Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Matthew Correia Worksheet Chemical Bonding and Types of Substances
Matthew Correia Worksheet Chemical Bonding and Types of Substances
Uploaded by
Frank MassiahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Matthew Correia Worksheet Chemical Bonding and Types of Substances
Matthew Correia Worksheet Chemical Bonding and Types of Substances
Uploaded by
Frank MassiahCopyright:
Available Formats
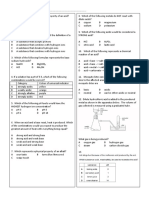
1.
(a)Depending on their structures and properties, solids may be classified as having metallic, giant covalent, simple molecular or giant
ionic lattice structures. The structure and conductivity of selected solids are summarized in table 1.
Copy and complete table 1 to show the structure and conductivity of EACH solid substance listed. The first one is done as an
example.
TABLE 1: Structure and conductivity of selected solids
Solid Structure Conducts electricity in solid state
Magnesium chloride Giant Ionic No
Iodine
Zinc
Diamond
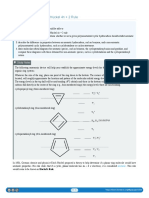
b) Diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon. (6 marks)
(i) What is meant by the term ‘allotropes’? (1 mark)
(ii) Draw a diagram to represent the structure of
- Diamond - graphite (6 marks)
c) Use the diagrams in (b) (ii) above to explain the following:
i) Diamond can be used as drill bits (2 marks)
ii )Rubbing lead pencil on a key makes it turn easily in the lock. (The “lead” in lead pencil contains graphite) (2marks)
d) The melting point of chlorine and sodium chloride are -101 o C and 800 o C respectively. Explain why the melting point of sodium
chloride is much higher than that of chlorine. (3 marks)
TOTAL 20 MARKS
2
a) Define Ionic bonding. [2 marks]
b) Define Covalent bonding. [2 marks]
c) State the type of bonding found in the following and illustrate that bonding using “dot cross” diagrams.
i) CO2 ii) H2O iii) MgF2 iv) NaCl [8 marks]
d) State and account for the forces connecting the particles found in:
(i) NaCl
(ii) H2O [6 marks]
e) Using the diagrams below explain the bonding found in the ammonium ion. [2 marks]
Hydrogen ion
Ammonia
TOTAL 20 MARKS
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5811)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Grade 10 Science Book OntarioDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Science Book OntarioPaul0% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Kadry - EJSR2 Corrosion Analysis of Stainless SteelDocument10 pagesKadry - EJSR2 Corrosion Analysis of Stainless SteelPrateep UntimanonNo ratings yet
- A Review of General ChemistryDocument13 pagesA Review of General ChemistryValerie Mae Librero AreñoNo ratings yet
- Feb 7 For Feb 13 2020 3rd Form Homework Acids and BasesDocument2 pagesFeb 7 For Feb 13 2020 3rd Form Homework Acids and BasesFrank MassiahNo ratings yet
- Reactivity of Metals and Nonmetals MATTHEW CORREIADocument6 pagesReactivity of Metals and Nonmetals MATTHEW CORREIAFrank MassiahNo ratings yet
- Matthew Correia Dot and Cross Diagrams WorksheetDocument2 pagesMatthew Correia Dot and Cross Diagrams WorksheetFrank MassiahNo ratings yet
- MATTHEW CORREIA Acids Bases and Salts WORKSHEETDocument4 pagesMATTHEW CORREIA Acids Bases and Salts WORKSHEETFrank MassiahNo ratings yet
- 3rd Form Atomic Structure Home-WorkDocument2 pages3rd Form Atomic Structure Home-WorkFrank MassiahNo ratings yet
- Fri Oct 18 2013 MATTHEW CORREIA Electrolysis and EnergeticsDocument3 pagesFri Oct 18 2013 MATTHEW CORREIA Electrolysis and EnergeticsFrank MassiahNo ratings yet
- Wed April 16 2014 Practice Multiple Choice Paper FULL 60 QuesDocument5 pagesWed April 16 2014 Practice Multiple Choice Paper FULL 60 QuesFrank MassiahNo ratings yet
- Nynas Transformer Oil - Nytro Orion I: Naphthenics Product Data Sheet 2006-08-21Document1 pageNynas Transformer Oil - Nytro Orion I: Naphthenics Product Data Sheet 2006-08-21Yudis MercadoNo ratings yet
- MdsDocument23 pagesMdsBilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Retrofitting of RC Structure Using FRP Laminate: AbstractDocument10 pagesRetrofitting of RC Structure Using FRP Laminate: AbstractYo Yo AkNo ratings yet
- 569 Pages, Chapter 15.3-23.10Document569 pages569 Pages, Chapter 15.3-23.10SanyaNo ratings yet
- Solubility of Stearic Acid in Various Organic SolvDocument5 pagesSolubility of Stearic Acid in Various Organic SolvAmir QayyumNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Mcdonald 21 Days Observation ObservationDocument3 pagesLab Report: Mcdonald 21 Days Observation Observationapi-256986280No ratings yet
- Nesvadba 2012Document36 pagesNesvadba 2012Bryan Acosta AnguloNo ratings yet
- 墊子構裝Document17 pages墊子構裝Michael KaoNo ratings yet
- Case Hardening Heat TreatmentDocument15 pagesCase Hardening Heat TreatmentHazrat BelalNo ratings yet
- Chap9 StudentDocument22 pagesChap9 StudentIsabel GohNo ratings yet
- Dowclene 1601Document4 pagesDowclene 1601Castle Jing100% (1)
- Spent Catalyst ReportDocument14 pagesSpent Catalyst Reportstarzgazer100% (1)
- Solid Phase ExtractionDocument12 pagesSolid Phase ExtractionNgọc MaiNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Liquids Recovery Processes in Natural Gas ProcessingDocument27 pagesNatural Gas Liquids Recovery Processes in Natural Gas ProcessingVictor Ali MentaNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid Perchloric Acid Digestion of SolidsDocument4 pagesNitric Acid Perchloric Acid Digestion of SolidspomodoroNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Peroxide PDFDocument6 pagesHydrogen Peroxide PDFlufiNo ratings yet
- NCHE 211 UNIT 2 VOLUMETRY and Complexometry TitrationDocument49 pagesNCHE 211 UNIT 2 VOLUMETRY and Complexometry Titrationkamohelo tsoeuNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.-1To prepare microscopic structure for examination & to examine the micro structure of specimens of various metals and alloys (Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Stainless steel, Mild steel etc.).Document4 pagesExperiment No.-1To prepare microscopic structure for examination & to examine the micro structure of specimens of various metals and alloys (Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Stainless steel, Mild steel etc.).Dogra AmitNo ratings yet
- Buesing&Fasch Gel&TopDocument6 pagesBuesing&Fasch Gel&TopBen Abdallah BecemNo ratings yet
- ParaffinDocument14 pagesParaffinSalman Hussain100% (2)
- Recovery Boiler: Esa VakkilainenDocument20 pagesRecovery Boiler: Esa Vakkilainenmarcus vinicius silva de souzaNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Gypsum ProductsDocument17 pagesSeminar On Gypsum ProductsHarish Khundrakpam0% (1)
- Azelis Indonesia DistribusiDocument7 pagesAzelis Indonesia Distribusifauzi.muhammad143No ratings yet
- The Sorbead Quick Cycle Process - LRGCC 2007Document13 pagesThe Sorbead Quick Cycle Process - LRGCC 2007aavianiacNo ratings yet
- IX H 727 10 Photo Atlas of Weld Appearance FiguresDocument21 pagesIX H 727 10 Photo Atlas of Weld Appearance FiguressexmanijakNo ratings yet
- Carbonation Test Principle of The TestDocument16 pagesCarbonation Test Principle of The Testjoechengsh100% (1)
- Heat Treatment Furnaces and AtmospheresDocument12 pagesHeat Treatment Furnaces and AtmospheresmiteshNo ratings yet