Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Zylem and Phloem
Uploaded by
Aurea Jasmine Dacuycuy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
160 views2 pageslesson
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentlesson
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
160 views2 pagesZylem and Phloem
Uploaded by
Aurea Jasmine Dacuycuylesson
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
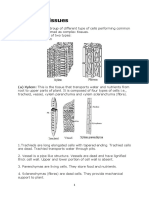
What is xylem and phloem and its function?
Xylem is the complex tissue of plants, responsible for
transporting water and other nutrients to the plants. Phloem is
living tissue, responsible for transporting food and other
organic materials.
What is phloem and xylem?
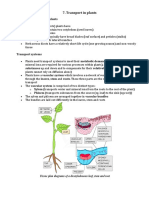
Plants have tissues to transport water, nutrients and
minerals. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to
other parts of the plant, while phloem transports sucrose and amino
acids between the leaves and other parts of the plant.
What are the structural differences between xylem and phloem?
Differences Between Xylem and Phloem
Xylem Phloem
Definition
Xylem tissues are the tubular-
Phloem tissues are tubular-shaped,
shaped structure, with the absence of
elongated, structures with the presence of
cross walls. This tissue resembles the
walls with thin sieve tubes.
shape of a star.
What is the direction of transport in xylem and phloem?
Question 1: Movement of substances in xylem is unidirectional while
in phloem it is bidirectional. Explain. Answer: Xylem transports water.
Since transportation of water always takes place from roots to leaves,
the direction of transport always remains in the upward direction.
What is the main function of xylem?
Xylem is the specialised tissue of vascular plants that transports water
and nutrients from the plant–soil interface to stems and leaves, and
provides mechanical support and storage. The water-
conducting function of xylem is one of the major distinguishing
features of vascular plants.
What is an example of phloem?
Phloem is the tissue in plants that transport food to the parts of the plant where it
needs to go. An example of the phloem is the tissue in plants that distributes the
sugar that plants eat. ... In mature woody plants it forms a sheathlike layer of tissue
in the stem, just inside the bark.
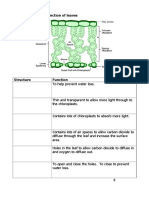
Where is xylem and phloem located?
In leaves, the vascular bundles are located among the spongy
mesophyll. The xylem is oriented toward the adaxial surface of the leaf
(usually the upper side), and phloem is oriented toward the abaxial
surface of the leaf.
How do you identify phloem?
Phloem, also called bast, tissues in plants that conduct foods made in the leaves to
all other parts of the plant. Phloem is composed of various specialized cells called
sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres, and phloem parenchyma cells.
What is an example of xylem?
Xylem is a type of tissue in plants that carries water. An example of xylem is what
moves water and some nutrients through a plant. ... In a tree trunk, the innermost
part of the wood is dead but structurally strong xylem, while the outer part consists
of living xylem, and beyond it, layers of cambium and phloem.
You might also like
- Science Assignment: Made By: Syed Ammar Ahmed Viii - CDocument4 pagesScience Assignment: Made By: Syed Ammar Ahmed Viii - CSYED AMMAR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Plant Transportation ProjectDocument8 pagesPlant Transportation ProjectA NayeemNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument14 pagesTransport in PlantsMuhammad Faizan KaleemNo ratings yet
- Biology PosterDocument5 pagesBiology PosterMenara RathnayakeNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument24 pagesTissuesAGRANI GOTHWALNo ratings yet
- Life Processes TransportDocument12 pagesLife Processes TransportYashaswini.V.No ratings yet
- The Vascular Structure of PlantsDocument7 pagesThe Vascular Structure of PlantsAathifa ThowfeekNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 (2) - RemovedDocument249 pagesBiology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 (2) - RemovedMathableNo ratings yet
- Complex tissues: Xylem and phloem transport in plantsDocument3 pagesComplex tissues: Xylem and phloem transport in plantsJayadi yadav ShubhamNo ratings yet
- 7.transport in Plants NotesDocument18 pages7.transport in Plants NotesAhmed Noor100% (1)
- Transport System in PlantsDocument20 pagesTransport System in PlantsAkiela JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Complex Permanent Tissues: Xylem and PhloemDocument4 pagesComplex Permanent Tissues: Xylem and PhloemAnonymous nrnwKSmNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport Paper 2Document2 pagesPlant Transport Paper 2Heneral Drew de LunaNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORT IN PLANTSDocument6 pagesTRANSPORT IN PLANTSAbhyudaya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument16 pagesTransport in PlantsJayzl Lastrella CastanedaNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants - Xylem and PhloemDocument10 pagesTransport in Plants - Xylem and PhloemYasmin YehiaNo ratings yet
- Cells (2)Document11 pagesCells (2)Vinisha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants: By:-Mr - Deepak Upreti Biology Teacher Gmis, JakartaDocument26 pagesTransport in Plants: By:-Mr - Deepak Upreti Biology Teacher Gmis, Jakartakiera angNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument8 pagesTransport in PlantsKomalsh TheeranNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3.1_ TRANSPORTATION IN PLANTSDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 3.1_ TRANSPORTATION IN PLANTSbabylen bahalaNo ratings yet
- Xylem and Phloem Make Up The Big Transportation System of VascularDocument2 pagesXylem and Phloem Make Up The Big Transportation System of VascularYap Hooi CheinNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsDocument49 pagesBiology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsPeter Osundwa Kiteki100% (2)
- Plant Transport Systems ExplainedDocument2 pagesPlant Transport Systems ExplainedViviana PlacentinoNo ratings yet
- Biology - DynessDocument45 pagesBiology - DynessmalikachinyantaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Transport in PlantsDocument8 pagesLecture 12 - Transport in PlantsAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Document6 pagesPlant Transport - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Zhi En LeeNo ratings yet
- A Blog Class 9 First Bell Biology Chapter 3 Science Diary Class 20 em 1Document3 pagesA Blog Class 9 First Bell Biology Chapter 3 Science Diary Class 20 em 1Anaina AnnaNo ratings yet
- Plant Vs Animal TransportCirculatory System PDFDocument46 pagesPlant Vs Animal TransportCirculatory System PDFJezreel IsipinNo ratings yet
- Report in ScienceDocument22 pagesReport in Scienceaileen amadaNo ratings yet
- Ch-8 Transport in PlantsDocument12 pagesCh-8 Transport in Plantsdaveymilan36No ratings yet
- TRANSPORT in PLANTSDocument27 pagesTRANSPORT in PLANTSRish HeeNo ratings yet
- Types of Cells (Plant & Animal)Document2 pagesTypes of Cells (Plant & Animal)WajurumnaNo ratings yet
- Y10 Plant Transport Lesson 1Document27 pagesY10 Plant Transport Lesson 1Sherry LeeNo ratings yet
- Transport of Materials in Flowering PlantsDocument22 pagesTransport of Materials in Flowering PlantsMd SafwatNo ratings yet
- Conducting TissuesDocument7 pagesConducting TissuesDhruv PalNo ratings yet
- How Plants Survive: The Structure and Functions of Plant Organs, Tissues, and CellsDocument27 pagesHow Plants Survive: The Structure and Functions of Plant Organs, Tissues, and CellsAlejandro SantosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Structure and Functions of Leaves Student WorksheetDocument3 pagesLesson 5 Structure and Functions of Leaves Student WorksheetEunice Xiiao Wenn100% (2)
- 3.1.2 Transport in PlantsDocument9 pages3.1.2 Transport in PlantssjNo ratings yet
- Describe The Structure and Function of The Five Major Types of Cells Found in Plant TissueDocument3 pagesDescribe The Structure and Function of The Five Major Types of Cells Found in Plant TissueIshaHenryNo ratings yet
- Ke L-SciDocument5 pagesKe L-SciMaricar BautistaNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument3 pagesTransport in Plantsoten.temotika02No ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Plant TissuesDocument8 pagesStructure and Functions of Plant Tissuesdina aribahNo ratings yet
- Complex TissueDocument3 pagesComplex TissueMayur KambleNo ratings yet
- Transportation: FunctionDocument21 pagesTransportation: Functionvivek tripathiNo ratings yet
- 06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Document24 pages06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Saurabh ShivakumarNo ratings yet
- Complex Permanent TissueDocument1 pageComplex Permanent TissueFirliana PramesdyaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Xylem and PhloemDocument2 pagesBiology Notes Xylem and PhloemMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- Biology Summer Study Transport in PlantsDocument9 pagesBiology Summer Study Transport in PlantsAya100% (1)
- Vascular PlantsDocument2 pagesVascular PlantsAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Meristem Parenchyma Sclerenchyma 5: Figure 5: Cell Types and TissuesDocument8 pagesMeristem Parenchyma Sclerenchyma 5: Figure 5: Cell Types and Tissuessandy waskitoNo ratings yet
- Life Science Some Important Points - 21355313 - 2023 - 08 - 09 - 23 - 12Document2 pagesLife Science Some Important Points - 21355313 - 2023 - 08 - 09 - 23 - 12tripbrataNo ratings yet
- Plant and Their Systems, Gr-7, AdyalaDocument15 pagesPlant and Their Systems, Gr-7, AdyalaSidra UsmanNo ratings yet
- Xylem: A Vascular Tissue in Land PlantsDocument4 pagesXylem: A Vascular Tissue in Land PlantsJoshua-Jonai JulyeNo ratings yet
- Quarter: 4 / Semester: 2 / WEEK: 4: Online Resource/sDocument17 pagesQuarter: 4 / Semester: 2 / WEEK: 4: Online Resource/sTristan Paul PagalananNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note Plant Structure and FunctionDocument22 pagesLecture Note Plant Structure and FunctionMilka Rahman100% (1)
- How Minerals Are Transported in PlantsDocument2 pagesHow Minerals Are Transported in PlantsMariam KidwaiNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 2 NotesDocument80 pagesBiology Form 2 NotesLutern RayNo ratings yet
- Simple Tissue and Complex TissueDocument4 pagesSimple Tissue and Complex TissueHappy RoyNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument18 pagesTransport in PlantsmichaeltrobiaNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- LegitimateDocument2 pagesLegitimateAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- What Exactly Does An Anesthesiologist DoDocument1 pageWhat Exactly Does An Anesthesiologist DoAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Of The Child's Birth. Even If The Parents Later Married, The Child Would Still Be ConsideredDocument2 pagesOf The Child's Birth. Even If The Parents Later Married, The Child Would Still Be ConsideredAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- From The Module On Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development, I Learned That.. TheDocument2 pagesFrom The Module On Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development, I Learned That.. TheAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Early Signs of An Ectopic Pregnancy IncludeDocument2 pagesEarly Signs of An Ectopic Pregnancy IncludeAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument2 pagesAnswer KeyAurea Jasmine Dacuycuy75% (4)
- For Elaborative Learning: AnswerDocument1 pageFor Elaborative Learning: AnswerAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Proper Nouns and Formal Names of Departments and Individuals Are Capitalized. inDocument2 pagesProper Nouns and Formal Names of Departments and Individuals Are Capitalized. inAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Reflection: 5 - Minute Non Stop Writing Begins NowDocument2 pagesReflection: 5 - Minute Non Stop Writing Begins NowAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- How To Become A Self-Made ScholarDocument2 pagesHow To Become A Self-Made ScholarAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Taking It To The Net: AnswerDocument1 pageTaking It To The Net: AnswerAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- DIDocument2 pagesDIAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Which Is Most DifficultDocument2 pagesWhich Is Most DifficultAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Analysis: 2. Does Physical Development Begin From The Top or Below? From The Side To The Canter? Explain Your AnswerDocument2 pagesAnalysis: 2. Does Physical Development Begin From The Top or Below? From The Side To The Canter? Explain Your AnswerAurea Jasmine Dacuycuy100% (4)
- Individual Activity - For Reflection: AnswerDocument2 pagesIndividual Activity - For Reflection: AnswerAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Information That Helps Faculty Determine How They Might Improve Courses And/orDocument1 pageInformation That Helps Faculty Determine How They Might Improve Courses And/orAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Non Stop ActivityDocument2 pagesNon Stop ActivityAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Non Stop Activity Module 11Document2 pagesNon Stop Activity Module 11Aurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument4 pagesReflectionAurea Jasmine Dacuycuy100% (1)
- Curriculum's Would Be Pointless. If The Students Do Not Actually Comprehend andDocument1 pageCurriculum's Would Be Pointless. If The Students Do Not Actually Comprehend andAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Problem or Situation and Figure Out A Way To Solve It. Teachers Expect Students To Use TheirDocument1 pageProblem or Situation and Figure Out A Way To Solve It. Teachers Expect Students To Use TheirAurea Jasmine Dacuycuy100% (1)
- Application of Hidden CurriculumDocument2 pagesApplication of Hidden CurriculumAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Stage 2: Autonomy Vs Shame and Doubt (Infancy and Childhood) ScoreDocument4 pagesStage 2: Autonomy Vs Shame and Doubt (Infancy and Childhood) ScoreAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Answer:: Describe WDocument3 pagesAnswer:: Describe WAurea Jasmine Dacuycuy100% (1)
- Inductive Tends To Be More Efficient in The Long Run, But Deductive Is Less TimeDocument2 pagesInductive Tends To Be More Efficient in The Long Run, But Deductive Is Less TimeAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- CurriculumDocument1 pageCurriculumAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Child Centered ApproachDocument2 pagesChild Centered ApproachAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- What Is LearnerDocument2 pagesWhat Is LearnerAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- And Perspectives That Students Learn in School. ... The Hidden Curriculum Is Described AsDocument2 pagesAnd Perspectives That Students Learn in School. ... The Hidden Curriculum Is Described AsAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Subject CenteredDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Subject CenteredAurea Jasmine Dacuycuy100% (3)
- Laboratory 2022 1Document9 pagesLaboratory 2022 1DIAYANARA ROSE CACHONo ratings yet
- Screening For Low-Temperature Stress Tolerance in Boro RiceDocument6 pagesScreening For Low-Temperature Stress Tolerance in Boro RiceIRRI_resourcesNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide to Home CompostingDocument24 pagesComplete Guide to Home CompostingDeah Etan100% (2)
- Botany of Oil PalmDocument17 pagesBotany of Oil PalmAnonymous DJrec250% (2)
- Tree Roots Versus Sidewalks and Sewers: William R. ComeryDocument2 pagesTree Roots Versus Sidewalks and Sewers: William R. ComeryENORTE EngenhariaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Plant Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesUnit 9 Plant Structure and FunctionRebekah ShafferNo ratings yet
- Increasing Cherry Fruit SizeDocument6 pagesIncreasing Cherry Fruit SizeKathryn BaxNo ratings yet
- Production Technology of LentilDocument17 pagesProduction Technology of LentilHAMZA'S VLOGSNo ratings yet
- Diseases of SorghumDocument16 pagesDiseases of SorghumJagtap RamNo ratings yet
- Growing Chili Peppers with Bone MealDocument15 pagesGrowing Chili Peppers with Bone MealYsandra Declaro100% (1)
- Preserving Physical and Physiological Quality of COCOA SEEDS (Theobroma Cacao L.) DURING STORAGE With The Addition of Organic AcidsDocument18 pagesPreserving Physical and Physiological Quality of COCOA SEEDS (Theobroma Cacao L.) DURING STORAGE With The Addition of Organic AcidsIchaNo ratings yet
- Seed Marketing Slide PresentationDocument30 pagesSeed Marketing Slide PresentationChona Dancel-cayetanoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Natural DrugsDocument8 pagesClassification of Natural DrugsAjinkya Jagtap67% (3)
- Botany PrelimsDocument3 pagesBotany Prelimsசுப.தமிழினியன்No ratings yet
- Icar JRF Syllabus HorticultureDocument2 pagesIcar JRF Syllabus HorticultureRiya PandeyNo ratings yet
- Organic Products and Their Recommended UsesDocument25 pagesOrganic Products and Their Recommended UsesSeok Heon KimNo ratings yet
- AHMEDABAD AUTHORITY AIMS TO INCREASE GREEN COVER WITH MASS PLANTATIONDocument91 pagesAHMEDABAD AUTHORITY AIMS TO INCREASE GREEN COVER WITH MASS PLANTATIONKshitij SoniNo ratings yet
- Gmelina Arborea Plan BDocument5 pagesGmelina Arborea Plan BDawn Regile MorilloNo ratings yet
- AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE SBA Quada - Copy (Repaired)Document29 pagesAGRICULTURAL SCIENCE SBA Quada - Copy (Repaired)Tracy CharlesNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Herbs: We Are Offering Large Range of Medicinal Herbs. Some of Them Are FollowingDocument3 pagesMedicinal Herbs: We Are Offering Large Range of Medicinal Herbs. Some of Them Are FollowingTayyab Tahir MinhasNo ratings yet
- 7th Class ScienceDocument10 pages7th Class ScienceM Saadat SaeediNo ratings yet
- Alley CroppingDocument5 pagesAlley CroppingSwadhin DuttaNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Pas Ganjil Kelas XDocument8 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Pas Ganjil Kelas Xririny9No ratings yet
- Tree Fruit Production Guide (Pennsylvania 2012-2013) PDFDocument340 pagesTree Fruit Production Guide (Pennsylvania 2012-2013) PDFAlexandraIoannou100% (1)
- Teakplantation 1Document4 pagesTeakplantation 1Smit kalamkarNo ratings yet
- Bot - Cot Test - 1Document6 pagesBot - Cot Test - 1Mayur BelsareNo ratings yet
- Hele 4 PPT - 2nd QT - Week 1Document47 pagesHele 4 PPT - 2nd QT - Week 1jerico juarezNo ratings yet
- Controlling Hagonoy Weed with Gall FliesDocument2 pagesControlling Hagonoy Weed with Gall FliesCarlo MakilingNo ratings yet
- Brusnica - History of CranberryDocument3 pagesBrusnica - History of CranberrycajceNo ratings yet
- Tamarix Aphylla - Useful Tropical PlantsDocument2 pagesTamarix Aphylla - Useful Tropical PlantsAiouche Djamel EddineNo ratings yet