Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Septic Tank Handout
Uploaded by
Debkumar MukherjeeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Septic Tank Handout
Uploaded by
Debkumar MukherjeeCopyright:
Available Formats
Arup Guha Niyogi 41
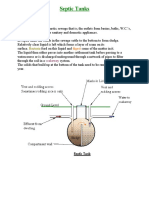
In areas where municipal underground sewage system is Soak pit is a simple pit, square or round dug in the
absent, septic tanks are used to treat WC solid waste. ground to dispose the septic tank effluent deep under
It is a sedimentation-cum-digestion tank where the flow ground.
of raw sewage is slowed down so that the solids settle They are good when the water table is sufficiently low
down at the bottom of the tank by sedimentation. and the soil is porous.
Simultaneously the settled sewage is enacted upon by
anaerobic bacteria, which digests it to reduce the solid A layer of sand and fine gravel is spread across the
by 60-70% producing gaseous & liquid resultants. The bottom to help disperse the flow. Depth should be
sludge settles at bottom & scum (grease, fat, etc. floats). between 1.5 and 4m deep, but never less than 1.5m
We must ensure airtight condition in this chamber to above the ground water table. The Soak Pit is filled
ensure anaerobic condition. The effluent that flows out with coarse rocks and gravel. The rocks and gravel will
of the anaerobic chamber still contains large amount of prevent the walls from collapsing, but will still
dissolved & suspended organic matter and must be provide adequate space for the waste-water.
disposed off carefully into a soak pit or dispersion
trenches of absorption in soil.
A detention period of 24-48 hours is allowed. Walls must
be plastered with rich cement mortar to make it
impervious. The invert level of the outlet pipe is kept 7-
10 cm lower than the inlet pipe and tee ends are
provided at the ends so that the scum does not flow
out. Long vent pipes are added to disperse the gaseous
waste. The sludge is cleared regularly, say @ 1 year.
Arup Guha Niyogi 42
Details for small septic tanks:
Recommended construction for small septic tanks:
Top: Reinforced concrete poured 3- to 4-in. thick with two 3/8-
in. steel rods per ft, or equivalent, and a 20”×20” manhole over
inlet, or precast reinforced concrete 1’ slabs with sealed joints.
Bottom: 4” RC thick with reinforcing as in “top” or plain
poured concrete 6in. thick.
Walls: RCC poured 4” thick with 3/8” steel rods on 6” centers
both ways, or equivalent; plain poured concrete 6in. thick; 8”
brick masonry with 1” cement plaster inside finish and block
cells filled with mortar.
Concrete mix: One bag of cement to 2.25” of sand to 3cft of
gravel with 5gal of water for moist sand. Use 1:3 cement
mortar for masonry and 1:2 mortar for plaster finish. Gravel or
crushed stone and sand shall be clean, hard material. Gravel
shall be 0.25” to 0.5” in size; sand from fine to 0.25”
Bedding: At least 3” of sand or pea gravel, leveled.
Ref: Environmental engineering. Water, wastewater, soil, and
groundwater treatment and remediation - edited by Franklin J.
Agardy and Patrick Sullivan.—6th ed., Wiley, 2009
Arup Guha Niyogi 43
Ref: Environmental engineering. Water, wastewater, soil, and groundwater treatment and remediation - edited by Franklin J. Agardy and Patrick
Sullivan.—6th ed. Wiley, 2009
Arup Guha Niyogi 44
450߶ manhole 100 thick 200߶ gas pipe
cover RCC slab
550 WL Scum
board
1200
Inspection Chlorination
chamber chamber
75 thk BFS 150 thk PCC
Sectional elevation of septic tank
1000
100 dia
outlet
100 dia inlet
250 600 250 750 125 1200 125 750 250 600 250
Plan of Septic tank Scale 1:50
Arup Guha Niyogi 45
Soak Pit Schematic Diagram A-masonry ring B-stone or brick
aggregate C-brick chamber D-30cm thick outer casing with
coarse sand E-effluent from septic tank
Arup Guha Niyogi 46
Arup Guha Niyogi 47
NBC 2016 4.5.14.5.2 Septic tanks
Septic tanks can function only when it can be ensured that the contents inside these do not freeze at low
temperature. For this purpose, the septic tanks shall be located well below the frost line. The location of
manhole openings shall be marked by staves. Fencing around the septic tanks shall be provided for
discouraging traffic over them. As the rate of biological activity is reduced by 50 percent for every 10°C fall in
temperature, the capacity of septic tanks shall be increased by 100 percent for operation at 10°C over that
for operation at 20°C.
The construction of septic tanks is preferred in rural and fringe areas of suburban and isolated buildings where
underground system may neither be feasible nor economical. Septic tanks are only recommended for small
communities and institutions whose contributory population does not exceed 300.
4.5.14.5.3 Seepage pits
Seepage pits can function only when the soil and subsoil conditions are favourable. Frozen soil extending to a
great depth would preclude the use of such disposal devices in view of the lower water absorption capacity. The
discharge of effluent should be made below the frost line.
Arup Guha Niyogi 48
You might also like
- Concrete Construction for the Home and the FarmFrom EverandConcrete Construction for the Home and the FarmNo ratings yet
- Cementing Oil and Gas Wells EffectivelyDocument25 pagesCementing Oil and Gas Wells EffectivelyvastaguenNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Septic Tank & SoakpitDocument3 pagesChecklist For Septic Tank & SoakpitRupesh KhandekarNo ratings yet
- Septic Tank and Soak PitDocument36 pagesSeptic Tank and Soak PitRouny Paul100% (2)
- Cementing Oil and Gas WellsDocument25 pagesCementing Oil and Gas WellshusnainzaidiNo ratings yet
- Septic Tank Concept and DesignDocument35 pagesSeptic Tank Concept and Designanil kumarNo ratings yet
- Septic Tank Purpose - FunctionDocument35 pagesSeptic Tank Purpose - FunctionMasnun Rahman100% (2)
- Designing A Septic TankDocument2 pagesDesigning A Septic TankPoru ManNo ratings yet
- Designing A Septic TankDocument2 pagesDesigning A Septic TankMamoun Awad HassanNo ratings yet
- CE 312 - Sewage Disposal in Unsewered Areas PDFDocument9 pagesCE 312 - Sewage Disposal in Unsewered Areas PDFkennysawegNo ratings yet
- Grey Water Management Resource Book GoIDocument38 pagesGrey Water Management Resource Book GoIsalilNo ratings yet
- Bihar Urban Infrastructure Development Corporation Ltd. Drinking Water Supply SchemeDocument19 pagesBihar Urban Infrastructure Development Corporation Ltd. Drinking Water Supply Schemesumit249100% (1)
- Estimate & Costing 3rd Unit1Document18 pagesEstimate & Costing 3rd Unit1pasmanupendra539No ratings yet
- Fibreglass Septic Tanks: SpecificationsDocument4 pagesFibreglass Septic Tanks: SpecificationsAnonymous 2ZiabUZNo ratings yet
- SPT SPTDocument7 pagesSPT SPTRadoNounNo ratings yet
- Septic Tank Components and Design of Septic TankDocument21 pagesSeptic Tank Components and Design of Septic TankChau Suktana EnlingNo ratings yet
- Septic Tank Installation ManualDocument12 pagesSeptic Tank Installation Manualingeni0sNo ratings yet
- Low Cost SanitationDocument13 pagesLow Cost Sanitation27euphoriaNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Control Room Septic Tank & SoakpitDocument2 pagesChecklist For Control Room Septic Tank & SoakpitRupesh KhandekarNo ratings yet
- Well Completion Development and Maintenance of WellsDocument33 pagesWell Completion Development and Maintenance of WellsArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Session 23. Inlet Outlet StructureDocument47 pagesSession 23. Inlet Outlet StructureLilu. sahuNo ratings yet
- Septic TankDocument19 pagesSeptic TankDevendra Sharma100% (1)
- Proposed Swimming Pool Specs for Yadavindra School PatialaDocument6 pagesProposed Swimming Pool Specs for Yadavindra School PatialaEr Jc Ajay ThakulNo ratings yet
- Type of WellsDocument10 pagesType of WellsAddrien Daniel100% (1)
- Seminar Report EditedDocument14 pagesSeminar Report Editedgreeshma cNo ratings yet
- Guidelines of Septic Systems DesignDocument16 pagesGuidelines of Septic Systems DesignJowie100% (1)
- Wickes Underground DrainageDocument6 pagesWickes Underground DrainageMohammed Asimuddin FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Water Pan For Runoff Water Harvesting PDFDocument4 pagesWater Pan For Runoff Water Harvesting PDFmulwa2009No ratings yet
- CE335 - Sewage Disposal SystemDocument49 pagesCE335 - Sewage Disposal Systemmdnitollamastem12hNo ratings yet
- Lec 11Document4 pagesLec 11Ashutosh ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Groundwater ProductionDocument24 pagesChapter 11 - Groundwater Productionنيرمين احمدNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 (83-87Document5 pagesChapter 8 (83-87Affinity HydroNo ratings yet
- Professor Dr. Md. Jahangir AlamDocument47 pagesProfessor Dr. Md. Jahangir AlamShah Mohammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Inclined Plate ClarifierDocument2 pagesInclined Plate ClarifierKelvin SiewNo ratings yet
- Septic Tank - Components and Design of Septic Tank Based On PopulationDocument7 pagesSeptic Tank - Components and Design of Septic Tank Based On Populationمنير أحمدNo ratings yet
- Water Supply & Waste DisposalDocument17 pagesWater Supply & Waste DisposalRNo ratings yet
- An Inexpensive, Do It Yourself Water WellDocument44 pagesAn Inexpensive, Do It Yourself Water WellKasiaNo ratings yet
- CMHC Septic and Well Question ChecklistDocument8 pagesCMHC Septic and Well Question Checklistwahixo2362No ratings yet
- PlumbingDocument3 pagesPlumbingLiezel FabellaNo ratings yet
- Building DesignDocument31 pagesBuilding DesignSave YuNo ratings yet
- Dewatering Revised Oct 98Document11 pagesDewatering Revised Oct 98Mahmoud BreamaNo ratings yet
- Secondary Containment InspectionsDocument3 pagesSecondary Containment InspectionsNishtha SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Dewatering Techniques ExplainedDocument45 pagesDewatering Techniques ExplainedMadhu AsopaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER MPDocument6 pagesREVIEWER MPAn-gela Dar-lene MangahisNo ratings yet
- Sewer Appurtenances of BuildingsDocument10 pagesSewer Appurtenances of Buildingsdaniyalahmad119No ratings yet
- Cannal Systems For IrrigationDocument27 pagesCannal Systems For IrrigationGretchen CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Types of Tube Wells & Its ConstructionDocument51 pagesTypes of Tube Wells & Its Constructionrbroy_dwsd88% (8)
- Under-Drainageoflinedcanals-Codeofpractice /: Indian StandardDocument8 pagesUnder-Drainageoflinedcanals-Codeofpractice /: Indian StandardAnonymous oVmxT9KzrbNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Rain PDFDocument34 pagesUnit 4 Rain PDFNaGamani KanDanNo ratings yet
- Instalatii Complete de DrenajDocument6 pagesInstalatii Complete de DrenajCatalinaLixandruNo ratings yet
- Unit 3B Sewer AppurtenancesDocument61 pagesUnit 3B Sewer AppurtenancesNaGamani KanDanNo ratings yet
- pdf3 - Builders - Detailed - Manual - Upgradeable - Blair - VIP PDFDocument34 pagespdf3 - Builders - Detailed - Manual - Upgradeable - Blair - VIP PDFHannah Schreckenbach100% (1)
- GW 5-Tube Well, Parts and TypesDocument28 pagesGW 5-Tube Well, Parts and Typeswajid malik100% (1)
- DewateringDocument6 pagesDewateringIsife OlisaemekaNo ratings yet
- pond-installationDocument70 pagespond-installationaraojose19No ratings yet
- GROUTING RULES FOR WELLSDocument23 pagesGROUTING RULES FOR WELLSMohd IllahiNo ratings yet
- Well Completion2Document36 pagesWell Completion2kuda kwasheNo ratings yet
- Well Water BasicsDocument5 pagesWell Water Basicsbontu gadisaNo ratings yet
- Riprap Shear Stress DesignDocument5 pagesRiprap Shear Stress DesignphatmatNo ratings yet
- Design of Septic Tank: Engineering Utilities 2Document23 pagesDesign of Septic Tank: Engineering Utilities 2Jovy AndoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bridge FoundationDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Bridge FoundationAbinash MandalNo ratings yet
- Basf Masterseal NP 473u TdsDocument3 pagesBasf Masterseal NP 473u TdsAaaNo ratings yet
- Nverted Double T-Beams and SlabsDocument20 pagesNverted Double T-Beams and SlabsAref AbadelNo ratings yet
- Accelerating - and Retarding Admixtures - IcoldDocument34 pagesAccelerating - and Retarding Admixtures - IcoldTansel YılmazNo ratings yet
- Wollastonite Irjet PDFDocument5 pagesWollastonite Irjet PDFChidananda GNo ratings yet
- Think Wood 2022 Timber Trends - FINAL - 02222022Document9 pagesThink Wood 2022 Timber Trends - FINAL - 02222022Andrew EckNo ratings yet
- Sushant School of Art and ArchitectureDocument6 pagesSushant School of Art and Architectureankushsingla.barch21No ratings yet
- Holcim CementsDocument4 pagesHolcim CementsIMJ JNo ratings yet
- Design of Composite Columns v3 - Ver1 (KJ) AMDDocument104 pagesDesign of Composite Columns v3 - Ver1 (KJ) AMDImran SaikatNo ratings yet
- IS Code: 12330Document11 pagesIS Code: 12330AEENo ratings yet
- Admixtures For ShotcreteDocument4 pagesAdmixtures For ShotcreteJesús Luis Arce GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Structures Deliverables For DTACDocument2 pagesStructures Deliverables For DTACAndreea BaciuNo ratings yet
- Haramaya University Haramaya Institute of Technolgy School of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument62 pagesHaramaya University Haramaya Institute of Technolgy School of Electrical and Computer EngineeringHailu HailuNo ratings yet
- Rcdprob34 66Document45 pagesRcdprob34 66Grachelle Andrea Capiral80% (25)
- Design Standards For Park and Trail DevelopmentDocument319 pagesDesign Standards For Park and Trail DevelopmentturcanupaulNo ratings yet
- Trailer Mounted Concrete Pump Catalog - Taian Sinotep Machinery Co.,Ltd - Concrete Pump Manufacturer in ChinaDocument25 pagesTrailer Mounted Concrete Pump Catalog - Taian Sinotep Machinery Co.,Ltd - Concrete Pump Manufacturer in ChinasinotepconcretepumpNo ratings yet
- Poultry Cost Estimates - 01Document10 pagesPoultry Cost Estimates - 01Joseph RoyNo ratings yet
- Method Statement External Application of Corrosion InhibitorDocument4 pagesMethod Statement External Application of Corrosion InhibitorKannan MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Datasheet File Nitoflor FC150Document4 pagesDatasheet File Nitoflor FC150hendra wahyuNo ratings yet
- Cimenturi Hibride Alcaline - Modelo Gluvosky PDFDocument6 pagesCimenturi Hibride Alcaline - Modelo Gluvosky PDFMiguelAngelDelgadoD'AppollonioNo ratings yet
- Hollow Block MasonryDocument4 pagesHollow Block MasonrySandeep ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- BT - Top 1 ImhotepDocument23 pagesBT - Top 1 Imhotepchanelle gutierrezNo ratings yet
- CivilDocument14 pagesCivilDebendra Dev KhanalNo ratings yet
- Tech Spec of Hume Pipes OF NP GRADEDDocument5 pagesTech Spec of Hume Pipes OF NP GRADEDManash HalderNo ratings yet
- 75 Civil Engineering Questions & AnswersDocument2 pages75 Civil Engineering Questions & AnswersTimothy James M. MadridNo ratings yet
- Holorib Metal Decking PDFDocument12 pagesHolorib Metal Decking PDFRichard KansinallyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-1Document25 pagesUnit 2-1Tharun SampathNo ratings yet
- FRP Lamella V3 Manual EngDocument96 pagesFRP Lamella V3 Manual EngNaida AdemovicNo ratings yet
- Cube Test RQ, FormDocument1 pageCube Test RQ, FormardsilvaNo ratings yet
- PresconDocument3 pagesPresconsam dorilloNo ratings yet
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- Practical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionFrom EverandPractical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionFrom EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- Upcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)From EverandUpcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Power Quality in Power Systems and Electrical MachinesFrom EverandPower Quality in Power Systems and Electrical MachinesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- C++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingFrom EverandC++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialFrom EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Off-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemFrom EverandOff-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemNo ratings yet
- Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignFrom EverandOpen Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignNo ratings yet
- The Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026From EverandThe Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Digital Gold: The Beginner's Guide to Digital Product Success, Learn Useful Tips and Methods on How to Create Digital Products and Earn Massive ProfitsFrom EverandDigital Gold: The Beginner's Guide to Digital Product Success, Learn Useful Tips and Methods on How to Create Digital Products and Earn Massive ProfitsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesFrom EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsFrom EverandLithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Collection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsFrom EverandCollection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)