Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Zonguldak Bülent Ecevit University Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Uploaded by
YiğitOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Zonguldak Bülent Ecevit University Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Uploaded by
YiğitCopyright:
Available Formats
ZONGULDAK BÜLENT ECEVİT UNIVERSITY
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
Question 1:
The load of a power plant is not the same at all hours of the day. As the load increases, other
alternators are connected in parallel to the working alternator to meet the increasing load. 2. It
is not appropriate to meet the maximum load value of the power plants with a large powerful
alternator. As is known, the efficiency of electrical machines; the machine is at its highest
value when working at full load. Since the power plant will not always operate at the same
load, efficiency decreases. In this case, it is necessary to have several smaller alternators in
the plant to increase efficiency. 3. By having more than one alternator in the plant, operational
safety is also provided. The alternator that fails is deactivated and instead of it, solid
alternators are activated. Thus, the continuity of the supply is ensured and the system does not
remain without energy. 4. Energy requirement can be met by exchanging energy with other
power plants, depending on the load conditions of the power plants feeding the regions. 5.
Maintenance of alternators in the power plant from time to time extends their life. In the
network fed by an alternator, subscribers remain without energy during the maintenance of
this alternator.
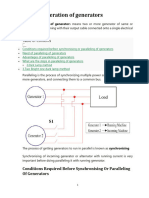
Voltages of alternators to be connected in parallel must be equal to each other.
The frequencies of the alternators to be connected in parallel must be equal to each other.
The phase sequence of the alternators to be connected in parallel must be the same.
There should be no phase difference between the voltages of the alternators to be connected in
parallel.
In addition to these, it is a desirable feature that both alternator voltages to be connected in
parallel should have a sinusoidal character.
Question 2:
The flashing speed of the lamps depends on the difference between the frequencies of the
alternators. The flashing speed of the lamps is slowed down with the rotational speed
(frequency) of the alternator to be connected in parallel. The moment the lamps turn off is the
moment of synchronism.
Question 3:
The microcontroller will try to increase the DC motor speed and the alternator end voltage in
order to put a load on the alternator. Since the speed of the DC motor will not increase after
the parallel connection is made, it starts to take active load on the alternator.
Question 4:
The moment of synchronism is determined separately by the synchroscope, zero voltmeter
and lamp connections. Synchronoscope is a kind of asynchronous motor. When the
synchroscope is connected to the circuit, the pointer rotates in a certain direction depending
on the frequency difference of the alternators. The smaller the frequency difference, the
slower the rotation of the pointer. When the pointer stops at the marked place, it means that
the alternator phases have overlapped and the phase difference between the voltages is zero. If
the frequency of the 1st alternator is higher than the frequency of the 2nd alternator, the
synchronoscope will turn in one direction, if the frequency of the 2nd alternator is higher than
the frequency of the 1st alternator, the pointer will rotate in the opposite direction.
Synchronization moment is detected with various lamp connections instead of synchroscope.
You might also like
- Generator Synchronization and TransformerDocument9 pagesGenerator Synchronization and TransformerAyberk ArdıçNo ratings yet
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Transformers Generators and Protection Theory 69Document1 pageTransformers Generators and Protection Theory 69Satyasrinivas PulavarthiNo ratings yet
- AC Generator ConstructionDocument4 pagesAC Generator ConstructionKen Andrie Dungaran Guariña100% (1)
- Episode 416 - Generators and Transformers - 0Document31 pagesEpisode 416 - Generators and Transformers - 0ibrahim fadelNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Interview Guide BookDocument8 pagesElectrical Engineering Interview Guide BookshubhampattiNo ratings yet
- Parallel Operation of GeneratorsDocument8 pagesParallel Operation of GeneratorsVladimir100% (1)
- Parallel Operation of AlternatorDocument3 pagesParallel Operation of AlternatorfaqdaniNo ratings yet
- Motors & GeneratorsDocument18 pagesMotors & GeneratorsLouisLou100% (3)
- TG SynchronizationDocument7 pagesTG SynchronizationDurjoy ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Defination of Ignition SystemDocument28 pagesDefination of Ignition SystemDawood KhanNo ratings yet
- AC Generator InvestigatoryDocument22 pagesAC Generator InvestigatoryTarun NNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Operation of GeneratorDocument4 pagesSynchronous Operation of GeneratorShazmaniaNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionDocument49 pagesInterview Questionshubha christopherNo ratings yet
- Kolodziej JamesDocument49 pagesKolodziej JamesPradeep RajasekeranNo ratings yet
- Ee 21 AsssignmentDocument1 pageEe 21 AsssignmentIVAN JOHN BITONNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines II AnswerDocument24 pagesElectrical Machines II AnswerGurulathan SoosairajNo ratings yet
- MP008 Basic ElectricityDocument25 pagesMP008 Basic ElectricityMizan Al Hakim100% (1)
- ANSWERAssessment AlternatorsDocument10 pagesANSWERAssessment Alternatorsjenixson tamondongNo ratings yet
- If An Alternator Is To Be Connected To An Infinite BusDocument4 pagesIf An Alternator Is To Be Connected To An Infinite Buswaleed mohiNo ratings yet
- Engineering QuestionsDocument31 pagesEngineering QuestionsRizwan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Parallel Operation of DC GeneratorsDocument11 pagesParallel Operation of DC GeneratorsSangeen Panezai0% (1)
- Met 1Document5 pagesMet 1Ářvíňď PřášáďNo ratings yet
- Generator Interview QuestionsDocument12 pagesGenerator Interview QuestionsMuhammad Ali Khan Awan100% (1)
- Three Phase Induction MotorsDocument6 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorsMohamed KamelNo ratings yet
- Starting of Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage Asynchronous Motor - CompressedDocument2 pagesStarting of Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage Asynchronous Motor - Compressedfahrid mudoriNo ratings yet
- Alternator ToyotaDocument5 pagesAlternator ToyotaAYON_MSNNo ratings yet
- Wind Engineering - Chap08 - LectureDocument37 pagesWind Engineering - Chap08 - LectureKağan YalçınNo ratings yet
- Parallel Operation of AlternatorsDocument2 pagesParallel Operation of AlternatorsLearn ElectricalNo ratings yet
- SPH3U - Unit #5: Electricity & MagnetismDocument38 pagesSPH3U - Unit #5: Electricity & MagnetismKunwoo JooNo ratings yet
- How Synchronous Motor Is Used For Power Factor Correction?Document10 pagesHow Synchronous Motor Is Used For Power Factor Correction?alisha27No ratings yet
- How To Synchronize Generators On A ShipDocument6 pagesHow To Synchronize Generators On A ShipTammam HassanNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Science AnswerDocument2 pagesModule 6 Science AnswerKai 1No ratings yet
- Module 1Document52 pagesModule 1HimanshuNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument11 pagesUntitledAashutosh PratapNo ratings yet
- Voltage ControlDocument49 pagesVoltage ControlGraphic DesignerNo ratings yet
- Final ELTA - GA 2Document13 pagesFinal ELTA - GA 2ldvsoundsNo ratings yet
- Definition of TransformerDocument11 pagesDefinition of TransformerAbdul BasitNo ratings yet
- Application Note AriDocument7 pagesApplication Note AriRaj AryanNo ratings yet
- AlternatorDocument16 pagesAlternatorMitz Mae DatuNo ratings yet
- Ignition SystemDocument7 pagesIgnition SystemAndrew kashobondoNo ratings yet
- SolarDocument14 pagesSolarHassanNajjarNo ratings yet
- An Automatic Load Sharing of Transformer Using Phase Locked Loop SynchronizationDocument4 pagesAn Automatic Load Sharing of Transformer Using Phase Locked Loop SynchronizationKudzai DubeNo ratings yet
- Parallel Operation of Generators - Marinerspoint ProDocument29 pagesParallel Operation of Generators - Marinerspoint Prothm5tqdvsdNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument20 pagesInduction MotorVenkata SubramanianNo ratings yet
- PSOC Unit 2 - Reactive Power ControlDocument79 pagesPSOC Unit 2 - Reactive Power Controlvishal kambleNo ratings yet
- Lab Viva QuestionDocument13 pagesLab Viva QuestionNarasimman Don100% (1)
- Electrical MachinesDocument11 pagesElectrical MachinesCelo GontiñasNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: 1.1 What Are Dewatering Pumps?Document22 pagesChapter One: 1.1 What Are Dewatering Pumps?Odejobi Oluseyi JonathanNo ratings yet
- 3.study of Ignition SystemDocument10 pages3.study of Ignition SystemShridhar RaskarNo ratings yet
- 2 Comparing Electric Machine Sys-TemsDocument6 pages2 Comparing Electric Machine Sys-TemsAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Electricity 2 Tecno 12-18Document7 pagesElectricity 2 Tecno 12-18Iraia Osuna GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Eee Div-C Group 12Document13 pagesEee Div-C Group 12Parth GajjarNo ratings yet
- Generation of Electrical Energy-1Document46 pagesGeneration of Electrical Energy-1ABRAR AHMADNo ratings yet
- Battery SizingDocument41 pagesBattery Sizingअंकित अरोड़ा100% (1)
- Interview Questions: Collected by Asif AhmedDocument15 pagesInterview Questions: Collected by Asif Ahmedashish sahaNo ratings yet
- Lab Maunal EE462Document77 pagesLab Maunal EE462Hussain MasoodNo ratings yet
- Power Plant ReportDocument17 pagesPower Plant ReportLanz de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Tertiary WindingDocument3 pagesTertiary WindingAtulya Kumar Naik100% (4)
- Basic Signals and Systems PDFDocument7 pagesBasic Signals and Systems PDFSanjeev Kumar T MNo ratings yet
- 100 Questions 100 Min. Capacitance NEET-2017/IIT MAINS 2017Document11 pages100 Questions 100 Min. Capacitance NEET-2017/IIT MAINS 2017umved singh yadav100% (9)
- Online Homework 9Document6 pagesOnline Homework 9Hoang PhuonghaNo ratings yet
- Three Phase SystemDocument41 pagesThree Phase SystemAnita PanthiNo ratings yet
- As Built PlanDocument16 pagesAs Built PlanPaul Cortez Rival100% (1)
- Stripping: Coaxstrip 6380Document2 pagesStripping: Coaxstrip 6380Azzeddine BendahakNo ratings yet
- Radio Command Systems: Table of ContentsDocument30 pagesRadio Command Systems: Table of Contentsjackie_fisher_email8329No ratings yet
- VHDL FirDocument21 pagesVHDL FirSiva ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- 05 PEmag Assorted Features - v2017Document15 pages05 PEmag Assorted Features - v2017ShradhaSharma100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Single Phase Motors EE 342Document32 pagesChapter 10 Single Phase Motors EE 342Umar AftabNo ratings yet
- Delivery Programme: Circuit-Breaker, 3 P, 320A Part No. LZMC3-A320-I Article No. 111954Document9 pagesDelivery Programme: Circuit-Breaker, 3 P, 320A Part No. LZMC3-A320-I Article No. 111954Rodolfo Manuel Alarcón TroncosoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Telecommunications 1Document34 pagesFundamentals of Telecommunications 1hvrkNo ratings yet
- Visualizing SoundsDocument13 pagesVisualizing SoundsRhythm DuttaNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: HCD-GT22/GT44/GT55Document98 pagesService Manual: HCD-GT22/GT44/GT55Ing Jose FloresNo ratings yet
- 2022 05 Kostal Kontakt Systeme POP HV Class1 SLK 2-3011048Document3 pages2022 05 Kostal Kontakt Systeme POP HV Class1 SLK 2-3011048Caio “BiigBR” TeodósioNo ratings yet
- SoundGrid DriverDocument14 pagesSoundGrid DriverThechany VeraNo ratings yet
- Beckhoff - CX8091 (2016)Document63 pagesBeckhoff - CX8091 (2016)Jorge_Andril_5370No ratings yet
- Thrane & Thrane Explorer 700Document2 pagesThrane & Thrane Explorer 700alamgir77No ratings yet
- E Brooks MT3809 OKDocument19 pagesE Brooks MT3809 OKravichandran0506No ratings yet
- Ridder RW45 Motor Gearbox 1-Phase (3-Wire) : Product ManualDocument16 pagesRidder RW45 Motor Gearbox 1-Phase (3-Wire) : Product ManualrublasterNo ratings yet
- FBD ExamplesDocument13 pagesFBD Exampleskalpi99999No ratings yet
- Verilog HDL Module 1 (1)Document23 pagesVerilog HDL Module 1 (1)Sammed UpadhyeNo ratings yet
- P6 Unit 16 - ExerciseDocument2 pagesP6 Unit 16 - ExerciseIvan Prasetya0% (1)
- Faa StandartDocument13 pagesFaa StandartBagas SaputraNo ratings yet
- Energy Stored in CapacitorDocument9 pagesEnergy Stored in Capacitoradimegha100% (2)
- Q Model Instuction CommonDocument442 pagesQ Model Instuction CommonTài TrầnNo ratings yet
- Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions: Vibratory FeedersDocument12 pagesInstallation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions: Vibratory FeedersdeepakNo ratings yet
- Manual: Distribution Earthing Manual ForewordDocument65 pagesManual: Distribution Earthing Manual Forewordzaheeruddin_mohdNo ratings yet
- MFL67468023 - 42LS3450 Da - Awc Awh AwmDocument28 pagesMFL67468023 - 42LS3450 Da - Awc Awh AwmAndres Fermin OchoaNo ratings yet
- 5620 K QT-II Data SheetDocument4 pages5620 K QT-II Data SheetJulio GuardiolaNo ratings yet