Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WK 2 HR 1 &2 Project Planning & WBS
Uploaded by
Ting Aik SengOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WK 2 HR 1 &2 Project Planning & WBS
Uploaded by
Ting Aik SengCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIMAS 2019
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
PROJECT PLANNING
Planning is the cornerstone of Project Management. It is actually a
vital if not the most important process in Project Management.
It provides the baselines
It sets the momentum for the project – the timing and budget
It insists on the right people with the right skill set for the job
It acknowledges the availability of the right tools/machinery
and techniques to do the job
It puts forward the risks for the projects
It gathers information on operation, technical, contractual,
management, bureaucratic constraints
It provides directions – objectives and goals
It provides understanding of the requirements and needs of
the stakeholders, clients and professionals involved and maps
out the quality of the end products/facilities
The primary purpose of planning is of course to establish a set of
directions in sufficient details to tell the project team exactly
o What must be done
o When it must be done
o What resources to be used
o What is the cost attach
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PREPARED BY SNTING
UNIMAS 2019
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
o Who is to do what
o How the works are supposed to be carried out
Planning effort must be adequate in accordance with type, size
and the project environment.
“Plans are only good intentions unless they immediately
degenerate into hard work” ~ Reader’s Digest (March 1998,
p. 49)
Planning is often neglected or done inadequately. Poor planning
may not be entirely blamed for poor project performance but it
contributes to problems and issues during execution.
Please note that planning is a collective effort – not just top down
or client based. Members of other agencies especially contractors
could have involvement and should be consulted to provide at least
basic data on scheduling and construction techniques and material.
With planning, we looked into resource allocations, which includes
time and other physical resources as well
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PREPARED BY SNTING
UNIMAS 2019
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
What is a Project Plan?
It is good if we can make the planning process as simple and
straightforward as possible. However, as much as project engineers
would like it that way though it is tedious and sometimes torturous.
Having a system would definitely help.
--- Software involvement – the idea of BIM, Scheduling
softwares, construction management softwares
Basic elements of a project plan:
o Activities/Events ~ establishing the technical scope of the
work
o Time Schedules ~ planned schedules
o Resources
o Site labour, machinery, material plans
o Cost estimation of the activities ~ planned budget
o Personnel ~ basic areas if performance responsibility
accepted by the participants
o Quality and safety plans
o Risk assessment and analysis **
**In some cases, a specific risk management group is created
for managing risk in terms budgets and schedules.
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PREPARED BY SNTING
UNIMAS 2019
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
The project plans include processes (what – work flow diagram)
and procedures (how- steps), and tools and techniques that works
towards delivering the end products desired.
1.1 WORK BREAKDOWN ANALYSIS
Work Breakdown Structures and Statements
Work Breakdown Structures and Statements is an established tool
for structuring a project so that all the individual component and
elements are identified in a hierarchical format. It addresses the
technical scope of the work, to which resources are allocated.
Note: In this course we are concentrating on one project at a time
not multiple projects. With multiple projects, the planning and
resource allocation task can be even more complicated.
Complications will arise when we deal with trade-offs.
WBS are used because they:
Provide a framework for the organization and management of
the project.
Provide a framework for planning and controlling
Breakdown the project into manageable components
Provide a mean to cover all the works in an easy to
understand way.
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PREPARED BY SNTING
UNIMAS 2019
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
Useful as a quantitative for pricing, allocating responsibilities
and costs, durations and quality and safety related
requirements.
In civil engineering, works are breakdown into various key
operations. Work breakdown analysis assists PM in dividing
the overall project into manageable tasks/operations/activities.
The WBS often appears as an outline with the Level 1 tasks on
the left side and successive levels appropriately indented. It is a
picture of a project subdivided into units of tasks, subtasks.
Each activity has to be properly defined and can be further
breakdown into sub-activity Normally three layers of
breakdown are able to well define the project. Work
breakdown Structure is the end product of the process. Please
refer to following “How to do Work Breakdown Analysis”
How do we conduct a WBS exercise?
1) Identify the major components of project, which can be clearly
obtained from the scope and the drawings and specifications. Say,
1. Preliminaries
2. Building 1
3. Building 2
4. Drainage Work
5. Road Work
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PREPARED BY SNTING
UNIMAS 2019
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
6. Water Work
7. Sewer Work
8. Landscaping, etc
2) With Layering System, breakdown the work into sub-tasks
2. Building Work
Foundation Work
Piling
Hacking of piles
Pile caps
Work Breakdown is the backbone for any planning and
controlling of time and cost. Not only that schedule of operations
are based on these analysis, estimates and costing revolves
around Work Breakdown and resources (machinery, material
and labour) can be allocated efficiently and accordingly. Quality
and safety plans can be drafted based on WBS.
1.2 RESOURCES PLANNING
Resources are about the people and things that are required to
complete the tasks or activities of a project. Consideration of the
resources has to be at the earliest stage of the project, even at the
conceptual stage. They are determinants and considerations in
many cases. Resources at its most basic consist of
Staffing/ Team/Human/Labor
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PREPARED BY SNTING
UNIMAS 2019
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
Material
Special Facilities and Equipment
Financial resources – cash and funds needed
Organisational resources –Other departments, subcontractors,
suppliers
Prior to any scheduling and costing exercise, Project Manager
would need to properly identify and select the resources which are
required. The amount, type and quality of resources available will
directly and indirectly affect the production rate on site.
Staffing/Team/Labour
By Project Staffing, we are looking at the management team,
technical team who has the knowledge and expertise to put
together the project plan, guide the project towards delivery,
organized and carry out monitoring and controlling on site.
By Labour we are specifying the construction site personnel under
direct employment ~ site supervisors, tradesman, skilled, semi-
skilled and unskilled labour.
All elements of construction work will involve the expenditure of
people’s time, which means incurring a cost in terms of labour.
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PREPARED BY SNTING
UNIMAS 2019
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
This applies across all skills and disciplines, but they are directly
involved in the project.
Material
The largest component of the cost of an engineering project is the
cost of materials. These can be recognized inseveral forms such as
Building and construction materials required for the structure
(“permanent” materials);
Temporary materials required during the project delivery
phase;
Consumables materials required during the operation and
maintenance phase of the facility.
Special Facilities and Equipment
A selection of plant and equipment may be necessary for the
project delivery and operational phases. This could be
major plant eg. Cranes, tunneling machines, earth moving
plant, barges, tugs
minor plant and equipment eg. Hoists, compressors,
generators, pumps, piling hammers and equipment.
Special facilities include testing facilities and equipment, batching
plants, storage facilities.
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PREPARED BY SNTING
UNIMAS 2019
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
Organisational resources
Interdepartmental supports – office administration support,
technical and operations skills from other teams, procurement and
logistics support.
Design team from external organizations.
Subcontractors for any civil engineering projects can usually be
categorized to provide
o Labour only
o Labour and material together with equipment and machinery
o Specialised technology or items and labour and supervisory
team
Suppliers’ support for credit terms, delivery and pricing.
Resources Data
Formal planning needs to be carried out. Tools and Techniques:
Resources bar charts and tables
Resources histograms show loading of a particular resources
Summaries of resources usage
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PREPARED BY SNTING
UNIMAS 2019
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
Softwares
PROJECT MANAGEMENT PREPARED BY SNTING
You might also like
- Construction Project Planning and Scheduling L4Document10 pagesConstruction Project Planning and Scheduling L4Mel'aku Gebr'elNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Construction Methods and Project ManagementDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Construction Methods and Project ManagementAries MalicdemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - SchedulingDocument21 pagesChapter 6 - Schedulingmuliye tarekegnNo ratings yet
- Bjectives OF CourseDocument24 pagesBjectives OF CourseAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Aviation Manager’s Toolkit: How to Develop Php/Mysql-Based Interactive Communication Platform: A Computational Approach to Aviation MaintenanceFrom EverandAviation Manager’s Toolkit: How to Develop Php/Mysql-Based Interactive Communication Platform: A Computational Approach to Aviation MaintenanceNo ratings yet
- Arcenas Bait2c Is104 Midterm Assignment-1Document3 pagesArcenas Bait2c Is104 Midterm Assignment-1Arcenas KenNo ratings yet
- Prof Prac 03: Saint Louis CollegeDocument12 pagesProf Prac 03: Saint Louis CollegeAnghelikaaaNo ratings yet
- Project Management and PracticesDocument29 pagesProject Management and PracticesNur SyafiqahNo ratings yet
- Planning and Scheduling ProceduresDocument8 pagesPlanning and Scheduling ProceduresMohd SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- SC431 Lecture No. 6 - Introduction To Construction Planning ProcDocument84 pagesSC431 Lecture No. 6 - Introduction To Construction Planning ProcJoseph BaruhiyeNo ratings yet
- Project Management ConceptsDocument18 pagesProject Management Conceptskami_r202No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - CEMDocument54 pagesUnit 1 - CEMC ABHISHEK (RA1811001010005)No ratings yet
- SathyanandMaroju - PMIBC-19-1-016 - Interactive Voice Based Tool Project ManagementDocument8 pagesSathyanandMaroju - PMIBC-19-1-016 - Interactive Voice Based Tool Project ManagementabiNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper On Module 5Document3 pagesReaction Paper On Module 5tine.torio05No ratings yet
- Specialization 03 Construction Management (Lecture 1) I. The Need For Construction Management The Construction IndustryDocument8 pagesSpecialization 03 Construction Management (Lecture 1) I. The Need For Construction Management The Construction IndustryJosua MenisNo ratings yet
- Ebook & Notes - Construction Planning and SchedulingDocument47 pagesEbook & Notes - Construction Planning and SchedulingprakashNo ratings yet
- Major Elements of Project Execution Planning For Construction of BuildingsDocument5 pagesMajor Elements of Project Execution Planning For Construction of BuildingsAndré ChanNo ratings yet
- Conman II Full NotesDocument167 pagesConman II Full NotesCelestine kairuNo ratings yet
- All Concept of - Unit - 1Document11 pagesAll Concept of - Unit - 1Manesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Construction Technology & Management 7th Sem.Document12 pagesConstruction Technology & Management 7th Sem.sanjay kumarNo ratings yet
- Operational ManagementDocument5 pagesOperational ManagementJiya HaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 & 3-1Document79 pagesChapter 1 & 3-1disasa abebeNo ratings yet
- Construction Engineering and ManagementDocument53 pagesConstruction Engineering and ManagementArnie Juliene AbogadoNo ratings yet
- CM310-Assignment No.1 (Jesse PETER)Document12 pagesCM310-Assignment No.1 (Jesse PETER)Jesse PeterNo ratings yet
- Course Mba - 2 Semester Subject Assignment MB0049 - Set1: Project ManagementDocument37 pagesCourse Mba - 2 Semester Subject Assignment MB0049 - Set1: Project ManagementMaheder AdmassuNo ratings yet
- Project Management For Civil WorksDocument10 pagesProject Management For Civil WorksKhurram JavedNo ratings yet
- G1 - Pre-ConstructionDocument19 pagesG1 - Pre-ConstructionjaybeelibrauxNo ratings yet
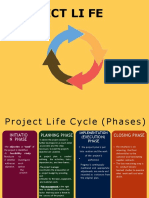
- Project Life Cycle & Framework, Franz B.Document21 pagesProject Life Cycle & Framework, Franz B.Lady TashaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - SchedulingDocument21 pagesChapter 6 - SchedulingjohnNo ratings yet
- Mar 2020 - The Importance of Engineering and Construction Alignment Throughout The Project LifecycleDocument3 pagesMar 2020 - The Importance of Engineering and Construction Alignment Throughout The Project LifecycleNong.TankhunNo ratings yet
- Rizal Technological University: Department of ArchitectureDocument5 pagesRizal Technological University: Department of ArchitectureMharcianeMaxineMagoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term Project Management SystemDocument60 pages2nd Term Project Management SystemShreedhar100% (1)
- Project Planning, SchedulingDocument20 pagesProject Planning, Schedulingnzb1234No ratings yet
- Project Management: SyllabusDocument16 pagesProject Management: SyllabusNiket KawaleNo ratings yet
- Constructability (Value Engineering) GuidelinesDocument60 pagesConstructability (Value Engineering) GuidelinesIgnacio Manzanera50% (2)
- Lecture 2 and 3Document14 pagesLecture 2 and 3عبدالرحمن الحازميNo ratings yet
- CE2353 CPS 2 and 16 Marks With AnsDocument74 pagesCE2353 CPS 2 and 16 Marks With AnsSathiya SeelanNo ratings yet
- Project Design and ManagementDocument64 pagesProject Design and ManagementMiliyonNo ratings yet
- (Basics (Book 154) ) Bert Bielefeld - Basics Construction Scheduling-Birkhäuser Architecture (2013)Document79 pages(Basics (Book 154) ) Bert Bielefeld - Basics Construction Scheduling-Birkhäuser Architecture (2013)uci100% (1)
- Project ManagementDocument16 pagesProject ManagementAjay KaundalNo ratings yet
- Rizal Technological University: Department of ArchitectureDocument13 pagesRizal Technological University: Department of ArchitectureMharcianeMaxineMagoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Project Cost Estimation'17Document54 pagesChapter 2. Project Cost Estimation'17wossen76% (25)
- Project Management Tools and TechniquesDocument28 pagesProject Management Tools and Techniquesumar100% (1)
- Term Paper 3 - Civil Engineering and Other ProfessionsDocument9 pagesTerm Paper 3 - Civil Engineering and Other ProfessionsREPORT ACCOUNTNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2 (CM-Management & Planning)Document13 pagesLecture-2 (CM-Management & Planning)Kabiraj KhatriNo ratings yet
- Reviewer CPMDocument18 pagesReviewer CPMAIRA BEATRIS PONo ratings yet
- Leveling Resources Without Impacting Pure LogicDocument11 pagesLeveling Resources Without Impacting Pure LogiclexloxNo ratings yet
- 4Ms and Their Management: Construction IndustryDocument35 pages4Ms and Their Management: Construction IndustryMuhammad Husnain IjazNo ratings yet
- Major Elements of Project Execution Planning For Construction of BuildingsDocument4 pagesMajor Elements of Project Execution Planning For Construction of BuildingsAjinkya KaleNo ratings yet
- Project Cost ManagementDocument30 pagesProject Cost ManagementZahid Nazir100% (1)
- Standard Planning ProcedureDocument16 pagesStandard Planning ProcedureNicholas PorterNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Project Management: Syed Momin Ali ShahDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Project Management: Syed Momin Ali ShahQaiser M. SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Construction Project ManagementDocument51 pagesConstruction Project Managementocduran4200486% (57)
- Construction Project ManagementDocument51 pagesConstruction Project Managementocduran42004100% (5)
- Planning and Scheduling of High Rise Building Using PrimaveraDocument5 pagesPlanning and Scheduling of High Rise Building Using PrimaveraSahilNo ratings yet
- Project ControlDocument4 pagesProject ControlVishal TiwariNo ratings yet
- Construction Period For Matading-Bedengan Subcentre Rev - Eot1Document6 pagesConstruction Period For Matading-Bedengan Subcentre Rev - Eot1Ting Aik SengNo ratings yet
- Earned Value: Earned Value Provides A Means of Detecting The Nature and Extent ofDocument6 pagesEarned Value: Earned Value Provides A Means of Detecting The Nature and Extent ofTing Aik SengNo ratings yet
- Universiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringDocument3 pagesUniversiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringTing Aik SengNo ratings yet
- Universiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringDocument5 pagesUniversiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringTing Aik SengNo ratings yet
- Universiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringDocument3 pagesUniversiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringTing Aik SengNo ratings yet
- Universiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringDocument3 pagesUniversiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringTing Aik SengNo ratings yet
- Universiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringDocument3 pagesUniversiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringTing Aik SengNo ratings yet
- Universiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringDocument3 pagesUniversiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringTing Aik SengNo ratings yet
- WK 8 HR 3 4 Planning Quality Labour SafetyDocument27 pagesWK 8 HR 3 4 Planning Quality Labour SafetyTing Aik SengNo ratings yet
- Wk13 HR 3 4 Engineering EconomicsDocument18 pagesWk13 HR 3 4 Engineering EconomicsTing Aik SengNo ratings yet
- Wk14 HR 2 3 Risk ManagementDocument27 pagesWk14 HR 2 3 Risk ManagementTing Aik SengNo ratings yet
- WK 1 HR 1 & 2 Engineering Management1Document15 pagesWK 1 HR 1 & 2 Engineering Management1Ting Aik SengNo ratings yet
- Shear Force Diagram: The Black Line Represents EnvelopeDocument2 pagesShear Force Diagram: The Black Line Represents EnvelopeTing Aik SengNo ratings yet
- Fiduciary Oath-GeneralDocument1 pageFiduciary Oath-GeneralTing Aik SengNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Transfer Plate Design and ConstructionDocument16 pagesPrestressed Transfer Plate Design and Constructiona96lhf0% (1)
- MICA 4scaleDocument3 pagesMICA 4scaleMadawi AlotaibiNo ratings yet
- Ryan Higa's How To Write Good: PrologueDocument9 pagesRyan Higa's How To Write Good: PrologueIsabella Biedenharn89% (9)
- Magdusa vs. AlbaranDocument4 pagesMagdusa vs. AlbaranXtine CampuPotNo ratings yet
- City of Manila V IACDocument1 pageCity of Manila V IACCel GamoNo ratings yet
- E Brochure-Fdc PDFDocument6 pagesE Brochure-Fdc PDFJahjaNo ratings yet
- Transport Layer: Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachDocument108 pagesTransport Layer: Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachSSNShimogaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Account Determination (MM-FI)Document19 pagesAutomatic Account Determination (MM-FI)Ankit BudheNo ratings yet
- Solved - The Data in WAGE2.RAW On Working Men Was Used To Estima...Document1 pageSolved - The Data in WAGE2.RAW On Working Men Was Used To Estima...kharismapb0% (1)
- ACCT 250 - Principles of Auditing Spring 2022, Section 2 Handout 11 - Power BI Exercise QuestionsDocument6 pagesACCT 250 - Principles of Auditing Spring 2022, Section 2 Handout 11 - Power BI Exercise QuestionsRaza HashmeNo ratings yet
- Rapid Visual Screening of Buildings For Potential Seismic Hazards FEMA P-154 Data Collection FormDocument1 pageRapid Visual Screening of Buildings For Potential Seismic Hazards FEMA P-154 Data Collection FormFauzy AslyNo ratings yet
- Aldinga Bay's Coastal Views December 2014Document40 pagesAldinga Bay's Coastal Views December 2014Aldinga BayNo ratings yet
- Profit and LossDocument7 pagesProfit and LossSanjuSanjayNo ratings yet
- ME 522 - Power Plant Engineering - Steam Power Plant - Part 1 - LectureDocument56 pagesME 522 - Power Plant Engineering - Steam Power Plant - Part 1 - LectureJom Ancheta BautistaNo ratings yet
- How To Add Field To Print Continued in MSWord FootersDocument2 pagesHow To Add Field To Print Continued in MSWord FootersvishraniNo ratings yet
- SDDSDDocument2 pagesSDDSDKaushalya PereraNo ratings yet
- Burke - Oxidizing and Reducing AgentsDocument607 pagesBurke - Oxidizing and Reducing AgentscapranzoloNo ratings yet
- Economía EnergéticaDocument8 pagesEconomía EnergéticaSERGIO MANZO ANDRADENo ratings yet
- Wipro Offer LetterDocument14 pagesWipro Offer Lettertapan kumar singhaNo ratings yet
- Motion For ReconsiderationDocument6 pagesMotion For ReconsiderationLoumari Crea100% (1)
- Idaho Proof of Use of TitleDocument2 pagesIdaho Proof of Use of TitleRam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Development Strategies of The Bahari Jawai Marine Tourism Coast Area Based On Community Empowerment in Sambas RegencyDocument10 pagesDevelopment Strategies of The Bahari Jawai Marine Tourism Coast Area Based On Community Empowerment in Sambas Regencyberagam09No ratings yet
- Trial9 Ora 17055 Inform Answer Close Query - TRCDocument76 pagesTrial9 Ora 17055 Inform Answer Close Query - TRCManoj MohapatraNo ratings yet
- 3UG46161CR20 Datasheet enDocument6 pages3UG46161CR20 Datasheet envoNo ratings yet
- JSF TutorialDocument346 pagesJSF TutorialMarwa GhozNo ratings yet
- Problem Set: Exchange Rates: International EconomicsDocument16 pagesProblem Set: Exchange Rates: International EconomicsLucia Yuste MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Sri Lanka Media Audience Study 2019Document64 pagesSri Lanka Media Audience Study 2019methlalNo ratings yet
- Workplace Mental Health PolicyDocument4 pagesWorkplace Mental Health PolicyNolen Endaya100% (2)
- Manual TV Sansumg UN40F5500Document170 pagesManual TV Sansumg UN40F5500albafloNo ratings yet
- The PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeFrom EverandThe PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeFrom EverandThe PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (36)
- Project Management: The Ultimate Guide for Managing Projects, Productivity, Profits of Enterprises, Startups and Planning with Lean, Scrum, Agile.From EverandProject Management: The Ultimate Guide for Managing Projects, Productivity, Profits of Enterprises, Startups and Planning with Lean, Scrum, Agile.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Administrative Procedures and ManagementFrom EverandAdministrative Procedures and ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Agile Project Management: Scrum Master: 21 Tips to Facilitate and Coach Agile Scrum TeamsFrom EverandAgile Project Management: Scrum Master: 21 Tips to Facilitate and Coach Agile Scrum TeamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (34)
- Building a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialFrom EverandBuilding a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (240)
- PMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamFrom EverandPMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Harvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsFrom EverandHarvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (16)
- Secrets of Home Staging: The Essential Guide to Getting Higher Offers Faster (Home décor ideas, design tips, and advice on staging your home)From EverandSecrets of Home Staging: The Essential Guide to Getting Higher Offers Faster (Home décor ideas, design tips, and advice on staging your home)No ratings yet
- Agile Practice GuideFrom EverandAgile Practice GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- Scrum: Understanding Scrum at a Deeper Level and Mastering Agile Project ManagementFrom EverandScrum: Understanding Scrum at a Deeper Level and Mastering Agile Project ManagementRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- PMP Exam Prep: Master the Latest Techniques and Trends with this In-depth Project Management Professional Guide: Study Guide | Real-life PMP Questions and Detailed Explanation | 200+ Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP Exam Prep: Master the Latest Techniques and Trends with this In-depth Project Management Professional Guide: Study Guide | Real-life PMP Questions and Detailed Explanation | 200+ Questions and AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Q & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionFrom EverandQ & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Lean Six Sigma: A Practical Guide for Getting Started with Lean Six Sigma along with How It Can Be Integrated with Agile and ScrumFrom EverandLean Six Sigma: A Practical Guide for Getting Started with Lean Six Sigma along with How It Can Be Integrated with Agile and ScrumRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- 300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionFrom Everand300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeFrom EverandThe Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (99)
- The Complete Project Manager: Integrating People, Organizational, and Technical SkillsFrom EverandThe Complete Project Manager: Integrating People, Organizational, and Technical SkillsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Scrum: Step-by-Step Agile Guide to Scrum (Scrum Roles, Scrum Artifacts, Sprint Cycle, User Stories, Scrum Planning)From EverandScrum: Step-by-Step Agile Guide to Scrum (Scrum Roles, Scrum Artifacts, Sprint Cycle, User Stories, Scrum Planning)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (13)
- Focus: The Hidden Driver of ExcellenceFrom EverandFocus: The Hidden Driver of ExcellenceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (158)
- Delegating Work (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)From EverandDelegating Work (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Red Pill Executive: Transform Operations and Unlock the Potential of Corporate CultureFrom EverandThe Red Pill Executive: Transform Operations and Unlock the Potential of Corporate CultureNo ratings yet
- Project Management All-in-One For DummiesFrom EverandProject Management All-in-One For DummiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Building a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialFrom EverandBuilding a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (119)
- The Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationFrom EverandThe Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationNo ratings yet
- Project Control Methods and Best Practices: Achieving Project SuccessFrom EverandProject Control Methods and Best Practices: Achieving Project SuccessNo ratings yet
- Fractional Leadership: Landing Executive Talent You Thought Was Out of ReachFrom EverandFractional Leadership: Landing Executive Talent You Thought Was Out of ReachRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)