Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Supply of Cerebral Cortex
Uploaded by
ashraf0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
123 views3 pagesThe arterial supply of the brain comes from two main systems - the vertebrobasilar system and the internal carotid system. The vertebrobasilar system includes the vertebral arteries, basilar artery, and posterior cerebral arteries. The internal carotid system includes the internal carotid arteries and their terminal branches, the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. These arteries anastomose at the base of the brain in the cerebral arterial circle of Willis to ensure adequate blood supply to the brain.
Original Description:
Original Title
Blood supply of Cerebral cortex
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe arterial supply of the brain comes from two main systems - the vertebrobasilar system and the internal carotid system. The vertebrobasilar system includes the vertebral arteries, basilar artery, and posterior cerebral arteries. The internal carotid system includes the internal carotid arteries and their terminal branches, the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. These arteries anastomose at the base of the brain in the cerebral arterial circle of Willis to ensure adequate blood supply to the brain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
123 views3 pagesBlood Supply of Cerebral Cortex
Uploaded by
ashrafThe arterial supply of the brain comes from two main systems - the vertebrobasilar system and the internal carotid system. The vertebrobasilar system includes the vertebral arteries, basilar artery, and posterior cerebral arteries. The internal carotid system includes the internal carotid arteries and their terminal branches, the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. These arteries anastomose at the base of the brain in the cerebral arterial circle of Willis to ensure adequate blood supply to the brain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
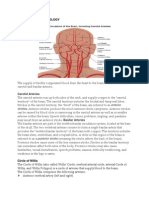
Blood supply of Cerebral cortex
Arterial supply of the brain (central nervous system):
The arterial supply of the brain (central nervous system) conies chiefly from main sources
1. Vertebro basllar system.
2. Internal carotid system.
Vertebrobasilar system It consists of:
1. 4th part of vertebral artery (two).
2. Basilar artery (single).
3. Posterior cerebral artery (two).
Vertebral artery 4th part
Origin; the vertebral artery arises in the neck from 1st part of subclavian artery.
Course & relations:
• The course of vertebral artery is divided Into 4 parts.
• The 1st part: from its origin to the foramen transversarium of
the 6th cervical vertebra.
• The 2nd part: ascends to foramen transversarium of atlas.
• The 3rd part lies in the suboccipital triangle.
• The 4th part: of the artery enters the skull through the
foramen magnum. It ascends on each side of the medulla
oblongata in front of the rootlets of the hypoglossal nerve.
Termination: The two vertebral arteries (right and left) unite
together at the lower border of pons to form a single artery;
basilar artery.
Basilar artery
Origin: At the lower border of Pons by the union of the 2 vertebral
arteries.
Course & relations: It passes on the front of the pons in the midline
(pontine sulcus, groove for basilar artery). The artery is related to
abducent nerve (at its beginning) and occulomotor nerve (at its
termination).
Termination: At the upper border of Pons by bifurcation into the 2
posterior cerebral arteries
Posterior cerebral artery
Origin: The 2 posterior cerebral arteries begin at the upper border
of Pons as the 2 terminal branches of the basilar artery.
Course & relations: The artery passes round the midbrain to reach
the occipital pole of the cerebrum. It sinks Inside the calcarine
sulcus.
Termination: It terminates by dividing into its terminal cortical branches.
Internal carotid system:
• It consists of the intracranial part of the internal carotid artery and its two terminal branches; (the anterior and
middle cerebral) arteries.
Internal carotid artery (intracranial part): The ICA enters the middle cranial fossa by passing through the foramen
lacerum.
Course: the artery has a sinuous course, it first passes forward and then upward, Inside the cavernous sinus, lastely
it pierces the roof of the cavernous sinus and passes backward above it.
• The abducent nerve lies inferolateral to the ICA.
• At the base of the brain (anterior perforated substance) the artery terminates into anterior and middle cerebral
arteries.
Anterior cerebral artery:
• It is the smaller of the 2 terminal branches of the ICA.
• It passes on the medial surface of the brain below the rostrum then in front of genu then backward above corpus
callosum through the callosal sulcus.
• It gives: Cortical branches and Central branches.
Middle cerebral artery:
• It is the larger of the two terminal branches of the ICA,
• It passes through the stem of the lateral sulcus then in the posterior ramus of the lateral sulcus.
• It gives: 1- Central branches.2- Cortical branches.
Cortical branches of the cerebral arteries:
The superolateral surface:
It supplied by middle cerebral artery
except: one finger breadth at the upper
border supplied by the interior cerebral
and the occipital lobe supplied by posterior
cerebral artery.
The medial surface: It Is supplied by
the anterior cerebral artery except the
occipital lobe, (behind the parietal occipital
sulcus) Applied by the posterior cerebral
artery.
The inferior surface: The medial part
of orbital surface Is supplied by anterior
cerebral artery. The temporal pole and
lateral part of orbital surface are supplied
the middle cerebral artery.
The remaining tentorial surface is supplied
by the posterior cerebral artery.
The cerebral arterial circle (of
Willis):
Formed at the base of the brain by the interconnecting vertebrobasilar and internal carotid systems of vessels. This
anastomotic interconnection is accomplished by:
• An anterior communicating artery connecting the left and right anterior cerebral arteries to each other.
• Two posterior communicating arteries, one on each side, connecting the internal carotid artery with the posterior
cerebral artery.
Vancouver references
- 2016. Head&Neck neuroanatomy. 1st ed. Alexandria, pp.112-117.
- Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Braunwald E, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J: Harrison's Principles
of internal Medicine, 17th Edition: http://www. accessmedicine.com
Name: homam chab
ID:1952
You might also like
- Essential Clinically Applied Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System in the Head and NeckFrom EverandEssential Clinically Applied Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System in the Head and NeckNo ratings yet
- Registry of Outcome Measures With MDC 2010Document125 pagesRegistry of Outcome Measures With MDC 2010bdesai48100% (1)
- Computer Care and SafetyDocument13 pagesComputer Care and SafetyÏtz NëcïNo ratings yet
- ESP9000 Instruction Manual E 0303Document101 pagesESP9000 Instruction Manual E 0303David SigalinggingNo ratings yet
- Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Blood Supply To The BrainDocument6 pagesMedical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Blood Supply To The BrainsoyyosoloyoNo ratings yet
- Excitation of HeartDocument17 pagesExcitation of HeartdevdsantoshNo ratings yet
- Encephalitis Is An Acute Inflammation of The Brain. Encephalitis With Meningitis IsDocument4 pagesEncephalitis Is An Acute Inflammation of The Brain. Encephalitis With Meningitis IsDivya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Epidural Hematoma Neuro SurgeryDocument2 pagesEpidural Hematoma Neuro SurgeryA Novita Dewi AryantiNo ratings yet
- What Is AstigmatismDocument2 pagesWhat Is AstigmatismJA QuibzNo ratings yet
- Major Arteries and Their BranchesDocument6 pagesMajor Arteries and Their BranchesPriya Farooq100% (1)
- 3.7 Organ Transplantation PDFDocument3 pages3.7 Organ Transplantation PDFbrownieallennNo ratings yet
- ANAT3411Document51 pagesANAT3411Kai Dong ChoongNo ratings yet
- Motor TractDocument4 pagesMotor TractRaden Achmad Candra PutraNo ratings yet
- The Bony OrbitDocument3 pagesThe Bony OrbitxxyumeNo ratings yet
- The Pupillary Light Reflex PathwayDocument5 pagesThe Pupillary Light Reflex PathwayNauli PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Auditory SystemDocument2 pagesAuditory SystemLyron GuemoNo ratings yet
- Neurology: by Dennis Jason Alcantara, RN, USRN, MAN CanDocument213 pagesNeurology: by Dennis Jason Alcantara, RN, USRN, MAN CanKristel-Mia Dimalanta RamosNo ratings yet
- Neuro 3 Brainstem and Spinal Cord BriefDocument68 pagesNeuro 3 Brainstem and Spinal Cord BriefYasimini Ramadhani100% (1)
- Oculomotor Nerve 3Document30 pagesOculomotor Nerve 3Sanreet RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Skills Week 1Document3 pagesClinical Skills Week 1Aishah SiddiqahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture 3 - Encephalon-SectionalAnatomyDocument30 pagesAnatomy Lecture 3 - Encephalon-SectionalAnatomyLazaros TsiatsiosNo ratings yet
- Orbital AnatomyDocument45 pagesOrbital AnatomyDevdutta NayakNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Nadz FinalDocument58 pagesCranial Nerve Nadz Finalnadzirah ruslanNo ratings yet
- Brainstem Bravo AnnotatedDocument13 pagesBrainstem Bravo AnnotatedMia CadizNo ratings yet
- Pons MedullaDocument32 pagesPons MedullaEnaWahahaNo ratings yet
- Basal GangliaDocument29 pagesBasal Gangliaapi-19916399No ratings yet
- BDS1040 The Orbit and Its Contents (Lecture)Document49 pagesBDS1040 The Orbit and Its Contents (Lecture)Aya OsamaNo ratings yet
- The Neck PDFDocument67 pagesThe Neck PDFAhmad Akram NatshehNo ratings yet
- Histology of Kidney, Ureter and Urinary BladderDocument28 pagesHistology of Kidney, Ureter and Urinary Bladderkhairul_azhar_27No ratings yet
- LECTURE Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesLECTURE Nervous SystemanonymousNo ratings yet
- The Brainstem: Ot1024: NeuroscienceDocument6 pagesThe Brainstem: Ot1024: NeuroscienceReyna MedinaNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy of The EarDocument16 pagesReview of Anatomy of The EarSahrish IqbalNo ratings yet
- Vestibular Appratus: BY: Harshita YadavDocument49 pagesVestibular Appratus: BY: Harshita YadavNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY OF THE EYE (Organ of Vision) by DR Omeje EmmanuelDocument31 pagesANATOMY OF THE EYE (Organ of Vision) by DR Omeje Emmanuelchidera100% (2)
- Blood Suppy of BrainDocument54 pagesBlood Suppy of BrainZoya MoraniNo ratings yet
- GRSANA - Lec5 Temporal Fossa, Infratemporal Fossa, and TMJ - WongDocument9 pagesGRSANA - Lec5 Temporal Fossa, Infratemporal Fossa, and TMJ - WongRainier Raul Echipare100% (1)
- ANA3203 (Neuroanatomy) Lecture, 2020-2021Document33 pagesANA3203 (Neuroanatomy) Lecture, 2020-2021M sarauta Tv100% (1)
- Anatomy of Eyelid: Presenter:-Dr. Vijayalaxmi Moderator:-Dr. SanjanaDocument49 pagesAnatomy of Eyelid: Presenter:-Dr. Vijayalaxmi Moderator:-Dr. SanjanaRidhi Bhandari100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Visual SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Visual SystemMahrukhNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesModule 5 Nervous TissueHermione MalfoyNo ratings yet
- CerebellumDocument22 pagesCerebellumSalman XahirNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply To The Brain: Presenter: Kondapaneni AnushaDocument44 pagesBlood Supply To The Brain: Presenter: Kondapaneni Anushaabhi4manyuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Labyrinth by DR Inam Ur RehmanDocument29 pagesAnatomy of Labyrinth by DR Inam Ur RehmanasssadulllahNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye - Nov. 3 - Dr. CastilloDocument13 pages3.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye - Nov. 3 - Dr. CastilloHanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- CNS Histology 1Document60 pagesCNS Histology 1naderipourkianaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nervous SystemDocument26 pagesAnatomy of Nervous Systemrey martinoNo ratings yet
- The Meninges and The Cerebrospinal Fluid: Bagian Anatomi Fkik-Uin Alauddin MakassarDocument23 pagesThe Meninges and The Cerebrospinal Fluid: Bagian Anatomi Fkik-Uin Alauddin MakassaryuyuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyaldrin19No ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument30 pagesCardiac CycleAdel100% (1)
- Anatomy of Visual Pathway, Field Defects AND Its Lesions.: By-Dr. Ruchi PherwaniDocument43 pagesAnatomy of Visual Pathway, Field Defects AND Its Lesions.: By-Dr. Ruchi Pherwanisafasayed100% (1)
- PONSDocument40 pagesPONSveegeer100% (1)
- 2 - Bones of The Lower LimbDocument23 pages2 - Bones of The Lower LimbHamzaNo ratings yet
- BIO 542 Lab PPT 01 - Neuroanatomy Review (Website)Document39 pagesBIO 542 Lab PPT 01 - Neuroanatomy Review (Website)NolanNo ratings yet
- The Posterior Fossa Cisterns: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.DDocument12 pagesThe Posterior Fossa Cisterns: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.DIndra HadianditeNo ratings yet
- 24 Cerebral Blood FlowDocument31 pages24 Cerebral Blood FlowZuhaib Ahmed100% (1)
- Spinal Cord LesionsDocument110 pagesSpinal Cord Lesionsgtaha80100% (1)
- Joints of Upper LimbDocument70 pagesJoints of Upper LimbHaania KhanNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue: Dr. Tianbao SongDocument53 pagesNervous Tissue: Dr. Tianbao Songapi-19916399100% (1)
- Anatomy of RetinaDocument39 pagesAnatomy of Retinadr_dev100% (1)
- Anatomy of Vestibular SystemDocument25 pagesAnatomy of Vestibular SystemFranciscus BuwanaNo ratings yet
- 1028 - Temporal LobeDocument19 pages1028 - Temporal LobeEdward LinNo ratings yet
- Nerve TissueDocument148 pagesNerve TissuePatriciaMariskaKrisnawatiSenjaya100% (1)
- Lowe Syndrome (Oculocerebrorenal syndrome) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLowe Syndrome (Oculocerebrorenal syndrome) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Research 20Document92 pagesResearch 20James KeithNo ratings yet
- Biamp Manual Apart cm20dts cm30dtd cm60dtd PDFDocument28 pagesBiamp Manual Apart cm20dts cm30dtd cm60dtd PDFBono646No ratings yet
- AudiometryDocument68 pagesAudiometrySanjana GaneshNo ratings yet
- Verification SheetDocument2 pagesVerification Sheetprince gian condeNo ratings yet
- Surgery Trans 1 - Systemic Response To InjuryDocument29 pagesSurgery Trans 1 - Systemic Response To InjuryJoan Caacbay De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Personal Injury Liability Waiver FormDocument3 pagesPersonal Injury Liability Waiver Formirish sedilllNo ratings yet
- JR FPR - Pectoralis Major Myocutaneous Flap - EdwinaDocument41 pagesJR FPR - Pectoralis Major Myocutaneous Flap - EdwinaRatna WindyaningrumNo ratings yet
- Intracranial Pressure Monitor PDFDocument15 pagesIntracranial Pressure Monitor PDFansyemomoleNo ratings yet
- 06.24.14 Game NotesDocument8 pages06.24.14 Game NotesRyan DivishNo ratings yet
- الهيئة 3Document10 pagesالهيئة 3mohsenNo ratings yet
- En Ox A Par inDocument3 pagesEn Ox A Par inapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Swords Under The Sun (Open Beta) GM SheetDocument1 pageSwords Under The Sun (Open Beta) GM SheetAlissa PikkNo ratings yet
- Accident InvestigationDocument47 pagesAccident InvestigationAntonio Jose De Jesus100% (1)
- Oah Elbow ExercisesDocument4 pagesOah Elbow ExercisesPratik KadamNo ratings yet
- First Aid For Sprain Follow The Instructions For R.I.C.EDocument2 pagesFirst Aid For Sprain Follow The Instructions For R.I.C.EbokanegNo ratings yet
- Raynera v. Hiceta Et. Al., G.R. No. 120027 (April 21, 1999)Document1 pageRaynera v. Hiceta Et. Al., G.R. No. 120027 (April 21, 1999)Lara YuloNo ratings yet
- GTZZ14EJ 16EJ Maintenance Manual1Document90 pagesGTZZ14EJ 16EJ Maintenance Manual1Kris topher100% (1)
- Irregular VerbDocument15 pagesIrregular VerbVee MaNo ratings yet
- JSA FOR Concerate PlacementDocument1 pageJSA FOR Concerate Placementwahyu nugrohoNo ratings yet
- All of Me ChordsDocument5 pagesAll of Me Chordsjohn vargasNo ratings yet
- Acetabular FracturesDocument69 pagesAcetabular Fracturesmohammad farhanNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics in HousekeepingDocument15 pagesErgonomics in Housekeepingsarthak rathiNo ratings yet
- F3 ArgoDocument20 pagesF3 ArgoAdrian Quiambao0% (1)
- CSEC Physical Education and Sport Exam Questions With AnswersDocument182 pagesCSEC Physical Education and Sport Exam Questions With Answerschan chan100% (1)
- First Aid For UnconsciousnessDocument3 pagesFirst Aid For UnconsciousnessHazel Mjkristell Basallote FranceNo ratings yet
- Frida Kahlo: Visual Articulations of Suffering and Loss: LacivitaDocument12 pagesFrida Kahlo: Visual Articulations of Suffering and Loss: Lacivitadan grynNo ratings yet
- Course Notes J McMullanDocument159 pagesCourse Notes J McMullanPola OrregoNo ratings yet