Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atomic Structure: Atomic Number Number of Mass Number Number of
Uploaded by
Cindy LawOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atomic Structure: Atomic Number Number of Mass Number Number of
Uploaded by
Cindy LawCopyright:
Available Formats
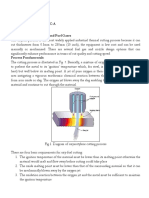
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Atoms consist of a central NUCLEUS containing protons and NEUTRONS. The nucleus is TINY compared to the size of the
whole atom. The nucleus is surrounded by ELECTRONS in energy levels (also called SHELLS). Atoms have no electric
charge because they contain the same number of protons and ELECTRONS. The electrons are arranged in energy levels
(SHELLS).
NUCLEUS
sub-atomic particle relative mass relative charge
(protons + neutrons)
proton 1 +1
neutron 1 0 Electrons in shells
electron 0.0005 or -1
Atomic number = number of PROTONS
Mass number = number of PROTONS + number of NEUTRONS
The number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom can be worked out using the atomic number and mass number.
Number of protons = ATOMIC NUMBER
Number of neutrons = MASS NUMBER - ATOMIC NUMBER
Number of electrons = ATOMIC NUMBER
Atoms can be represented as follows:
e.g. protons = 9 neutrons = 10 electrons = 9
Atoms of the same element have the same number of PROTONS. In fact, it is the number of PROTONS that determines
what type of atom it is (e.g. all atoms with 6 protons are carbon atoms). Atoms of different elements have different numbers
of PROTONS.
Isotopes are atoms with the same number of PROTONS but a different
number of NEUTRONS . This means they are atoms of the same protons 17 17
ELEMENT with the same ATOMIC number but a different MASS number. neutrons
18 20
electrons
17 17
Atom Atomic number Mass number Number of protons Number of neutrons Number of electrons
11 23 11 12 11
3 7
3 4 3
40 18
18 22 18
19 20
19 39 19
14 13
13 27 13
92 235 92 143 92
92 238 92 146 92
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 2-Jun-2015 Chemsheets AS 1001
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Learning Online With Futurelearn: Be ConsiderateDocument2 pagesLearning Online With Futurelearn: Be ConsiderateYasir AliNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Brain React and RespondDocument1 page1.3 Brain React and RespondCindy LawNo ratings yet
- Learning Online With Futurelearn: Be ConsiderateDocument2 pagesLearning Online With Futurelearn: Be ConsiderateYasir AliNo ratings yet
- Newsletter Title: Newsletter 3-Column Template For Business School or Private UseDocument3 pagesNewsletter Title: Newsletter 3-Column Template For Business School or Private UseCindy LawNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- II If en April2015 EquitycompoundersDocument8 pagesII If en April2015 EquitycompoundersbgyggghjkkNo ratings yet
- Graduate Study at KIMEPDocument20 pagesGraduate Study at KIMEPKIMEPNo ratings yet
- Past:: Simple Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect ContinuousDocument12 pagesPast:: Simple Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect ContinuousAhmed Abd El HafeezNo ratings yet
- Government and BusinessDocument2 pagesGovernment and BusinessJoshua BrownNo ratings yet
- GSPANN Returns To Adobe Summit 2021 As A Showcase SponsorDocument2 pagesGSPANN Returns To Adobe Summit 2021 As A Showcase SponsorPR.comNo ratings yet
- World CurrenciesDocument7 pagesWorld Currenciespraiseonyinye3No ratings yet
- Bridge Operation Maintenance COWIDocument19 pagesBridge Operation Maintenance COWIAhmadKhattabNo ratings yet
- PIRCHLDocument227 pagesPIRCHLapi-3703916No ratings yet
- Barotac Nuevo POP PDFDocument10 pagesBarotac Nuevo POP PDFJason Barrios PortadaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Registry Standard Operating ProceduresDocument3 pagesCancer Registry Standard Operating ProceduresAnan AghbarNo ratings yet
- Level 5 Part 1: Listening Comprehension (V.9) : Nro. de Control: ......Document16 pagesLevel 5 Part 1: Listening Comprehension (V.9) : Nro. de Control: ......Maco cacoseNo ratings yet
- Three Steps For Reducing Total Cost of Ownership in Pumping SystemsDocument13 pagesThree Steps For Reducing Total Cost of Ownership in Pumping SystemsJuan AriguelNo ratings yet
- JSA of Materila Handling ApproviedDocument2 pagesJSA of Materila Handling Approviedsakthi venkatNo ratings yet
- Physiology 102Document5 pagesPhysiology 102Javed AkhlaqNo ratings yet
- Scib RC PipesDocument4 pagesScib RC PipesterrylimNo ratings yet
- Scenario - Taxation 2019 UNISA - Level 1 Test 4Document7 pagesScenario - Taxation 2019 UNISA - Level 1 Test 4Tyson RuvengoNo ratings yet
- Catalogue For TubingDocument1 pageCatalogue For Tubingprabhakaran.cNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo de Ingles Grado 4 PrimariaDocument37 pagesCuadernillo de Ingles Grado 4 PrimariaMariaNo ratings yet
- Model Teaching CompetenciesDocument12 pagesModel Teaching CompetenciesTeachers Without BordersNo ratings yet
- Effects of Brainstorming On Students' Achievement in Senior Secondary ChemistryDocument8 pagesEffects of Brainstorming On Students' Achievement in Senior Secondary ChemistryzerufasNo ratings yet
- ToRs ESIA Maputo Sewerage System FinalDocument36 pagesToRs ESIA Maputo Sewerage System FinalVirgilio MuandoNo ratings yet
- Application Icx Sales ManagerDocument5 pagesApplication Icx Sales ManagerPersy LópezNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1CDocument4 pagesLaboratory Activity 1CAini HasshimNo ratings yet
- H2S Personal Gas MonitorDocument14 pagesH2S Personal Gas Monitormaher mansiNo ratings yet
- AWS Abbreviations Oxyfuel Cutting - OFC Oxyacetylene Cutting - OFC-A Oxyfuel Cutting - Process and Fuel GasesDocument8 pagesAWS Abbreviations Oxyfuel Cutting - OFC Oxyacetylene Cutting - OFC-A Oxyfuel Cutting - Process and Fuel GasesahmedNo ratings yet
- Q4 Tle 9 WK3Document5 pagesQ4 Tle 9 WK3Mj MartNo ratings yet
- Science Experiment Week 5 Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesScience Experiment Week 5 Lesson Planapi-451266317No ratings yet
- Pressure Transducer Davs 311-1-0 Volt - XCMG PartsDocument1 pagePressure Transducer Davs 311-1-0 Volt - XCMG Partsej ejazNo ratings yet
- Inter 10 - Third ClassDocument96 pagesInter 10 - Third ClassRicardo Jackichan Barzola LopezNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: This Activity Contains 15 QuestionsDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: This Activity Contains 15 QuestionsRaman Kulkarni100% (1)