer Ross-Comptis100% (1)
- Basic Concepts, Development & Classification of TheoryDocument40 pagesBasic Concepts, Development & Classification of TheoryReshmiNo ratings yet
- PROM SANJIDA FInal 2Document32 pagesPROM SANJIDA FInal 2Saiful islam RonyNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine PresentationDocument53 pagesFamily Medicine PresentationNancy BaggaNo ratings yet
- Prenatal ScreeningDocument61 pagesPrenatal Screeningjoycechicago100% (1)
- Antepartum Fetal Surveillance: Chandani PandeyDocument98 pagesAntepartum Fetal Surveillance: Chandani Pandeychandani pandeyNo ratings yet
- Changes During PregnancyDocument2 pagesChanges During PregnancyRalph Tama Mangacop BenitoNo ratings yet
- Past Years OSCE Answers - 2012Document30 pagesPast Years OSCE Answers - 2012christietwongNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DiagnosisDocument48 pagesPrenatal DiagnosisReshop NandaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child SemifinalsDocument31 pagesMaternal and Child SemifinalsKarl Symon AmperNo ratings yet
- Clinical Activities: A. Pre - ConsultationDocument13 pagesClinical Activities: A. Pre - ConsultationerykafadsNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologiesDocument26 pagesMedical TerminologiesKLENNY ADRIA BATISANNo ratings yet
- 109 TranscriptionDocument10 pages109 Transcriptionvienny kayeNo ratings yet
- Yulia AFDocument12 pagesYulia AFIlmiah Program studi ObginNo ratings yet
- Medical ExamDocument38 pagesMedical Examchikinlam900No ratings yet
- Case 13Document8 pagesCase 13irma suwandi sadikinNo ratings yet
- Ob NotesDocument63 pagesOb NotesRoger AcasusoNo ratings yet
- Feotal Measure: Presented by Sandhya Gupta M.SC - Nursing Previous YearDocument35 pagesFeotal Measure: Presented by Sandhya Gupta M.SC - Nursing Previous Yearsuman guptaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal Well BeingDocument90 pagesAssessment of Fetal Well BeingSherlinNo ratings yet
- Gastroschisis Final PresentationDocument43 pagesGastroschisis Final PresentationlhedavenNo ratings yet
- Adaptasi Fisiologis KehamilanDocument57 pagesAdaptasi Fisiologis KehamilannafisaaNo ratings yet
- Obgyn Notes Uwise QbankDocument11 pagesObgyn Notes Uwise QbankLaura Lopez Roca0% (1)
- Reproductive SystemDocument19 pagesReproductive SystemJohnmer AvelinoNo ratings yet
- Obgyn UWISE Notes (And Master The Boards)Document8 pagesObgyn UWISE Notes (And Master The Boards)Laura Lopez Roca100% (5)
- Antepartum Care: Preconception and Prenatal CareDocument60 pagesAntepartum Care: Preconception and Prenatal CareAbdul Rahman NarawiNo ratings yet
- Ob Revalida Review 2017 PDFDocument71 pagesOb Revalida Review 2017 PDFMara Medina - BorleoNo ratings yet
- File 1Document80 pagesFile 1Djo RamNo ratings yet
- Final Ob ChecklistDocument21 pagesFinal Ob ChecklistAlbino Fulgencio Santos III100% (1)
- Pregnancy Diagnosis: Peng Xuebing, M.D. Dept of Obs/Gyn Beijing Fu Xing Hospital Capital Medical UniversityDocument48 pagesPregnancy Diagnosis: Peng Xuebing, M.D. Dept of Obs/Gyn Beijing Fu Xing Hospital Capital Medical UniversityAhmed TarigNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of PregnencyDocument35 pagesDiagnosis of PregnencyescalatorNo ratings yet
- New Born Care PlanDocument21 pagesNew Born Care PlanSusmita SenNo ratings yet
- FDARDocument1 pageFDARMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Day 7 - FRACTUREDocument7 pagesDay 7 - FRACTUREMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- RationaleDocument2 pagesRationaleMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Indanan - Individual RequirementsDocument36 pagesIndanan - Individual RequirementsMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Individual Requirements - MS RLEDocument12 pagesIndividual Requirements - MS RLEMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Day 1 - SCHIZOPHRENIA DISORDERDocument16 pagesDay 1 - SCHIZOPHRENIA DISORDERMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Discussion OnDocument17 pagesType 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Discussion OnMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Presented by BSN Iii - A2Document90 pagesCase Presentation: Presented by BSN Iii - A2Maria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Rle Case 1 BasigDocument17 pagesNCM 105 Rle Case 1 BasigMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 RLE Case 2Document8 pagesNCM 105 RLE Case 2Maria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Outhwestern NiversityDocument22 pagesCollege of Nursing: Outhwestern NiversityMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Arcipe Iccu Case 5Document98 pagesArcipe Iccu Case 5Maria Charis Anne Indanan100% (1)
- A Case Presentation In: Assigned Area: Ob Concept: "Care of Family and Family Health"Document33 pagesA Case Presentation In: Assigned Area: Ob Concept: "Care of Family and Family Health"Maria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Case 1 FinalDocument70 pagesCase 1 FinalMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction: Classification of ACSDocument7 pagesMyocardial Infarction: Classification of ACSMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- NGT Insertion and FeedingDocument2 pagesNGT Insertion and FeedingMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Main Fluid and ElectrolyteDocument133 pagesMain Fluid and ElectrolyteMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AspirinDocument1 pageDrug Study AspirinMaria Charis Anne Indanan100% (1)
- Drug Study Case 1Document37 pagesDrug Study Case 1Maria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 COVID 19 Susspect Severe Pneumonia HCVD Cardiomegaly Sinus Tachycardia With Lateral Wall Ischemia CHF NYHA 4CDocument22 pagesCase Study 1 COVID 19 Susspect Severe Pneumonia HCVD Cardiomegaly Sinus Tachycardia With Lateral Wall Ischemia CHF NYHA 4CMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Case 1 ICCU CHARTDocument107 pagesCase 1 ICCU CHARTMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Case Study 3 CVD Bleed HCVD Type 2 DM CICD Stage 5 Sec To Hypertensive Nephrosclerosis Vs Urate NephropathyDocument15 pagesCase Study 3 CVD Bleed HCVD Type 2 DM CICD Stage 5 Sec To Hypertensive Nephrosclerosis Vs Urate NephropathyMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Case Study - BSN3A - IndananDocument10 pagesCase Study - BSN3A - IndananMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Essential NutrientsDocument1 pageEssential NutrientsMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Patricia Sawyer BennerDocument12 pagesPatricia Sawyer BennerMaria Charis Anne Indanan100% (1)
- Records in Family Health NursingDocument2 pagesRecords in Family Health NursingMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- KKPMT IV ICD 10 CAHPTER XV Kehamilan 2020 Ada ICD 9 NyaDocument55 pagesKKPMT IV ICD 10 CAHPTER XV Kehamilan 2020 Ada ICD 9 NyaClarains FriskaNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Fetal Surveillance ACOG Bulletin 2014-1Document11 pagesAntepartum Fetal Surveillance ACOG Bulletin 2014-1William Rodriguez CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid and ItDocument8 pagesAmniotic Fluid and ItSaman SarKoNo ratings yet
- History Taking of The NewbornDocument9 pagesHistory Taking of The NewbornRAPHAEL ALFREDO LUIS BUENAFENo ratings yet
- Emergencies ObsDocument7 pagesEmergencies ObsAshish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Meconium Aspiration SyndromeDocument29 pagesMeconium Aspiration SyndromeAlwin Varghese T0% (1)
- Obstetric Operations & Procedures2Document98 pagesObstetric Operations & Procedures2mohazemalhotraNo ratings yet
- Labor&DeliveryDocument8 pagesLabor&Deliverytomrey1533No ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Labor DystociaDocument8 pagesDysfunctional Labor Dystociamardsz100% (2)
- Premature Rupture of MembranesDocument38 pagesPremature Rupture of MembranesArwa QishtaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument30 pagesAssessment of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentWild Rose100% (2)
- Pentagon Maternal and Child PDFDocument38 pagesPentagon Maternal and Child PDFmarie89meNo ratings yet
- MCN - Milestones For Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesMCN - Milestones For Fetal Growth and DevelopmentBenjo Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination Print PDFDocument8 pagesAbdominal Examination Print PDFPooja HbNo ratings yet
- NotesCM (CEFI)Document30 pagesNotesCM (CEFI)Ces MangaNo ratings yet
- Maternity Nursing An Introductory Text 11th Edition Leifer Test BankDocument25 pagesMaternity Nursing An Introductory Text 11th Edition Leifer Test BankJenniferNicholsonqknj100% (63)
- Prom PPT 2Document31 pagesProm PPT 2NadikNo ratings yet
- The High Risk Prenatal ClientDocument46 pagesThe High Risk Prenatal ClientPaul Albert Agunod100% (2)
- NB Delivary Room ManagementDocument48 pagesNB Delivary Room ManagementDr.P.NatarajanNo ratings yet
- NURS325 04 Antepartum PeriodDocument58 pagesNURS325 04 Antepartum PeriodaliNo ratings yet
- BSN II Comprehensive Examination 2nd Sem 2017Document12 pagesBSN II Comprehensive Examination 2nd Sem 2017Andrea Broccoli100% (1)
- Oligohydramnios Literature Review and Case StudyDocument6 pagesOligohydramnios Literature Review and Case StudyofahxdcndNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal Growth and Development: Reporters: Sharlaine Benavidez Carla Caoctoy Nesreen Alapa BSN 2 - 2Document33 pagesAssessment of Fetal Growth and Development: Reporters: Sharlaine Benavidez Carla Caoctoy Nesreen Alapa BSN 2 - 2Wild RoseNo ratings yet
- High Risk PregnancyDocument14 pagesHigh Risk PregnancyJezrael PueblosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Staff Development DepartmentDocument15 pagesNursing Staff Development DepartmentJohnmer AvelinoNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 2 For StudentsDocument8 pagesCase Scenario 2 For StudentsPrince DetallaNo ratings yet
- Gabbes Obstetrics Essentials Normal Problem Pregnancies 1St Edition Mark B Landon Et Al Full ChapterDocument67 pagesGabbes Obstetrics Essentials Normal Problem Pregnancies 1St Edition Mark B Landon Et Al Full Chapterdana.nelson195100% (9)
- High Risk Pregnancy Part 2Document12 pagesHigh Risk Pregnancy Part 2Kenneth Noveno100% (1)
- Infectious Diseases in Pregnancy - 2005 Vol.32 Issues 3Document290 pagesInfectious Diseases in Pregnancy - 2005 Vol.32 Issues 3Rickky Kurniawan,MDNo ratings yet
- Role of Intravenous Amino Acid Infusion in Cases of Oligohydramnios and Its Effect On Amniotic Fluid Index and Fetal Weight GainDocument6 pagesRole of Intravenous Amino Acid Infusion in Cases of Oligohydramnios and Its Effect On Amniotic Fluid Index and Fetal Weight GainRahimshaikhNo ratings yet