Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lara Smelting
Uploaded by
Celine LaraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lara Smelting
Uploaded by
Celine LaraCopyright:
Available Formats
LARA, Celine M. Engr. Juan C.
Tallara
MEC 0327-1 03/22/2021
SMELTING DEFINITION
a form of extractive metallurgy to produce a metal from its ore.
uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as
gasses or slag and leaving just the metal behind.
The reducing agent is commonly a source of carbon such as coke, charcoal, and coal.
PROCESS
Burning of fuel Impurities are
to CO CO reduces hematite to iron Decomposition removed
2𝐶 + 𝑂2 2𝐶𝑂 𝐹𝑒2 𝑂3 + 3𝐶𝑂 2𝐹𝑒 + 3𝐶𝑂2 𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑜3 𝐶𝑎𝑂 + 𝐶𝑂2 𝐶𝑎𝑂 + 𝑆𝑖𝑂2 𝐶𝑎𝑆𝑖𝑂3
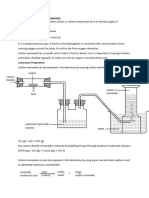
Bloomery
A bloomery was the earliest form of a smelter.
Bloomery consists of a heat resistant chimney + pipes at
the bottom for air + way to remove product called bloom
(reduced iron).
Air is added via natural draft or bellows which required
power (e.g. Water power).
Process: Heat bloomery by burning charcoal or coke;
when hot, add iron ore + more fuel + limestone.
During the process, iron in the ore is reduced as pure iron
pieces fall to bottom of chimney and weld together in a
spongy mass to form the bloom.
The rest of the ore (impurities) form the slag. It also ends
up at the bottom of the chimney including becoming
embedded in the bloom.
To remove the slag and thus further purify the iron
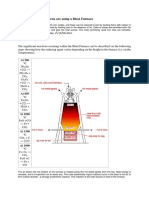
product, the bloom is reheated and then hammered. Blast Furnace
The product of this process is called wrought iron.
the required components are iron ore, fuel (originally
Charcoal and Coke charcoal), oxygen or air and a way to recover the
product.
Charcoal: Residue left when wood (carbohydrate) is
heated in absence of oxygen (anerobic) to drive off water The Method
and other volatile components. The porous residue is
about 85% carbon and burns hotter and cleaner than Three substances are needed to enable to extraction of
wood. iron from its ore. The combined mixture is called the
Coke: Residue left when coal is heated in absence of charge: Iron ore.
oxygen (anerobic) to drive off water and other gases (H2, Haematite - often contains sand with iron oxide,
Fe2O3.
Limestone (calcium carbonate).
Coke - mainly carbon.
Several reactions take place before the iron is finally
produced:
Oxygen in the air reacts with coke to give carbon
dioxide: C(s) + O 2(g) → CO2(g)
The limestone breaks down to form carbon dioxide:
CaCO3(s) → CO2 (g) + CaO(s)
Carbon dioxide produced in 1 + 2 react with more coke
to produce carbon monoxide: CO2(g) + C(s) →
2CO(g) Several reactions take place before the iron is
finally produced...
The carbon monoxide reduces the iron in the ore to give
molten iron: 3CO(g) + Fe2O3(s) → 2Fe(l) + 3CO2(g)
The limestone from 2, reacts with the sand to form slag
(calcium silicate): CaO(s) + SiO(s) → CaSiO3(l)
You might also like
- IndustrialchemistryDocument2 pagesIndustrialchemistryKimtuyen TranNo ratings yet
- 4 Extraction of Iron in A Blast Furnace PDFDocument1 page4 Extraction of Iron in A Blast Furnace PDFShashank pandeyNo ratings yet
- The Extraction of Metals: Mr. AgachaDocument9 pagesThe Extraction of Metals: Mr. AgachaMasaria LowlandNo ratings yet
- Extraction 2Document1 pageExtraction 2meganekokun kawaiiNo ratings yet
- 12S-2023 Chemistry 9Document9 pages12S-2023 Chemistry 9Alumbwe MubondaNo ratings yet
- Extracting Iron: The Blast FurnaceDocument2 pagesExtracting Iron: The Blast FurnacearwaNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Iron (Nehru Garden, JalandharDocument4 pagesExtraction of Iron (Nehru Garden, Jalandharapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Extraction of Metals: Galvanized Zinc Iron AlloysDocument1 pageExtraction of Metals: Galvanized Zinc Iron AlloysKarimNo ratings yet
- Production of IronDocument15 pagesProduction of IronMassy KappsNo ratings yet
- MetallurgyDocument26 pagesMetallurgySitabai JadhavNo ratings yet
- Carbon: Periodic Position: C 1s, 2s 2pDocument5 pagesCarbon: Periodic Position: C 1s, 2s 2pMandeep ShahNo ratings yet
- The Blast FurnaceDocument17 pagesThe Blast FurnaceAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy Theory PDFDocument17 pagesMetallurgy Theory PDFPrajwal TalwalkarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class - VIII Topic-MetallurgyDocument46 pagesChemistry Class - VIII Topic-Metallurgyrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Notes For 3rd Exam (Ferrous Metallurgy)Document2 pagesNotes For 3rd Exam (Ferrous Metallurgy)Fabie BarcenalNo ratings yet
- Iron Ore 01Document8 pagesIron Ore 01api-3731257No ratings yet
- Extraction of IRON FROM ORE - Putligarh (G) - AmritsarDocument6 pagesExtraction of IRON FROM ORE - Putligarh (G) - Amritsarapi-3731257No ratings yet
- EXtraction of IronDocument1 pageEXtraction of IronKirsten SusiloNo ratings yet
- CopperDocument26 pagesCopperShirjak ThokarNo ratings yet
- On Steel MakingDocument58 pagesOn Steel Makingallan arthur bare100% (1)
- Extraction of Metals Part 2Document4 pagesExtraction of Metals Part 2Ruchi MarajhNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document5 pagesCH 12gaminginsane372No ratings yet
- Points To Remember: at The End of The Topic, You Will Know AboutDocument31 pagesPoints To Remember: at The End of The Topic, You Will Know AboutShoaib SamimNo ratings yet
- Extraction of IronDocument4 pagesExtraction of Ironapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Cha 15 (Latest)Document38 pagesCha 15 (Latest)Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Reading Material by TeacherDocument8 pagesReading Material by TeacherAnusha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry With Boos Chapter 1.5, 4.1 and 4.2Document1 pageChemistry With Boos Chapter 1.5, 4.1 and 4.2jos huaNo ratings yet
- Metals KS3 4 Iron and Aluminium Extraction Methods Info SheetDocument5 pagesMetals KS3 4 Iron and Aluminium Extraction Methods Info SheetHappy NthakomwaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Its Applications-1Document112 pagesMetals and Its Applications-1amaandeshmukh4No ratings yet
- PRODUCTION OF STEEL-Lecture 2Document68 pagesPRODUCTION OF STEEL-Lecture 2Nyanda MalashiNo ratings yet
- Module 2BDocument22 pagesModule 2BOluwasegun OkajareNo ratings yet
- Coal and Petroleum ProcessingDocument37 pagesCoal and Petroleum ProcessingtesfayeNo ratings yet
- 1.1iron Ores: Iron and Steel MakingDocument5 pages1.1iron Ores: Iron and Steel Makingزينب عبد الخالق كاملNo ratings yet
- By Chan, Sam and EllyDocument10 pagesBy Chan, Sam and EllyrajatguptNo ratings yet
- Engineering Material - : Chapter TwoDocument41 pagesEngineering Material - : Chapter TwoAla ZiNo ratings yet
- Blast Furnace Year 10Document10 pagesBlast Furnace Year 10Neldson TrancosoNo ratings yet
- Blast Furnace Year 10Document10 pagesBlast Furnace Year 10Sapan KansaraNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Iron From HaematiteDocument7 pagesExtraction of Iron From HaematiteFurqan AhmedNo ratings yet
- LimestoneDocument19 pagesLimestoneKev WattsNo ratings yet
- Destructive Distillation of CoalDocument1 pageDestructive Distillation of CoalMuskan RangrejNo ratings yet
- Metal Extrctn. Notes: Ores: Haematite FeDocument4 pagesMetal Extrctn. Notes: Ores: Haematite FeAlex noslen100% (1)
- The Extraction of IronDocument2 pagesThe Extraction of IronAshleigh JarrettNo ratings yet
- General PrinciplesDocument14 pagesGeneral PrinciplesRaena SwamiNo ratings yet
- Extracting IronDocument5 pagesExtracting IronThunderNo ratings yet
- This Lecture Metallurgy: (Extracting Metal From Ore) : - Extraction of Metals From OresDocument4 pagesThis Lecture Metallurgy: (Extracting Metal From Ore) : - Extraction of Metals From Oreshnl27No ratings yet
- DR Khin Maung Toe: ChemistryDocument25 pagesDR Khin Maung Toe: ChemistryHan Zin OoNo ratings yet
- c1 Revision Notes - Set 1 OnlyDocument10 pagesc1 Revision Notes - Set 1 Onlyapi-320022467No ratings yet
- Extraction of IronDocument4 pagesExtraction of IronNadita100% (1)
- 9.1 The Extraction of Metals by Carbon ReductionDocument9 pages9.1 The Extraction of Metals by Carbon ReductionPoppyNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 Principles and Processes of Extraction of Metals.: I. One Mark QuestionsDocument5 pagesUnit-6 Principles and Processes of Extraction of Metals.: I. One Mark Questionsnawal2007No ratings yet
- Iron ExtractionDocument14 pagesIron Extractionapi-3729258No ratings yet
- Iron Part 1Document6 pagesIron Part 1lovelyridu8No ratings yet
- Metallurgy of IronDocument18 pagesMetallurgy of IronEliasNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Iron: By: Lalit Kumar ROLL NO:191Document5 pagesExtraction of Iron: By: Lalit Kumar ROLL NO:191191 Lalit KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Metals and PolymerDocument14 pagesLecture Notes in Metals and PolymerjoyandreaNo ratings yet
- Blastfurnace 140331091507 Phpapp02Document10 pagesBlastfurnace 140331091507 Phpapp02Farah Moiz AliNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Laboratory Chemical Reactions Results: Reaction Observations Balanced Chemical Equation Type of Chemical ReactionDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistry Laboratory Chemical Reactions Results: Reaction Observations Balanced Chemical Equation Type of Chemical ReactionArianeNo ratings yet
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelFrom EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelNo ratings yet
- Effect of Metal Related VariablesDocument3 pagesEffect of Metal Related VariablesCeline LaraNo ratings yet
- Force Exerted On Pressure ConduitsDocument30 pagesForce Exerted On Pressure ConduitsCeline LaraNo ratings yet
- Differential and Integral FormulasDocument1 pageDifferential and Integral FormulasCeline LaraNo ratings yet
- 5 Current-Electricityexericse PDFDocument50 pages5 Current-Electricityexericse PDFCeline LaraNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Problems by Louis FrenzelDocument5 pagesCompilation of Problems by Louis FrenzelKim Castro AntonioNo ratings yet
- 2 Antidifferentiation and Basic FormulasDocument15 pages2 Antidifferentiation and Basic FormulasCeline LaraNo ratings yet
- Types of LayoutDocument7 pagesTypes of LayoutCeline LaraNo ratings yet
- Series V100 Ball ValveDocument20 pagesSeries V100 Ball ValvejenniferNo ratings yet
- HGVNBDocument14 pagesHGVNBiexNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers About Corrosion TestingDocument2 pagesQuestions and Answers About Corrosion Testingprabhu_trichy100% (1)
- B02-S05 Rev 3 Sep 2017 Design, Fabri and Inst of GratingsDocument9 pagesB02-S05 Rev 3 Sep 2017 Design, Fabri and Inst of Gratings15150515715No ratings yet
- Ghibson ButterflyHotAirSmoke BrochureDocument5 pagesGhibson ButterflyHotAirSmoke Brochurejhon jairo arangoNo ratings yet
- Sprinkler Hydraulic Calculation-Tailor ShopDocument16 pagesSprinkler Hydraulic Calculation-Tailor ShopsakhrNo ratings yet
- Welding Joint Design and Welding Symbols123Document5 pagesWelding Joint Design and Welding Symbols123JACKMAAAANo ratings yet
- Effect of Usage of Sinter in BOF Steelmaking As A Replacement To Iron Ore As Coolant For Thermal BalanceDocument11 pagesEffect of Usage of Sinter in BOF Steelmaking As A Replacement To Iron Ore As Coolant For Thermal BalancesomnathNo ratings yet
- UNit 3 Part A RevisedDocument76 pagesUNit 3 Part A Revisedraymon sharmaNo ratings yet
- Welding ConsumablesDocument79 pagesWelding Consumablesazam RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Astm A276Document7 pagesAstm A276tony100% (1)
- FDC FlexDuctConn SubmittalDocument2 pagesFDC FlexDuctConn SubmittalRaj SekharNo ratings yet
- BSI Standards PublicationDocument18 pagesBSI Standards PublicationMartijn GrootNo ratings yet
- MSU Copper Casting Alloys 2011Document10 pagesMSU Copper Casting Alloys 2011Daniel CringusNo ratings yet
- Reducer M-F An912 - NPTDocument7 pagesReducer M-F An912 - NPTDaniel SantacruzNo ratings yet
- Thermanit Mts 3 (G Crmo91, Er90s-B9)Document1 pageThermanit Mts 3 (G Crmo91, Er90s-B9)brunizzaNo ratings yet
- 600+ TOP MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Interview Questions & AnswersDocument37 pages600+ TOP MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Interview Questions & AnswersNikhil Prasanna100% (1)
- Supapurlins Supazeds & Supacees: Design and Installation Guide For Building ProfessionalsDocument104 pagesSupapurlins Supazeds & Supacees: Design and Installation Guide For Building ProfessionalsFrank SunNo ratings yet
- Whole DepthDocument217 pagesWhole DepthCaptain AmericaNo ratings yet
- R1116010 Toss 10 005 - Rev0aDocument7 pagesR1116010 Toss 10 005 - Rev0a高欣东No ratings yet
- Valvula Tyco FlowDocument16 pagesValvula Tyco FlowVictor Timana SilvaNo ratings yet
- Design Aspects in Welding: Dr. V.P. RaghupathyDocument26 pagesDesign Aspects in Welding: Dr. V.P. RaghupathyPalani KarthiNo ratings yet
- System No. HW-D-0256: (UL/cUL)Document2 pagesSystem No. HW-D-0256: (UL/cUL)ibrahimNo ratings yet
- BrooksBank GateValve FlangeBelow4Document3 pagesBrooksBank GateValve FlangeBelow4T KelvinNo ratings yet
- Roof DrainsDocument1 pageRoof DrainsAhmed RamzyNo ratings yet
- 2.211 DONUT Specification SheetDocument4 pages2.211 DONUT Specification SheetNhat CaoNo ratings yet
- Test 21 1Document1,020 pagesTest 21 1Niaz KilamNo ratings yet
- Thermal Aspects of Machining Module 1Document75 pagesThermal Aspects of Machining Module 1Libin AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Material Used in Ship BuildingDocument13 pagesMaterial Used in Ship BuildingSayantan MondalNo ratings yet
- Cadweld CatalogoDocument123 pagesCadweld CatalogoRaul Gerardo SilvaNo ratings yet