Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CS8392 Object Oriented Programming L T P C
CS8392 Object Oriented Programming L T P C
Uploaded by
sureshvk.20087147Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CS8392 Object Oriented Programming L T P C
CS8392 Object Oriented Programming L T P C
Uploaded by
sureshvk.20087147Copyright:
Available Formats
CS8392 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING LTPC
3 003
OBJECTIVES:
To understand Object Oriented Programming concepts and basic characteristics of Java
To know the principles of packages, inheritance and interfaces
To define exceptions and use I/O streams
To develop a java application with threads and generics classes
To design and build simple Graphical User Interfaces
UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO OOP AND JAVA FUNDAMENTALS 10
Object Oriented Programming - Abstraction – objects and classes - Encapsulation- Inheritance -
Polymorphism- OOP in Java – Characteristics of Java – The Java Environment - Java Source
File -Structure – Compilation. Fundamental Programming Structures in Java – Defining classes in
Java – constructors, methods -access specifiers - static members -Comments, Data Types,
Variables, Operators, Control Flow, Arrays , Packages - JavaDoc comments.
UNIT II INHERITANCE AND INTERFACES 9
Inheritance – Super classes- sub classes –Protected members – constructors in sub classes- the
Object class – abstract classes and methods- final methods and classes – Interfaces – defining an
interface, implementing interface, differences between classes and interfaces and extending
interfaces - Object cloning -inner classes, Array Lists - Strings
UNIT III EXCEPTION HANDLING AND I/O 9
Exceptions - exception hierarchy - throwing and catching exceptions – built-in exceptions, creating
own exceptions, Stack Trace Elements. Input / Output Basics – Streams – Byte streams and
Character streams – Reading and Writing Console – Reading and Writing Files
UNIT IV MULTITHREADING AND GENERIC PROGRAMMING 8
Differences between multi-threading and multitasking, thread life cycle, creating threads,
synchronizing threads, Inter-thread communication, daemon threads, thread groups. Generic
Programming – Generic classes – generic methods – Bounded Types – Restrictions and
Limitations.
UNIT V EVENT DRIVEN PROGRAMMING 9
Graphics programming - Frame – Components - working with 2D shapes - Using color, fonts, and
images - Basics of event handling - event handlers - adapter classes - actions - mouse events -
AWT event hierarchy - Introduction to Swing – layout management - Swing Components – Text
Fields , Text Areas – Buttons- Check Boxes – Radio Buttons – Lists- choices- Scrollbars –
Windows –Menus – Dialog Boxes.
TOTAL: 45 PERIODS
OUTCOMES:
Upon completion of the course, students will be able to:
Develop Java programs using OOP principles
Develop Java programs with the concepts inheritance and interfaces
Build Java applications using exceptions and I/O streams
Develop Java applications with threads and generics classes
Develop interactive Java programs using swings
TEXT BOOKS:
1. Herbert Schildt, ―Java The complete reference‖, 8th Edition, McGraw Hill Education, 2011.
2. Cay S. Horstmann, Gary cornell, ―Core Java Volume –I Fundamentals‖, 9th Edition,
Prentice Hall, 2013.
REFERENCES:
1. Paul Deitel, Harvey Deitel, ―Java SE 8 for programmers‖, 3rd Edition, Pearson, 2015.
2. Steven Holzner, ―Java 2 Black book‖, Dreamtech press, 2011.
3. Timothy Budd, ―Understanding Object-oriented programming with Java‖, Updated Edition,
Pearson Education, 2000.
You might also like
- Mirror Therapy - Practical Protocol For Stroke Rehabilitation, 2013Document25 pagesMirror Therapy - Practical Protocol For Stroke Rehabilitation, 2013Nacho Castro Izquierdo75% (4)
- PeopleSoft Component Interface - A Complete GuideDocument73 pagesPeopleSoft Component Interface - A Complete Guidevasubandi8100% (3)
- NatalyStephany Pinguil - Copy of IonicBondsSEDocument5 pagesNatalyStephany Pinguil - Copy of IonicBondsSEnataly natiNo ratings yet
- Conscious UncouplingDocument2 pagesConscious Uncouplingdaniel berg100% (1)
- LabVIEW PPT PresentationDocument27 pagesLabVIEW PPT PresentationRanadeep DeyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Networking SyllabusDocument1 pageAdvanced Networking SyllabusSuyash PrakashNo ratings yet
- Client Server Architecture A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandClient Server Architecture A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Danger: 50 Things You Should Not Do With A Narcissist BY H G TudorDocument219 pagesDanger: 50 Things You Should Not Do With A Narcissist BY H G TudorPaola De Carli100% (2)
- Blueprints of Cosmic Consciousness Book 1Document129 pagesBlueprints of Cosmic Consciousness Book 1Donald William50% (2)
- Cs8392 Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument2 pagesCs8392 Object Oriented ProgrammingarunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming CS504D SyllabusDocument2 pagesObject Oriented Programming CS504D SyllabusSuvadeep BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Databases IntroDocument16 pagesDatabases IntroJaskiran KaurNo ratings yet
- Principles of Computer NetworkDocument21 pagesPrinciples of Computer Networkamit_datasoftechNo ratings yet
- Core PHP (Duration 20-22 Classes) Topics: PHP, Mysql, JavascriptDocument6 pagesCore PHP (Duration 20-22 Classes) Topics: PHP, Mysql, JavascriptGautam Mukherjee0% (1)
- OOP NotesDocument4 pagesOOP NotesUdit BansalNo ratings yet
- Research and Latest Trends in Mobile ComputingDocument50 pagesResearch and Latest Trends in Mobile ComputingDurgaprasad MadamsettyNo ratings yet
- PC Hardware & Networking Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesPC Hardware & Networking Syllabus PDFSalmaanNo ratings yet
- NormalizationDocument27 pagesNormalizationPooja WankhedeNo ratings yet
- 15cs81-Iot SyllabusDocument3 pages15cs81-Iot SyllabusAnu CadzieNo ratings yet
- Lecture-0 - AiDocument34 pagesLecture-0 - AiRadha KrishnanNo ratings yet
- SAD 03 Object Oriented ConceptsDocument41 pagesSAD 03 Object Oriented ConceptsNooh NiaziNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document47 pagesUnit 4A21126512117 SUKALA ABHIRAMNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Object Oriented Programming: UNIT-1Document30 pagesIntroduction To Object Oriented Programming: UNIT-1jittuNo ratings yet
- MCT619 - Syllabus Object Oriented Programming (Java)Document15 pagesMCT619 - Syllabus Object Oriented Programming (Java)Laura CraigNo ratings yet
- HTML & Css Syllabus PDFDocument7 pagesHTML & Css Syllabus PDFnihalNo ratings yet
- Data ModelingDocument26 pagesData ModelingSyed adfarNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDocument4 pagesObject Oriented Programming - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TVNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument105 pagesSyllabusLadaaki Kudi100% (1)
- Free PDF of Computer NetworkDocument2 pagesFree PDF of Computer NetworkRavenNo ratings yet
- Web Technologies PDFDocument139 pagesWeb Technologies PDFSNEHITH INJAMNo ratings yet
- 01.introducing To Routing and Packet ForwardingDocument4 pages01.introducing To Routing and Packet ForwardingjentriNo ratings yet
- 715ECT04 Embedded Systems 2M & 16MDocument32 pages715ECT04 Embedded Systems 2M & 16Msumathi0% (1)
- Memory Management PagingDocument87 pagesMemory Management PagingAditya PratapNo ratings yet
- Oops ConceptsDocument8 pagesOops ConceptsManoj ManoharanNo ratings yet
- 4 RamDocument35 pages4 Ramlynnlahloh100% (1)
- Computer Networks Notes (17CS52) PDFDocument174 pagesComputer Networks Notes (17CS52) PDFKeerthiNo ratings yet
- Advantages of OOPDocument2 pagesAdvantages of OOPUneeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture2-Multimedia SystemsDocument23 pagesLecture2-Multimedia SystemsChiratoNo ratings yet
- Grid and Cloud Unit IIDocument16 pagesGrid and Cloud Unit IIcsisajurajNo ratings yet
- IctdipNetworking NotesDocument86 pagesIctdipNetworking NotesJoshua Kioko100% (1)
- EC8551 CN SyllabusDocument2 pagesEC8551 CN SyllabusRagavanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Fundamental Iot Mechanism & Key Technologies: Prof. Rajashree SutraweDocument48 pagesUnit 2 Fundamental Iot Mechanism & Key Technologies: Prof. Rajashree SutraweECE N.V.Satyanarayana Murthy100% (1)
- Cs8494 Software Engineering: Course Instructor Mrs.A.Tamizharasi, AP/CSE, RMDEC Mrs. Remya Rose S, AP/CSE, RMDECDocument23 pagesCs8494 Software Engineering: Course Instructor Mrs.A.Tamizharasi, AP/CSE, RMDEC Mrs. Remya Rose S, AP/CSE, RMDECTamizharasi ANo ratings yet
- MCT619 Object-Oriented Programming: Module HandbookDocument15 pagesMCT619 Object-Oriented Programming: Module HandbookLaura CraigNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual B.tech IT (FACULTY COPY) - CNDocument41 pagesLab Manual B.tech IT (FACULTY COPY) - CNBinuVargisNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.4 Wired and Wireless Networks - Lesson 1: Activity 1 - Local Area Network (LAN) Vs Wide Area Network (WAN)Document4 pagesUnit 1.4 Wired and Wireless Networks - Lesson 1: Activity 1 - Local Area Network (LAN) Vs Wide Area Network (WAN)api-350342129No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To DatabasesDocument35 pages1 Introduction To DatabasesBricious Mulimbi100% (1)
- Network ManagementDocument39 pagesNetwork ManagementDhanraj DSNo ratings yet
- Intruders: Tran Song Dat Phuc Department of Computer Science and Engineering Seoultech 2014Document65 pagesIntruders: Tran Song Dat Phuc Department of Computer Science and Engineering Seoultech 2014Pavan Kumar NNo ratings yet
- Operating System ServiceDocument6 pagesOperating System ServiceJONAS J JONASNo ratings yet
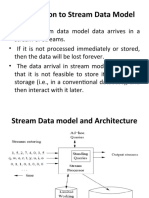
- Introduction To Stream Data ModelDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Stream Data ModelGeorge FernandezNo ratings yet
- EX - NO:1 Date: Implementation of Stop and Wait Protocol and Sliding Window Protocol AimDocument12 pagesEX - NO:1 Date: Implementation of Stop and Wait Protocol and Sliding Window Protocol Aimcs0814No ratings yet
- Java ProgrammingDocument416 pagesJava ProgrammingUma ADIKINo ratings yet
- Introduction To HCI: Human Computer Interaction Thanks To Indiana University USA For BSIT-2 (M+E)Document26 pagesIntroduction To HCI: Human Computer Interaction Thanks To Indiana University USA For BSIT-2 (M+E)aliiiiNo ratings yet
- 05 Chapter 18 Concurrency Control TechniquesDocument28 pages05 Chapter 18 Concurrency Control TechniquesArvind LalNo ratings yet
- Web DevelopmentDocument10 pagesWeb DevelopmentTeam MarketingNo ratings yet
- 6 Android UI ArchitectureDocument24 pages6 Android UI ArchitectureMarichris VenturaNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented ConceptsDocument39 pagesObject Oriented ConceptsObaidUllah NaqviNo ratings yet
- ACA Notes TechJourney PDFDocument206 pagesACA Notes TechJourney PDFPrakhyath JainNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On PRTG Monitoring Software Used in Managing A NetworkDocument10 pagesA Presentation On PRTG Monitoring Software Used in Managing A NetworkkingNo ratings yet
- Unit - II RDocument61 pagesUnit - II RManoj BabuNo ratings yet
- DBMS Chapter 2 - Data ModelsDocument60 pagesDBMS Chapter 2 - Data ModelsJM RosaldesNo ratings yet
- VB Net Unit IDocument25 pagesVB Net Unit Ishamalu2011100% (1)
- Computer Careers and CertificationDocument35 pagesComputer Careers and CertificationAngelina LimNo ratings yet
- Network Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandNetwork Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nursing Care During Prenatal PeriodDocument7 pagesNursing Care During Prenatal Periodsands32No ratings yet
- Andhra Bank StatementDocument2 pagesAndhra Bank StatementDarren Joseph VivekNo ratings yet
- YersiniaDocument46 pagesYersiniajamal nasir50% (2)
- Activity 1.1 & 1.2Document2 pagesActivity 1.1 & 1.2marriette joy abadNo ratings yet
- (Variorum Collected Studies Series) Paola Zambelli-Astrology and Magic From The Medieval Latin and Islamic World To Renaissance Europe - Theories and Approaches-Routledge (2012)Document155 pages(Variorum Collected Studies Series) Paola Zambelli-Astrology and Magic From The Medieval Latin and Islamic World To Renaissance Europe - Theories and Approaches-Routledge (2012)Vlad Alexandru100% (1)
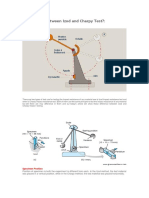
- Difference Between Izod and Charpy Test?:: Specimen PositionDocument3 pagesDifference Between Izod and Charpy Test?:: Specimen Positionbader jomaaNo ratings yet
- Pemanfaatan Copepoda Oithona SP SebagaiDocument386 pagesPemanfaatan Copepoda Oithona SP SebagaihajijojonNo ratings yet
- Negolas - Death House PCDocument11 pagesNegolas - Death House PCgarrett kirkNo ratings yet
- O Examinare A Simțurilor Copiilor - Puppetry - ThesisDocument146 pagesO Examinare A Simțurilor Copiilor - Puppetry - Thesisdeva deviNo ratings yet
- Balthazar's Marvelous Afternoon PPT-1Document11 pagesBalthazar's Marvelous Afternoon PPT-1Jean Alric AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Megemy at Last - Online EditionDocument5 pagesMegemy at Last - Online EditionJeremy St-OngeNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Imaging: Approaches and ProtocolsDocument9 pagesEpilepsy Imaging: Approaches and ProtocolsNatalia E PenagosNo ratings yet
- Amidah PrayersDocument2 pagesAmidah Prayerscrorex1100% (3)
- Ajeeth Pingle Brand Extention PlanDocument17 pagesAjeeth Pingle Brand Extention PlanAjeeth PingleNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Tablet Mefenamic Acid, Quality Tablet, UV SpectrophotometryDocument8 pagesKeywords: Tablet Mefenamic Acid, Quality Tablet, UV SpectrophotometryNanang KedokteranNo ratings yet
- Why We SleepDocument6 pagesWhy We SleepJustine MenesesNo ratings yet
- Paleth ReportDocument51 pagesPaleth ReportMarlon Rey AnacletoNo ratings yet
- Tauhid Islamic Monotheism.Document2 pagesTauhid Islamic Monotheism.Mikel AlonsoNo ratings yet
- QR Codes: What, How and Why?Document18 pagesQR Codes: What, How and Why?coleesenseiNo ratings yet
- Ben Franklin Advice To A Young ManDocument2 pagesBen Franklin Advice To A Young ManAditya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 and 6Document35 pagesChapter 5 and 6Onetwothree TubeNo ratings yet
- b4391 QuantumDocument8 pagesb4391 QuantumlailiNo ratings yet
- Modulo Pagador WincorDocument287 pagesModulo Pagador Wincoradrien100% (1)
- Influence of Inquiry-Based Science Activities On Students' AchievementDocument14 pagesInfluence of Inquiry-Based Science Activities On Students' AchievementPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary Journal100% (2)