Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Curriculum and Syllabus Under Semester System: Bs (H) in Mathematics
Uploaded by
Amna AmnaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Curriculum and Syllabus Under Semester System: Bs (H) in Mathematics
Uploaded by
Amna AmnaCopyright:
Available Formats
Curriculum and Syllabus of BS (H) Mathematics
CURRICULUM AND SYLLABUS
BS (H) IN MATHEMATICS UNDER
SEMESTER SYSTEM
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS
GOVERNMENT COLLEGE UNIVERSITY,
FAISALABAD.
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 1
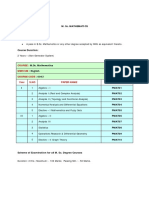
Scheme of Studies
BS Mathematics
Total Semesters = 8
Duration of Each Semester = 18 Weeks
Cumulative Credits of BS (8 Semesters) = 142
SEMESTER-II
No Course Code Course Title Cr. Hours
1 MTH-302 Calculus-II 3(3-0)
2 MTH-304 Linear Algebra and Its Applications 3(3-0)
3 STA-323 Introduction to Statistical Theory-II 3(3-0)
4 PHY-425 Introduction to Heat and Thermodynamics 3(2-1)
5 ENG-322 English Comprehension and Composition 3(3-0)
6 PST-321 Pakistan Studies 2(2-0)
Total 17
SEMESTER-IV
No Course Code Course Title Cr. Hours
1 MTH-402 Affine and Euclidean Geometry 3(3-0)
2 MTH-404 Mechanics –II 3(3-0)
3 MTH-406 Differential Equations-II 3(3-0)
4 MTH-408 Combinatorics 3(3-0)
5 MTH-410 C++ 3(2-1)
6 PSY-321 Introduction to Psychology 3(3-0)
Total 18
SEMESTER-VI
No Course Code Course Title Cr. Hours
1 MTH-502 Real Analysis-II 3(3-0)
2 MTH-504 Complex Analysis-II 3(3-0)
3 MTH-506 Algebra-II 3(3-0)
4 MTH-508 Mechanics 3(3-0)
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 2
5 MTH-510 Functional Analysis 3(3-0)
6 MTH-512 Mathematical Methods 3(3-0)
Total 18
SEMESTER-VIII
Course
No Course Title Cr. Hours
Code
1 MTH-602 Numerical Analysis-II 3(3-0)
MTH-604 Computing Tools for Mathematics 3(2-1)
2
3 MTH-606 Mathematical Statistics 3(3-0)
Optional Papers (3 out of following)
Applied Group Pure Group
Course Cr. Course
No Course Title No Course Title Cr. Hours
Code Hours Code
3(3-0) Advanced
Theory of
1 MTH-608 1 MTH-622 Group 3(3-0)
Optimization
Theory-II
Fluid 3(3-0) Measure 3(3-0)
2 MTH-610 2 MTH-624
Mechanics-II Theory
Special 3(3-0) MTH-634 Rings and
3 MTH-614 3 3(3-0)
Functions Fields
Total 18
Course Contents for BS (Mathematics)
Semester-II
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-302 Calculus II 3(3-0) 60
Integration: Anti derivatives and integrals. Riemann sums and the definite integral. Properties of Integral.
The fundamental theorem of calculus.
Techniques of integration: Integrals of elementary, hyperbolic, trigonometric, logarithmic and exponential
functions. Integration by parts, substitution and partial fractions. Approximate integration. Improper
integrals. Gamma functions.
Applications of integrals: Area between curves, average value. Volumes. Arc length. Area of a surface of
revolution. Applications to Economics, Physics, Engineering and Biology.
Infinite series: Sequences and series. Convergence and absolute convergence. Tests for convergence:
divergence test, integral test, p-series test, comparison test, limit comparison test, alternating series test, ratio
test, root test. Power series. Convergence of power series. Representation of functions as power series.
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 3
Differentiation and integration of power series. Taylor and Maclaurin series. Approximations by Taylor
polynomials.
Conic section, parameterized curves and polar coordinates: Curves defined by parametric equations.
Calculus with parametric curves: tangents, areas, arc length. Polar coordinates. Polar curves, tangents to
polar curves. Areas and arc length in polar coordinates.
Recommended Books:
1. H. Anton, I. Bevens, S. Davis, Calculus (10th ed.), John Wiley & Sons, 2012.
2. J. R. Hass, C. E. Heil, M. D. Weir, Thomas’s Calculus (14th ed.), Pearson, 2017.
3. D. Hughes-Hallett, A. M. Gleason, W. G. McCallum et al. Calculus: Single Variable (6th ed.),
Wiley, 2012.
4. J. Stewart, Calculus (8th ed.), Cengage Learning, Boston, 2012.
5. E. W. Swokowski, Calculus with Analytic Geometry (6th ed.), PWS-Kent Publishing Company,
1994.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-304 Linear Algebra 3(3-0) 60
Basic concepts of matrices. Types of matrices. Algebraic properties of matrices. Row and column operations
on matrices. Echelon and reduce echelon form of matrices. Rank of a matrix.
Definition and properties of determinants. Minor and cofactor. Inverse of a matrix. Singular and non-singular
matrices. Basic structure of system of linear equations. Method to solve system of linear equations (Gauss
Jordan method, Gauss elimination method).Consistency of system of linear equations. Non-trivial solution of
system of homogeneous linear equations.
Recommended Books:
1. Anton, H., Rorres, C., Elementary Linear Algebra: Applications Version (10th edition), John Wiley
& Sons, 2010.
2. Kolman, B., Hill, D. R., Introductory Linear Algebra (8th edition), Pearson Education India, 2008.
3. Lay, D. C., Linear Algebra and Its Applications (3rd edition), Pearson Education India, 2002.
4. Lipschutz, S., Lipson, M., Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Linear Algebra (3rd
edition), Erlangga, 2001
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
STA-323 Introduction to Statistical Theory-II 3(3-0) 60
Introduction of Simple Linear Regression. Scatter Diagram. Simple Linear Regression Model. Assumptions
of Linear regression model. Least Squares Estimators. Properties of the Least Square Regression Line.
Standard Errors of Estimates.
Correlation, Pearson’s Product Moment Correlation Coefficient with its application in daily life. Properties
of Correlation Coefficient, Coefficient of Determination, Correlation Coefficient for group data. Rank
Correlation and its properties. Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient and its derivation. Tied ranks.
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 4
Multiple Linear Regression with two Regressors, Coefficient of Multiple Determination, Standard Error of
Estimate. Coefficient of Partial and Multiple Correlations. Relation between Partial and Multiple Correlation
Coefficients.
Curve Fitting by Method of Least Squares. Fitting a straight line, fitting of a Second and third degree
Parabola, Change of Origin and Unit, Exponential Curves, Criteria for a Suitable Curve, Finding Plausible
Values by LS Method.
Recommended Books:
1. T.H. Wonnacott, R.J. Wannacott, Introductory Statistics. John Wily & Sons. New York, 1990.
2. R.E. Walpole, Introduction to Statistics. Macmillan Publishing Company, 2001
3. M. Rauf, Polymers Modern Statistics. Polymer Publication, Urdu Bazar, Lahore, 2001.
4. S.M. Chaudhray, S. Kamal, Introduction to Statistical Theory. IlmiKitabKhana, Urdu Bazar,
Lahore, 2002.
5. Koller, D., Friedman, N., Džeroski, S., Sutton, C., McCallum, A., Pfeffer, A., ... & Neville, J.
(2007). Introduction to statistical relational learning. MIT press.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
PHY-324 Introduction to Heat and 3(2-1) 60
Thermodynamics
Kinetic theory of the ideal gas; work done on an ideal gas, material energy of an ideal gas, intermolecular
forces. Statistical mechanics, statistical distribution and mean values, distribution molecular speeds,
distribution of energies, Brownian motion. Heat, different theories of heat, specific heat, gram molecular
specific heat, laws of thermodynamics. Zeroth law, first law, second law, third law of thermodynamics,
reversible and irreversible processes, indicator diagram, entropy, law of thermodynamics, reversible and
irreversible processes, indicator diagram, entropy law of increase of entropy, temperature-entropy diagram.
Maxwell’s thermodynamics relations, TDS equations, Clapeyron’s equation, entropy and second law of
thermodynamics. Temperature scale, entropy, low temperature physics. Thermoelectricity, Seabeck effect,
Peltier effect, thermocouple.
1. The determination of wavelength of light by Diffraction grating.
2. Design a full-wave rectifier and study its output without and with a capacitor filter.
3. Design a Half-wave rectifier and study its output without and with a capacitor filter.
4. To study characteristics of NOT, AND, NOR, NOR, NAND and XOR and verify their truth
table.
Recommended Books:
1. Halliday, Resnick and Walker, 2011, Fundamental Physics, 9th Ed, John Wiley and Sons Inc.
New York.
2. Halliday, Resnick and Krane, 2002. Physics Vol. I & II, 5th Ed, John Wiley and Sons Inc. New
York.
3. Sears, Zemansky and Young, 2000, University Physics, 8th Ed, Addison-Wesley. Reading (MA)
USA.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
ENG-322 English Comprehension and Composition 3(3-0) 60
English Comprehension and Composition
1 Reading Comprehension
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 5
• Identify Main Idea/Topic Sentence
• Find Specific Information quickly
• Recognize and Interpret Cohesive Devices
• Distinguish Between Fact and Opinion
• Skimming and scanning
• Notes taking techniques
•Analyzing paragraph structure
•Identifying the writer’s intent such as cause effect, reasons, comparison and contrast, exemplification.
• Interpreting charts and diagrams
•Making appropriate notes using strategies such as mind maps, tables, lists, lists, graphs.
2. Enhancing Vocabulary Through Reading
3. General Study Skills Like Time Management, Finding Learning Style, Developing Reading Keys And
Systems
4. Getting organized and knowing one’s target
5. Dictionary skills
6. Using the library
7. Remembering and learning
8. Techniques for reading
9. Critical thinking
10. Tackling a book
Recommended Books:
1. Wallace Catherine: Study Skills: CUP
2. Yorky R.: Study Skills.
3. Smazler. : Write to be Read: reading, reflection and writing. CUP
4. Wallace, M. 1980 Study Skills in English. CUP
5. Langan, J. 1981 English Skills McGraw Hill Book Co.
6. McWhorter, K.T. 1983 College Reading and Study Skills Little Brown & Co.
7. O’Brien & Jordan. 1985 Developing Reference Skills Collins
8. Price-Machado, D. 1998 Skills for Success. CUP
9. Birsh, J. R. (2011). Multisensory teaching of basic language skills. Brookes Publishing Company.
PO Box 10624, Baltimore, MD 21285.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 6
PST-321 Pakistan Studies 2(2-0) 40
Regeneration of Muslim Society in sub-continent and causes of decline of Muslim Rule.
War of Independence 1857 and its impacts upon the politics of South Asia.
Sir Syed Ahmed Khan and Aligarh Movement:
Educational Services
Political Services
Rational Interpretation of Islam
All India Muslim League:
Multiple approaches and causes of the formation of Muslim League.
Objectives of the party.
Comparison of the policies of All Indian National congress and All India
Muslim League.
Politics of Muslim League after the creation of Pakistan
Luckhnow Pact 1916, high water mark of Hindu-Muslim Unity.
Khilafat Movement:
Khilafat as an institution.
Hindu-Muslim Unity.
Role of Gandhi
Emergence of Muslim Ulma in Indian politics.
Causes of the failure and impacts of the movement.
Iqbal’s Address at Allahabad 1930 and political thoughts of Ch. Rehmat Ali.
Congress Ministries.
Pakistan Resolution 1940.
Muhammad Ali Jinnah:
Jinnah’s role in Indian politician.
As a governor General
Initial problems and constitutional development in Pakistan.
The study of constitutions of Pakistan (1956-1962-1973)
Political culture of Pakistan.
Foreign Policy of Pakistan:
Major determinants and objectives
Overview.
Recommended Books:
1. K.B. Saeed, Pakistan the Formative Phase.
2. I.H. Qureshi,. Struggle for Pakistan, Karachi: Oxford, 1995.
3. S. Mahmood, Pakistan Political Roots and Development, 1947-1999, Karachi, Oxford,
2000.
4. M.R. Afzal, Political Parties in Pakistan 1947-1958, Islamabad, NIHCR, 2002.
5. Choudhry, G.W. Constitutional Development in Pakistan, London, second Edition, 1969.
6. Ali, Ch. Muhammad, The Emergence of Pakistan, Lahore, 1973.
7. Mohiuddin, Y. N. (2007). Pakistan: a global studies handbook. ABC-CLIO.
SEMESTER-IV
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-402 Affine and Euclidean Geometry 3(3-0) 60
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 7
Vector spaces and affine geometry: Collinearity of three points, ratio AB/BC. Linear combinations and
linear dependent set versus affine combinations and affine dependent sets. Classical theorems in affine
geometry: Thales, Menelaus, Ceva, Desargues. Affine subspaces, affine maps. Dimension of a linear
subspace and of an affine subspace.
Euclidean geometry: Scalar product, Cauchy-Schwartz inequality: norm of a vector, distance between two
points, angles between two non-zero vectors. Pythagoras theorem, parallelogram law, cosine andesine rules.
Elementary geometric loci.
Orthogonal transformations: Isometries of plane (four types), Isometries of space (six types). Orthogonal
bases.
Platonic polyhedra: Euler theorem on finite planar graphs. Classification of regular polyhedra in space.
Isometries of regular polygons and regular polyhedra.
Recommended Books:
1. E. Rees, Notes on Geometry, Springer, 2004.
2. M. A. Armstrong, Groups and Symmetry, Springer, 1998.
3. H. Eves, Fundamentals of Modern Elementary Geometry, Jones and Bartlett
Publishers International, 1992
4. S. Stahl, The Poincare Half-Plane A Gateway to Modern Geometry, Jones and
Bartlett Publishers International, 1993.
1. Dattorro, J. (2010). Convex optimization & Euclidean distance geometry. Lulu. com.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-404 Mechanics-II 3(3-0) 80
Velocity and Acceleration. Cartesian components of velocity and acceleration. Tangential and Normal
Components of Velocity and Acceleration. Transverse and Radial Components of Velocity and Acceleration.
Motion with constant Acceleration. Motion with Variable Acceleration. Graphical Methods. Motion of a
Free Particle along the vertical Line, Simple Harmonic Motion. The Nature of Simple Harmonic Motion.
Geometrical Representation. Speed of the Projectile Parabola of Safety. Range on the Inclined Plane.
Maximum range on horizontal and Inclined Plane. Time Period, Maximum Height. Motion under a Central
Force. Elliptic Orbit Under a central force. Polar form of the orbit. Apse and apsidal distance. Planetary
orbits. Kepler’s Laws. Damped Harmonic Oscillator, Damped force oscillations, Vertical motion with air
Resistance
Recommended Books:
1. Synge & Griffith, Principles of Mechanics, McGraw Hill Book Company Inc., New York.
2. D.T. Greenwood, Principles of Dynamics, Prentice Hall, Inc.
3. W. Huser, Introduction to Principles of Mechanics, Addison Wesley, New York.
4. R.A Becker, Introduction to Theoretical Mechanics, McGraw Hill Book
Company, Inc., New York.
5. F. Chorlton, A Text Book of Dynamics.
6. K .L. Mir, Theoretical Mechanics, IlmiKitab Khan.
7. Landau, R. H. (2008). Quantum mechanics II: a second course in quantum theory. John Wiley
& Sons.
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 8
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-406 Differential Equations-II 3(3-0) 60
Power Series Solutions: Solutions About Ordinary Points, Power Series Solutions, Solutions About
Singular Points, Special Functions, Bessel’s Equation, Legendre’s Equation.
System of differential equations: Basic Theory of First Order Linear Systems, Systems of Two First Order
Linear Differential Equations, Homogeneous Linear Systems, Non-homogeneous Linear Systems, Complex
Eigen values, Repeated Eigen values, Introduction to Nonlinear Systems.
Laplace transforms: Definition of the Laplace Transform, Properties of the Laplace Transform, The Inverse
Laplace Transform, Solving Differential Equations with Laplace Transforms.
Sturm-Liouville systems: Introduction to SL-systems, Properties of SL-systems, Sturm–Liouville Boundary
Value Problems, Non-homogeneous Boundary Value Problems, Singular Sturm–Liouville Problems.
Recommended Books:
1. Zill D G, Cullen M.R. Differential Equations with Boundary-Value Problems (3rd Edition), 1997,
PWS Publishing Co.
2. Muhammad Amin, Mathematical Methods, 2007, Ilmi KitabKhana Lahore.
3. Eisgolts L, Differential Equations and the Calculus of Variations, 1970, Mir Publishers Moscow.
4. Simmons, G.F., Differential Equations with Applications and Historical Notes, Second Edition,
McGraw-Hill, Inc., 1991.
5. Boyce, W. E. and DiPrima, R.C., Elementary Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems,
Sixth Edition, John Wiley and Sons, 1997
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-408 Combinatorics 3(3-0) 60
To basic counting principles, Permutations, Combinations. The injective and bijective principles,
Arrangements and selections with repetitions. Graphs in Combinatorics. The Binomial theorem,
combinatorial identities. Properties of binomial coefficients, Multinomial coefficients, The multinomial
theorem. The Pigeonhole principle, Examples, Ramsay numbers, The principle of inclusion and exclusion,
Generalization. Integer solutions. Surjective mapping, Stirling numbers of the second kind, The Sieve of
Eratostheries, Euler φ-function, The Problem des Manages. Ordinary Generating Functions, Modeling
problems. Partition of integers, Exponential generating functions. Linear homogeneous recurrence relations,
Algebraic solutions of linear recurrence relations and constant functions, The method of generating
functions, A non-linear recurrence relation and Catalpa numbers
Recommended Books:
1. A Tucker, Applied Combinatorics, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2nd Edition, 1985.
2. C.C. Chen and K.M.Koh, Principles and Techniques in Combinatorics, World Scientific
Pub. Co. Pte. Ltd, Singapore. 1992.
3. V.K. Balakrishnan, Theory and Problems of Combunatorics, Schaum’s Outline Series,
MeGraw-Hill International Edition, Singapore, 1995.
4. C.L. Liu, Introduction to Combinatorial Mathematics, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1968.
5. J.H. Van Ling & R.M. Wilson, A course on Combinatorics, 2nd Edition, Cambridge
University Press, Cambridge, 2001.
6. Flajolet, P., & Sedgewick, R. (2009). Analytic combinatorics. cambridge University press.
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 9
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-410 C++ 3(2-1) 60
Introduction to operating systems, one language C++, building blocks, variables, input/output, loops (FOR,
WHILE, DO), decisions (IF, IF ELSE, ELSE IF) construct switch statement, conditional statement, function
hat returns a value using argument to pass data to another function, external variable, arrays and strings,
pointers, structure, files and introduction to object-oriented programming
Recommended Books:
1. Aho, A. V. and Ulman, J. D. (1995). Foundation of Computer Science. Computer Science Press, WH
Freeman, New York
2. Ein, J. L. Theory of Computation: An Introduction, 1st edition. Jones & Bartlett, Boston
3. Laffor. Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming. McGraw Hill, New York
4. Musser, D. R., Derge, G. J., & Saini, A. (2009). STL tutorial and reference guide: C++
programming with the standard template library. Addison-Wesley Professional.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
PSY-422 Introduction to Psychology 3(3-0) 60
Objectives
• To describe psychology with major areas in the field and identify the parameters of this discipline.
• To distinguish between the major perspectives on human thought and behavior.
• To appreciate the variety of ways psychological data are gathered and evaluated.
• To gain insight into human behavior and into one’s own personality or personal relationships.
• To explore the ways that psychological theories are used to describe, understand, predict and control
or modify behavior
Course Contents
1. Introduction to psychology
a. Nature and application of Psychology with special reference to Pakistan.
b. Historical Background and Schools of Psychology
2. Methods of psychology
a. Observation
b. Case History Method, Experimental Method
c. Interviewing Techniques
3. Biological Basis of Behavior
a. Neuron: Structure and Functions
b. Central Nervous system &Peripheral Nervous System
c. Endocrine Glands
4. Sensation, Perception and Attention
a. Sensation
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 10
a. Characteristics and Major Functions of different Sensations
b. Vision: Structure and Function of the Eye.
c. Audition: Structure and Function of the Ear.
b. Perception
a. Nature of perception
b. Factors of perception: Subjective, Objective and Social.
c. Kinds of Perception
d. Spatial Perception (Perception of depth and distance)
e. Temporal Perception; Auditory Perception
c. Attention
a. Factors, Subjective and Objective
b. Span of Attention
c. Fluctuation of Attention
d. Distraction of Attention (Causes and Control)
Practicum:
Following experiments shall be performed by the students:
• Color Zones of Retina
• Fluctuation in Attention
• Muller-Layer Illusion
• Perceptual Grouping
• Size Constancy
• Span of Attention
Books Recommended
1. Atkinson R. C. & Smith E. E. (2000). Introduction to psychology (13th Ed.). USA: Harcourt
Brace College Publishers.
2. Femald, L.D, & Femald, P. S. (2005). ). Introduction to psychology. USA: WMC Brown
Publishers.
3. Glassman, W.E. (2000). Approaches to Psychology. Open university Press.
4. Hayes,N (2000). Foundation of Psychology (3rd Ed.). Thomson Learning.
5. Lahey, B.B (2004). Physchology: An Introduction (8th Ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc.
6. Lindsay, P. H., & Norman, D. A. (2013). Human information processing: An introduction to
psychology. Academic press.
SEMESTER-VI
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-502 Real Analysis II 3(3-0) 60
The Riemann-Stieltjes Integrals: Definition and existence of integrals. Properties of
integrals. Fundamental theorem of calculus and its applications. Change of variable
theorem. Integration by parts.
Functions of Bounded Variation: Definition and examples. Properties of functions
of bounded variation.
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 11
Improper Integrals: Types of improper integrals. Tests for convergence of improper
integrals. Beta and gamma functions. Absolute and conditional convergence of
improper integrals.
Sequences and Series of Functions: Definitions and examples of point-wise and uniform convergence.
Uniform convergence and continuity. Uniform convergence and integration. Uniform convergence and
differentiation. Series of functions. The Weierstrass M-test, Power series.
Recommended Books:
1. R. G. Bartle and D. R. Sherbert, Introduction to Real Analysis (4th Ed.), John Wiley, New York,
2011.
2. N. L. Carothers, Real Analysis, Cambridge University Press, New York, 2000.
3. K. R. Davidson and A. P. Donsig, Real Analysis with Applications: Theory in Practice, Springer-
Verlag, New York, 2010.
4. E. Fischer, Intermediate Real Analysis, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1982.
5. S. R. Ghorpade and B. V. Limaye, A First Course in Calculus and Real Analysis, Springer-Verlag,
New York, 2006.
6. S. G. Krantz, Real and Foundations (2nd Ed.), Chapman & Hall/CRC, New York, 2005.
7. W. Rudin, Principles of Mathematical Analysis, (3rd Ed.), McGraw-Hill, New York, 1976.
8. M. H. Protter and C. B. Morrey, A First Course in Real Analysis (2nd Ed.), Springer-Verlag, New
York, 1991.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-504 Complex Analysis II 3(3-0) 60
Properties of Analytic Functions: The argument principle and Rouche’s theorem. The local mapping. The
maximum principle. Schwarz’s lemma. Harmonic functions: maximum principle, Poisson’s formula.
Infinite Sums and Products: Analyticity at ∞. Polynomials. Rational functions. Meromorphic functions.
The Mittag-Leffler theorem. Weierstrass’s factorization theorem. Infinite products of numbers and functions.
Uniform convergence. Canonical products. The genus and order of entire functions. The Gamma functions:
infinite product and integral representations.
Conformal Mappings: Properties of simple mappings: powers, the bilinear map. The Riemann mapping
theorem. The Schwarz reflection principle. Mapping of Polygons: Schwartz-Christoffel theorem. Elliptic
integrals.
Analytic Continuation: Standard procedure of analytic continuation. Continuation along arcs. Points of
continuation and the natural boundary of analytic functions. The monodromy theorem. Picard’s theorem.
Elliptic Functions: Periodic functions. Elliptic functions and its properties. Weierstrass functions. Elliptic
functions in terms of Weierstrass functions with the same periods. Quasi periodic functions: the zeta and
sigma functions of Weierstrass. Jacobian elliptic function and its properties.
Recommended Books:
1. L. Ahlfors, Complex Analysis (3rd Ed.), McGraw-Hill, New York, 1979.
2. J. W. Brown and R. V. Churchill, Complex Variables and Applications (9th Ed.), McGraw-Hill, New
York, 2013.
3. J. B. Conway, Functions of One Complex Variable I, Springer, 1978.
4. W. Kaplan, Introduction to Analytic Functions, Addison-Wesley, 1966.
5. Z. Nehari, Conformal Mapping, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1952.
6. S. Ponnusamy, H. Silverman, Complex Variables with Applications, Birkhäuser, 2006.
7. E. D. Rainville, Special Functions, The Macmillan Company, New York, 1965.
8. R. Remmert, Theory of Complex Functions, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1991.
9. R. Remmert, Classical Topics in Complex Function Theory, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1998.
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 12
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-506 Algebra-II 3(3-0) 60
Prerequisites: Basic knowledge of elementary group theory.
Outline:
Vector space and its properties, Operations on vector space (Intersection, sum and direct sum). Subspace and
examples. Linear combination, Linear span and related concepts Basis and dimension, Linear transformations
and related results, Fundamental theorems of linear transformations, Algebra of linear transformations, Matrix
of linear transformation and related concepts, Dual space and its properties, Quotient space and its properties,
Eigen values and Eigen vectors, Inner product space and related concepts, Definition of a ring and its
properties, Units, Zero divisors and Integral Domain, Ideal and sub-ring, Principal Prime and Maximal ideals,
Quotient ring.
Recommended Books:
1. Fraleigh J. B., A First Course in Abstract Algebra (7th Edition), Pearson Education 2003
2. Gallian J. A., Contemporary Abstract Algebra (8th Ed.), Cengage Learning, India, 2013.
3. Khanna V. K., Bhambri S. K., A Course in Abstract Algebra (4th Edition), Vikas Publishing House, India,
2006.
4. P.R, Halmos, Finite Dimensional Vector Spaces, Von Nostrand.
5. David S. Dummit and Richard M. Foote, Abstract Algebra, 3rd edition, John Wiley and Sons, 2004.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-508 Mechanics 3(3-0) 60
Non Inertial Reference Systems. Accelerated coordinate systems and inertial forces. Rotating coordinate
systems. Velocity and acceleration in moving system: Coriolis. Centripetal and transverse acceleration.
Dynamics of a particle in a rotating coordinate system. Planar Motion of Rigid Bodies
Kinetics: Work, power, kinetic energy, conservative force fields. Conservation of energy, impulse, torque.
Conservation of linear and angular momentum. Non-conservative forces.
Planer Motion of Rigid Bodies: Introduction to rigid and elastic bodies, degree of freedom, translations,
rotations, instantaneous axis and center of rotation, motion of the center of mass. Euler’s theorem and
Chasles’ theorem. Rotation of a rigid body about a fixed axis, moments and products of inertia. Parallel and
perpendicular axis theorem.
Motion of Rigid Bodies in Three Dimensions: General motion of rigid bodies in space. The momental
ellipsoid and equimomental systems. Angular momentum vector and rotational kinetic energy. Principal axes
and principal moments of inertia. Determination of principal axes by diagonalizing the inertia matrix.
Euler Equations of Motion of a Rigid Body: Force free motion. Free rotation of a rigid body with an axis
of symmetry. Free rotation of a rigid body with three different principal moments. The Eulerian angles,
angular velocity and kinetic energy in terms of Euler angles. Motion of a spinning top and gyroscopes-steady
precession, sleeping top.
Recommended Books:
1. E. DiBenedetto, Classical Mechanics. Theory and Mathematical Modeling, ISBN: 978-0-8176-
4526-7, Birkhauser Boston, 2011.
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 13
2. John R. Taylor, Classical Mechanics, ISBN: 978-1-891389-22-1, University of Colorado, 2005.
3. H. Goldstein, Classical Mechanics, Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., 1980.
4. C. F. Chorlton, Text Book of Dynamics, Ellis Horwood, 1983.
5. M. R. Spiegel, Theoretical Mechanics, 3rd Edition, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, 2004.
6. G. R. Fowles and G. L. Cassiday, Analytical Mechanics, 7th edition, Thomson Brooks/COLE, USA,
2005.
7. L. N. Hand and J. D. Finch, Analytical Mechanics, Cambridge University Press, 1998
8. K .L. Mir, Theoretical Mechanics IlmiKitabKhana. 2004
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-510 Functional Analysis 3(3-0) 60
Metric Spaces: Metric spaces. Separable metric spaces. Complete metric spaces. Isometric metric spaces.
Completion of metric spaces.
Normed Spaces: Normed spaces. Banach spaces. Infinite series in normed spaces. Absolute convergence.
Schauder basis. Seminorms. Quotient normed spaces. Finite dimensional normed spaces. Equivalent norms.
Compact sets in normed spaces. Compactness and finite dimension. Compactness and continuity. Bounded
linear operators. Continuity and boundedness. Bounded linear functionals. Linear operators and functionals
on finite dimensional normed spaces. Dual spaces.
Inner Product Spaces: Inner product spaces. Properties of inner product spaces. Hilbert spaces.
Completion of inner product spaces. Direct Sums. Orthogonal complements. Orthonormal sets and
sequences. Bessel inequality. Total orthonormal sets and sequences. Parseval identity. Separable Hilbert
spaces. Bounded linear functionals on Hilbert spaces. Hilbert-adjoint operator.
Recommended Books:
1. J. B. Conway, A Course in Functional Analysis (2nd Ed.), Springer-Verlag, New York, 1990.
2. Y. Eidelman, V. Milman, and A. Tsolomitis, Functional Analysis: An Introduction, American
Mathematical Society, Providence, Rhode Island, 2004.
3. E. Kreyszig, Introductory Functional Analysis with Applications, John Wiley & Sons Inc., New
York, 1989.
4. B. P. Rynn, and M. A. Youngson, Linear Functional Analysis (2nd Ed.),Springer-Verlag, London,
2008.
5. A. Torchinsky, Problems in Real and Functional Analysis, American Mathematical Society,
Providence, Rhode Island, 2015.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-512 Mathematical Methods 3(3-0) 60
Basics of differential equations, linear homogeneous differential equations of order n, fundamental set of
solutions, linearly dependent and independent solutions, Wronskian determinant, adjoint and self - adjoint
equations, self - adjoint operator, symmetric operator, Lagrange’s identity, Green’s identity, Eigen value
problem, Eigen functions and Eigen values, self-adjoint Eigen value problems, orthogonality of Eigen
functions, real Eigen values, regular, periodic and singular Sturm-Liouville systems, orthogonal sets of
functions, expansion of functions in terms of Eigen functions. Power series solutions, Legendre’s equation,
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 14
Legendre’s polynomials, generating function, Rodrigue’s formula, recursion relations, orthogonality and
normality of Legendre’s polynomials, Legendre’s series, Bessel equation, Bessel functions, generating
function, recurring relations, orthogonality of Bessel functions, Bessel series. Green’s function in one and
two dimensions, Green’s function methods applied to boundary value problems.
Recommended Books:
1. I. Stakgold, Boundary Value Problems of Mathematical Physics, Vol. I, II.
Macmillan,1968.
2. Lal Din BaigMethods of Mathematical Physics, IlmiKitabGhar Lahore, 2000.
3. H. Sagan, Boundary and Eigenvalue Problems in Mathematical Physics. John Wiley &Sons.New
York/London, 1961.
4. E.L Butkov, Mathematical Physics, Addison-Wesley 1968
5. H. J. Weber, G. B. Arfken, Essential Mathematical Methods for Physicists, ISE, lsevier. 2003.
6. Arnol'd, V. I. (2013). Mathematical methods of classical mechanics (Vol. 60). Springer Science &
Business Media.
SEMESTER-VIII
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-602 Numerical Analysis-II 3(3-0) 60
Numerical Differentiation: Forward, backward and central difference formulae,
Numerical Integration: Trapezoidal, Simpson and Gaussian quadrature using a system of orthogonal
polynomials (Legendre and Laguere polynomials).
Difference Equations: Formulation of difference equations, solution of linear (homogeneous and non-
homogeneous) difference equations with constant coefficients.
Numerical Solutions of Initial Value Problems: Picard’s method, Euler method, Modified Euler method,
Improved Euler method, Predictor-corrector type methods for solving initial value problems along with
convergence and instability criteria.
Recommended Books:
1. C.F. Gerald and P.O. Wheatley, Applied Numerical Analysis, Pearson Education, Singapore, 2005.
2. R. L. Burden and J.D. Faires: Numerical Analysis, latest Edition, PWS Pub. Co.
3. J.H. Mathews, Numerical Methods for Mathematics, latest Edition, Prentice Hall International.
4. S. C. Chapra and R. P. Canale: Numerical Methods for Engineers, 6th edition, McGraw Hill.
5. Iserles, A. (2009). A first course in the numerical analysis of differential equations (No. 44).
Cambridge university press.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-604 Computing Tools For Mathematics 3(2-1) 60
The contents of the course are not fixed; however, the following points should be kept in mind while
teaching the course. The purpose of this course is to teach students the use of mathematical software like
MATLAB, MAPLE, MATHEMATICA for solving computationally-difficult problems in mathematics. The
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 15
student shall become well versed in using at least one mathematical software and shall learn a number of
techniques that are useful in calculus as well as in other areas of mathematics. The course should be taught in
a computer lab setting. Besides learning to use the software, the students must be able to utilize the software
to solve computationally difficult problems in calculus and other areas of mathematics. At the end of the
course, the students should have a good command on at least two of the three programs mentioned above.
Note: The software to teach for affiliated colleges is Mathemtica to avoid inconvenience in final
examination.
Recommended Books:
1. Etter DM, Kuncicky D, Hull D, Introduction to MATLAB 6, 2001, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs,
NJ, USA.
2. Garvan F, The Maple Book, 2002, Chapman & Hall/CRC.
3. Kaufmann S, Mathematica As a Tool: An Introduction with Practical Examples, 1994, Springer,
New York.
4. Monaghan, J., Trouche, L., & Borwein, J. M. (2016). Tools and mathematics. Berlin: Springer
International Publishing.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-606 Mathematical Statistics 3(3-0) 60
Probability Distributions and Probability Densities: Probability distribution, Continuous Random
Variables, Probability Density Functions, Multivariate Distributions, Marginal Distributions, Conditional
Distributions
Mathematical Expectations: The Expected Value of a Random Variable, Moments, Chebyshev’s Theorem,
Moment-Generating Functions, Product Moments, Moments of Linear Combinations of Random Variables,
Conditional Expectations
Special Probability Distributions: Distributions of the Discrete Uniform, Bernoulli, Binomial, Negative
Binomial, Geometric, Poisson, Multinomial, and Hyper geometric
Special Probability Densities: Distributions of Uniform, Exponential, Gamma, Beta, and Normal
Functions of Random Variables: Distribution Function Technique, Transformation Techniques of One-
and Several, Moment-Generating Function Technique
Sampling Distributions: The distribution of the Mean, The Chi-Square Distribution, The t-Distribution, The
f-Distribution, Estimation of Means, Estimations of Proportions, Estimation of Variance, Testing of
Statistical Hypothesis Concerning Means, Proportions, and Variances
Recommended Books:
1. Mood, A.M. Graybill, F.A. Boes, D.C. Introduction to the Theory of Statistics, (2nd Edition),
McGraw-Hill Book Company New York, 1986.
2. Degroot, M.H. Probability and Statistics, (2nd Edition) Addison Wesley Company New York 1986.
3. Walpole-Myers. Myers. Ye Probability and Statistics (7th Edition)
4. M. H Degroot,. Probability and Statistics, (2nd Edition), Addison-Wesle Publishing Company, USA,
1986.
5. K.V. Mardia, Kent, J.T. Bibby, J.M. Multivariate Analysis. Academic Press New York, 1979.
6. Allen. T Craig, Robert V. Hogg, Introduction to Mathematical Statistics, (5th edition) publish by
Pearson education Singapore (Pvt) Ltd.
7. Miller, I. and Miller, M. (1997). Mathematical Statistics. Prentice-Hall.
8. Seymour, L. and John, J. S. (2011). Introduction to Probability and Statistics. McGraw-Hill
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 16
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-608 Theory of Optimization 3(3-0) 60
Introduction to optimization. Relative and absolute extreme. Convex. Concave and unimodal functions.
Constants. Mathematical programming problems.
Optimization of one, two and several variables functions and necessary and sufficient conditions for their
optima. Direct substitution method and Lagrange multiplier method, necessary and sufficient conditions for
an equality-constrained optimum with bounded independent variables. Inequality constraints and Lagrange
multipliers. Kuhn- Tucker Theorem. Multidimensional optimization by Gradient method. Convex and
concave programming, Calculus of variation and Euler Language equations, Functions depending on several
independent variables. Variational problems in parametric form. Generalized mathematical formulation of
dynamics programming. Non-Linear continuous models, Dynamics programming and Variational calculus.
Control theory.
Recommended Books:
1. Gotfried B.S and Weisman, J. Introduction to Optimization Theory (Prentice-Inc. New Jersey,
1973).
2. Elsgolts. L. Differential Equations and the Calculus of Variations (Mir Publishers- Moscow,
1970).
3. Wismer D.A and Chattergy R. Introduction to Nonlinear Optimization (North -Holland, New
York, 1978).
4. Intriligator M.D. Mathematical Optimization and Economic Theory (Prentice-Hall, Inc, New
Jersey, 1971).
5. Rao, S. S. (2009). Engineering optimization: theory and practice. John Wiley & Sons.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-610 Fluid Mechanics-II 3(3-0) 60
Vortex motion, Line Vortex, Vortex row Image System, Kelvin’s minimum energy theorem, Uniqueness
theorem, Fluid streaming past a circular cylinder, Irrational motion produced by a vortex filament. The
Helmholtz vorticity equation, Karman’s vortex-street. Constitutive equations; Navier- Stoke’s equations;
Exact solution of Navier-Stoke’s equations; Steady unidirectional flow; Poiseuille flow; Couette flow;
Unsteady unidirectional flow, Sudden motion of a plane boundary in a fluid at rest; Flow due to an
oscillatory boundary; Equations of motion relative to a rotating system; Ekman flow; Dynamical similarity
of turbulent motion.
Recommended Books:
1. L.D. Landan & E. M. Lifshitz, Fluid Mechanics, Pergamon Press, 1966.
2. Batchelor, G.K. An Introduction to Fluid Dynamics, Cambridge University Press, 1969.
3. Walter Jaunzemis, Continuum Mechanics, McMillan Company, 1967.
4. Milne-Thomas, Theoretical Hydrodynamics, McMillan Company, 1967.
5. D. J Tritton, Physical Fluid Dynamics, 2nd Edition Oxford.
6. Morrison, F. A. (2013). An introduction to fluid mechanics. Cambridge University Press.
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 17
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-614 Special Functions 3(3-0) 60
The Gamma function: definition, relations satisfied by Gamma function, Euler’s constant, the order symbols
o and O, asymptotic representation of the Gamma function for large O(Z), Beta function; Tye-
Hypergeometric function, the function F(a,b;c;z) and F(a,b;c;I), the hypergeometric differential equation,
simple transformations, a theorem due to Kummer, orthogonal polynomials, simple sets of polynomials,
orthogonality, the three term recurrence relation, the Christofell-Darboux formula, normalization, Bessel’s
inequality, Legendere Polynomials, generating function, differential equation, the Rodrigues formula,
recurrence relations, hypergeometric form of Pn(x), Some bounds on Pn(x), orthogonality, Hermite
Polynomials, definition of Hn(x), recurrence relations, the Rodringues formula, the Hermite polynomials as 2
Fo , orthogonality, Laguerre Polynomials, The polynomial Ln(x), generating functions, Rodrigues formula,
the differential equation, orthogonality.
Recommended Books:
1. Rainville, E.D., Special Functions. 2nd Ed. Chelsea Publishing Co. 1971
2. Lebedev, N.N., Special Functions and their Applications. 2nd Ed. Prentice Hall,
1972.
3. Whittaker & Watson. A Course in Modern analysis. 2nd Ed. Cambridge
University Press, 1978.
4. Mathai, A. M., & Haubold, H. J. (2008). Special functions for applied scientists.
New York:Springer Science+ Business Media.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-622 Advanced Group Theory-II 3(3-0) 60
Prerequisites: Elementary group Theory.
Outline:
• Series in group, upper and lower central series, Butterfly lemma, Schreier refinement theorem,
Jordan Holder Theorem, Solvable groups definition and examples, Theorems on solvable groups,
Nilpotent groups, characterization of finite nilpotent groups, Free groups and their basic theorems,
Definition and examples of free products of groups, Definition of action of a group and examples ,
orbit and stabilizer, transitive and intransitive action, Regular action and basic theorems. Linear
groups and types of linear groups.
Recommended Books:
1. David S. Dummit and Richard M. Foote, Abstract Algebra, 3rd edition, John Wiley and Sons, 2004.
2. Derek John, Scott Robinson, A Course in the Theory of Groups, Springer, 1996.
3. MacDonald, The Theory of Groups, Oxford University Press, 1968.
4. P.M. Cohn, Classic Algebra, London: John Wiley, 2000.
5. D. Burton, Abstract and Linear Algebra, Addison-Wesley publishing Co, 1987.
6. P.B. Bhattacharya, S.K. Jain and S.R. Nagpaul, Basic Abstract Algebra, 2nd Ed.C.U.P. 1995.
7. V. J Khanna, S.K Bhambri, A course in Abstract Algebra,
8. Robinson, D. J. (2012). A Course in the Theory of Groups (Vol. 80). Springer Science & Business
Media.
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 18
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-624 Measure Theory 3(3-0) 60
Introduction, outer measure, Measurable sets and Lebesgue measure. A non-measurable set. Measurable
function, the Lebesgue integral and the Riemann integral, the Lebesgue integral of a bounded function over a
set of finite measure, The integral of a non-negative function. The general Lebesgue integral. Convergence in
measure.
Recommended Books:
1. G. B. Folland, (2013). Real analysis: modern techniques and their applications. John Wiley & Sons.
2. R. L. Wheeden, A. Zygmund (2015). Measure and integral: an introduction to real Analysis (Vol.
308). CRC Press.
3. P.R. Halmos, Naïve Set Theory, New York, Van Nostrand.
4. B. Rotman& G.T. Kneebone, The Theory of Sets and Transfinite Numbers, Old bourne London.
Course Number Title Credit Hours Marks
MTH-634 Rings and Fields 3(3-0) 80
Rings: Basic Definitions and Examples of Rings, Ring Homomorphism, Ring of Fractions, Quotient Rings,
Definitions of Ideals, Prime Ideals, Maximal Ideals, The Chinese Remainder Theorem, Euclidean Domains,
Principal Ideal Domains, Unique Factorization Domains, Polynomial Rings, Polynomial Rings Over Fields
Modules: Basic Definitions and Examples of Modules, Modules Homomorphism, Quotient Modules, Direct
Sums
Fields: Definition and examples of Fields, Finite Fields, Extension fields, Algebraic and transcendental
elements, simple extension, Introduction to Galois theory.
Recommended Books:
1. Hartley, B. and Hawkes, T.O. Rings, Modules and Linear Algebra, Chapman and Hall, 1980.
2. Herstein, I.N. Topics in Algebra, John Wiley and Sons, 1975.
3. Blyth, T.S., Module theory, Oxford University Press, 1977.
4. Adamson, J. Rings and Modules.
2. Dummit, D. and Foote. R. (2004). Abstract Algebra. John Wiley & Sons.
3. Fraleigh, B. (1967).A First Course in Abstract Algebra, Pearson Education
Outlines BS Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Government College University, Faisalabad. Page 19
You might also like
- Development of Mathematics 1900-1950 (English and French Edition)Document760 pagesDevelopment of Mathematics 1900-1950 (English and French Edition)Anderson Alfred100% (1)
- Methods for Applied Macroeconomic ResearchFrom EverandMethods for Applied Macroeconomic ResearchRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Quantum Computation and Logic - How Quantum Computers Have Inspired Logical Investigations (PDFDrive)Document192 pagesQuantum Computation and Logic - How Quantum Computers Have Inspired Logical Investigations (PDFDrive)Artem Sergeevich AkopyanNo ratings yet
- E. Brian Davies-Linear Operators and Their SpectraDocument465 pagesE. Brian Davies-Linear Operators and Their SpectraMahmood Kamil ShihabNo ratings yet
- Siddiqi A.H. Functional Analysis and Applications (Springer, 2018) (ISBN 9789811037245) (O) (565s) MCFDocument565 pagesSiddiqi A.H. Functional Analysis and Applications (Springer, 2018) (ISBN 9789811037245) (O) (565s) MCFRekha100% (1)
- (Mathematics and Statistics) Alexander Kukush - Gaussian Measures in Hilbert Space - Construction and Properties-Wiley-IsTE (2020) 2Document263 pages(Mathematics and Statistics) Alexander Kukush - Gaussian Measures in Hilbert Space - Construction and Properties-Wiley-IsTE (2020) 2Fernando CorrêaNo ratings yet
- Optimization With Vector Space MethodsDocument342 pagesOptimization With Vector Space MethodsEmmaTegling100% (1)
- Curriculum and Syllabus Under Semester System: Bs (H) in MathematicsDocument43 pagesCurriculum and Syllabus Under Semester System: Bs (H) in MathematicsPretty WorldNo ratings yet
- 01b - Curriculum and Syllabus of BS Mathematics and MSC Mathematics Only For Spring 2019Document46 pages01b - Curriculum and Syllabus of BS Mathematics and MSC Mathematics Only For Spring 2019Muhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- 2022 BS 5th Mathematics Scheme of StudiesDocument26 pages2022 BS 5th Mathematics Scheme of StudiesAteeq AhmedNo ratings yet
- 01a - Course Outline of BS and MSC Mathematics Only For Fall 2020Document37 pages01a - Course Outline of BS and MSC Mathematics Only For Fall 2020zaheer abbasNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Studies (2021-2025)Document6 pagesScheme of Studies (2021-2025)Bilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- BS Mathematics Scheme of StudiesDocument17 pagesBS Mathematics Scheme of StudiesanamNo ratings yet
- BS MathematicsDocument36 pagesBS MathematicsAnonymous 5UB7ARLBNo ratings yet
- Curriculum OF Bs Mathematics (5 Semester Intake) : W.E.F. Spring 2023 & OnwardDocument54 pagesCurriculum OF Bs Mathematics (5 Semester Intake) : W.E.F. Spring 2023 & OnwardMunawar SaeedNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument20 pagesSyllabusUmeshNo ratings yet
- MSC Mathematics (Cbegs) (Semester I-IV) 2019-20Document47 pagesMSC Mathematics (Cbegs) (Semester I-IV) 2019-20Sneha BhagatNo ratings yet
- BS MathsDocument81 pagesBS MathsHashmat AliNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Booklet-PhD-Mathematics (2019)Document68 pagesCurriculum Booklet-PhD-Mathematics (2019)Ali RajaNo ratings yet
- Cs-II Year BlownUp Syllabus2019-20Document39 pagesCs-II Year BlownUp Syllabus2019-20Kuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Course Contents BS-Physics (2018-22) - 1-1 2Document33 pagesCourse Contents BS-Physics (2018-22) - 1-1 2rabeaNo ratings yet
- Postgraduate Institute of ScienceDocument4 pagesPostgraduate Institute of ScienceMohamed AashiqNo ratings yet
- Mathematics CoreDocument29 pagesMathematics CoreKaushal SinghNo ratings yet
- MSC Scheme of Studies (From 2016 New)Document37 pagesMSC Scheme of Studies (From 2016 New)Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- BSC Hons Maths Syllabus 15oct19Document69 pagesBSC Hons Maths Syllabus 15oct19Sapna KumariNo ratings yet
- CURRICULUM OF STATISTICS BOS BS (Hons)Document48 pagesCURRICULUM OF STATISTICS BOS BS (Hons)Mujib RashidNo ratings yet
- 2018-19 F.y.b.sc. (Mathematics)Document10 pages2018-19 F.y.b.sc. (Mathematics)Jayesh RathodNo ratings yet
- B.S - Physics Semester SystemDocument47 pagesB.S - Physics Semester SystemIrfan NoorNo ratings yet
- Detailed Course Outlines for BS StatisticsDocument20 pagesDetailed Course Outlines for BS StatisticsHadia Azhar2558No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Ddu Gorakhpur University GORAKHPUR-273009 (U.P.) INDIADocument36 pagesMathematics: Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Ddu Gorakhpur University GORAKHPUR-273009 (U.P.) INDIAMr CandibotNo ratings yet
- R18B Tech CSE (AIML) IIYearSyllabusDocument32 pagesR18B Tech CSE (AIML) IIYearSyllabusRounak ReddyNo ratings yet
- Course Contents BS (Hons)Document28 pagesCourse Contents BS (Hons)wahabmaths0% (1)
- Scheme of Studies for Mathematics ProgramsDocument114 pagesScheme of Studies for Mathematics ProgramsRabia MalikNo ratings yet
- MSC Mathematics Cbcegs Semester I To Iv PDFDocument44 pagesMSC Mathematics Cbcegs Semester I To Iv PDFAmrendra SinghNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. II Year Study & Evaluation Scheme for Mechanical EngineeringDocument22 pagesB.Tech. II Year Study & Evaluation Scheme for Mechanical EngineeringAnil Kumar BNo ratings yet
- Semesterwise Detailed Course StructureDocument18 pagesSemesterwise Detailed Course StructureAbhik SarkarNo ratings yet
- CSD - III & IV Sem MR-21 SyllabusDocument48 pagesCSD - III & IV Sem MR-21 SyllabusrishaNo ratings yet
- B. Sc. (HONS) in MATHEMATICS SyllabusDocument12 pagesB. Sc. (HONS) in MATHEMATICS SyllabusNitish Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- S.Y.B.Tech Syllabus For Print Compengg PDFDocument29 pagesS.Y.B.Tech Syllabus For Print Compengg PDFHamza Demovireshsasin MotiwallaNo ratings yet
- S. Y. B. Sc. (Computer Science) Mathematics_18.062020Document11 pagesS. Y. B. Sc. (Computer Science) Mathematics_18.062020gaikwadkavita2007No ratings yet
- AD Mathematics Scheme of StudiesDocument31 pagesAD Mathematics Scheme of StudiesIslamic Status for WhatsAppNo ratings yet
- 202206140452Document47 pages202206140452nimrarauf85No ratings yet
- JNTUK CSE R-20 SyllabusDocument21 pagesJNTUK CSE R-20 SyllabusSubbu BudduNo ratings yet
- JNTU HYDERABAD B.Tech CSE (Data Science) SyllabusDocument32 pagesJNTU HYDERABAD B.Tech CSE (Data Science) Syllabusamarender309No ratings yet
- Mathematics-Msc-2020 Allahabad UniversityDocument41 pagesMathematics-Msc-2020 Allahabad Universityrahulkumarautian6797No ratings yet
- BTech CSEDocument12 pagesBTech CSEHimanshu kumarNo ratings yet
- Ms MathDocument4 pagesMs MathAANo ratings yet
- M.SC Mathematics Semester I.Document13 pagesM.SC Mathematics Semester I.Madhav patilNo ratings yet
- Sem 320Document14 pagesSem 320sg7365818621No ratings yet
- Btech2013curriculum After Ugpc CommentsDocument17 pagesBtech2013curriculum After Ugpc CommentsSoumya Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Government College University, Faisalabad: Model PaperDocument4 pagesGovernment College University, Faisalabad: Model PaperMalik AhsanNo ratings yet
- CSE 3rd Sem SyllabusDocument13 pagesCSE 3rd Sem SyllabusSurjit Kumar GandhiNo ratings yet
- M. Sc. Mathematics: Course: Medium: Course Code: Year S.No Paper Name Examination CodeDocument1 pageM. Sc. Mathematics: Course: Medium: Course Code: Year S.No Paper Name Examination CodebhavishNo ratings yet
- Mathematics General Cbcs Draft SyllabusDocument10 pagesMathematics General Cbcs Draft SyllabusHãrsh ShâwNo ratings yet
- Semester 1 End Semester ExaminationDocument27 pagesSemester 1 End Semester ExaminationsamushabuNo ratings yet
- M.SC - Mathematics 3rd Sem FinalDocument11 pagesM.SC - Mathematics 3rd Sem FinalGrace HoagnNo ratings yet
- 3 UG Syllabus With Preamble 07.02.2022docx 1Document49 pages3 UG Syllabus With Preamble 07.02.2022docx 1Jeeban BaralNo ratings yet
- AIML 2022 23 PEOs PSOs III and IV Sem Syllabu Corrected.Document35 pagesAIML 2022 23 PEOs PSOs III and IV Sem Syllabu Corrected.Abcd AbcdNo ratings yet
- Combinatorial Mathematics Business Mathematics Special Theory of Relativity-I Computational Mathematics Lab-IDocument13 pagesCombinatorial Mathematics Business Mathematics Special Theory of Relativity-I Computational Mathematics Lab-IBurnwal RNo ratings yet
- BS Maths CoursesDocument48 pagesBS Maths CoursesMuhammad Adil HussainNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Semester III PDFDocument9 pagesSyllabus Semester III PDFAaaaaNo ratings yet
- Statistics For BCADocument6 pagesStatistics For BCAsebastian cyriac100% (1)
- Appendix-54Document89 pagesAppendix-54Rohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Revised Scheme of Studies For MS in Mechanical EngineeringDocument18 pagesRevised Scheme of Studies For MS in Mechanical EngineeringMuhammad SaboorNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Study-BS Physics-Fall 19-Revised-1Document34 pagesScheme of Study-BS Physics-Fall 19-Revised-1Malik HammadNo ratings yet
- RmlauDocument31 pagesRmlauAbhinandanNo ratings yet
- Course Contents Full Copy MA MSCDocument21 pagesCourse Contents Full Copy MA MSCwahabmathsNo ratings yet
- EOMF Vol4 (P-S)Document672 pagesEOMF Vol4 (P-S)Chandler Robert SpencerNo ratings yet
- Functional Analysis Oral Exam Study Notes-Func - NotesDocument70 pagesFunctional Analysis Oral Exam Study Notes-Func - NotesshoroukNo ratings yet
- Optimal Recovery of Operator Sequences: V. F. Babenko, N. V. Parfinovych, D. S. Skorokhodov October 19, 2021Document21 pagesOptimal Recovery of Operator Sequences: V. F. Babenko, N. V. Parfinovych, D. S. Skorokhodov October 19, 2021Bart MaxNo ratings yet
- A Nehme 1 enDocument124 pagesA Nehme 1 enloubnanNo ratings yet
- Signal SpaceDocument3 pagesSignal SpaceAbhishek_SafuiNo ratings yet
- Bursikova Stanislava 12110 2Document7 pagesBursikova Stanislava 12110 2giantbodyNo ratings yet
- PDE Weak SolutionsDocument20 pagesPDE Weak SolutionsLucasMartinsRochaNo ratings yet
- Course Contents BS (Hons)Document28 pagesCourse Contents BS (Hons)wahabmaths0% (1)
- Quantum Entanglements NotesDocument11 pagesQuantum Entanglements Notesmr_wopsNo ratings yet
- Sampling-50 Years After Shannon: Michael UnserDocument19 pagesSampling-50 Years After Shannon: Michael UnserVenessa PerpetuaNo ratings yet
- Notes4 PDFDocument30 pagesNotes4 PDFeyenirNo ratings yet
- M.SC - Mathematics 2017-18 - 0Document57 pagesM.SC - Mathematics 2017-18 - 0Priyanka DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- The Low Register - New Beginnings DRAFTDocument8 pagesThe Low Register - New Beginnings DRAFTmaxeuphoniumNo ratings yet
- (Progress in Mathematics 1) Herbert Gross (Auth.) - Quadratic Forms in Infinite Dimensional Vector Spaces (1979, Birkhäuser Basel)Document432 pages(Progress in Mathematics 1) Herbert Gross (Auth.) - Quadratic Forms in Infinite Dimensional Vector Spaces (1979, Birkhäuser Basel)jrvv2013gmailNo ratings yet
- MSC Maths Bulletin2017Document22 pagesMSC Maths Bulletin2017Vicky SharmaNo ratings yet
- Oxford Math ClassesDocument62 pagesOxford Math ClassesChua Ying Li PamelaNo ratings yet
- Hilbert Space For Random ProcessesDocument11 pagesHilbert Space For Random ProcessesSafa ÇelikNo ratings yet
- DPP Maths & Computer-NewDocument18 pagesDPP Maths & Computer-NewMuhammad AtifNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory and Functional Analysis: A Perfect IllustrationDocument17 pagesQuantum Theory and Functional Analysis: A Perfect IllustrationpepeNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Mathematics Syllabus for Govt. Bilasa Girls' CollegeDocument26 pagesM.Sc. Mathematics Syllabus for Govt. Bilasa Girls' CollegeViswas Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Lindblad Master EquationDocument28 pagesIntroduction to the Lindblad Master EquationOscar Bohórquez100% (1)
- M.Sc. (Maths) Part II Sem-III Assignments PDFDocument10 pagesM.Sc. (Maths) Part II Sem-III Assignments PDFShubham PhadtareNo ratings yet