100% found this document useful (4 votes)
3K views31 pagesSynchronization Panel
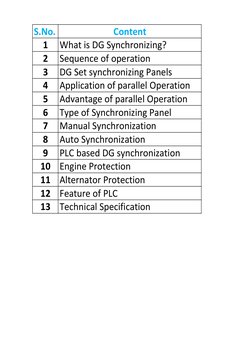
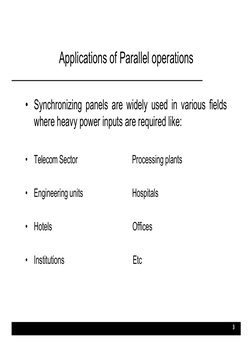
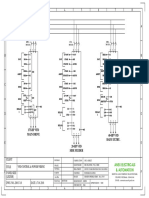
The document discusses diesel generator synchronization panels which allow multiple generators to run in parallel and share load automatically. It describes the sequence of operations for synchronizing two generators, including matching voltage, frequency, and phase before paralleling. The panels can start and stop generators automatically based on load to optimize fuel usage. Key components include synchronizing controllers, circuit breakers, and neutral isolating contactors to prevent circulating currents when generators are paralleled.
Uploaded by
Hariom ChaurasiyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (4 votes)
3K views31 pagesSynchronization Panel
The document discusses diesel generator synchronization panels which allow multiple generators to run in parallel and share load automatically. It describes the sequence of operations for synchronizing two generators, including matching voltage, frequency, and phase before paralleling. The panels can start and stop generators automatically based on load to optimize fuel usage. Key components include synchronizing controllers, circuit breakers, and neutral isolating contactors to prevent circulating currents when generators are paralleled.
Uploaded by
Hariom ChaurasiyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd