Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solve X 3 2 4 + + - (3) : 0606/23/O/N/19 © UCLES 2019
Uploaded by
Nirvaan PuriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solve X 3 2 4 + + - (3) : 0606/23/O/N/19 © UCLES 2019
Uploaded by
Nirvaan PuriCopyright:
Available Formats
3
1 Solve 3x + 2 = x + 4 . [3]
2 (i) Show that cosecx - cot x = cosecx . [3]
1 - cos x
(ii) Hence solve cosecx - cot x = 2 for 0° 1 x 1 180° . [2]
1 - cos x
© UCLES 2019 0606/23/O/N/19 [Turn over
4
3 The first four terms in the expansion of (1 + ax) 5 (2 + bx) are 2 + 32x + 210x 2 + cx 3 , where a, b and c are
integers. Show that 3a 2 - 16a + 21 = 0 and hence find the values of a, b and c. [8]
© UCLES 2019 0606/23/O/N/19
5
4 (i) Given that y = 2x 2 - 4x - 7 , write y in the form a (x - b) 2 + c , where a, b and c are constants. [3]
(ii) Hence write down the minimum value of y and the value of x at which it occurs. [2]
(iii) Using your answer to part (i), solve the equation 2p - 4 p - 7 = 0 , giving your answer correct to
2 decimal places. [3]
© UCLES 2019 0606/23/O/N/19 [Turn over
6
5 (a) Solve 3 cot 2 b y - rl = 1 for 0 1 y 1 r radians. [4]
4
(b) Solve 7 cot z + tan z = 7 cosec z for 0° G z G 360° . [6]
© UCLES 2019 0606/23/O/N/19
7
6 Do not use a calculator in this question.
3– 3
A 3+ 3 B
(i) Find tan ACB in the form r + s 3 , where r and s are integers. [3]
(ii) Find AC in the form t u, where t and u are integers and t ! 1. [3]
© UCLES 2019 0606/23/O/N/19 [Turn over
8
7
y x=2
6
y = x+
(3x + 2) 2
O x
6
The diagram shows part of the curve y = x + and the line x = 2 .
(3x + 2) 2
(i) Find, correct to 2 decimal places, the coordinates of the stationary point. [6]
© UCLES 2019 0606/23/O/N/19
9
(ii) Find the area of the shaded region, showing all your working. [4]
© UCLES 2019 0606/23/O/N/19 [Turn over
10
8 The roots of the equation x 3 + ax 2 + bx + 24 = 0 are 2, 3 and p, where p is an integer.
(i) Find the value of p. [1]
(ii) Show that a =-1 and find the value of b. [4]
© UCLES 2019 0606/23/O/N/19
11
Given that a curve has equation y = x 3 - x 2 + bx + 24 find, using your value of b,
dy
(iii) , [1]
dx
(iv) the integer value of x for which the gradient of the curve is 2 and the corresponding value of y. [3]
The coordinates of the point P on the curve are given by the values of x and y found in part (iv).
(v) Find the equation of the tangent to the curve at P. [1]
© UCLES 2019 0606/23/O/N/19 [Turn over
12
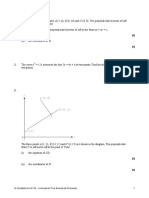
9
B
O A C
The diagram shows points O, A, B, C, D and X. The position vectors of A, B, and C relative to O are OA = a,
OB = 2b and OC = 3a . The vector CD = b .
(i) Given that AX = m AD , find OX in terms of m, a and b. [2]
(ii) Given that BX = n BC , find OX in terms of n, a and b. [2]
© UCLES 2019 0606/23/O/N/19
13
(iii) Hence find the value of m and of n. [4]
AX
(iv) Find the ratio . [1]
XD
© UCLES 2019 0606/23/O/N/19 [Turn over
14
10 The functions f and g are defined by
2
f (x) = ln (3x + 2) for x 2 - ,
3
2x
g (x) = e - 4 for x ! R .
(i) Solve gf (x) = 5 . [5]
© UCLES 2019 0606/23/O/N/19
15
(ii) Find f -1 (x) . [2]
(iii) Solve f -1 (x) = g (x) . [4]
© UCLES 2019 0606/23/O/N/19
You might also like
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- 5 3 3 2 + + - Where K Is An Integer To Be Found. (3) : 1 Without Using A Calculator, Show ThatDocument13 pages5 3 3 2 + + - Where K Is An Integer To Be Found. (3) : 1 Without Using A Calculator, Show ThatNirvaan PuriNo ratings yet
- 3 2 4 1 - +, Showing The Coordinates of The Points Where The Curve Intersects The Coordinate Axes.Document14 pages3 2 4 1 - +, Showing The Coordinates of The Points Where The Curve Intersects The Coordinate Axes.Nirvaan PuriNo ratings yet
- 8 CIE IGCSE Additional Mathematics Paper 2 Topical Past Paper Straight Line GraphsDocument23 pages8 CIE IGCSE Additional Mathematics Paper 2 Topical Past Paper Straight Line GraphsDkNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument4 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Levelyousee yusiNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument8 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- PM FM 5Document2 pagesPM FM 5biloma6323No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationBoxNo ratings yet
- Is Given by V 3 30 72 - + - Find The Distance Between The Particle's Two Positions of Instantaneous Rest.Document6 pagesIs Given by V 3 30 72 - + - Find The Distance Between The Particle's Two Positions of Instantaneous Rest.Tanzim RahmanNo ratings yet
- 2020 Specimen Paper 1Document10 pages2020 Specimen Paper 1Sajedul HassanNo ratings yet
- Difficult Add MathDocument5 pagesDifficult Add MathAyra MujibNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - June-2019-Question-Paper-21Document16 pagesIGCSE - June-2019-Question-Paper-21Arturo PizarroNo ratings yet
- On The Axes Below, Sketch The Graph of Cos 2 3 For ° 0 180 GG .Document13 pagesOn The Axes Below, Sketch The Graph of Cos 2 3 For ° 0 180 GG .Nirvaan PuriNo ratings yet
- Ejc h2 MathDocument5 pagesEjc h2 MathcannotknowNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument8 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationKhoo Kian ChaiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: PAPER 1 Pure Mathematics 1 (P1)Document8 pagesMathematics: PAPER 1 Pure Mathematics 1 (P1)Private of ScienceNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics 2010 November Paper 23Document8 pagesAdditional Mathematics 2010 November Paper 23Sharifa McLeodNo ratings yet
- Time Practice 1Document4 pagesTime Practice 1Mr Plays shitNo ratings yet
- Factors and PolynomialsDocument14 pagesFactors and PolynomialsBrioNo ratings yet
- T Cot An Cosec Cos + - (3) : 15 11 (A) (I) Show ThatDocument15 pagesT Cot An Cosec Cos + - (3) : 15 11 (A) (I) Show ThatRichard FernandezNo ratings yet
- SMSO 2004 Paper 1Document4 pagesSMSO 2004 Paper 1api-25887606No ratings yet
- Cls-Progression Stage 7 - 2024 - Paper-2 (M)Document14 pagesCls-Progression Stage 7 - 2024 - Paper-2 (M)king75% (4)
- Cambridge International Examinations General Certi Cate of EducationDocument8 pagesCambridge International Examinations General Certi Cate of EducationHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- 2018 JC2 H2 Maths SA2 Hwa Chong InstitutionDocument44 pages2018 JC2 H2 Maths SA2 Hwa Chong InstitutionZtolenstarNo ratings yet
- Ocr 18628 PP 08 Jan L GceDocument4 pagesOcr 18628 PP 08 Jan L GcePiriya RajakumarNo ratings yet
- Revision III AsDocument4 pagesRevision III AsTimaVNo ratings yet
- VVV Merged MergedDocument45 pagesVVV Merged Mergedjekeg27327No ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationMalcom MuchenjeNo ratings yet
- 2022 MYE - Practice - Paper - 3. - No AnspdfDocument5 pages2022 MYE - Practice - Paper - 3. - No AnspdfJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- D1 Diff With Normal & Tangents QPDocument19 pagesD1 Diff With Normal & Tangents QPvocalsfnNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument12 pagesCambridge Ordinary Levelshazrae2007No ratings yet
- Indices and Surds - QPDocument19 pagesIndices and Surds - QPMuhammad IbrahimNo ratings yet
- January 2006 QP - C3 OCR MEIDocument6 pagesJanuary 2006 QP - C3 OCR MEIPapersNo ratings yet
- Solomon K QP - C1 OCRDocument3 pagesSolomon K QP - C1 OCRMuhammad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper AM 2Document11 pagesPractice Paper AM 2Naveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1Document14 pagesMathematics 1keshav GopaulNo ratings yet
- 9709 s15 QP 12Document2 pages9709 s15 QP 12Tanzim RahmanNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics: 0.7, Giving Your Answer To 2 Decimal Places.Document7 pagesAdditional Mathematics: 0.7, Giving Your Answer To 2 Decimal Places.AadiNo ratings yet
- 0606 w17 QP 13Document16 pages0606 w17 QP 13Seong Hun LeeNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument49 pagesDifferentiationFawziah NabihaNo ratings yet
- 2021 JC1 Promo Practice Paper ADocument5 pages2021 JC1 Promo Practice Paper Avincesee85No ratings yet
- Alg3 & Trig2 - Practice QuestionsDocument8 pagesAlg3 & Trig2 - Practice QuestionsAbdullah NHNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument4 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelkeysNo ratings yet
- 2 CIE IGCSE Additional Mathematics Topical Past Paper Quadratic FunctionsDocument13 pages2 CIE IGCSE Additional Mathematics Topical Past Paper Quadratic FunctionsAng Kai JunNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation Ax bxc0 X A B B Ac: Mathematical FormulaeDocument15 pagesQuadratic Equation Ax bxc0 X A B B Ac: Mathematical FormulaeRishwin Singh Sinda a/l Karamjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- 4037 w05 QP 1Document8 pages4037 w05 QP 1Khurram AhmedNo ratings yet
- AIH 23-25 Assessment 2 (NOV EXAM) Revision 2Document7 pagesAIH 23-25 Assessment 2 (NOV EXAM) Revision 2Hoa Dinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Logs and IndicesDocument13 pagesLogs and Indicessharkfin1403No ratings yet
- P3 Vectors: 132 MinutesDocument22 pagesP3 Vectors: 132 MinutesShahid AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Ah Sam 1Document3 pagesAh Sam 1JASON_INGHAMNo ratings yet
- 0606 2014 May QP 13Document16 pages0606 2014 May QP 13SUNGMIN CHOINo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument8 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation B B Ac: For The Equation Ax + BX + C 0, 2 4 !Document14 pagesQuadratic Equation B B Ac: For The Equation Ax + BX + C 0, 2 4 !sshyam3No ratings yet
- Maths November 2001 Paper 1Document12 pagesMaths November 2001 Paper 1Tinashe KamusaireNo ratings yet
- C3 Integration PDFDocument5 pagesC3 Integration PDFRokonuddin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Grade XII - PT 3 - SMITA MADAMDocument4 pagesGrade XII - PT 3 - SMITA MADAMVijaya SaradhiNo ratings yet
- Rate of Change and Approximate ChangeDocument9 pagesRate of Change and Approximate ChangeThomas AlfieNo ratings yet
- Exam Pure MathsDocument4 pagesExam Pure MathsThabzgotkeyNo ratings yet
- 2022 Paper 1 AnswerDocument3 pages2022 Paper 1 AnswerNirvaan PuriNo ratings yet
- Notes For MathDocument15 pagesNotes For MathJames TjiptoNo ratings yet
- Cie Igcse Addmaths 0606 v2 ZnotesDocument6 pagesCie Igcse Addmaths 0606 v2 ZnotesNirvaan PuriNo ratings yet
- 0606 s16 QP 11Document16 pages0606 s16 QP 11StanleyNo ratings yet
- On The Axes Below, Sketch The Graph of Cos 2 3 For ° 0 180 GG .Document13 pagesOn The Axes Below, Sketch The Graph of Cos 2 3 For ° 0 180 GG .Nirvaan PuriNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Osmosis QuestionsDocument2 pagesDiffusion Osmosis QuestionsNirvaan PuriNo ratings yet
- Draw Three More Lines To Show Your Inequalities and Shade The Unwanted RegionsDocument1 pageDraw Three More Lines To Show Your Inequalities and Shade The Unwanted RegionsNirvaan PuriNo ratings yet
- IX Individual Assignment LetterDocument2 pagesIX Individual Assignment LetterNirvaan Puri100% (1)
- Stoichiometry 1 QPDocument9 pagesStoichiometry 1 QPTee Xin RuiNo ratings yet
- 5 - Objectives & StakeholdersDocument15 pages5 - Objectives & StakeholdersNirvaan PuriNo ratings yet
- Maths GCSE Mock Higher Non-CalculatorDocument13 pagesMaths GCSE Mock Higher Non-CalculatorbensonlawNo ratings yet
- 2-Length, Dot Product, Cross ProductDocument8 pages2-Length, Dot Product, Cross ProductslowjamsNo ratings yet
- ShapesDocument86 pagesShapessampoernahijauNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Equations of Motion - 2Document26 pagesAircraft Equations of Motion - 2UNsha bee komNo ratings yet
- Section 15-1 Dynamics HibbelerDocument17 pagesSection 15-1 Dynamics Hibbelershamik1978No ratings yet
- Cayley Graphs of Groups and Their ApplicationsDocument47 pagesCayley Graphs of Groups and Their ApplicationsAnjeliNo ratings yet
- Arun Sharma Formula Book by UnacademyDocument51 pagesArun Sharma Formula Book by Unacademyultron19stormNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document43 pagesClass 1psyclonesesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3-Hydrostatic Forces and Center of Pressure On PlaneDocument16 pagesLesson 3-Hydrostatic Forces and Center of Pressure On PlanePtah Ndung'uNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD COMMANDS and SHORTCUTS LISTDocument15 pagesAutoCAD COMMANDS and SHORTCUTS LISTRicky Jay PadasasNo ratings yet
- SMO Junior Mock Paper (2022) - ProblemsDocument6 pagesSMO Junior Mock Paper (2022) - ProblemsYHSNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem Math PDFDocument2 pagesPythagorean Theorem Math PDFapi-201420601No ratings yet
- NewtonDocument6 pagesNewtonJarrod MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Physics: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Document15 pagesPhysics: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Santhosh SenthilNo ratings yet
- 2D Model of Cable Stayed BridgeDocument21 pages2D Model of Cable Stayed BridgeSagar SakoreNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Project WORK 2012: Sekolah Berasrama Penuh Integrasi GombakDocument44 pagesAdditional Mathematics Project WORK 2012: Sekolah Berasrama Penuh Integrasi GombakREXTERYXNo ratings yet
- Gdtology GDTP Practice Exam 2009 Answers FDocument48 pagesGdtology GDTP Practice Exam 2009 Answers FSandeep Patnala100% (3)
- Perspective Drawing: Animation NC IiDocument8 pagesPerspective Drawing: Animation NC IiJoel BrizaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 MATH13-1Document51 pagesLesson 7 MATH13-1akladffja75% (4)
- Aschi Keys Code 1sdkjdDocument10 pagesAschi Keys Code 1sdkjdFazle ElahiNo ratings yet
- ST Line AssignmentDocument11 pagesST Line AssignmentbhaveshNo ratings yet
- WS Gr08 Maths Trig RatioDocument1 pageWS Gr08 Maths Trig RatioAnonymous YVvki6ENo ratings yet
- f4 Solution of TrianglesDocument0 pagesf4 Solution of TrianglesvioletgohNo ratings yet
- CommDocument7 pagesCommKen AbanihiNo ratings yet
- Sub-Junior PrmoDocument7 pagesSub-Junior PrmoPujan ShahNo ratings yet
- RRL Sa Smaw OfcDocument1 pageRRL Sa Smaw OfcRen ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- StewartCalcET8 14 04Document18 pagesStewartCalcET8 14 04OhoodKAlesayiNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling ConceptsDocument5 pages3D Modeling ConceptsMaurijones J. de Albuquerque100% (1)
- SEAMO 2017 Paper EDocument8 pagesSEAMO 2017 Paper ECht Geby100% (1)
- Geometry Module 1Document33 pagesGeometry Module 1Prince AmazonaNo ratings yet