100% found this document useful (1 vote)
462 views1 pagePeriodic Table Basics for Students
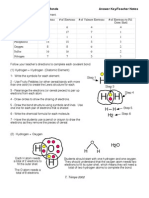
The document provides instructions for labeling and coloring a periodic table to help identify and classify elements based on their properties. The 10 steps include numbering groups and periods, identifying metals and nonmetals, labeling element families, noting physical states, and using color coding to distinguish element types such as halogens, noble gases, alkali metals and radioactive elements. Following these steps will allow one to use the periodic table to predict elemental behavior.
Uploaded by
Tristan RemplakowskiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
462 views1 pagePeriodic Table Basics for Students
The document provides instructions for labeling and coloring a periodic table to help identify and classify elements based on their properties. The 10 steps include numbering groups and periods, identifying metals and nonmetals, labeling element families, noting physical states, and using color coding to distinguish element types such as halogens, noble gases, alkali metals and radioactive elements. Following these steps will allow one to use the periodic table to predict elemental behavior.
Uploaded by
Tristan RemplakowskiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd