Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology PDF
Uploaded by
Vanessa JocellyneOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology PDF
Uploaded by
Vanessa JocellyneCopyright:
Available Formats
The amount of water in the body is important.
If there is too much, the volume of blood
swells and this puts stress on the heart. Too little water and fluid will be drawn from the
tissues (due to the osmotic effect of plasma proteins) and in to the blood. This causes
problems for the tissues involved (a hangover is caused by this). The water content of the
body will vary throughout the day. After fluids are drank the water levels rise. Sweating
causes water to be lost. The water content of the body must be monitored to keep it between
acceptable limits.
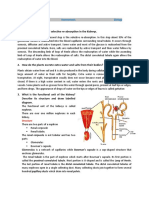
A part of the brain called the hypothalamus monitors the concentration of the blood. If the
concentration is too weak then it does nothing. The kidney therefore gets rid of more water,
making the urine more dilute.
If the blood is too concentrated then water needs to be conserved. The hypothalamus
stimulates a gland called the pituitary gland which releases a hormone called Anti-Diuretic
Hormone (ADH). This travels via the blood to the kidney. There, it makes the collecting duct
reabsorb more water and put it back into the blood. This makes the urine more concentrated
as more water is reabsorbed. When the levels of water return to their normal levels, it has
the effect of reducing the amount of ADH released and so prevents more water being
reabsorbed. This is called negative feedback and is a way of controlling the reabsorption of
water.
The length of the loop of Henle is linked to water reabsorption. The longer the loop the more
water can be reabsorbed. Animals, which do no need to worry about water loss, have
relatively short loop (such as beavers), while animals, which need to conserve water loss,
need to have relatively long loops (such as a desert rat).
Weather can have an effect on water loss from the body. Generally in summer, more water is
lost through sweat and so it needs to be conserved. Urine is more concentrated and smaller
in volume in warm conditions. The reverse is true in cold weather.
You might also like
- Chapter 17 Fluid Electrolytes and Acid-BDocument23 pagesChapter 17 Fluid Electrolytes and Acid-BKayan L.No ratings yet
- Water's Effectiveness On The BodyDocument4 pagesWater's Effectiveness On The BodyDennis MitchellNo ratings yet
- Control of The Body's Water ContentDocument3 pagesControl of The Body's Water ContentLADDER TIPSNo ratings yet
- Biology Class NotesDocument11 pagesBiology Class NotessnnvcqzgnbNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer: Endocrine System (Part 1)Document3 pagesScience Reviewer: Endocrine System (Part 1)aNo ratings yet
- Osmoregulation NotesDocument2 pagesOsmoregulation NotesGood AstraNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDocument3 pagesFluid and Electrolyte BalancejalajaraniNo ratings yet
- OsmoregulationDocument6 pagesOsmoregulationNIRBHAY_BARDIYANo ratings yet
- Water Balance Laboratory HandoutDocument8 pagesWater Balance Laboratory HandoutTheng.SethNo ratings yet
- Excretion 2 (Homeostasis)Document48 pagesExcretion 2 (Homeostasis)samskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- What Is DehydrationDocument7 pagesWhat Is DehydrationMarwan WijayaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Mammalian Physiology Laboratory Practice 2013: DEADLINE: March 2, 2013Document1 pageFundamental Mammalian Physiology Laboratory Practice 2013: DEADLINE: March 2, 2013Minh MinhNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument4 pagesHomeostasisJoNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument17 pagesExcretionsmbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- What Is Anti-Diuretic Hormone?Document1 pageWhat Is Anti-Diuretic Hormone?LADDER TIPSNo ratings yet
- Definition of Antidiuretic HormoneDocument2 pagesDefinition of Antidiuretic Hormonerienz nicnic peraltaNo ratings yet
- Secretion of Potassium Ions Into The NephronDocument1 pageSecretion of Potassium Ions Into The NephronDoraNo ratings yet
- Memo Thirst MechanismDocument2 pagesMemo Thirst MechanismEnrico de VriesNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis SS2Document4 pagesHomeostasis SS2Ezeh PrincessNo ratings yet
- The Effect of ADH On Tubule Permeability and in Water Balance - HigherDocument2 pagesThe Effect of ADH On Tubule Permeability and in Water Balance - HigherLisa HendenNo ratings yet
- Body Controls Water LevelsDocument8 pagesBody Controls Water Levelskitio anouchkaNo ratings yet
- Shock - Specific TypesDocument8 pagesShock - Specific Typeshenryvds5554No ratings yet
- Water Regulation in The BodyDocument8 pagesWater Regulation in The BodyDeath StarNo ratings yet
- Human & Social Biology NotesDocument1 pageHuman & Social Biology NotesDeidre-Ann RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 2Document34 pagesStudy Guide 2api-260095216No ratings yet
- Dehydration Facts: Body Weight Daily Fluid Requirements (Approximate)Document5 pagesDehydration Facts: Body Weight Daily Fluid Requirements (Approximate)liviuNo ratings yet
- Why Is Water ImportantDocument5 pagesWhy Is Water ImportantchapinatNo ratings yet
- Water MetabolismDocument3 pagesWater MetabolismJuber mansuriNo ratings yet
- Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid Base BalanceDocument23 pagesFluid, Electrolyte and Acid Base BalancenmdconahapNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument10 pagesHormonesAnanyaNo ratings yet
- How Do The Kidneys Control Things?: Why Do We Need To Maintain It?Document14 pagesHow Do The Kidneys Control Things?: Why Do We Need To Maintain It?api-246259817No ratings yet
- Diabetes InsipidusDocument1 pageDiabetes InsipidusAnold ShangaliNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument26 pagesWaterVandana JadhavNo ratings yet
- Intracellular Fluid Compartment and Extracellular Fluid CompartmentDocument21 pagesIntracellular Fluid Compartment and Extracellular Fluid CompartmentAnonymous iG0DCOfNo ratings yet
- General Biology PPT Darryl Arcillas & Dency TuastumbanDocument14 pagesGeneral Biology PPT Darryl Arcillas & Dency TuastumbanApril Rose Caquilala GalauraNo ratings yet
- Iv FluidsDocument6 pagesIv FluidsCrishara PalomoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Module 4Document26 pagesPathophysiology Module 4johnbryanmalonesNo ratings yet
- ATI Policy 2020Document12 pagesATI Policy 2020Abdullah AlsubhiNo ratings yet
- ADH Diagram AnimatedDocument8 pagesADH Diagram AnimatedCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- HEALTH BENEFITS OF WATER (Note1)Document2 pagesHEALTH BENEFITS OF WATER (Note1)Roshan SeegolamNo ratings yet
- SBI4U Unit 4 Homeostasis OsmoregulationDocument13 pagesSBI4U Unit 4 Homeostasis Osmoregulation전채연No ratings yet
- Water WordDocument3 pagesWater Wordjeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Why Is Water Vital For HumansDocument5 pagesWhy Is Water Vital For HumansBethania HernandezNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme AirDocument15 pagesMetabolisme AirKlara SintaNo ratings yet
- Water and Body FluidsDocument7 pagesWater and Body FluidsDeborah Chloe EnriquezNo ratings yet
- HomeostatisDocument14 pagesHomeostatisnagpal3No ratings yet
- HWF 2961 58522 HomeostasisandExcretionRevisionXOLBiologyDocument14 pagesHWF 2961 58522 HomeostasisandExcretionRevisionXOLBiologybasima jawaidNo ratings yet
- Excretion ExcretionDocument7 pagesExcretion ExcretionWaleed Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids Compartments and ExchangeDocument21 pagesBody Fluids Compartments and ExchangeLIDIYA MOL P VNo ratings yet
- Excretion and HomeostasisDocument12 pagesExcretion and HomeostasisMaisha IslamNo ratings yet
- Osmoregulation: Grade 11 BiologyDocument12 pagesOsmoregulation: Grade 11 Biologysenpai ozhonNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Biology LectureDocument14 pagesHomeostasis Biology LecturebluejackbroNo ratings yet
- Unit - 02 HomeostasisDocument12 pagesUnit - 02 HomeostasisAleena kazmiNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme AirDocument15 pagesMetabolisme AirAyu FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Feedback LoopsDocument3 pagesFeedback Loopsapi-320549212No ratings yet
- Biology - Chapter SummariesDocument26 pagesBiology - Chapter SummariesShivaani MohanrajNo ratings yet
- The Human Excretory SystemDocument7 pagesThe Human Excretory Systemdonnah_veraNo ratings yet
- Fluid & ElectrolyteDocument18 pagesFluid & Electrolytesaranya amuNo ratings yet