Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VVV Merged Merged
Uploaded by
jekeg27327Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
VVV Merged Merged
Uploaded by
jekeg27327Copyright:
Available Formats
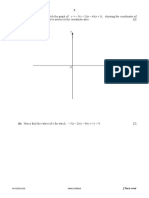
Question 377 (MJ 21 11 Q2)
7 (a) In this question, all lengths are in metres and time, t, is in seconds.
displacement
50
40
30
20
10
0 10 20 30 40 time
–10
The diagram shows the displacement–time graph for a runner, for 0 G t G 40 .
(i) Find the distance the runner has travelled when t = 40 . [1]
(ii) On the axes, draw the corresponding velocity–time graph for the runner, for 0 G t G 40 . [2]
velocity
6
5
4
3
2
1
0 10 20 30 40 time
–1
–2
–3
–4
–5
–6
© UCLES 2021 4037/11/M/J/21
9
(b) A particle, P, moves in a straight line such that its displacement from a fixed point at time t is s.
1
The acceleration of P is given by `2t + 4j
-
2, for t 2 0 .
(i) Given that P has a velocity of 9 when t = 6 , find the velocity of P at time t. [3]
1
(ii) Given that s = when t = 6 , find the displacement of P at time t. [3]
3
© UCLES 2021 4037/11/M/J/21 [Turn over
10
8 DO NOT USE A CALCULATOR IN THIS QUESTION.
A curve has equation y = `2 - 3j x 2 + x - 1. The x-coordinate of a point A on the curve is
3 +1
.
2- 3
(a) Show that the coordinates of A can be written in the form ` p + q 3, r + s 3j , where p, q, r and s
are integers. [5]
© UCLES 2021 4037/11/M/J/21
11
(b) Find the x-coordinate of the stationary point on the curve, giving your answer in the form a + b 3 ,
where a and b are rational numbers. [3]
© UCLES 2021 4037/11/M/J/21 [Turn over
6
d2y -
1
4 A curve is such that 2 = ( 3 x + 2) 3 . The curve has gradient 4 at the point (2, 6.2). Find the equation
of the curve. d x [6]
© UCLES 2021 4037/12/M/J/21
8
6 DO NOT USE A CALCULATOR IN THIS QUESTION.
A curve has equation y = `3 + 5j x 2 - 8 5 x + 60 .
(a) Find the x-coordinate of the stationary point on the curve, giving your answer in the form a + b 5 ,
where a and b are integers. [4]
© UCLES 2021 4037/12/M/J/21
9
(b) Hence find the y-coordinate of this stationary point, giving your answer in the form c 5, where c
is an integer. [3]
© UCLES 2021 4037/12/M/J/21 [Turn over
16
ln `x 2 + 2j
11 The normal to the curve y = at the point where x = 2 meets the y-axis at the point P.
2x - 3
Find the coordinates of P. [7]
Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every
reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included, the
publisher will be pleased to make amends at the earliest possible opportunity.
To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced online in the Cambridge
Assessment International Education Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download
at www.cambridgeinternational.org after the live examination series.
Cambridge Assessment International Education is part of the Cambridge Assessment Group. Cambridge Assessment is the brand name of the University of
Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which itself is a department of the University of Cambridge.
© UCLES 2021 4037/12/M/J/21
6
d 5
4 (a) Find (2x + 1) 2 . [2]
dx
(b) Hence find ; (2x + 1) 2 dx .
3
[2]
© UCLES 2021 4037/14/M/J/21
7
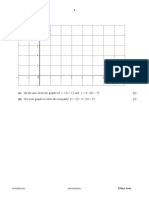
(c)
y
3
y = (2x + 1) 2
O a x
3
The diagram shows the graph of the curve y = (2x + 1) 2 for x H 0 . The shaded region enclosed
by the curve, the axes and the line x = a is equal to 48.4 square units. Find the value of a, showing
all your working. [3]
© UCLES 2021 4037/14/M/J/21 [Turn over
10
d2y
2 = 8 sin 2x . The curve has a gradient of 6 at the point e , 4r o .
r
7 A curve is such that
dx 2
Find the equation of the curve. [8]
© UCLES 2021 4037/14/M/J/21
14
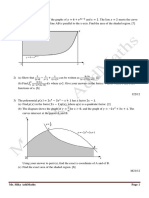
10
A C
B
x cm
θ rad
G D
x cm
F E 3
The diagram shows the figure ABCDEFG, where ABFG and BCDE are rectangles of length x cm and
x
width cm . The sector BFE of the circle, centre B, radius x cm, has an angle of i radians. It is given
3
that the area of BFE is 2 cm 2 .
10x 4
(a) Show that the perimeter, P cm, of the figure ABCDEFG is given by P = + . [5]
3 x
© UCLES 2021 4037/14/M/J/21
15
(b) Given that x can vary, find the minimum value of P in the form q 30, where q is a rational
number. [4]
(c) Verify that P is a minimum. [1]
Question 11 is printed on the next page.
© UCLES 2021 4037/14/M/J/21 [Turn over
16
11 The tangent at the point where x = 1 on the curve y = 6x ln (x 2 + 1) intersects the y-axis at the
point P. This tangent also intersects the line x = 2 at the point Q. A line through P, parallel to the
x-axis, meets the line x = 2 at the point R. Find the exact area of triangle PQR. [10]
Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every
reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included, the
publisher will be pleased to make amends at the earliest possible opportunity.
To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced online in the Cambridge
Assessment International Education Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download
at www.cambridgeinternational.org after the live examination series.
Cambridge Assessment International Education is part of the Cambridge Assessment Group. Cambridge Assessment is the brand name of the University of
Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which itself is a department of the University of Cambridge.
© UCLES 2021 4037/14/M/J/21
7
x
6 Variables x and y are such that y = e 2 + x cos 2x , where x is in radians. Use differentiation to find the
approximate change in y as x increases from 1 to 1 + h , where h is small. [6]
© UCLES 2021 4037/21/M/J/21 [Turn over
10
d2y dy 1
9 A curve is such that b r
l br 13rl
2 = sin 6x - 2 . Given that dx = 2 at the point 4 , 12 on the curve, find
dx
the equation of the curve. [7]
© UCLES 2021 4037/21/M/J/21
14
12
y
y = (9 - x) (x - 3)
C (k, k - 3)
y = k-3
O A B x
The diagram shows part of the curve y = (9 - x) (x - 3) and the line y = k - 3, where k 2 3. The line
through the maximum point of the curve, parallel to the y‑axis, meets the x‑axis at A. The curve meets
the x‑axis at B, and the line y = k - 3 meets the curve at the point C(k, k - 3). Find the area of the
shaded region. [9]
© UCLES 2021 4037/21/M/J/21
9
8 A particle moves in a straight line so that, t seconds after passing through a fixed point O, its velocity,
v ms -1 , is given by v = 3t 2 - 30t + 72 .
(a) Find the distance between the particle’s two positions of instantaneous rest. [6]
(b) Find the acceleration of the particle when t = 2 . [2]
© UCLES 2021 4037/22/M/J/21 [Turn over
11
10 (a) Find y (e x+1 3
) dx . [2]
(b) (i) Differentiate, with respect to x, y = x sin 4x . [2]
r
1 r 3
(ii) Hence show that y
r
3
4x cos 4xdx =
8
-
6
. [4]
4
© UCLES 2021 4037/22/M/J/21 [Turn over
12
11 In this question all lengths are in centimetres.
4 3
The volume and surface area of a sphere of radius r are rr and 4rr 2 respectively.
3
The diagram shows a solid object made from a hemisphere of radius x and a cylinder of radius x and
height y. The volume of the object is 500 cm3.
(a) Find an expression for y in terms of x and show that the surface area, S, of the object is given by
5 1000
S = rx 2 + . [4]
3 x
© UCLES 2021 4037/22/M/J/21
13
(b) Given that x can vary and that S has a minimum value, find the value of x for which S is a minimum.
[4]
© UCLES 2021 4037/22/M/J/21 [Turn over
14
12 DO NOT USE A CALCULATOR IN THIS QUESTION.
A
1
y=
2x + 1
5y = x - 1
O B x
1
The diagram shows part of the curve y = and part of the line 5y = x - 1.
2x + 1
The curve meets the y‑axis at point A. The line meets the x‑axis at point B. The line and curve intersect
at point C.
(a) (i) Find the coordinates of A and B. [1]
(ii) Verify that the x‑coordinate of C is 2. [2]
© UCLES 2021 4037/22/M/J/21
15
(b) Find the exact area of the shaded region. [5]
Question 13 is printed on the next page.
© UCLES 2021 4037/22/M/J/21 [Turn over
Question 394 (MJ 21 24 Q2)
5
4 The normal to the curve y = x 5 - 2x 3 + x 2 + 3 at the point on the curve where x =-1, cuts the x-axis at
the point P. Find the equation of the normal and the coordinates of P. [7]
© UCLES 2021 4037/24/M/J/21 [Turn over
7
3
6 The variables x and y are such that y = x 3 - 91 .
dy
(a) Find an expression for . [2]
dx
(b) Hence, find the approximate change in y as x increases from 6 to 6 + h , where h is small. [2]
© UCLES 2021 4037/24/M/J/21 [Turn over
12
10 (a) A particle P travels in a straight line so that, t seconds after passing through a fixed point O, its
displacement, s metres from O, is given by
31 e t
s= - - 10e -t .
3 3
(i) Find the value of t when P is at instantaneous rest, giving your answer correct to 2 significant
figures. [4]
(ii) Find the distance travelled in the first two seconds. [3]
© UCLES 2021 4037/24/M/J/21
13
(b) A particle Q travels in a straight line so that t seconds after leaving a fixed point O, its velocity,
v ms -1 , is given by
v = 2t for 0 G t G 5 ,
v = t 2 - 8t + 25 for t 2 5 .
(i) On the axes below, sketch the velocity-time graph for the first 8 seconds of the motion of
particle Q. [2]
v ms–1
30
25
20
15
10
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ts
(ii) Showing all your working, find the distance travelled by Q in the first 8 seconds of its motion.
[5]
© UCLES 2021 4037/24/M/J/21 [Turn over
12
10
y
1 3
y= 2+
(x + 2) (x + 2)
-1 0 2 x
1 3
The diagram shows the graph of the curve y = + for x 2- 2 . The points A and B lie
`x + 2j
2
(x + 2)
on the curve such that the x-coordinates of A and of B are -1 and 2 respectively.
(a) Find the exact y-coordinates of A and of B. [2]
(b) Find the area of the shaded region enclosed by the line AB and the curve, giving your answer in the
p
form - ln r , where p, q and r are integers. [6]
q
© UCLES 2021 4037/12/O/N/21
14
11 (a)
v ms-1
60
30
0 10 25 35 55 ts
The diagram shows the velocity–time graph for a particle P, travelling in a straight line with
velocity v ms -1 at a time t seconds. P accelerates at a constant rate for the first 10 s of its motion,
and then travels at constant velocity, 30 ms -1 , for another 15 s. P then accelerates at a constant
rate for a further 10 s and reaches a velocity of 60 ms -1 . P then decelerates at a constant rate and
comes to rest when t = 55.
(i) Find the acceleration when t = 12 . [1]
(ii) Find the acceleration when t = 50 . [1]
(iii) Find the total distance travelled by the particle P. [2]
© UCLES 2021 4037/12/O/N/21
15
(b) A particle Q travels in a straight line such that its velocity, v ms -1 , at time t s after passing through
a fixed point O is given by v = 4 cos 3t - 4 .
5r
(i) Find the speed of Q when t = . [2]
9
(ii) Find the smallest positive value of t for which the acceleration of Q is zero. [3]
(iii) Find an expression for the displacement of Q from O at time t. [2]
© UCLES 2021 4037/12/O/N/21
Question 400 (ON 21 13 Q2)
13
d2y
` j
- 21
10 A curve with equation y = f (x) is such that = 2 x + 3 + 5 for x 2 0 . The curve has gradient
dx 2
10 at the point b3, l.
19
2
dy
(a) Show that, when x = 11, = 52 . [5]
dx
(b) Find f (x) . [4]
© UCLES 2021 4037/13/O/N/21 [Turn over
14
`x 2 - 5j3
1
11 A curve has equation y = for x 2- 1.
x+1
dy Ax 2 + Bx + C
(a) Show that = where A, B and C are integers. [6]
dx
3 `x + 1j `x 2 - 5j
2
2 3
© UCLES 2021 4037/13/O/N/21
15
(b) Find the x-coordinate of the stationary point on the curve. [2]
(c) Explain how you could determine the nature of this stationary point. [2]
[You are not required to find the nature of this stationary point.]
© UCLES 2021 4037/13/O/N/21
6
4 (a) Find the x-coordinates of the stationary points on the curve y = 3 ln x + x 2 - 7x , where x 2 0 .
[5]
(b) Determine the nature of each of these stationary points. [3]
© UCLES 2021 4037/22/O/N/21
9
d2y 2x 1
7 It is given that 2 =e + for x 2- 1.
dx ( x + 1) 2
dy dy
(a) Find an expression for given that = 2 when x = 0 . [3]
dx dx
(b) Find an expression for y given that y = 4 when x = 0 . [3]
© UCLES 2021 4037/22/O/N/21 [Turn over
12
9 (a) Find the equation of the normal to the curve y = x 3 + x 2 - 4x + 6 at the point (1, 4) . [5]
© UCLES 2021 4037/22/O/N/21
13
(b) DO NOT USE A CALCULATOR IN THIS PART OF THE QUESTION.
Find the exact x-coordinate of each of the two points where the normal cuts the curve again. [5]
© UCLES 2021 4037/22/O/N/21 [Turn over
8
6 It is given that x = 2 + sec i and y = 5 + tan 2 i .
(a) Express y in terms of x. [2]
dy
(b) Find in terms of x. [1]
dx
(c) A curve has the equation found in part (a). Find the equation of the tangent to the curve when
r
i= . [4]
3
© UCLES 2021 4037/23/O/N/21
10
8
y
5
y= + 2x
x-1
2y = 9x
x=4
0 x
5
The diagram shows part of the curve y = + 2x , and the straight lines x = 4 and 2y = 9x .
x-1
5
(a) Find the coordinates of the stationary point on the curve y = + 2x . [5]
x-1
© UCLES 2021 4037/23/O/N/21
11
(b) Given that the curve and the line 2y = 9x intersect at the point (2, 9), find the area of the shaded
region. [5]
© UCLES 2021 4037/23/O/N/21 [Turn over
14
10 (a) It is given that f (x) = 4x 3 - 4x 2 - 15x + 18 . Find the equation of the normal to the curve y = f (x)
at the point where x = 1. [5]
© UCLES 2021 4037/23/O/N/21
15
(b) DO NOT USE A CALCULATOR IN THIS PART OF THE QUESTION.
It is also given that x + a , where a is an integer, is a factor of f (x) . Find a and hence solve the
equation f (x) = 0 . [6]
© UCLES 2021 4037/23/O/N/21
You might also like
- F4 Maths Past Paper 17-18 SCC F4 Math FinalDocument101 pagesF4 Maths Past Paper 17-18 SCC F4 Math FinalChun Kit LauNo ratings yet
- 3 2 4 1 - +, Showing The Coordinates of The Points Where The Curve Intersects The Coordinate Axes.Document14 pages3 2 4 1 - +, Showing The Coordinates of The Points Where The Curve Intersects The Coordinate Axes.Nirvaan PuriNo ratings yet
- Is Given by V 3 30 72 - + - Find The Distance Between The Particle's Two Positions of Instantaneous Rest.Document6 pagesIs Given by V 3 30 72 - + - Find The Distance Between The Particle's Two Positions of Instantaneous Rest.Tanzim RahmanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1Document14 pagesMathematics 1keshav GopaulNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument49 pagesDifferentiationFawziah NabihaNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal SubjectDocument4 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subjectlaksh bissoondialNo ratings yet
- 2014-2015 (L-2, T-1) - Che - (Upl)Document19 pages2014-2015 (L-2, T-1) - Che - (Upl)AE06 AvionicsNo ratings yet
- Solve X 3 2 4 + + - (3) : 0606/23/O/N/19 © UCLES 2019Document13 pagesSolve X 3 2 4 + + - (3) : 0606/23/O/N/19 © UCLES 2019Nirvaan Puri0% (1)
- Sin 6 2 D D - B L. Given That X 2 1 D D at The Point, 4 12 13 B L On The Curve, Find The Equation of The Curve.Document4 pagesSin 6 2 D D - B L. Given That X 2 1 D D at The Point, 4 12 13 B L On The Curve, Find The Equation of The Curve.Tanzim RahmanNo ratings yet
- 11 Derivative Paper2Document7 pages11 Derivative Paper2Selahattin GüntaşNo ratings yet
- Ah Sam 1Document3 pagesAh Sam 1JASON_INGHAMNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument4 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Levelyousee yusiNo ratings yet
- On The Axes Below, Sketch The Graph of Cos 2 3 For ° 0 180 GG .Document13 pagesOn The Axes Below, Sketch The Graph of Cos 2 3 For ° 0 180 GG .Nirvaan PuriNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics 2010 June Paper 21Document8 pagesAdditional Mathematics 2010 June Paper 21Sharifa McLeodNo ratings yet
- Modulus FunctionsDocument19 pagesModulus FunctionsayeshaNo ratings yet
- Time Practice 1Document4 pagesTime Practice 1Mr Plays shitNo ratings yet
- VVV MergedDocument11 pagesVVV Mergedjekeg27327No ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary LevelDocument4 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary LevelKelvin SerimweNo ratings yet
- 2012 MJC MBT QN Paper For JC2 MBT RevisionDocument3 pages2012 MJC MBT QN Paper For JC2 MBT RevisionAng Wei NengNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional GeometryDocument8 pagesThree Dimensional GeometryTRY UP GamingNo ratings yet
- 4037 w05 QP 1Document8 pages4037 w05 QP 1Khurram AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1Document15 pagesMathematics 1keshav GopaulNo ratings yet
- A13 Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument10 pagesA13 Co-Ordinate GeometryjamshedNo ratings yet
- Indices and Surds - QPDocument19 pagesIndices and Surds - QPMuhammad IbrahimNo ratings yet
- T Cot An Cosec Cos + - (3) : 15 11 (A) (I) Show ThatDocument15 pagesT Cot An Cosec Cos + - (3) : 15 11 (A) (I) Show ThatRichard FernandezNo ratings yet
- 2020 Specimen Paper 1Document10 pages2020 Specimen Paper 1Sajedul HassanNo ratings yet
- ZIMSEC 2018 June Paper 1Document6 pagesZIMSEC 2018 June Paper 1Iati Raymond ChishiriNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument8 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- A-Levels Pure Mathematics ExemplarDocument16 pagesA-Levels Pure Mathematics ExemplarDarlingtonNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics: Zimbabwe School Examinations CouncilDocument8 pagesPure Mathematics: Zimbabwe School Examinations CouncilLustreNo ratings yet
- C3 Integration PDFDocument5 pagesC3 Integration PDFRokonuddin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics 2009 June Paper 1Document8 pagesAdditional Mathematics 2009 June Paper 1lornarifaNo ratings yet
- O Level Additional Maths SpecimenDocument8 pagesO Level Additional Maths SpecimenGershom MahoriNo ratings yet
- 4037 w10 QP 13Document8 pages4037 w10 QP 13mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics 2010 June Paper 12Document8 pagesAdditional Mathematics 2010 June Paper 12Sharifa McLeodNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation Ax bxc0 X A B B Ac: Mathematical FormulaeDocument15 pagesQuadratic Equation Ax bxc0 X A B B Ac: Mathematical FormulaeRishwin Singh Sinda a/l Karamjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- M12 WK28TS 2028 Vector Algebra I QuestionsDocument2 pagesM12 WK28TS 2028 Vector Algebra I Questionssagarikaarun06No ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge Ordinary LevelMUHAMMAD SHAZIL AYUBNo ratings yet
- Add Math Specimen 2011Document16 pagesAdd Math Specimen 2011dann_991No ratings yet
- 2023 - PAPER - 1 - (A'LEVEL - PURE MATHEMATICS) - FINAL REVISION MR SHAREDocument9 pages2023 - PAPER - 1 - (A'LEVEL - PURE MATHEMATICS) - FINAL REVISION MR SHAREprofessobopoto04No ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Revision Worksheet Month 8Document4 pagesPure Mathematics Revision Worksheet Month 8Le Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Integration PYQDocument2 pagesChapter 15 Integration PYQWyndham WooNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Mock 2 Examination: Subject Teacher'S NameDocument16 pagesGrade 10 Mock 2 Examination: Subject Teacher'S NameMuskan HardwaniNo ratings yet
- June 2019 QP - Unit 4 WJEC Further Maths A-LevelDocument7 pagesJune 2019 QP - Unit 4 WJEC Further Maths A-LevelDarren DowlingNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument12 pagesCambridge Ordinary Levelshazrae2007No ratings yet
- Vectors and 3-D Geometry Test - XII (13.02.22) +2 Maths India (NCERT)Document3 pagesVectors and 3-D Geometry Test - XII (13.02.22) +2 Maths India (NCERT)Shivansh KatochNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument8 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- 2 10 10 8 3 11 11 MergedDocument8 pages2 10 10 8 3 11 11 Mergedyanewo5099No ratings yet
- PM FM 5Document2 pagesPM FM 5biloma6323No ratings yet
- Ass 4 O Level Pure Maths Paper 1Document16 pagesAss 4 O Level Pure Maths Paper 1peterchiyanjaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-23-07 - 11th (J-Batch) SOLUTIONDocument3 pagesPHYSICS-23-07 - 11th (J-Batch) SOLUTIONRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- CP2 - Paper 2Document3 pagesCP2 - Paper 2prashasti0410No ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper - 6 Mathematics (041) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22Document8 pagesSample Question Paper - 6 Mathematics (041) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22Om AroraNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Revision Worksheet Month 5Document4 pagesPure Mathematics Revision Worksheet Month 5Le Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- Grade10 99256 12 5189.qDocument2 pagesGrade10 99256 12 5189.qLAKHAN KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Trial STPM P2 2018 SMJK JT SINDocument3 pagesTrial STPM P2 2018 SMJK JT SINMelody OngNo ratings yet
- 4037 s08 QP 1Document8 pages4037 s08 QP 1mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Sem III OLD-1Document119 pagesSem III OLD-1sanket0% (1)
- B y Ax C X Ab andDocument4 pagesB y Ax C X Ab andjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- James WattDocument5 pagesJames WattweldharishNo ratings yet
- Em Ut1Document30 pagesEm Ut1david josephNo ratings yet
- Virtual Work and Variational PrinciplesDocument9 pagesVirtual Work and Variational PrinciplesBill Erick CastilloNo ratings yet
- NSTC Sample Paper 2006Document24 pagesNSTC Sample Paper 2006Irfan Ali0% (2)
- Refrigerant PumpDocument2 pagesRefrigerant PumpbarelihbNo ratings yet
- ANChor DesignDocument16 pagesANChor DesignAditya KNo ratings yet
- Design Assignment TU Noord: February 2012Document38 pagesDesign Assignment TU Noord: February 2012frankydadNo ratings yet
- Failure Identification in Smart GridsDocument11 pagesFailure Identification in Smart GridsUsama MalikNo ratings yet
- Detailed Solutions A-07 JUNE 2003: I X X F F IDocument32 pagesDetailed Solutions A-07 JUNE 2003: I X X F F IAdzLinkBalaoangNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument6 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumenthelenarajNo ratings yet
- Sherwood 1939Document7 pagesSherwood 1939Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- MSDS Bio ChemicalsDocument8 pagesMSDS Bio ChemicalsfauziahNo ratings yet
- 2013 Sec 3 WS8.1 - 8.4 AnswersDocument11 pages2013 Sec 3 WS8.1 - 8.4 AnswersAmelia RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Shree Shankara Sr. Sec. School Subject Enrichment Class-10Document4 pagesShree Shankara Sr. Sec. School Subject Enrichment Class-10Govind kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- GR 11 Salt Analysis 1 and 2Document6 pagesGR 11 Salt Analysis 1 and 2dineshgarg2404No ratings yet
- Pcmflash 71Document163 pagesPcmflash 71Emi DNo ratings yet
- Periodical Test in MathDocument4 pagesPeriodical Test in MathRonel Sayaboc AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Report BHushan Steel Tube MillDocument58 pagesReport BHushan Steel Tube MillVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission and DistributionDocument50 pagesPower Transmission and DistributionGhayath OmerNo ratings yet
- Lecture13 - Chapter 3 - The Semiconductor in Equilibrium-Density of States Function-Equilibrium Distribution of Electrons and HolesDocument10 pagesLecture13 - Chapter 3 - The Semiconductor in Equilibrium-Density of States Function-Equilibrium Distribution of Electrons and HolesZakrya NadanNo ratings yet
- CHAP 4 Periodic TablebDocument73 pagesCHAP 4 Periodic TablebLily MardyanaNo ratings yet
- Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar InSAR ItsDocument6 pagesInterferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar InSAR ItskridatimaNo ratings yet
- JEE (Advanced) 2016: Memory Based Questions & SolutionsDocument19 pagesJEE (Advanced) 2016: Memory Based Questions & SolutionsResonance EduventuresNo ratings yet
- Laser Maker Manual (YLM) - 95p - ENGDocument95 pagesLaser Maker Manual (YLM) - 95p - ENGsebastianandrei2008008No ratings yet
- 3d Max - Water Drops and LeafDocument5 pages3d Max - Water Drops and LeafNesshi S. OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification Robbins 91RH C - tcm835-3329419 PDFDocument4 pagesTechnical Specification Robbins 91RH C - tcm835-3329419 PDFNicole Pavez VivadoNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Saving Lebanon: Group MembersDocument13 pagesRenewable Energy Saving Lebanon: Group Membersjulien dahrNo ratings yet
- EE21 Lecture 1Document32 pagesEE21 Lecture 1R SuyaoNo ratings yet