Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mikrobiologi Farmasi "Fungi": Anggun Hari Kusumawati M.Si.,Apt
Uploaded by
SEPTIANA SAPUTRI0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views26 pagesThe document discusses fungi and their characteristics. It notes that fungi can grow as single cells or multicellular filaments. They do not contain chlorophyll and obtain nutrients from dead or living organic matter. The kingdom that includes yeast, molds and mushrooms is termed fungi. Fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction involves spores while sexual reproduction involves the fusion of nuclei from two cells.
Original Description:
Original Title
FUNGI-5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses fungi and their characteristics. It notes that fungi can grow as single cells or multicellular filaments. They do not contain chlorophyll and obtain nutrients from dead or living organic matter. The kingdom that includes yeast, molds and mushrooms is termed fungi. Fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction involves spores while sexual reproduction involves the fusion of nuclei from two cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views26 pagesMikrobiologi Farmasi "Fungi": Anggun Hari Kusumawati M.Si.,Apt
Uploaded by
SEPTIANA SAPUTRIThe document discusses fungi and their characteristics. It notes that fungi can grow as single cells or multicellular filaments. They do not contain chlorophyll and obtain nutrients from dead or living organic matter. The kingdom that includes yeast, molds and mushrooms is termed fungi. Fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction involves spores while sexual reproduction involves the fusion of nuclei from two cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI Anggun Hari Kusumawati
“FUNGI” M.Si.,Apt
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 1
FUNGI
It has been duly observed and amply demonstrated that fungi invariably grow
as single cells, as in yeast, or as multicellular filamentous colonies, as in molds
and mushrooms. Interestingly, fungi do not contain chlorophyll (i.e., the nature’s
organic green matter), hence they are saprophytic (i.e., they obtian food from
dead organic matter) or parasitic (i.e., they obtain nourishment from the living
organisms), and above all the body’s normal flora categorically contains
several fungi. However, most fungi are not pathogenic in nature.
The kingdom of organisms that essentially includes yeast, molds, and
mushrooms, is termed as fungi.
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 2
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 3
FUNGI
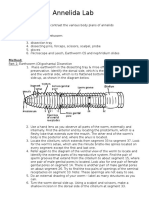
Molds and Fleshy Fungi The thallus (body) of a mold or fleshy fungus
consists of long filaments of cells joined together; these filaments are called
hyphae (singular: hypha).
Hyphae can grow to immense proportions. Using DNA fingerprinting,
scientists mapped the hyphae of a single fungus in Oregon (a mushroom)
that extended over 4 square miles.
In most molds, the hyphae contain cross-walls called septa (singular:
septum), which divide them into distinct, uninucleate (one-nucleus) cell-like
units. These hyphae are called septate hyphae
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 4
Dikutip dari Tortora, 2016
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 5
FUNGI
Importantly, the fungi that essentially cause disease belong to a
specific group known as fungi imperfecti. In immunocompetent
humans these fungi usually cause minor infections of the hair, nails,
mucous membranes, or skin. It is, however, pertinent to mention here
that in a person having a compromised immune system due to AIDS
or immunosuppressive drug therapy, fungi critically serve as a
source of the viable opportunistic infections that may even cause
death ultimately.
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 6
Dikutip dari Hugo and Rusel’s, 2016
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 7
The portion of a hypha that obtains nutrients is called the
vegetative hypha; the portion concerned with reproduction is
the reproductive or aerial hypha, so named because it projects
above the surface of the medium on which the fungus is growing. Aerial hyphae
often bear reproductive spores.
When Environmental Conditions Are Suitable,
The Hyphae Grow To Form A Filamentous Mass Called A Mycelium,
Which Is Visible To The Unaided Eye.
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 8
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 9
YEAST
Yeasts are non filamentous, unicellular fungi that
are typically spherical or oval. Like molds, yeasts
are widely distributed in nature; they are
frequently found as a white powdery coating on
fruits and leaves. Budding yeasts, such as
Saccharomyces divide unevenly.
In budding, the parent cell forms a protuberance
(bud) on its outer surface. As the bud elongates, the
parent cell’s nucleus divides, and one nucleus
migrates into the bud. Cell wall material is then laid
down between the bud and parent cell, and the
bud eventually breaks away.
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 10
10/31/2017
Dikutip dari Ashutosh Kar, 2008 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 11
FUNGI
In fact, fungi are considered to be mostly saprophytic, making use of
dead organic matter as a source of energy, vital natural organic
decomposers, and destroyers of food stuffs.
While a major segment of species happen to be facultative parasites that
specifically able to feed upon either live or dead organic matter, and a
relatively minor quantum of species may only survive on the living
protoplasms.
These fungi are designated as obligate parasites thereby overwhelmingly
causing disease of man, animals, and plants. They also prove to be of
reasonably great economic and medicaL importance.
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 12
REPRODUCTION OF FUNGI
A large number of fungi invariably get reproduced both asexually
and sexually. Nevertheless, the ensuing morphology, and the cycle
of these reproductive structures is employed extensively in carrying
out their elaborated and logical classification.
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 13
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
The most common procedure of asexual reproduction is usually accomplished
by the help of spores. In common practice most of them are found to be
colourless (hyaline), while a few of them are duly pigmented as green, yellow,
red, orange, black or brown. In fact, their size may invariably range from
small to large and their shape from globose via oval, oblong, needle-shaped
to helical.
Virtually, the ensuing infintie variation in adequate spore appearance and
their arrangement prove to be of immense utility for proper identification.
Asexual reproduction may be borne particularly in a sac-like structure
termed as sporangium ; and the spores being referred to as
sporangiospores being called as conidia
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 14
ASEXUAL SPORES
Asexual spores are produced by an individual fungus through mitosis and
subsequent cell division; there is no fusion of the nuclei of cells. Two types of
asexual spores are produced by fungi. One type is a conidiospore, or
conidium (plural: conidia), a unicellular or multicellular spore that is not
enclosed in a sac. Conidia are produced in a chain at the end of a
conidiophore. Such spores are produced by Penicillium and Aspergillus.
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 15
ASEXUAL SPORES
Conidia formed by the fragmentation of a septate hypha into single, slightly
thickened cells are called arthroconidia. Another type of conidium,
blastoconidia, are formed from the buds of its parent cell. Such spores are
found in some yeasts, such as Candida albicans and Cryptococcus.
The other type of asexual spore is a sporangiospore, formed within a
sporangium, or sac, at the end of an aerial hypha called a sporangiophore.
The sporangium can contain hundreds of sporangiospores. Such spores are
produced by Rhizopus.
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 16
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 17
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 18
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 19
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 20
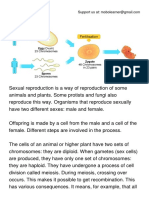
A FUNGAL SEXUAL SPORE RESULTS FROM SEXUAL
REPRODUCTION, WHICH CONSISTS OF THREE PHASES:
1. Plasmogamy. A haploid nucleus of a donor cell (+) penetrates the
cytoplasm of a recipient cell (-).
2. Karyogamy. The (+) and (-) nuclei fuse to form a diploid zygote
nucleus.
3. Meiosis. The diploid nucleus gives rise to haploid nuclei (sexual
spores), some of which may be genetic recombinants.
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 21
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 22
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Importantly, the sexual reproduction is characterized by the strategical union of
two compatible nuclei ; and the entire phenomenon may be distinctly divided into
three phases, namely :
Phase I : The union of the gametangia (i.e., sex-organs) brings the nuclei into
close proximity within the same protoplast. It is also referred to as plasmogamy.
Phase II : It is known as karyogamy, which takes place with the fusion of two
nuclei. It has been duly observed that in the lower fungi the said two processes
may take place in immediate equence ; whereas, in the higher fungi they do occur
at two altogether different time periods in the course of their life-cycle.
Phase III : It is known as meiosis that essentially takes care of the nuclear fusion
whereby the actual number of the chromosomes is distinctly and significantly
reduced to its original haploid state.
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 23
FUNGAL DISEASE
Subcutaneous mycoses are fungal infections beneath the skin caused by saprophytic fungi that
live in soil and on vegetation. Sporotrichosis is a subcutaneous infection acquired by
gardeners and farmers. Infection occurs by direct implantation of spores or mycelial fragments
into a puncture wound in the skin.
Fungi that infect only the epidermis, hair, and nails are called dermatophytes, and their
infections are called dermatomycoses or cutaneous mycoses.
Dermatophytes secrete keratinase, an enzyme that degrades keratin, a protein found in hair,
skin, and nails. Infection is transmitted from human to human or from animal to human by direct
contact or by contact with infected hairs and epidermal cells (as from barber shop clippers or
shower room floors).
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 24
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 25
10/31/2017 MIKROBIOLOGI FARMASI UBP KARAWANG 26
You might also like
- Mikrobiologi Farmasi "Fungi": Dewi Chusniasih, M.SCDocument26 pagesMikrobiologi Farmasi "Fungi": Dewi Chusniasih, M.SCAulia Fitri Handayani SiregarNo ratings yet
- FUNGI MICROBIOLOGY LECTUREDocument65 pagesFUNGI MICROBIOLOGY LECTURELouella ArtatesNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument15 pagesFungisukikiwaNo ratings yet
- Sporulation of Fungus Project Biology (Cbse 12)Document24 pagesSporulation of Fungus Project Biology (Cbse 12)Nandita Banerjee89% (19)
- Victorian Toadstools and Mushrooms: A Key and Descriptive Notes to 120 Different Gilled Fungi (Family Agaricaceae) , with Remarks on Several Other Families of the Higher FungiFrom EverandVictorian Toadstools and Mushrooms: A Key and Descriptive Notes to 120 Different Gilled Fungi (Family Agaricaceae) , with Remarks on Several Other Families of the Higher FungiNo ratings yet
- Module On FungiDocument10 pagesModule On FungiIsha GishNo ratings yet
- Fungi Lab: Michael Ngim Biosc 145 Dr. DixonDocument6 pagesFungi Lab: Michael Ngim Biosc 145 Dr. DixonSelella NgimNo ratings yet
- The Lives of Fungi: A Natural History of Our Planet's DecomposersFrom EverandThe Lives of Fungi: A Natural History of Our Planet's DecomposersNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument3 pagesFUNGIDevanand DongreNo ratings yet
- Mold in Cleanroom (JVT)Document11 pagesMold in Cleanroom (JVT)Thu Trang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument15 pagesLab ReportValentinoDullSatinNo ratings yet
- Common Edible and Poisonous Mushrooms of Southeastern Michigan - Bulletin No. 14From EverandCommon Edible and Poisonous Mushrooms of Southeastern Michigan - Bulletin No. 14No ratings yet
- G 12 FungiDocument11 pagesG 12 Fungibenyamsolomon444No ratings yet
- Mushrooms of the Great Lake Region - The Fleshy, Leathery, and Woody Fungi of Illinois, Indiana, Ohio and the Southern Half of Wisconsin and of MichiganFrom EverandMushrooms of the Great Lake Region - The Fleshy, Leathery, and Woody Fungi of Illinois, Indiana, Ohio and the Southern Half of Wisconsin and of MichiganNo ratings yet
- Bio English Fungi Made Ayu Malina Dewi 1913041005Document7 pagesBio English Fungi Made Ayu Malina Dewi 1913041005Ayu MalinaNo ratings yet
- Fungi Structure Classification ReplicationDocument23 pagesFungi Structure Classification ReplicationDoc RomeoNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Mushrooms: An Illustrated Guide to the Extraordinary Power of MushroomsFrom EverandThe Little Book of Mushrooms: An Illustrated Guide to the Extraordinary Power of MushroomsNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Fungi Group 3 Post LabDocument64 pagesKingdom Fungi Group 3 Post LabClemence Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Fungi Reproduction ExplainedDocument11 pagesFungi Reproduction ExplainedEesha NoorNo ratings yet
- Fungi Are Not Plants - Biology Book Grade 4 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandFungi Are Not Plants - Biology Book Grade 4 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Reproduction of FungiDocument12 pagesReproduction of FungiIDSP Uttarakhand100% (1)
- Botany Lab Exercises 3 To 8 Group 7 2B7 PDFDocument7 pagesBotany Lab Exercises 3 To 8 Group 7 2B7 PDFRicky Justin NgoNo ratings yet
- Outlines of Dairy Bacteriology, 8th edition A Concise Manual for the Use of Students in DairyingFrom EverandOutlines of Dairy Bacteriology, 8th edition A Concise Manual for the Use of Students in DairyingNo ratings yet
- Did Apomixis Evolve From Sex or Was It The Other Way Around?Document14 pagesDid Apomixis Evolve From Sex or Was It The Other Way Around?FatkurNo ratings yet
- The Liars of Nature and the Nature of Liars: Cheating and Deception in the Living WorldFrom EverandThe Liars of Nature and the Nature of Liars: Cheating and Deception in the Living WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Chapter 9-FungiDocument14 pagesChapter 9-FungiAurora IslamNo ratings yet
- Mushroom Spotter's Deck: A Field Guide to Fungi & Their Age-Old WisdomFrom EverandMushroom Spotter's Deck: A Field Guide to Fungi & Their Age-Old WisdomNo ratings yet
- Morphology, Life Cycle and Economic Importance ofDocument21 pagesMorphology, Life Cycle and Economic Importance ofMofoluwaso OyinloyeNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of the First International Congress of Parasitology: Roma, 21-26 September 1964From EverandProceedings of the First International Congress of Parasitology: Roma, 21-26 September 1964Augusto CorradettiNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument9 pagesFungiMAHESH KOUJALAGINo ratings yet
- The Eukaryotes: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa, and Helminths: Presentation Based On Tortora Et Al, MicrobiologyDocument68 pagesThe Eukaryotes: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa, and Helminths: Presentation Based On Tortora Et Al, MicrobiologyalirezaNo ratings yet
- Spores, Dormancy and DispersalDocument59 pagesSpores, Dormancy and DispersalMaria MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Zhukoca Et Al., 2017Document14 pagesZhukoca Et Al., 2017JorgeVictorMauriceLiraNo ratings yet
- Ebook - Mushrooms - The Mushroom CultivatorDocument374 pagesEbook - Mushrooms - The Mushroom CultivatorSunny ChosaNo ratings yet
- The Mushroom CultivatorDocument374 pagesThe Mushroom CultivatorClaude-MichelNo ratings yet
- Understanding, Preventing, and Remediating Mold in CleanroomsDocument9 pagesUnderstanding, Preventing, and Remediating Mold in CleanroomsaugustoxavierNo ratings yet
- Mycology IntroDocument15 pagesMycology IntroParikesit MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Fungal Fundamentals: An Introduction to FungiDocument20 pagesFungal Fundamentals: An Introduction to Fungisehrish iqbalNo ratings yet
- BSECSCI 14 (Fungi) Patinga, Christine Mae V.Document4 pagesBSECSCI 14 (Fungi) Patinga, Christine Mae V.Christian PatingaNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument31 pagesFungiTADIWANASHE TINONETSANANo ratings yet
- Sporulation of FungiDocument41 pagesSporulation of FungiSmit Mecklin100% (1)
- SaprophytesDocument40 pagesSaprophytesRami Aldalistar100% (1)
- Fungi: Great Resources!Document5 pagesFungi: Great Resources!GUIDO ERNESTO VILLOTA CALVACHINo ratings yet
- SMB3103Document147 pagesSMB3103xasantalan3No ratings yet
- General Structure and Classification of Fungus: Sakshi SinghDocument12 pagesGeneral Structure and Classification of Fungus: Sakshi SinghShiksha singh Shiksha singhNo ratings yet
- Stuyvesant Biology Lab Explores Algae, Fungi Nutrition and ReproductionDocument3 pagesStuyvesant Biology Lab Explores Algae, Fungi Nutrition and ReproductionPeace123No ratings yet
- Classifications of Fungi - Biology For Majors IIDocument12 pagesClassifications of Fungi - Biology For Majors IISaviru SandivNo ratings yet
- The Eukaryotes: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa, & HelminthsDocument14 pagesThe Eukaryotes: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa, & HelminthsApryll DarlineNo ratings yet
- Fungi: Diverse Group of Heterotrophs That Absorb NutrientsDocument16 pagesFungi: Diverse Group of Heterotrophs That Absorb NutrientsWahyu NurhaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Fungi: Classification, Morphology and ReproductionDocument8 pagesIntroduction to Fungi: Classification, Morphology and ReproductionAnandNo ratings yet
- p8 Jurnal Tolerability and Safety of Black Cumin Seed OilDocument7 pagesp8 Jurnal Tolerability and Safety of Black Cumin Seed OilSEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- P10 Nejmoa1805489Document10 pagesP10 Nejmoa1805489SEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Nilai Diagnostik Indikator Fisik.... (Samsudin M, Kumorowulan S, Supadmi S)Document14 pagesNilai Diagnostik Indikator Fisik.... (Samsudin M, Kumorowulan S, Supadmi S)SEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Comparation of HbA1C and Fasting Blood SugarDocument8 pagesComparation of HbA1C and Fasting Blood SugarIez FatihahNo ratings yet
- Remdesivir For 5 or 10 Days in Patients With Severe Covid-19Document11 pagesRemdesivir For 5 or 10 Days in Patients With Severe Covid-19David FlorianNo ratings yet
- p8 Jurnal The - Efficacy - of - Black - Cumin - Seed - Nigella - Sativa - OiDocument9 pagesp8 Jurnal The - Efficacy - of - Black - Cumin - Seed - Nigella - Sativa - OiSEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Mikrobiologi Farmasi "Virus": Anggun Hari Kusumawati M.Si.,AptDocument22 pagesMikrobiologi Farmasi "Virus": Anggun Hari Kusumawati M.Si.,AptSEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Priani., 2020Document8 pagesPriani., 2020ftmrdrNo ratings yet
- What Is Critical AppraisalDocument8 pagesWhat Is Critical AppraisalAllen FallenNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine For Treatment of Severe Hypertension in Pregnancy Meta-AnalysisDocument10 pagesHydralazine For Treatment of Severe Hypertension in Pregnancy Meta-AnalysisSEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Medicinal Ethnobotany and Potential of Medicine Plants of Anak Rawa Ethnic at The Penyengat Village Sungai Apit Siak RiauDocument11 pagesMedicinal Ethnobotany and Potential of Medicine Plants of Anak Rawa Ethnic at The Penyengat Village Sungai Apit Siak RiauisramelliyantiiNo ratings yet
- A Randomized Trial of Hydroxychloroquine As Postexposure Prophylaxis For Covid-19Document9 pagesA Randomized Trial of Hydroxychloroquine As Postexposure Prophylaxis For Covid-19Nestor AzuaraNo ratings yet
- Chemopreventive Effects of Soursop LeavesDocument9 pagesChemopreventive Effects of Soursop LeavesSEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Submited As Partial Fulfillment For The Requirement To Obtain The Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan in English Education ProgramDocument64 pagesSubmited As Partial Fulfillment For The Requirement To Obtain The Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan in English Education ProgramYudhie RahmanNo ratings yet
- An Overview On Medicinal Plants For The TreatmentDocument8 pagesAn Overview On Medicinal Plants For The TreatmentSEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Current Drugs With Potential For Treatment of COVID-19Document7 pagesCurrent Drugs With Potential For Treatment of COVID-19wiwiNo ratings yet
- Urological Survey: J. R. Price, L. A. Guran, W. T. Gregory and M. S. McdonaghDocument2 pagesUrological Survey: J. R. Price, L. A. Guran, W. T. Gregory and M. S. McdonaghSEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- MDR - RR TB TaskForce FAQs v1Document19 pagesMDR - RR TB TaskForce FAQs v1SEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Accuracy of Serological Tests For Diagnosis of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument17 pagesAccuracy of Serological Tests For Diagnosis of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisSEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Clinical ImmunologyDocument37 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Clinical ImmunologySEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Superoksida Dismutase (Sod) Dan Radikal BebasDocument6 pagesSuperoksida Dismutase (Sod) Dan Radikal BebasIvon PalenteNo ratings yet
- 3 Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections in PDFDocument6 pages3 Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections in PDFOltg GalNo ratings yet
- Uti 2011Document7 pagesUti 2011Kamolporn JongchanapongNo ratings yet
- J Ajog 2016 07 040Document43 pagesJ Ajog 2016 07 040SEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Bmjopen 2016 015233Document7 pagesBmjopen 2016 015233SEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- DKH 414Document4 pagesDKH 414SEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA) Treatment For COVID-19 Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) : A Case SeriesDocument9 pagesTissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA) Treatment For COVID-19 Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) : A Case SeriesSEPTIANA SAPUTRINo ratings yet
- Uncomplicated Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument18 pagesUncomplicated Urinary Tract InfectionsAndreas IoannouNo ratings yet
- EAU Guidelines On Urological Infections 2018Document66 pagesEAU Guidelines On Urological Infections 2018indra wijayaNo ratings yet
- Annelida LabDocument4 pagesAnnelida Labapi-297841438No ratings yet
- CestodesDocument86 pagesCestodesPidchayathanakorn Paemika0% (1)
- Biology Q PDFDocument9 pagesBiology Q PDFsumon chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- #1 Anatomi Fisiologi Urogenital SystemDocument4 pages#1 Anatomi Fisiologi Urogenital SystemNur azriyati PutriNo ratings yet
- PuerperiumDocument12 pagesPuerperiumsubhro kanti duttaNo ratings yet
- Reassessing The Labor Curve in Nulliparous WomenDocument5 pagesReassessing The Labor Curve in Nulliparous WomenPercy Astocaza FloresNo ratings yet
- Dr. Dwi Rita Anggraini, M.Kes Dr. Sufitni, M.Kes Anatomy Department Medicine Faculty of North SumatraDocument19 pagesDr. Dwi Rita Anggraini, M.Kes Dr. Sufitni, M.Kes Anatomy Department Medicine Faculty of North SumatraAnnDianaJaiminNo ratings yet
- What Is Klinefelter SyndromeDocument11 pagesWhat Is Klinefelter SyndromeFatima Adessa PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Motilitas dan Viabilitas Spermatozoa Itik LokalDocument7 pagesMotilitas dan Viabilitas Spermatozoa Itik LokalNimas Alya IstiqlalaNo ratings yet
- Criptorquidia en PerrosDocument4 pagesCriptorquidia en PerrosDanielaNo ratings yet
- Maternal Health - Blogs Comment On Women Deliver Conference, Birth Control Coverage, Other Topics (Medical News Today - 10 June 2010)Document3 pagesMaternal Health - Blogs Comment On Women Deliver Conference, Birth Control Coverage, Other Topics (Medical News Today - 10 June 2010)National Child Health Resource Centre (NCHRC)No ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction PDFDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FungiDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Fungikep1313No ratings yet
- SPM 2011 Biology Paper 2 Answer SchemeDocument7 pagesSPM 2011 Biology Paper 2 Answer SchemeJoe Lidy50% (4)
- VBAC Guide: Risks, Benefits & ManagementDocument12 pagesVBAC Guide: Risks, Benefits & Managementnyangara50% (2)
- Avalmoja HAWAIIANculture ChildbirthDocument6 pagesAvalmoja HAWAIIANculture ChildbirthAlona KaleiNo ratings yet
- Transgender Discrimination in The WorkplaceDocument32 pagesTransgender Discrimination in The WorkplacePriyaAlikaEliasNo ratings yet
- Hormonii Axei Reproductive Andra CaragheorgheopolDocument70 pagesHormonii Axei Reproductive Andra CaragheorgheopolMadalina PavelNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Microscopic Observations of GametogenesisDocument5 pagesExperiment 1: Microscopic Observations of Gametogenesisarianne_ucagNo ratings yet
- 03 Cells and Human ReproductionDocument10 pages03 Cells and Human ReproductionYan WongNo ratings yet
- 2014reVITALizeObstetricDataDefinitionsV10 PDFDocument5 pages2014reVITALizeObstetricDataDefinitionsV10 PDFAloah122346No ratings yet
- Latest KPI LOW OF WEIGHT 2023Document2 pagesLatest KPI LOW OF WEIGHT 2023NICU LEVELNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument46 pagesCellsErfanShekarrizNo ratings yet
- Transgeder - Analytical Exposition - Maharani Bening Khatulistiwa XI IIS 1Document2 pagesTransgeder - Analytical Exposition - Maharani Bening Khatulistiwa XI IIS 1reksi alimNo ratings yet
- Human BodyDocument27 pagesHuman Bodyvigyanashram100% (2)
- Gynaecology Illustrated PDFDocument425 pagesGynaecology Illustrated PDFFairuz Indira100% (2)
- Biology HSC NotesDocument44 pagesBiology HSC Notesleachers100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical BotanyDocument132 pagesPharmaceutical BotanyShawn Chain100% (8)
- Zebra Fish Egg and Sperm CollectionDocument3 pagesZebra Fish Egg and Sperm CollectionJosh ShaevitzNo ratings yet
- Infertility MarthaDocument56 pagesInfertility MarthaMonika Bagchi100% (2)