Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IASB Framework Sets Financial Reporting Standards
Uploaded by
FaizSheikhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IASB Framework Sets Financial Reporting Standards
Uploaded by
FaizSheikhCopyright:
Available Formats
IASB FRAMEWORK
The framework sets out the concept undefined the preparation and presentation of financial
statements prepared by companies for external user.
Purpose of Framework:
1. To assist accounting standard board in its task of develop and review of Accounting
Standard.
2. To help auditors in forming an opinion as to whether financial statements confirm the
accounting standard.
3. To help the users in interpretation of financial statements.
Financial Statement
The principle means of reporting general purpose financial information to person outside of a
business organization. It is a set of accounting record of financial position.
The persons receiving these reports are called users of financial statements. A complete set of
financial statement includes Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Owner’s Equity and Cash flow
statement.
1. Balance Sheet:
A balance sheet indicating at a specific date the financial position of the company by showing
the resources that it owns the debts that it owes and the amount of the owner’s equity
(investment) in the business.
2. Income Statement
It indicates the profitability of the business, over the preceding years (or other time period).
3. Owner’s equity
It explains certain changes in the amount of owner’s equity (investment) in the business. In
business which is organized as corporations the statement of owner’s equity replaced by a
statement of retained earnings.
4. Cash flow statement
A statement of cash flows summarizing the cash receipts and cash payments of the business over
the same time period covers by the income statement.
OBJECTIVES OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The framework identifies seven broad groups of financial statements user.
1. Investor
2. Employer
3. Lender
4. Supplier
5. Customer
6. Government Agencies
7. Public
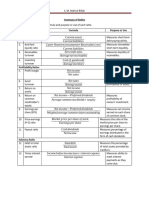
Financial Ratios
It is an index that relates to accounting numbers and it is obtained by dividing one number by the
other. These ratios are calculated to determine whether the firm is performing well or not.
So we can define financial ratios as an index that relates two pieces of financial date by dividing
one quantity by the other. It means operating a business with borrowed money.
Current Assets
1. Current Ratio = Current liabilities
Measures short run debt paying ability.
Quick Assets
2. Quick Ratio = Current liabilities
Measures the short run liquidity of firm
3. Working capital = Current assets - current liabilities
Measures short run debt paying ability
Net Income−Preferred dividend
4. Earnings per share of common stock= Shares of common outstanding
It indicates the amount of earning applicable to a share of a common stock.
Market price per share
5. Price earnings ratio =
Earnings price per share
It indicates if price of the stock is in line with the earnings.
Dividend per share
6. Dividend yield =
market price per share
It shows the rate of return earned by stock holders
Operating expense
7. Operating expense ratio=
Net sales
It indicates management ability to control expenses.
Operatingincome
8. Return on assets=
Average total assets
It measures the productivity of assets regardless of capital structure.
Net income−Preferred dividend
9. Return on common stockholder’s equity =
Average common shareholder ’ s equity
It indicates the earning power of common stock equity.
Total stockholder ’ s equity
10. Equity ratio=
Total assets
It shows the protection to creditors and the extent of leverage being used.
Total liabilities
11. Debt ratio=
Total assets
It indicates the percentage of assets financed through borrowing. It shows the extent of
leverage being used.
Cost of goods sold
12. Inventory turnover rate =
Average inventory
It indicates marketability of inventory.
Net sales
13. Account receivable turnover rate =
Average receivable
It indicates reasonable of Account balance and effectiveness of collection.
You might also like
- Summary of William H. Pike & Patrick C. Gregory's Why Stocks Go Up and DownFrom EverandSummary of William H. Pike & Patrick C. Gregory's Why Stocks Go Up and DownNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement RatioDocument7 pagesFinancial Statement RatioJordan P Hunter100% (1)
- Itc LTD PDFDocument18 pagesItc LTD PDFKriti BansalNo ratings yet
- Measure Profitability & EfficiencyDocument2 pagesMeasure Profitability & EfficiencyMeghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- Measurement Levels Liquidity Solvency Stability ProfitabilityDocument19 pagesMeasurement Levels Liquidity Solvency Stability ProfitabilityKimberly FloresNo ratings yet
- Module - Financial Statement AnalysisDocument3 pagesModule - Financial Statement AnalysisCATHERINE FRANCE LALUCISNo ratings yet
- Midterm ReviewerDocument19 pagesMidterm ReviewerDeseree De RamosNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument11 pagesMidtermDeseree De RamosNo ratings yet
- 04 Fs Analysis With StudentDocument10 pages04 Fs Analysis With StudentarianasNo ratings yet
- Financial Reporting and Analysis 21BAT-602: Master of Business AdministrationDocument38 pagesFinancial Reporting and Analysis 21BAT-602: Master of Business AdministrationAshutosh prakashNo ratings yet
- Handouts Review On FSDocument2 pagesHandouts Review On FSMaetherese SaradponNo ratings yet
- Analyze key financial statementsDocument2 pagesAnalyze key financial statementsRene Castillo JrNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument31 pagesAnalysis of Financial StatementsCadet ShaniNo ratings yet
- FM Term Paper On Financial Statement AnalysisDocument8 pagesFM Term Paper On Financial Statement Analysisnahidctg100% (1)
- Financial Statements Analysis Formulae AnalysisDocument13 pagesFinancial Statements Analysis Formulae AnalysisChico ChanchanNo ratings yet
- RATIO ANALYSIS Fall 2020 OctDocument7 pagesRATIO ANALYSIS Fall 2020 Octwafa aljuaidNo ratings yet
- FS ANALYSIS FORMULA: Management Efficiency Ratios & Financial RatiosDocument2 pagesFS ANALYSIS FORMULA: Management Efficiency Ratios & Financial RatiosSamantha JoseNo ratings yet
- Major Accounting Terms: Asset - Any Item of Economic Value Owned by ADocument21 pagesMajor Accounting Terms: Asset - Any Item of Economic Value Owned by Aranisweta44No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 and 5 DiscussionDocument7 pagesChapter 4 and 5 DiscussionRhedeline LugodNo ratings yet
- BSA 4301 Analysis of Financial Statements Mendoza, MVDocument5 pagesBSA 4301 Analysis of Financial Statements Mendoza, MVMik Darren Carl WongNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis & Cash Flow MetricsDocument29 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis & Cash Flow MetricsRamesh GyawaliNo ratings yet
- Fabm2 G12 Q1 M7 WK7 PDFDocument8 pagesFabm2 G12 Q1 M7 WK7 PDFJhoanna Odias100% (2)
- Analyzing Financial RatiosDocument6 pagesAnalyzing Financial RatiosLan Phương ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis Notes: Liquidity RatiosDocument7 pagesRatio Analysis Notes: Liquidity RatiosShaigari VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument6 pagesRatio AnalysisMilcah QuisedoNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document4 pagesWeek 7ZsazsaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Interpretation of Financial StatementsDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Interpretation of Financial StatementsuaenaNo ratings yet
- Analyze Financial Performance with RatiosDocument6 pagesAnalyze Financial Performance with RatiosLysss EpssssNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis Advisory ServicesDocument14 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis Advisory ServicesWilsonNo ratings yet
- Measure a Company's Ability to Pay Debt With Liquidity RatiosDocument4 pagesMeasure a Company's Ability to Pay Debt With Liquidity RatiosKeahlyn BoticarioNo ratings yet
- Profitability, Liquidity, Efficiency & Leverage Ratios ExplainedDocument2 pagesProfitability, Liquidity, Efficiency & Leverage Ratios Explainedrachel anne belangelNo ratings yet
- Working Capital: Liquidity RatiosDocument4 pagesWorking Capital: Liquidity RatiosSanjib BabuNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument10 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisBeth Diaz LaurenteNo ratings yet
- BA 569 Financial RatiosDocument7 pagesBA 569 Financial RatiosMariaNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio Analysis OverviewDocument27 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysis OverviewWijdan Saleem EdwanNo ratings yet
- Metalanguage: Big Picture in Focus: UlocDocument24 pagesMetalanguage: Big Picture in Focus: Ulocedwen pajeNo ratings yet
- I. Liquidity Ratios No Ratio Method of Computation SignificanceDocument14 pagesI. Liquidity Ratios No Ratio Method of Computation SignificanceVictor M Akbar TukanNo ratings yet
- FABM2 Wk7Document6 pagesFABM2 Wk7john lester pangilinanNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis 2022Document34 pagesRatio Analysis 2022Asanka8522No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2Document38 pagesFundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2wendell john medianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document39 pagesChapter 3Hibaaq AxmedNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument12 pagesRatio AnalysisSachinNo ratings yet
- Financial ratios and conceptsDocument12 pagesFinancial ratios and conceptssimon berksNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: 2.1 Liquidity RatiosDocument8 pagesRatio Analysis: 2.1 Liquidity RatiosRifat HasanNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio AnalysisDocument8 pagesFinancial Ratio AnalysisSyeda AtikNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: A Guide to Financial Statement RatiosDocument13 pagesRatio Analysis: A Guide to Financial Statement Ratiosmuralib4u5No ratings yet
- Types of Financial Ratios 19mar 2012Document8 pagesTypes of Financial Ratios 19mar 2012ndmudhosiNo ratings yet
- 38 - Ratio - Analysis - KPMGDocument12 pages38 - Ratio - Analysis - KPMGjatin sainaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter (8) : Financial Ratios Analysis: February 2019Document31 pagesChapter (8) : Financial Ratios Analysis: February 2019ALAQMARRAJNo ratings yet
- The Analysis and Interpretation of Financial StatementsDocument5 pagesThe Analysis and Interpretation of Financial StatementsBrenda ChatendeukaNo ratings yet
- Lec 14 Fin Perf ManagementDocument21 pagesLec 14 Fin Perf ManagementHaroon RashidNo ratings yet
- IBF-AFS - Theory & Questions TVM, EOQ & Basic Accounting ConceptsDocument40 pagesIBF-AFS - Theory & Questions TVM, EOQ & Basic Accounting ConceptsArsalan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis!Document16 pagesRatio Analysis!Sashil ReddyNo ratings yet
- Valuation Methods Financial RatiosDocument9 pagesValuation Methods Financial RatiosJacinta Fatima ChingNo ratings yet
- United International University: Assignment On Ratio Analysis & Dupont AnalysisDocument8 pagesUnited International University: Assignment On Ratio Analysis & Dupont AnalysisMostofa Reza PigeonNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Week 7 and 8Document45 pagesBusiness Finance Week 7 and 8Jonathan De villaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis RatiosDocument3 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis RatiosshahbazsiddikieNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio HANDOUTSDocument3 pagesFinancial Ratio HANDOUTSMichelle GoNo ratings yet
- Summary of RatiosDocument1 pageSummary of RatiosShamima AkterNo ratings yet
- Marketing concepts, functions & importance explainedDocument18 pagesMarketing concepts, functions & importance explainedFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Marketing Process: by Amina KhudadadDocument18 pagesMarketing Process: by Amina KhudadadFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- 12Document1 page12FaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Principals of MarketDocument17 pagesPrincipals of MarketFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- 12Document1 page12FaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument1 pageQuestionsFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IasbDocument19 pagesChapter 1 IasbFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Questions On Cash Flow StatementDocument5 pagesQuestions On Cash Flow StatementFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument1 pageQuestionsFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Mcgraw-Hill Technology Education Mcgraw-Hill Technology EducationDocument12 pagesMcgraw-Hill Technology Education Mcgraw-Hill Technology EducationFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementsDocument2 pagesCash Flow StatementsFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Questions On Cash Flow StatementDocument5 pagesQuestions On Cash Flow StatementFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Characterstic of Comp-1Document7 pagesCharacterstic of Comp-1FaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument1 pageQuestionsFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Asaasae Shab by Rafeeq SandelviDocument113 pagesAsaasae Shab by Rafeeq SandelviFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Computer ScienceDocument22 pagesBasic Concepts of Computer ScienceFaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Characterstic of Comp-1Document7 pagesCharacterstic of Comp-1FaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Network Types of Types Network Topologies: Presented by Faiz Muhammad Roll No: 21 Muhammad Ishaque Roll No: 22Document22 pagesNetwork Types of Types Network Topologies: Presented by Faiz Muhammad Roll No: 21 Muhammad Ishaque Roll No: 22FaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Problem 31.2Document4 pagesProblem 31.2Arian AmuraoNo ratings yet
- m20 ATX MYS QPDocument13 pagesm20 ATX MYS QPizzahderhamNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document23 pagesChap 5my miNo ratings yet
- Ias 7 Cash Flow Statement ContinuedDocument8 pagesIas 7 Cash Flow Statement ContinuedMichael Bwire100% (1)
- Akmen MandiriDocument6 pagesAkmen Mandiricalsey aNo ratings yet
- 06) Theory of Cost PDFDocument79 pages06) Theory of Cost PDFAby Reji ChemmathuNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document58 pagesCH 5marwan2004acctNo ratings yet
- CFA - Research Preparation - ULTJDocument177 pagesCFA - Research Preparation - ULTJYunita PutriNo ratings yet
- Annex D CNPF Annual Report 2020 - Consolidated Financial StatementsDocument113 pagesAnnex D CNPF Annual Report 2020 - Consolidated Financial StatementsJC LastimosoNo ratings yet
- Arcelormittal Takeover CaseDocument24 pagesArcelormittal Takeover CaseJerry K FloaterNo ratings yet
- 16 - (S4) Sma Sa PDFDocument7 pages16 - (S4) Sma Sa PDFSaalim FaheemNo ratings yet
- Accounting Project - EMBA Cohort 43 Group33 - FinalSubmissionDocument4 pagesAccounting Project - EMBA Cohort 43 Group33 - FinalSubmissionodlivingstonNo ratings yet
- Old Bridge Mutual Fund - Factsheet March 2024Document8 pagesOld Bridge Mutual Fund - Factsheet March 2024Bharathi 3280No ratings yet
- Accountancy IIDocument304 pagesAccountancy IIuirehfvbidfNo ratings yet
- Null 001.2001.issue 139 enDocument36 pagesNull 001.2001.issue 139 enMark RiveraNo ratings yet
- TeraSteel PresentationDocument27 pagesTeraSteel PresentationDIANA CRACIUNNo ratings yet
- Commissions and InterestsDocument8 pagesCommissions and InterestsAxl Fitzgerald Bulawan100% (1)
- Week 3 - Lecture Note - Absorption Costing and Variable CostingDocument24 pagesWeek 3 - Lecture Note - Absorption Costing and Variable CostingLăng DiệpNo ratings yet
- Staff Welfare Schemes at a GlanceDocument13 pagesStaff Welfare Schemes at a GlanceArchana HarishankarNo ratings yet
- MA 3103 Market ApproachDocument7 pagesMA 3103 Market ApproachJacinta Fatima ChingNo ratings yet
- Feb 2019 SGVDocument26 pagesFeb 2019 SGVBien Bowie A. CortezNo ratings yet
- Forex TransactionsDocument3 pagesForex TransactionsDing CostaNo ratings yet
- RIBA Benchmarking 2019 Summary PDFDocument6 pagesRIBA Benchmarking 2019 Summary PDFAlanNo ratings yet
- Translation Methods: - Current/Noncurrent Method - Monetary/Nonmonetary Method - Temporal Method - Current Rate MethodDocument29 pagesTranslation Methods: - Current/Noncurrent Method - Monetary/Nonmonetary Method - Temporal Method - Current Rate MethodAruna SurapureddyNo ratings yet
- Plan and track your event budgetDocument3 pagesPlan and track your event budgetRolan Mart SasongkoNo ratings yet
- Acctg 029 - Mod 3 Conso Fs Subs DateDocument8 pagesAcctg 029 - Mod 3 Conso Fs Subs DateAlliah Nicole RamosNo ratings yet
- CA Inter FM ECO Suggested Answer May2023Document35 pagesCA Inter FM ECO Suggested Answer May2023sreeramireddigari abhishekreddyNo ratings yet
- JOURNALIZINGDocument2 pagesJOURNALIZINGArneld SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Articulate AprilDocument117 pagesArticulate AprilSAURAV12345No ratings yet
- FR Assignment 4Document4 pagesFR Assignment 4shashalalaxiangNo ratings yet