Professional Documents
Culture Documents
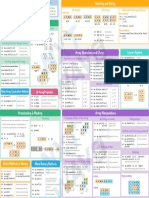
Rendering and Customizing Plots in Bokeh
Uploaded by
locutoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rendering and Customizing Plots in Bokeh
Uploaded by
locutoCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Renderers & Visual Customizations
Python For Data Science
Glyphs Legend Location
Inside Plot Area
Bokeh Cheat Sheet
Scatter Markers
>>> p.legend.location = 'bottom_left'
>>> p1.circle(np.array([1,2,3]), np.array([3,2,1]),
fill_color='white')
Outside Plot Area
>>> p2.square(np.array([1.5,3.5,5.5]), [1,4,3],
Learn Bokeh online at www.DataCamp.com
color='blue', size=1) >>>
>>>
from bokeh.models import Legend
r1 = p2.asterisk(np.array([1,2,3]), np.array([3,2,1])
taught by Bryan Van de Ven, core contributor >>> r2 = p2.line([1,2,3,4], [3,4,5,6])
>>> legend = Legend(items=[("One" ,[p1, r1]),("Two",[r2])],
Line Glyphs location=(0, -30))
>>> p1.line([1,2,3,4], [3,4,5,6], line_width=2)
>>> p.add_layout(legend, 'right')
Plotting With Bokeh
>>> p2.multi_line(pd.DataFrame([[1,2,3],[5,6,7]]),
pd.DataFrame([[3,4,5],[3,2,1]]),
color="blue") Legend Orientation
The Python interactive visualization library Bokeh enables high-performance >>> p.legend.orientation = "horizontal"
visual presentation of large datasets in modern web browsers.
Customized Glyphs Also see Data
>>> p.legend.orientation = "vertical"
Bokeh’s mid-level general purpose bokeh.plotting interface is centered Legend Background & Border
around two main components: data
and glyphs. Selection and Non-Selection Glyphs
>>> p = figure(tools='box_select')
>>> p.legend.border_line_color = "navy"
>>> p.circle('mpg', 'cyl', source=cds_df,
>>> p.legend.background_fill_color = "white"
selection_color='red',
nonselection_alpha=0.1)
Rows & Columns Layout
Hover Glyphs
>>> from bokeh.models import HoverTool
Rows
>>> hover = HoverTool(tooltips=None, mode='vline')
>>> from bokeh.layouts import row
The basic steps to creating plots with the bokeh.plotting
interface are:
>>> p3.add_tools(hover) >>> layout = row(p1,p2,p3)
1. Prepare some data (Python lists, NumPy arrays, Pandas DataFrames and other sequences of values)
Columns
2. Create a new plot
>>> from bokeh.layouts import columns
3. Add renderers for your data, with visual customizations
Colormapping >>> layout = column(p1,p2,p3)
4. Specify where to generate the output
>>> from bokeh.models import CategoricalColorMapper
Nesting Rows & Columns
5. Show or save the results >>> color_mapper = CategoricalColorMapper(
>>>layout = row(column(p1,p2), p3)
factors=['US', 'Asia', 'Europe'],
>>> from bokeh.plotting import figure
palette=['blue', 'red', 'green'])
>>> from bokeh.io import output_file, show
>>> x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] #Step 1
>>> p3.circle('mpg', 'cyl', source=cds_df,
color=dict(field='origin',
Grid Layout
>>> y = [6, 7, 2, 4, 5]
transform=color_mapper),
>>> p = figure(title="simple line example", #Step 2
legend='Origin') >>> from bokeh.layouts import gridplot
x_axis_label='x',
>>> row1 = [p1,p2]
y_axis_label='y')
>>> row2 = [p3]
>>> p.line(x, y, legend="Temp.", line_width=2) #Step 3
4 Output & Export
>>> layout = gridplot([[p1,p2],[p3]])
>>> output_file("lines.html") #Step 4
>>> show(p) #Step 5
Tabbed Layout
Notebook
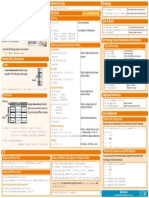
1 Data Also see Lists, NumPy & Pandas
>>> from bokeh.io import output_notebook, show
>>>
>>>
>>>
from bokeh.models.widgets import Panel, Tabs
tab1 = Panel(child=p1, title="tab1")
tab2 = Panel(child=p2, title="tab2")
>>> output_notebook() >>> layout = Tabs(tabs=[tab1, tab2])
Under the hood, your data is converted to Column Data Sources.
You can also do this manually: HTML Linked Plots
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(np.array([[33.9,4,65, 'US'],
Standalone HTML Linked Axes
[32.4, 4, 66, 'Asia'],
>>> from bokeh.embed import file_html
>>> p2.x_range = p1.x_range
[21.4, 4, 109, 'Europe']]),
>>> from bokeh.resources import CDN
>>> p2.y_range = p1.y_range
columns=['mpg','cyl', 'hp', 'origin'],
>>> html = file_html(p, CDN, "my_plot")
index=['Toyota', 'Fiat', 'Volvo'])
Linked Brushing
>>> from bokeh.io import output_file, show
>>> p4 = figure(plot_width = 100, tools='box_select,lasso_select')
>>> from bokeh.models import ColumnDataSource
>>> output_file('my_bar_chart.html', mode='cdn') >>> p4.circle('mpg', 'cyl', source=cds_df)
>>> cds_df = ColumnDataSource(df) >>> p5 = figure(plot_width = 200, tools='box_select,lasso_select')
Components >>> p5.circle('mpg', 'hp', source=cds_df)
>>> from bokeh.embed import components
>>> layout = row(p4,p5)
>>> script, div = components(p)
2 Plotting
PNG
>>> from bokeh.plotting import figure
5 Show or Save Your Plots
>>> p1 = figure(plot_width=300, tools='pan,box_zoom')
>>> from bokeh.io import export_png
>>> p2 = figure(plot_width=300, plot_height=300,
>>> show(p1)
>>> export_png(p, filename="plot.png")
x_range=(0, 8), y_range=(0, 8))
>>> show(layout)
>>> p3 = figure() >>> save(p1)
SVG >>> save(layout)
>>> from bokeh.io import export_svgs
>>> p.output_backend = "svg"
>>> export_svgs(p, filename="plot.svg") Learn Data Skills Online at www.DataCamp.com
You might also like
- Solution Manual For An Introduction To Management Science 15th Edition by Anderson Complete Downloadable File atDocument6 pagesSolution Manual For An Introduction To Management Science 15th Edition by Anderson Complete Downloadable File at时家欣0% (1)
- Peavey Semiconductor Cross Reference ListDocument24 pagesPeavey Semiconductor Cross Reference Listren_theoriginalpunks100% (10)
- Pandas Python For Data ScienceDocument1 pagePandas Python For Data Sciencechowdamhemalatha100% (1)
- Bayes CPH - Tutorial RDocument9 pagesBayes CPH - Tutorial RyogobaskoroNo ratings yet
- CS236 Project 2: The Datalog ParserDocument3 pagesCS236 Project 2: The Datalog ParserJeff PrattNo ratings yet
- Con9579 SQL Tune Cookbook 2031472 PDFDocument57 pagesCon9579 SQL Tune Cookbook 2031472 PDFPraveen LaxmanNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Metallic Materials - Vickers Hardness Test - Verification and Calibration of Testing MachinesDocument6 pagesInternational Standard: Metallic Materials - Vickers Hardness Test - Verification and Calibration of Testing MachinesNilesh PatilNo ratings yet
- KPIs IN SCAFFOLDING OPERATIONSDocument6 pagesKPIs IN SCAFFOLDING OPERATIONSSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Set 1Document21 pagesSet 1Soumava BasuNo ratings yet
- Bokeh Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: 3 Renderers & Visual CustomizationsDocument26 pagesBokeh Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: 3 Renderers & Visual CustomizationsAyuro TechNo ratings yet
- Bokeh Cheat SheetDocument1 pageBokeh Cheat Sheetcuneyt noksanNo ratings yet
- Python 数据科学速查表 Bokeh 渲染器与自定义可视化Document1 pagePython 数据科学速查表 Bokeh 渲染器与自定义可视化Keith NgNo ratings yet
- Python Bokeh Cheat Sheet VisualizationsDocument51 pagesPython Bokeh Cheat Sheet VisualizationsJhoan Manuel Venegas OlmosNo ratings yet
- Bokeh Cheat SheetDocument1 pageBokeh Cheat SheetsreekarscribdNo ratings yet
- Python Bokeh Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pagePython Bokeh Cheat Sheet PDFrakesharumallaNo ratings yet
- Numpy MergedDocument2 pagesNumpy MergedvenkateshNo ratings yet
- SPARKDocument36 pagesSPARKchenna kesavaNo ratings yet
- PySpark CheatSheet EdurekaDocument1 pagePySpark CheatSheet EdurekaBL PipasNo ratings yet
- Pandas Python For Data ScienceDocument1 pagePandas Python For Data ScienceaaaaNo ratings yet
- Pandas Basics: Learn Python For Data Science InteractivelyDocument1 pagePandas Basics: Learn Python For Data Science InteractivelySofia HerreraNo ratings yet
- R-Tutorial - IntroductionDocument30 pagesR-Tutorial - Introductionlamaram32No ratings yet
- Apache Spark: CS240A Winter 2016. T YangDocument36 pagesApache Spark: CS240A Winter 2016. T Yangomegapoint077609No ratings yet
- Python Matplotlib Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePython Matplotlib Cheat SheetsreedharNo ratings yet
- Python Matplotlib Cheat Sheet Plot Anatomy & WorkflowDocument1 pagePython Matplotlib Cheat Sheet Plot Anatomy & Workflowyama kenezonoNo ratings yet
- Download R and work with basic data typesDocument11 pagesDownload R and work with basic data typeslamaram32No ratings yet
- OBIEE 11g Architecture: in This Article We Will Briefly Explain The New OBIEE 11g Architecture and Its ComponentsDocument25 pagesOBIEE 11g Architecture: in This Article We Will Briefly Explain The New OBIEE 11g Architecture and Its ComponentsjawadNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument1 pagePythonEsad Seyid Mahmud DemirciNo ratings yet
- Python NumPy cheat sheet for data scienceDocument14 pagesPython NumPy cheat sheet for data scienceraghavandra ethish manickam100% (1)
- Numpy Python Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNumpy Python Cheat SheetJosh Iz100% (1)
- Numpy Python Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageNumpy Python Cheat Sheet PDFAbhijith S AnchanNo ratings yet
- Numpy Basics: Arithmetic OperationsDocument6 pagesNumpy Basics: Arithmetic Operationsmanish chavhanNo ratings yet
- ML CheatsheetsDocument17 pagesML CheatsheetsGhikjh100% (2)
- Numpy Basics: Arithmetic OperationsDocument7 pagesNumpy Basics: Arithmetic OperationsDeepak Gupta100% (13)
- Numpy Python Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNumpy Python Cheat Sheetyellow_birdNo ratings yet
- What Is PCA: When Should You Use PCA?Document21 pagesWhat Is PCA: When Should You Use PCA?sailushaNo ratings yet
- Python - Adv - 3 - Jupyter Notebook (Student)Document18 pagesPython - Adv - 3 - Jupyter Notebook (Student)Mesbahur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Matplotlib: Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMatplotlib: Cheat SheetJaimy HessNo ratings yet
- R Session ADocument107 pagesR Session Adivya kolluriNo ratings yet
- The Basics of R Programming LanguageDocument6 pagesThe Basics of R Programming LanguageGuilliane GallanoNo ratings yet
- The Basics of R Programming Language Data SimulationDocument6 pagesThe Basics of R Programming Language Data SimulationGuilliane GallanoNo ratings yet
- Banker's Algorithm: Import As Import AsDocument2 pagesBanker's Algorithm: Import As Import AsBrijesh KuvadiyaNo ratings yet
- Handwritten Text Recognition TechniquesDocument27 pagesHandwritten Text Recognition TechniquesThe PhongNo ratings yet
- Data Science Workflow with R - Learn Tidyverse & TidymodelsDocument3 pagesData Science Workflow with R - Learn Tidyverse & TidymodelsMBA_2011No ratings yet
- Data Science With R Workflow: Click The Links For DocumentationDocument3 pagesData Science With R Workflow: Click The Links For Documentationenrique gonzalez duranNo ratings yet
- Scipy Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Linear AlgebraDocument1 pageScipy Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Linear AlgebraLourdes Victoria UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Ip pb1 QP Ms Agra Set ADocument17 pagesIp pb1 QP Ms Agra Set AMayank MishraNo ratings yet
- R BasicDocument16 pagesR BasicTaslima ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Python Matplotlib SheetDocument1 pagePython Matplotlib SheetHIDINo ratings yet
- Data Science With R Workflow: Important ResourcesDocument2 pagesData Science With R Workflow: Important Resourceskumar kumarNo ratings yet
- Python Bokeh Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePython Bokeh Cheat Sheeternest hamNo ratings yet
- RSTUDIODocument44 pagesRSTUDIOsamarth agarwalNo ratings yet
- Advance Python Sheet 1696337837Document237 pagesAdvance Python Sheet 1696337837Anjineyulu NaikNo ratings yet
- Advanced Python CheatsheetDocument200 pagesAdvanced Python CheatsheetDavid EsparzaArellanoNo ratings yet
- Numpy Python Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNumpy Python Cheat SheetSahil BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Pandas: Learn Python For Data Science InteractivelyDocument1 pagePandas: Learn Python For Data Science InteractivelySofia HerreraNo ratings yet
- Data Wrangling (Data Preprocessing)Document4 pagesData Wrangling (Data Preprocessing)Siddharth RaulNo ratings yet
- Pandas Basics Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Retrieving Series/Dataframe InformationDocument1 pagePandas Basics Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Retrieving Series/Dataframe InformationlocutoNo ratings yet
- Automated Materials Science ML Workflows Speed TestingDocument5 pagesAutomated Materials Science ML Workflows Speed Testinggfdsal878No ratings yet
- Learning Pandas 2.0: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Manipulation and Analysis for Data Scientists and Machine Learning ProfessionalsFrom EverandLearning Pandas 2.0: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Manipulation and Analysis for Data Scientists and Machine Learning ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive CSS3 Command List, With Descriptions And Typical Mark UpFrom EverandComprehensive CSS3 Command List, With Descriptions And Typical Mark UpNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management in Indonesia: Important Issues to Know before Establishing a Subsidiary in IndonesiaFrom EverandHuman Resource Management in Indonesia: Important Issues to Know before Establishing a Subsidiary in IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Visualizing Data in R 4: Graphics Using the base, graphics, stats, and ggplot2 PackagesFrom EverandVisualizing Data in R 4: Graphics Using the base, graphics, stats, and ggplot2 PackagesNo ratings yet
- Learn Python through Nursery Rhymes and Fairy Tales: Classic Stories Translated into Python Programs (Coding for Kids and Beginners)From EverandLearn Python through Nursery Rhymes and Fairy Tales: Classic Stories Translated into Python Programs (Coding for Kids and Beginners)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Adaptive Server Enterprise: Performance and Tuning Series: Monitoring TablesDocument66 pagesAdaptive Server Enterprise: Performance and Tuning Series: Monitoring TableslocutoNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Server Enterprise: Performance and Tuning Series: Locking and Concurrency ControlDocument158 pagesAdaptive Server Enterprise: Performance and Tuning Series: Locking and Concurrency ControllocutoNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Server® Enterprise: Performance and Tuning Series: Monitoring Adaptive Server With SP - SysmonDocument158 pagesAdaptive Server® Enterprise: Performance and Tuning Series: Monitoring Adaptive Server With SP - SysmonlocutoNo ratings yet
- Migration StrategiesDocument244 pagesMigration StrategieslocutoNo ratings yet
- DB 21c ArchitectureDocument43 pagesDB 21c ArchitectureNikolya SmirnoffNo ratings yet
- 2015-K-Db-Kellyn Potvin-gorman-The Power of The Awr Warehouse and Beyond-ManuskriptDocument14 pages2015-K-Db-Kellyn Potvin-gorman-The Power of The Awr Warehouse and Beyond-ManuskriptDaniel NelsonNo ratings yet
- Pandas Data Wrangling Cheatsheet Datacamp PDFDocument1 pagePandas Data Wrangling Cheatsheet Datacamp PDFPamungkas AjiNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Server Enterprise: Performance and Tuning Series: Physical Database TuningDocument158 pagesAdaptive Server Enterprise: Performance and Tuning Series: Physical Database TuninglocutoNo ratings yet
- AWR Warehouse: An IntroductionDocument38 pagesAWR Warehouse: An IntroductionlocutoNo ratings yet
- Vmware Oracle Databases On Vmware Best Practices Guide PDFDocument81 pagesVmware Oracle Databases On Vmware Best Practices Guide PDFRoshni SuvarnaNo ratings yet
- Oracle SQL Tuning: For Day-to-Day Data Warehouse SupportDocument68 pagesOracle SQL Tuning: For Day-to-Day Data Warehouse SupportlocutoNo ratings yet
- Pandas Basics Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Retrieving Series/Dataframe InformationDocument1 pagePandas Basics Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Retrieving Series/Dataframe InformationlocutoNo ratings yet
- Visual SQL Tuning (VST) Kyle HaileyDocument136 pagesVisual SQL Tuning (VST) Kyle HaileylocutoNo ratings yet
- US3 Performance Stability Tips Tricks and UnderscoresDocument167 pagesUS3 Performance Stability Tips Tricks and UnderscoreslocutoNo ratings yet
- Arma 3 Keylayout ENGDocument1 pageArma 3 Keylayout ENGlocutoNo ratings yet
- Active Session History 129612Document50 pagesActive Session History 129612suresh_scribidNo ratings yet
- 1.what Is Opactch in Oracle?Document5 pages1.what Is Opactch in Oracle?locutoNo ratings yet
- MColgan SQL TuningDocument95 pagesMColgan SQL TuninglocutoNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database 19c Auto-Indexing FeatureDocument15 pagesOracle Database 19c Auto-Indexing FeaturelocutoNo ratings yet
- Matplotlib Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Plotting Cutomize Plot Plotting RoutinesDocument1 pageMatplotlib Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Plotting Cutomize Plot Plotting RoutineslocutoNo ratings yet
- Python For Data Science: Advanced Indexing Data Wrangling in Pandas Cheat Sheet Combining DataDocument1 pagePython For Data Science: Advanced Indexing Data Wrangling in Pandas Cheat Sheet Combining DatalocutoNo ratings yet
- Seaborn Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: 3 Plotting With Seaborn 3 Plotting With SeabornDocument1 pageSeaborn Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: 3 Plotting With Seaborn 3 Plotting With SeabornlocutoNo ratings yet
- Owp Awr Historical AnalysisDocument22 pagesOwp Awr Historical Analysisrav1234No ratings yet
- Exploring Your Data in PythonDocument1 pageExploring Your Data in PythonlocutoNo ratings yet
- Seaborn Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: 3 Plotting With Seaborn 3 Plotting With SeabornDocument1 pageSeaborn Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: 3 Plotting With Seaborn 3 Plotting With SeabornlocutoNo ratings yet
- 1.what Is Opactch in Oracle?Document5 pages1.what Is Opactch in Oracle?locutoNo ratings yet
- Chuleta Consultas UtilesDocument20 pagesChuleta Consultas UtileslocutoNo ratings yet
- Jupyter Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Working With Different Programming Languages WidgetsDocument1 pageJupyter Cheat Sheet Python For Data Science: Working With Different Programming Languages WidgetslocutoNo ratings yet
- Profit TakerDocument9 pagesProfit TakerCososoNo ratings yet
- Coupling and Cohesion StudentDocument40 pagesCoupling and Cohesion Studentzxcvbnm04No ratings yet
- Text Chapter 2 Basic ObjectsDocument126 pagesText Chapter 2 Basic ObjectsLevinNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document6 pagesWeek 2rrNo ratings yet
- Daftar Siswa SNMPN 2022Document7 pagesDaftar Siswa SNMPN 2022Bestie EpribadehNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Circuit Explanation: Travel, Swing, Boom, Arm & Bucket FunctionsDocument96 pagesHydraulic Circuit Explanation: Travel, Swing, Boom, Arm & Bucket FunctionsOscar ItzolNo ratings yet
- Logic Programming: - About The CourseDocument68 pagesLogic Programming: - About The CourseABeerNo ratings yet
- Computer Awareness Capsule (Studyniti) - Kapil KathpalDocument62 pagesComputer Awareness Capsule (Studyniti) - Kapil KathpalVijay RaghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- 29718101-Rexroth Demo System PSP-I01.1-01 IndraDrive M With SERCOS InterfaceDocument70 pages29718101-Rexroth Demo System PSP-I01.1-01 IndraDrive M With SERCOS InterfaceVan Lap NguyenNo ratings yet
- Computer Storage EvolutionDocument2 pagesComputer Storage EvolutionRics SanchezNo ratings yet
- Quality Standards and MetricsDocument2 pagesQuality Standards and MetricsAniqaNo ratings yet
- CAT D7H Track-Type Tractor Electrical System Schematic - SENR4182SENR4182 - SIS PDFDocument2 pagesCAT D7H Track-Type Tractor Electrical System Schematic - SENR4182SENR4182 - SIS PDFKomatsu Perkins HitachiNo ratings yet
- 2Document27 pages2Giby MathewNo ratings yet
- EPOS4 50 5 Hardware Reference enDocument76 pagesEPOS4 50 5 Hardware Reference en63597822No ratings yet
- Powerpoint AnimationsDocument16 pagesPowerpoint AnimationsRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Use The Azure Portal To Upload A File To Azure StorageDocument2 pagesUse The Azure Portal To Upload A File To Azure Storagejeppoo1No ratings yet
- MG 585 Project ManagementDocument17 pagesMG 585 Project ManagementPaula PlataNo ratings yet
- Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument20 pagesAdvantages and DisadvantagesParvathi Iyer67% (3)
- Laptop Price Prediction in Machine Learning Using Random Forest Classifier TechniqueDocument5 pagesLaptop Price Prediction in Machine Learning Using Random Forest Classifier TechniqueInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- R12 Overview of Oracle Asset ManagementDocument36 pagesR12 Overview of Oracle Asset ManagementIvo Huaynates100% (1)
- A Survey On Computer System Memory ManagementDocument7 pagesA Survey On Computer System Memory ManagementMuhammad Abu Bakar SiddikNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Oracle Property ManagerDocument120 pagesEssentials of Oracle Property ManagerOsamaAzizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document24 pagesChapter 13assaNo ratings yet
- Python Highway 2 Books in 1 The Fastest Way For Beginners To Learn Python Programming, Data Science and Machine Learning in 3 Days (Or Less) + Practical Exercises Included by Cox, AaronDocument174 pagesPython Highway 2 Books in 1 The Fastest Way For Beginners To Learn Python Programming, Data Science and Machine Learning in 3 Days (Or Less) + Practical Exercises Included by Cox, AaronAlberto FasceNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Data Science Lab RecordDocument59 pagesFundamentals of Data Science Lab RecordtbhumuytjNo ratings yet