Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Two Types of Weathering: Weathering - Caused by Elements (Weather) Wearing Away The Surface of A Rock. Breaking
Uploaded by
zrie premes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageand understand the procedure for determining the specific gravity and absorption of coarse aggregates. 2. To understand the importance of SSD in determining the absorption capacity of the aggregate. 3. To determine the following properties of a coarse aggreg
Original Title
1234
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentand understand the procedure for determining the specific gravity and absorption of coarse aggregates. 2. To understand the importance of SSD in determining the absorption capacity of the aggregate. 3. To determine the following properties of a coarse aggreg
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageTwo Types of Weathering: Weathering - Caused by Elements (Weather) Wearing Away The Surface of A Rock. Breaking
Uploaded by
zrie premesand understand the procedure for determining the specific gravity and absorption of coarse aggregates. 2. To understand the importance of SSD in determining the absorption capacity of the aggregate. 3. To determine the following properties of a coarse aggreg
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Weathering - caused by elements (weather) wearing away the surface of a rock.
Breaking
of rocks into smaller rocks or sediments.
Two Types of weathering
Physical Weathering- breaking down of rocks without a change in composition.
Frost Action – results from the alternating freezing and thawing of water.
Abrasion – Rocks and sediment grinding against each other wear away surfaces.
The rocks become smoother as rough and jagged edges break off.
Exfoliation - term used to describe the peeling away of sheets of rock millimeters
to meters in thickness from a rock's surface.
Root Wedging - is the process in which roots grow into the cracks in rocks and
force the cracks open as they continue to grow.
Chemical Weathering - breaking down of rocks with a change in composition.
Oxidation – is when oxygen reacts with the minerals of a rock.
Carbonation - carbon dioxide gas dissolves in groundwater forming weak
carbonic acid. Large masses of limestone can be dissolved, forming caves,
stalactites, and sink holes.
Hydration/hydrolysis - is the chemical breakdown of a substance when
combined with water.
Organic activity - breaks down rock minerals by altering the rock’s chemical
composition.
Deposition
• Deposition is the geological process in which sediments, soil and rocks are added to
a landform or land mass.
• Wind, ice, water, and gravity transport previously weathered surface material,
which, at the loss of enough kinetic energy in the fluid, is deposited, building up
layers of sediment.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
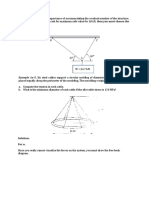
- Least Numerical Value.: Example 1a-5. Six Steel Cables Support A Circular Molding of Diameter 2 M. The Cables AreDocument2 pagesLeast Numerical Value.: Example 1a-5. Six Steel Cables Support A Circular Molding of Diameter 2 M. The Cables Arezrie premes100% (2)
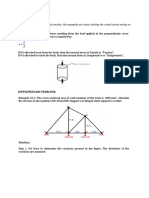
- Example 1a-9. The Bell Crank, Which Is in Equilibrium Under The Forces Shown in The Figure, IsDocument3 pagesExample 1a-9. The Bell Crank, Which Is in Equilibrium Under The Forces Shown in The Figure, Iszrie premesNo ratings yet
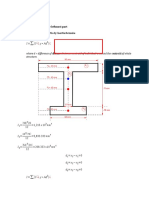
- Axis of An Unsymmetrical Beam and Moment of InertiaDocument4 pagesAxis of An Unsymmetrical Beam and Moment of Inertiazrie premesNo ratings yet
- D t=25 mm σ P A PDocument3 pagesD t=25 mm σ P A Pzrie premesNo ratings yet
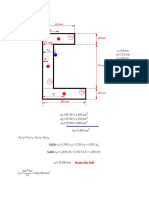
- To Compute For I - yDocument5 pagesTo Compute For I - yzrie premesNo ratings yet
- RotoinversionDocument3 pagesRotoinversionzrie premesNo ratings yet
- Mineralogy: - It Is A Naturally Occurring Solid Homogenous Substance Which Has DefiniteDocument2 pagesMineralogy: - It Is A Naturally Occurring Solid Homogenous Substance Which Has Definitezrie premesNo ratings yet
- Geological Works of The Rivers, Winds and Seas: Ocean, Sea, Lake or Another RiverDocument3 pagesGeological Works of The Rivers, Winds and Seas: Ocean, Sea, Lake or Another Riverzrie premesNo ratings yet
- Fracture: Example:QuartzDocument3 pagesFracture: Example:Quartzzrie premesNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument4 pagesSolutionzrie premesNo ratings yet
- Part 5: Thin-Walled Pressure VesselsDocument2 pagesPart 5: Thin-Walled Pressure Vesselszrie premesNo ratings yet
- Three Types of Tectonics BoundaryDocument2 pagesThree Types of Tectonics Boundaryzrie premesNo ratings yet
- The Member) .: Normal Stress, Is The Stress Resulting From The Load Applied To The Perpendicular CrossDocument3 pagesThe Member) .: Normal Stress, Is The Stress Resulting From The Load Applied To The Perpendicular Crosszrie premesNo ratings yet
- The Maximum Force Applied or Minimum Area/dimension For The Design, Given That The Allowable Stress of The Material Is Indicated)Document3 pagesThe Maximum Force Applied or Minimum Area/dimension For The Design, Given That The Allowable Stress of The Material Is Indicated)zrie premesNo ratings yet
- Earths MantleDocument2 pagesEarths Mantlezrie premesNo ratings yet
- Work of Seas - The Expanse of Salt Water That Covers Most of The Earth's Surface andDocument2 pagesWork of Seas - The Expanse of Salt Water That Covers Most of The Earth's Surface andzrie premesNo ratings yet
- A Glaring Question How To Become An EntrepreneurDocument1 pageA Glaring Question How To Become An Entrepreneurzrie premesNo ratings yet
- Importance of Entrepreneurship (Baijal, 2016 Seth, 2019 Awlaqi and AltheebDocument1 pageImportance of Entrepreneurship (Baijal, 2016 Seth, 2019 Awlaqi and Altheebzrie premesNo ratings yet