Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Control of The Body's Water Content
Uploaded by
LADDER TIPS0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Control of the body's water content
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesControl of The Body's Water Content
Uploaded by
LADDER TIPSCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
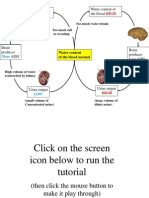
Control of the body’s water content
If the blood becomes too concentrated, the kidneys produce a smaller
volume of urine. These changes are controlled by a hormone produced
by the pituitary gland, at the base of the brain. The hormone is called
anti-diuretic hormone, or ADH
‘Diuresis’ means the flow of urine from the body, so ‘anti-diuresis’
means producing less urine. ADH starts to work when your body
loses too much water, for example if you are sweating heavily and
not replacing lost water by drinking.
The loss of water means that the concentration of the blood starts to
increase. This is detected by special cells in a region of the brain called
the hypothalamus.
These cells are sensitive to the solute concentration of the blood, and
cause the pituitary gland to release more ADH. The ADH travels in the
blood stream to the kidney. At the kidney tubules, it causes the
collecting ducts to become more permeable to water, so that more
water is reabsorbed back into the blood. This makes the urine more
concentrated, so that the body loses less water and the blood becomes
more dilute.
When the water content of the blood returns to normal, this acts as a
signal to ‘switch off’ the release of ADH. The kidney tubules then
reabsorb less water. Similarly, if someone drinks a large volume of
water, the blood will becomes too dilute. This leads to lower levels of
ADH secretion, the kidney tubules become less permeable to water, and
more water passes out of the body in the urine. In this way, through the
action of ADH, the level in the internal environment is kept constant
Selective Reabsorption
The kidney tubule reabsorbs different amounts of various
substances. This is called selective reabsorption.
As well as causing the pituitary gland to release ADH, the receptor
cells in the hypothalamus also stimulate a ‘thirst Centre’ in the brain.
This makes the person feel thirsty, so that they will drink water,
diluting the blood.
Endotherm
An endotherm is an organism that maintains its body at a metabolically
favorable temperature, largely by the use of heat set free by its
internal bodily functions instead of relying almost purely on
ambient heat.
An endotherm is an organism that generates heat to maintain its
body temperature.
You might also like
- Why Your Body Water Balance Is a Key to Health and Great Shape?From EverandWhy Your Body Water Balance Is a Key to Health and Great Shape?No ratings yet
- Biology PDFDocument1 pageBiology PDFVanessa JocellyneNo ratings yet
- Biology Class NotesDocument11 pagesBiology Class NotessnnvcqzgnbNo ratings yet
- OsmoregulationDocument6 pagesOsmoregulationNIRBHAY_BARDIYANo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer: Endocrine System (Part 1)Document3 pagesScience Reviewer: Endocrine System (Part 1)aNo ratings yet
- Osmoregulation NotesDocument2 pagesOsmoregulation NotesGood AstraNo ratings yet
- Secretion of Potassium Ions Into The NephronDocument1 pageSecretion of Potassium Ions Into The NephronDoraNo ratings yet
- Excretion 2 (Homeostasis)Document48 pagesExcretion 2 (Homeostasis)samskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Memo Thirst MechanismDocument2 pagesMemo Thirst MechanismEnrico de VriesNo ratings yet
- Diabetes InsipidusDocument1 pageDiabetes InsipidusAnold ShangaliNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Mammalian Physiology Laboratory Practice 2013: DEADLINE: March 2, 2013Document1 pageFundamental Mammalian Physiology Laboratory Practice 2013: DEADLINE: March 2, 2013Minh MinhNo ratings yet
- The Effect of ADH On Tubule Permeability and in Water Balance - HigherDocument2 pagesThe Effect of ADH On Tubule Permeability and in Water Balance - HigherLisa HendenNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDocument3 pagesFluid and Electrolyte BalancejalajaraniNo ratings yet
- What Is Anti-Diuretic Hormone?Document1 pageWhat Is Anti-Diuretic Hormone?LADDER TIPSNo ratings yet
- General Biology PPT Darryl Arcillas & Dency TuastumbanDocument14 pagesGeneral Biology PPT Darryl Arcillas & Dency TuastumbanApril Rose Caquilala GalauraNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument4 pagesHomeostasisJoNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument17 pagesExcretionsmbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- Definition of Antidiuretic HormoneDocument2 pagesDefinition of Antidiuretic Hormonerienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- Body Controls Water LevelsDocument8 pagesBody Controls Water Levelskitio anouchkaNo ratings yet
- Osmoregulation: Grade 11 BiologyDocument12 pagesOsmoregulation: Grade 11 Biologysenpai ozhonNo ratings yet
- Water Regulation in The BodyDocument8 pagesWater Regulation in The BodyDeath StarNo ratings yet
- Water Balance Laboratory HandoutDocument8 pagesWater Balance Laboratory HandoutTheng.SethNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument10 pagesHormonesAnanyaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 2Document34 pagesStudy Guide 2api-260095216No ratings yet
- Negative Feedback Mechanism: (Renal Electrolyte System)Document4 pagesNegative Feedback Mechanism: (Renal Electrolyte System)Dip ThapaNo ratings yet
- How Do The Kidneys Control Things?: Why Do We Need To Maintain It?Document14 pagesHow Do The Kidneys Control Things?: Why Do We Need To Maintain It?api-246259817No ratings yet
- Biology 7C 1Document4 pagesBiology 7C 1Abdullayev KamranNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis SS2Document4 pagesHomeostasis SS2Ezeh PrincessNo ratings yet
- HomeostatisDocument14 pagesHomeostatisnagpal3No ratings yet
- What Is DehydrationDocument7 pagesWhat Is DehydrationMarwan WijayaNo ratings yet
- Human & Social Biology NotesDocument1 pageHuman & Social Biology NotesDeidre-Ann RobinsonNo ratings yet
- DLC911 FeedbackDocument29 pagesDLC911 FeedbackJessecaNo ratings yet
- Gland (Or Hypophysis), A Bean-Sized Organ Suspended From It by A Stem CalledDocument3 pagesGland (Or Hypophysis), A Bean-Sized Organ Suspended From It by A Stem CalledJoyce Ann CumlatNo ratings yet
- Excretion and HomeostasisDocument12 pagesExcretion and HomeostasisMaisha IslamNo ratings yet
- HWF 2961 58522 HomeostasisandExcretionRevisionXOLBiologyDocument14 pagesHWF 2961 58522 HomeostasisandExcretionRevisionXOLBiologybasima jawaidNo ratings yet
- Hormones: Hormonal Control of Digestion and Water BalanceDocument5 pagesHormones: Hormonal Control of Digestion and Water BalanceAhmed OmaarNo ratings yet
- Feedback LoopsDocument3 pagesFeedback Loopsapi-320549212No ratings yet
- PP24 Functioning of The KidneyDocument81 pagesPP24 Functioning of The KidneyLeloNo ratings yet
- Case AbstractDocument8 pagesCase AbstractRj DimaandalNo ratings yet
- Cold DiuresisDocument9 pagesCold Diuresisknaina507No ratings yet
- The Two Forms of Diabetes InsipidusDocument1 pageThe Two Forms of Diabetes InsipidusAgustina PurbaNo ratings yet
- 26 HomeostasisDocument12 pages26 Homeostasismcalmontsarah612No ratings yet
- The Human Excretory SystemDocument7 pagesThe Human Excretory Systemdonnah_veraNo ratings yet
- Biology - Chapter SummariesDocument26 pagesBiology - Chapter SummariesShivaani MohanrajNo ratings yet
- Shock - Specific TypesDocument8 pagesShock - Specific Typeshenryvds5554No ratings yet
- Iv FluidsDocument6 pagesIv FluidsCrishara PalomoNo ratings yet
- Bio PrsentationDocument1 pageBio Prsentation4L Anisha SieudassNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Biology LectureDocument14 pagesHomeostasis Biology LecturebluejackbroNo ratings yet
- Antidiuretic Hormone PDFDocument3 pagesAntidiuretic Hormone PDFMcRo UndiNo ratings yet
- Feedback MechanismDocument25 pagesFeedback Mechanismkaloy domanaisNo ratings yet
- Water Balance Grade 12 BioDocument27 pagesWater Balance Grade 12 BioAllan AnthiahNo ratings yet
- Notes - HomeostasisDocument2 pagesNotes - HomeostasisNathan mwapeNo ratings yet
- ADH Diagram AnimatedDocument8 pagesADH Diagram AnimatedCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument6 pagesHomeostasisjpkaomeNo ratings yet
- 12.1 Waste Excretion and Equilibrium: Anatomy of The Urinary SystemDocument4 pages12.1 Waste Excretion and Equilibrium: Anatomy of The Urinary SystemVivian TangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Homeostasis and ExcretionDocument15 pagesChapter 8: Homeostasis and ExcretionZheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Booklet: Done By: Sonali AmbasanaDocument4 pagesHomeostasis Booklet: Done By: Sonali AmbasanaambasanaNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Chapter 3Document33 pagesBiology Form 5 Chapter 3Nuraain AmalinaNo ratings yet
- Water's Effectiveness On The BodyDocument4 pagesWater's Effectiveness On The BodyDennis MitchellNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument2 pagesKidneyLADDER TIPSNo ratings yet
- The Box Below Lists Various Substances Found in The Human BodyDocument3 pagesThe Box Below Lists Various Substances Found in The Human BodyLADDER TIPSNo ratings yet
- Kidney Transplant-DialysisDocument3 pagesKidney Transplant-DialysisLADDER TIPSNo ratings yet
- What Is Anti-Diuretic Hormone?Document1 pageWhat Is Anti-Diuretic Hormone?LADDER TIPSNo ratings yet