Professional Documents
Culture Documents
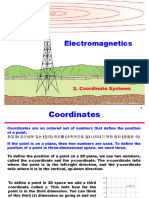
Coordinate Systems For Industrial Robots
Uploaded by
LenaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Coordinate Systems For Industrial Robots
Uploaded by
LenaCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal For Technological Research In Engineering ISSN (Online): 2347 - 4718
International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Engineering, Biomedical, Medical and Science
(ETEBMS - November 2016)
COORDINATE SYSTEMS FOR INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
Bhavin C. Shah1, Dr. Devendra Nagal2, Dr. Swati Sharma3
1
Research Scholar, 2Assistant Professor, 3Associate Professor,
1
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, 2,3Department of Electrical Engineering,
Jodhpur National University, Jodhpur, Rajasthan
ABSTRACT: For any industrial robot there has to be
certain coordinate system for proper functioning of
program. The coordinate system as defined by geometry are
Cartesian Coordinate System, Polar Coordinate System,
Cylindrical or Spherical Coordinate Systems. Industrial
robots used for medium payload has 6 Degrees of freedom
& uses mostly Cartesian Coordinate System. There are
various coordinate system in industrial robot which follow
any of the three coordinate system & widely used among it
is Cartesian coordinate system. The coordinate system used
in industrial robots are Robroot, World coordinate system,
Tool Coordinate System, Flange coordinate system & Base
coordinate system.
I. INTRODUCTION
Cartesian coordinate system is a system that uniquely
specifies each point in plane by a pair of numerical
coordinates, i.e. the signed distances to the point from two
FIG.2: ILLUSTRATION OF CARTESIAN COORDINATE
fixed perpendicular directed lines. Each reference line is
SYSTEM
known as coordinate axis and the point where they meet is
Polar coordinate system is a 2Dcoordinate system . Here
known as its origin (0, 0). The coordinates can also be
each point on a plane is found by a distance from a reference
defined as the perpendicular projections of the point onto the
point and an angular distance from a reference direction[2].
two axes also known to as signed distances from the
The reference point isanalogous to the origin of a Cartesian
origin[1]. Fig 1 & 2 shows the illustration of Cartesian
coordinate system and is called the pole. The ray from the
Coordinate System. Fig 1 shows the point of intersection in
pole in the reference direction is known as the polar axis.
space such as (-3, 1), (2, 3) & (-1.5, -2.5). Fig 2 shows the
The distance from the pole is called the radius of the
circle whose radius is 2 & centered at origin & illustrates the
coordinate and the angle is called the angular coordinate or
equation for the coordinate system as X2 + Y2 = 4. Cartesian
polar angle or azimuth. Fig 3 shows the polar coordinate
coordinate system resembles the X, Y & Z plane in 3
system whose representation in 2D is given as (3.60º) & (4,
Dimensional plane which can help in finding the effect of the
210º)[3].
point of intersection of that axes in space i.e. in Z plane. This
gives the translational motions to the industrial robots i.e. X,
Y & Z.
FIG.1: ILLUSTRATION OF CARTESIAN COORDINATE FIG.3: ILLUSTRATION OF POLAR COORDINATE
SYSTEM SYSTEM
www.ijtre.com Copyright 2016.All rights reserved. 191
International Journal For Technological Research In Engineering ISSN (Online): 2347 - 4718
International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Engineering, Biomedical, Medical and Science
(ETEBMS - November 2016)
Spherical coordinate system is a 3D space where the position B. WORLD COORDINATE SYSTEM:
of a point is specified by the radial distance, its polarand World Coordinate System in most cases is located in the
azimuthal angle on a reference plane,that passes through its robot base.World coordinate system is freely definable and
origin and is orthogonal to the zenith.The polar angle is also uses the origin of Robroot& Base. It uses the Cartesian
known as zenith angle, colatitudes, inclination angle, coordinate system i.e. X, Y, Z plane to define the
ornormal angle. Spherical coordinate is denoted by (r, θ, Translational Motion of the robot axes & A, B, C to define
φ)[4] Fig 4 shows the illustration of spherical coordinate the Rotational Motion of the robot axes with regards to the
system where the X, Y,Z plane represents the (r, θ, φ) in 3D translational motion of the robot axes where X//C, Y//B,
space & is resembling the radial distance, polar angle & Z//A.
azimuthal angle. Spherical coordinate can also be extended to
higher standard polar form also referred to as Hyperspherical
coordinate System[5].
FIG.6: WORLD COORDINATE SYSTEM
FIG.4: ILLUSTRATION OF SPHERICAL COORDINATE
SYSTEM
II. ROBOTCOORDINATE SYSTEM
The industrial robot coordinate system widely follows the
Cartesian coordinate system. Most industrial robot comprises FIG.7: TRANSLATIONAL & ROTATIONAL MOTION
of 6 Degrees of freedom i.e. 6 axis arm robot. The coordinate RELATIVE TO WORLD COORDINATE SYSTEM
system for industrial robot are Robroot, World, Tool, Flange,
Base coordinate system. C. FLANGE COORDINATE SYSTEM:
Flange coordinate system is fixed at the robot flange & the
origin is the center of the robot flange. It is used as the origin
for the tool.
FIG.5: ROBOT COORDINATE SYSTEM
FIG.8: FLANGE COORDINATE SYSTEM
A. ROBROOT COORDINATE SYSTEM:
Robroot is the default coordinate system of the robot. D. TOOL COORDINATE SYSTEM:
Robrootdefines the position of the robot relative to the World Tool coordinate system is freely definable. The origin of the
Coordinate System.The origin of the robot for tool coordinate system is called the Tool Center Point (TCP)
RobrootCordinate system is fixed in the robot base. and is used for tools.
www.ijtre.com Copyright 2016.All rights reserved. 192
International Journal For Technological Research In Engineering ISSN (Online): 2347 - 4718
International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Engineering, Biomedical, Medical and Science
(ETEBMS - November 2016)
[6] Use & programming of industrial robots, KUKA
Gmbh
FIG.9: TOOL COORDINATE SYSTEM
E. BASE COORDINATE SYSTEM:
Base coordinate system defines the position of the base
relative to the World Coordinate System. Base coordinate
system is freely definable and is used for tools &fixtures[6].
FIG.10: BASE COORDINATE SYSTEM
III. CONCLUSION
From the above discussion it is clear that Cartesian
coordinate system is well suited and widely used coordinate
system for industrial robots. The other coordinate systems
may be used depending on the manufacturer’s way of
embedding the system, but due to 3D space of Cartesian
coordinate system & the use of Translational & Rotational
motion relative to World coordinate system, which is best
suited for 6 axes industrial robot i.e. 6 D.O.F. industrial
robot, Cartesian coordinate system is widely used for
industrial robots.
REFERENCES
[1] A Tour of the Calculus, David Berlinski
[2] Brown, Richard G. (1997). Andrew M. Gleason,
Advanced Mathematics: Precalculus with Discrete
Mathematics and Data Analysis. Evanston, Illinois:
McDougal Littell.
[3] David J. Griffiths (1999). Introduction to
Electrodynamics. Prentice Hall
[4] Korn GA, Korn TM (1961). Mathematical
Handbook for Scientists and Engineers. New York:
McGraw-Hill. pp. 174–175.
[5] Sauer R, Szabó I (1967). MathematischeHilfsmittel
des Ingenieurs. New York: Springer Verlag. pp. 95–
96
www.ijtre.com Copyright 2016.All rights reserved. 193
You might also like
- Javi ProgrammingDocument8 pagesJavi ProgrammingJoseNo ratings yet
- Phycc101 Assignment Dr. AmritaDocument1 pagePhycc101 Assignment Dr. Amritaनमस्कारम्No ratings yet
- CAD U1 Lectures VJDocument31 pagesCAD U1 Lectures VJMARUTHISH KUNCHAMNo ratings yet
- Coordinate SystemsDocument7 pagesCoordinate SystemsPrashanth BnNo ratings yet
- Emft Report (MOMINA JAVED)Document11 pagesEmft Report (MOMINA JAVED)Fatima SheikhNo ratings yet
- Novel Coordinate Transformations For Antenna Applications: IEEE Transactions On Antennas and Propagation January 1985Document7 pagesNovel Coordinate Transformations For Antenna Applications: IEEE Transactions On Antennas and Propagation January 1985serk serkNo ratings yet
- Robot-Sensor System Integration by Means Vision Ultrasonic Sensing For Localization and Recognition ObjectsDocument7 pagesRobot-Sensor System Integration by Means Vision Ultrasonic Sensing For Localization and Recognition ObjectsRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Photogrammetric ConceptsDocument48 pagesPhotogrammetric Conceptsthereals.contactNo ratings yet
- Robotic ArmDocument22 pagesRobotic ArmEbru SayılganNo ratings yet
- Ahmad Najib 135833 - Assigment (Part DR Wan) - Eem345 ManufactDocument9 pagesAhmad Najib 135833 - Assigment (Part DR Wan) - Eem345 ManufactNajib HairiNo ratings yet
- Experimental Determination of Robot Workspace by MDocument9 pagesExperimental Determination of Robot Workspace by MThanh Hai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ma11 4Document6 pagesMa11 4이길현No ratings yet
- Referensi TrilaterasiDocument15 pagesReferensi TrilaterasiAlf DzoelkiefliNo ratings yet
- A New Aproach For Line Following RobotDocument6 pagesA New Aproach For Line Following RobotmonauliputriNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document96 pagesPart 1andenet100% (1)
- Aeletters 2023 8 2 2Document8 pagesAeletters 2023 8 2 2miskoscribdNo ratings yet
- Week3 VTE465 LectureDocument69 pagesWeek3 VTE465 LecturePontakorn HomkhaoNo ratings yet
- Robust Control For A Delta Robot: Hui-Hung Lin, Chih-Chin Wen, Shi-Wei Lin, Yuan-Hung Tai and Chao-Shu LiuDocument6 pagesRobust Control For A Delta Robot: Hui-Hung Lin, Chih-Chin Wen, Shi-Wei Lin, Yuan-Hung Tai and Chao-Shu LiuDandro-LinkNo ratings yet
- Robot Reference FramesDocument12 pagesRobot Reference Framespreethu02No ratings yet
- 2-Coordinate SystemsDocument16 pages2-Coordinate Systemsjunwoo3614No ratings yet
- A New Approach To The Design of A Delta Robot With A Desired Workspace PDFDocument17 pagesA New Approach To The Design of A Delta Robot With A Desired Workspace PDFRauLasH26No ratings yet
- SNI 19-6724-2002 Horizontal Control NetworkDocument88 pagesSNI 19-6724-2002 Horizontal Control Networkseirac.1782No ratings yet
- A Calibration Procedure For The Parallel Robot Delta 4: P. Maurine, E. DombreDocument6 pagesA Calibration Procedure For The Parallel Robot Delta 4: P. Maurine, E. DombreHoracio GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Modelling of Multirotor UAVDocument6 pagesMathematical Modelling of Multirotor UAVchernet tayeNo ratings yet
- Use of A Laser Tracker To Actively Coordinate The Motion of A 3 Meter Industrial Robot To Within 50 MicronsDocument7 pagesUse of A Laser Tracker To Actively Coordinate The Motion of A 3 Meter Industrial Robot To Within 50 MicronsClenaNo ratings yet
- Gantry Robot Kinematic Analysis User Interface Based On Visual Basic and MATLABDocument4 pagesGantry Robot Kinematic Analysis User Interface Based On Visual Basic and MATLABYuva NNo ratings yet
- The Kinematics Analysis of Robotic Arm ManipulatorDocument9 pagesThe Kinematics Analysis of Robotic Arm ManipulatorJorge Adrian Lucas SanchezNo ratings yet
- Advanced Techniques of Industrial Robot Programming 79Document21 pagesAdvanced Techniques of Industrial Robot Programming 79Pablo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Aa4262 05Document13 pagesAa4262 05abdelmoamen nosirNo ratings yet
- Handout #5 Theodolite and Total StationDocument5 pagesHandout #5 Theodolite and Total StationCCCCCCCNo ratings yet
- 7985 Origin Macro-PostDocument4 pages7985 Origin Macro-PostdiaboloboyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Review of Coordinate SystemDocument2 pagesChapter - 2 Review of Coordinate SystemAnandNo ratings yet
- 3D Surface Mapping Using Ultrasonic SensorsDocument3 pages3D Surface Mapping Using Ultrasonic SensorsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- What Is A Coordinate System?: Getting StartedDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Coordinate System?: Getting StartedVinothRajagopalNo ratings yet
- 雷达坐标系统Document16 pages雷达坐标系统myliberalbayNo ratings yet
- EUROCONTROL ASTERIX CAT017 Annex A (Co-Ordinate Transformation Algorithms For The Hand-Over of Targets Between POEMS Interrogators)Document16 pagesEUROCONTROL ASTERIX CAT017 Annex A (Co-Ordinate Transformation Algorithms For The Hand-Over of Targets Between POEMS Interrogators)IsaacNo ratings yet
- Tool GeometryDocument14 pagesTool GeometrydineshsettiNo ratings yet
- Robot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlFrom EverandRobot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlNo ratings yet
- Robotics - Module 1 (Part)Document8 pagesRobotics - Module 1 (Part)Habib MasumNo ratings yet
- Geometric Modeling: Principles of Computer GraphicsDocument10 pagesGeometric Modeling: Principles of Computer GraphicsNanda KishoreNo ratings yet
- Robotic Pool: An Experiment Automatic Potting: Johan Roth3, of Computing, 3dept. of ofDocument6 pagesRobotic Pool: An Experiment Automatic Potting: Johan Roth3, of Computing, 3dept. of ofVansala GanesanNo ratings yet
- CG Question BankDocument17 pagesCG Question BankAnonymous DFpzhrRNo ratings yet
- AM 8th Sem Solution 17.05.19 in CourseDocument16 pagesAM 8th Sem Solution 17.05.19 in CourseRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- Advanced Robotics DR BobDocument166 pagesAdvanced Robotics DR Bober_arun76No ratings yet
- Localization Data Fusion RobotinoDocument8 pagesLocalization Data Fusion RobotinoAlexandre RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Auto-Balancing Two Wheeled Inverted Pendulum RobotDocument6 pagesAuto-Balancing Two Wheeled Inverted Pendulum Robotsaran gowdaNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Finite Element Analysis Coordinate SystemDocument12 pagesANSYS Finite Element Analysis Coordinate SystemnahoNo ratings yet
- ASME B89.4.19 Performance Evaluation Tests and Geometric Misalignments in Laser Trackers VolumeDocument15 pagesASME B89.4.19 Performance Evaluation Tests and Geometric Misalignments in Laser Trackers VolumeJDNo ratings yet
- DC-Surveyor - The Coordinate SystemDocument11 pagesDC-Surveyor - The Coordinate SystemSibgatullah najarNo ratings yet
- MapInfoProUserGuide Projections ChapterDocument21 pagesMapInfoProUserGuide Projections ChapterJaakLa100% (1)
- O'Donnell, C. F. (1958) - Inertial Navigation PDFDocument30 pagesO'Donnell, C. F. (1958) - Inertial Navigation PDFAnonymous OARSwGsNo ratings yet
- Murcia 2018Document11 pagesMurcia 2018Nguyễn Khải ÂnNo ratings yet
- 51885.kopriva JSPT 99Document17 pages51885.kopriva JSPT 99eyob233No ratings yet
- Vision-Based Autonomous Approach and Landing For ADocument9 pagesVision-Based Autonomous Approach and Landing For AWei Jiang NgNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 StockDocument22 pagesUnit-3 StockRajiv MpwbNo ratings yet
- Methodology For Kinematics Modeling of Articulated Rovers, Enhanced With Fuzzy Logic SystemDocument6 pagesMethodology For Kinematics Modeling of Articulated Rovers, Enhanced With Fuzzy Logic SystemmaxamaxaNo ratings yet
- ADA484864Document42 pagesADA484864bambilibomsNo ratings yet
- Approaches For Low-Cost Robotic Prototypes: Figure 1 - The Dalton RobotDocument7 pagesApproaches For Low-Cost Robotic Prototypes: Figure 1 - The Dalton RobotEdna AramizoNo ratings yet
- Interactive Volume Rendering With Ray TracingDocument22 pagesInteractive Volume Rendering With Ray TracingzhangNo ratings yet
- Automation of Packaging and Material Handling Using Programmable Logic ControllerDocument5 pagesAutomation of Packaging and Material Handling Using Programmable Logic ControllerLenaNo ratings yet
- 2011 - SFMDocument6 pages2011 - SFMLenaNo ratings yet
- 2011 - Intelligent SFMDocument6 pages2011 - Intelligent SFMLenaNo ratings yet
- 1992 - Design and Planning Problems in FlexibleDocument25 pages1992 - Design and Planning Problems in FlexibleLenaNo ratings yet
- Integrales Tabla CompletaDocument6 pagesIntegrales Tabla CompletaArias Miguel100% (2)
- CT5251 Special StructuresDocument479 pagesCT5251 Special StructuresbsitlerNo ratings yet
- AnlysisDocument15 pagesAnlysisMoustafaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Cartesian Coordinate SystemDocument64 pagesLesson 1 The Cartesian Coordinate SystemJoy Christie LanciolaNo ratings yet
- Creo Parametric 2Document174 pagesCreo Parametric 2anuj singh100% (1)
- Introduction To TensorsDocument36 pagesIntroduction To TensorsMuhammad AdeelNo ratings yet
- Manual Ishida Astra Counter Printer Service 2001Document142 pagesManual Ishida Astra Counter Printer Service 2001Juan Alfonso Samayoa AzmitiaNo ratings yet
- Euclidean Equivalent of Minkowski's Space-Time Theory and The Corresponding Model of Elementary Particles ("Cuantex" Model)Document8 pagesEuclidean Equivalent of Minkowski's Space-Time Theory and The Corresponding Model of Elementary Particles ("Cuantex" Model)Premier PublishersNo ratings yet
- GD&TDocument138 pagesGD&Tأيمن أحمدNo ratings yet
- Franconeri ExperCeptionDotNet DataVisQuickRefDocument1 pageFranconeri ExperCeptionDotNet DataVisQuickRefDinh TranNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Math GraphingDocument2 pagesRubric For Math GraphingJM tuvieron100% (1)
- Fanuc - Teach Pendant BasicsDocument5 pagesFanuc - Teach Pendant BasicsRay WongNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics: - IntroductionDocument18 pagesComputer Graphics: - IntroductiondevilkingssNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7Document6 pagesTutorial 7nithinNo ratings yet
- STAAD 2.17.8 Design ParametersDocument3 pagesSTAAD 2.17.8 Design ParametersFWICIPNo ratings yet
- Advanced Flight Dynamics and Elements of Flight ControlDocument367 pagesAdvanced Flight Dynamics and Elements of Flight Controlpolfzxkwwavcrlnllz100% (1)
- Buildings 12 02092Document49 pagesBuildings 12 02092SUMAN CIVILNo ratings yet
- 2005 CXC PractiseDocument4 pages2005 CXC Practisesnowflakes21No ratings yet
- Euler AnglesDocument21 pagesEuler AnglesSachin ShendeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - MAAM SUKIEDocument4 pagesLesson Plan - MAAM SUKIEJenefer Suspeñe FernandezNo ratings yet
- Colombo Et Al ISR-Robotik06Document12 pagesColombo Et Al ISR-Robotik06Ravikumar NagulaNo ratings yet
- Polar-Coordinates 1Document8 pagesPolar-Coordinates 1Huncho7No ratings yet
- Trigonometric GraphsDocument35 pagesTrigonometric GraphsBomi KimNo ratings yet
- Alfano Visualdata Manual 2.0 enDocument34 pagesAlfano Visualdata Manual 2.0 enHendrik Castens100% (1)
- Scan 04-Nov-2018Document24 pagesScan 04-Nov-2018Burhan KanchwalaNo ratings yet
- Energy WorksheetDocument9 pagesEnergy Worksheetthethtertin17theinNo ratings yet
- FCS LectureNotes v7Document204 pagesFCS LectureNotes v7wifek meznyNo ratings yet
- Adm-td10-q1-m1-l1-Sub 3 Lesson 4 (Manipulate Cad Features As Per Job Requirement-2d)Document41 pagesAdm-td10-q1-m1-l1-Sub 3 Lesson 4 (Manipulate Cad Features As Per Job Requirement-2d)PRECIOUS FAITH VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Math LabDocument25 pagesMath LabnandinigourahaNo ratings yet
- Oracle SCM Cloud Using Planning CentralDocument114 pagesOracle SCM Cloud Using Planning CentralMiguel FelicioNo ratings yet
- Servocut 502: Abrasive CuttingDocument8 pagesServocut 502: Abrasive CuttingRepresentaciones y Distribuciones FALNo ratings yet