Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Csec Human and Social Biology Syllabus Outline
Uploaded by
CHRISTOPHER SCALE0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
113 views3 pagesThe Human and Social Biology course is divided into 5 sections:
(1) Living Organisms and the Environment, (2) Life Processes, (3) Hereditary and Variation, (4) Disease and its Impact on Humans, and (5) The Impact of Health Practices on the Environment. The examination consists of a multiple choice paper worth 40% and a structured response paper worth 60%, with questions covering topics from each section.
Original Description:
Original Title
HSB Syllabus Outline
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Human and Social Biology course is divided into 5 sections:
(1) Living Organisms and the Environment, (2) Life Processes, (3) Hereditary and Variation, (4) Disease and its Impact on Humans, and (5) The Impact of Health Practices on the Environment. The examination consists of a multiple choice paper worth 40% and a structured response paper worth 60%, with questions covering topics from each section.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
113 views3 pagesCsec Human and Social Biology Syllabus Outline
Uploaded by
CHRISTOPHER SCALEThe Human and Social Biology course is divided into 5 sections:
(1) Living Organisms and the Environment, (2) Life Processes, (3) Hereditary and Variation, (4) Disease and its Impact on Humans, and (5) The Impact of Health Practices on the Environment. The examination consists of a multiple choice paper worth 40% and a structured response paper worth 60%, with questions covering topics from each section.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
CSEC HUMAN AND SOCIAL BIOLOGY
SYLLABUS OUTLINE
The Human and Social Biology course is divided into FIVE sections as
follows:
Section A: Living Organisms And the Environment
- Characteristics of living organisms with focus on mammals (humans)
- Structure of animal and plant cells; microbes (bacteria, viruses, fungi)
- Function of cell organelles
- Cell specialization and levels of organization in humans
- Selected cells in the human body (sperm, egg, muscle, epithelial, nerve)
- Osmosis, diffusion and active transport
- Photosynthesis
- Food chains, webs, trophic levels, energy flow
- Nutrient cycling (carbon and nitrogen cycles)
Section B: Life Processes
- Nutrition (balanced diet, nutrients, malnutrition, causes of constipation
and diarrhea, tooth structure, tooth decay, digestion, importance of
enzymes, structure of villus)
- The Respiratory System (structure, breathing, vital capacity, gaseous
exchange, anaerobic/aerobic respiration, ADP/ATP, mouth to mouth
resuscitation, cigarette smoking)
- The Circulatory System (heart structure, blood components, blood
vessels, blood clotting, heart attack causes & effects, lymphatic system)
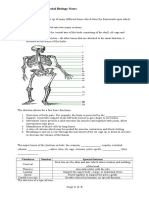
- Skeletal System (skeleton, bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, joints,
muscles)
- Excretion and Homeostasis (kidney, nephron structure & function,
excretory organs, homeostasis, feedback mechanisms, osmoregulation,
blood sugar regulation, heat, temperature regulation)
- Coordination and Control (nervous system, the brain, neurons, sense
organs, structure of eye, sight defects, endocrine system)
- The Reproductive System (sexual/asexual, male & female reproductive
systems, menstrual cycle, fertilization and pregnancy, birth process,
prenatal care, abortion, birth control methods, family planning)
Section C: Hereditary and Variation
- Cell division (mitosis and meiosis)
- Genetic variation
- Inheritance (DNA, RNA, chromosomes, genes, inheriting a single pair of
characteristics, sex determination, sex-linked traits, blood groups)
- Genetic Engineering (applications, pros and cons)
Section D: Disease and its Impact on Humans
- Health, diet, exercise
- Types of diseases, signs & symptoms
- Causes, prevention and treatment of obesity, diabetes (type 2),
hypertension
- Transmission of the following infectious diseases: HIV/AIDS, gonorrhea,
acute respiratory infections, ringworm, typhoid, tuberculosis, cholera,
dengue, herpes, gastroenteritis
- Effects of STDs on individuals including pregnant women
- Personal hygiene, sterilization, disinfection, antiseptics, antibiotics
- Vectors and life cycle, control e.g. mosquitoes, houseflies, rats
- Immunity, immunization, vaccination
- Drug use and dependence; social and physiological effects
Section E: The Impact of Health Practices on the Environment
- Pollution, pollutants and effects on the environment, control methods
- Water pollution, water cycle, small and large-scale water purification,
testing for bacteria, human activities on water supplies, contaminated
water
- Sewage treatment (biological filter, activated sludge methods), disposal
practices, pit latrine, landfills
- Solid waste management, recycling, domestic refuse disposal,
biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste
Examination Format
1. Paper 2- 6 compulsory questions (2hrs)
Section A- 4 structured questions; One question is investigative/practical-
based; Each question is worth 15 marks.
Section B- 2 structured essay questions;
Each question is worth 15 marks.
Total: 90 marks (60%)
2. Paper 1- 60 multiple choice questions (1hr 15 mins)
Total: 60 marks (40%)
You might also like
- Jamaica Driver's Education Handbook: A Comprehensive Driver Training GuideFrom EverandJamaica Driver's Education Handbook: A Comprehensive Driver Training GuideNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science Mark Scheme CXCDocument9 pagesIntegrated Science Mark Scheme CXCPeter MissoleNo ratings yet
- Ecology Test For CSEC StudentsDocument3 pagesEcology Test For CSEC Studentsnehru09No ratings yet
- Westwood High School Mock Examination Grade XII March 2015 Biology Paper 01Document9 pagesWestwood High School Mock Examination Grade XII March 2015 Biology Paper 01Rhondene WintNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2002 P1 Specimen PaperDocument13 pagesCSEC Biology June 2002 P1 Specimen PaperJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- CSEC HUMAN & SOCIAL BIOLOGY NOTESDocument29 pagesCSEC HUMAN & SOCIAL BIOLOGY NOTESOsmany MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Barama Plywood Factory Location AnalysisDocument25 pagesBarama Plywood Factory Location AnalysisannmarieNo ratings yet
- Csec Agricultural Science Syllabus With Specimen PapersDocument138 pagesCsec Agricultural Science Syllabus With Specimen Papersapi-508592459No ratings yet
- CSEC Biology: Key Topics for Nutrition, Ecosystems & ClassificationDocument43 pagesCSEC Biology: Key Topics for Nutrition, Ecosystems & ClassificationMarcellus Lee100% (1)
- Biology - Paper 02 PDFDocument17 pagesBiology - Paper 02 PDFAlexander CorvinusNo ratings yet
- Cape Pure Mathσmatics Unit 1: Video Solutions are available atDocument191 pagesCape Pure Mathσmatics Unit 1: Video Solutions are available atJuan HaynesNo ratings yet
- Csec Integrated Science - Radiation NotesDocument12 pagesCsec Integrated Science - Radiation NotesSelina SookhansinghNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Submitted By: Caimoso, Tricia Ann D. Quiambao, Aliyah Lourdes D. Bs Psychology 3-3Document9 pagesDigestive System: Submitted By: Caimoso, Tricia Ann D. Quiambao, Aliyah Lourdes D. Bs Psychology 3-3Tricia Ann CaimosoNo ratings yet
- CSEC Bio Notes 2Document14 pagesCSEC Bio Notes 2MiaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Integrated Science June 1991 P1Document8 pagesCSEC Integrated Science June 1991 P1Saintm101No ratings yet
- CSEC 2005 Chemistry P2 (Jan)Document15 pagesCSEC 2005 Chemistry P2 (Jan)Dunstan NesbitNo ratings yet
- HSB - Lesson A1Document31 pagesHSB - Lesson A1Osmany MadrigalNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2005 P042Document8 pagesCSEC Biology January 2005 P042Makayla AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Mathematics CXC 2013Document13 pagesMathematics CXC 2013dggoode50% (2)
- CAPE Env. Science 2010 U1 P2Document15 pagesCAPE Env. Science 2010 U1 P2Christina Francis100% (1)
- CSEC Physics June 2010 P032Document11 pagesCSEC Physics June 2010 P032aidan kamrajNo ratings yet
- Understanding Base Quantities and Derived QuantitiesDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Base Quantities and Derived QuantitiesKogeela Vani VeerasingamNo ratings yet
- The 7 Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument34 pagesThe 7 Characteristics of Living OrganismsTonique GordonNo ratings yet
- CXC Jan 2000 p2Document7 pagesCXC Jan 2000 p2omar_oj_40% (1)
- Human & Social Biology 4th FormDocument23 pagesHuman & Social Biology 4th Formhedasdudh100% (1)
- HSB Section ADocument12 pagesHSB Section AAshford Thom100% (1)
- CSEC Study Guide - March 22, 2011Document12 pagesCSEC Study Guide - March 22, 2011ChantelleMorrisonNo ratings yet
- SBA Research OutlineDocument2 pagesSBA Research Outlinetavier whiteNo ratings yet
- CSEC Integrated Science June 2009 P2Document18 pagesCSEC Integrated Science June 2009 P2Sachin Bahadoorsingh0% (1)
- CSEC Human and Social Biology - The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesCSEC Human and Social Biology - The Skeletal SystemSamantha ThomasNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2013 June P1 PDFDocument11 pagesMathematics 2013 June P1 PDFMichael TimsonNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology - Vegetative ReproductionDocument1 pageCSEC Biology - Vegetative ReproductionTamicka BonnickNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SBA P3 Jan 2015Document8 pagesChemistry SBA P3 Jan 2015ValNo ratings yet
- Biology Past PapersDocument20 pagesBiology Past Papersdemetri lanezNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics June 2005 P1 PDFDocument14 pagesCSEC Physics June 2005 P1 PDFLaimen Reveski100% (1)
- Biology Practical Booklet Updated-4th-Form-CsecDocument17 pagesBiology Practical Booklet Updated-4th-Form-CsecSashanna Morgan100% (1)
- Nutrition BookDocument5 pagesNutrition Bookemysameh100% (1)
- Living Organisms and Cells MCQDocument3 pagesLiving Organisms and Cells MCQOsmany Madrigal100% (1)
- CSEC Biology June 2010 P2Document16 pagesCSEC Biology June 2010 P2Joy Boehmer100% (1)
- CAPE Chemistry 2017 U2 P032Document8 pagesCAPE Chemistry 2017 U2 P032Kyle YearwoodNo ratings yet
- Human Biology Past PaperDocument3 pagesHuman Biology Past PaperCarl Agape Davis100% (1)
- Prep For Success Hookes Law Letter SizeDocument7 pagesPrep For Success Hookes Law Letter SizeRavin BoodhanNo ratings yet
- Human and Social Biology Paper 02 Jan 2023 CsecDocument24 pagesHuman and Social Biology Paper 02 Jan 2023 CsecKimikawa Stewart100% (1)
- F5 T1 Human Social Biology P2 2010-2011Document12 pagesF5 T1 Human Social Biology P2 2010-2011asjawolverineNo ratings yet
- How the Benedict's test identifies reducing sugarsDocument7 pagesHow the Benedict's test identifies reducing sugarsSaintm101No ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Chapter 6 - MolesDocument16 pagesCsec Chemistry Chapter 6 - Moleschelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- Section A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletDocument8 pagesSection A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology January 2012 P2Document18 pagesCSEC Biology January 2012 P2Troy SteadmanNo ratings yet
- Bio 2019 p1Document11 pagesBio 2019 p1Amarah MohammedNo ratings yet
- CAPE Applied Mathematics 2016 U1 P2Document28 pagesCAPE Applied Mathematics 2016 U1 P2Idris SegulamNo ratings yet
- Pob Production SbaDocument19 pagesPob Production SbaannmarieNo ratings yet
- CSEC Form 4 Human and Social Biology NotesDocument4 pagesCSEC Form 4 Human and Social Biology Notessmbdy tbhhh100% (1)
- CSEC Human and Social Biology SBA GuidelinesDocument2 pagesCSEC Human and Social Biology SBA Guidelinesmissjackson042No ratings yet
- SBA 2 ModifiedDocument3 pagesSBA 2 Modifiedannmarie100% (1)
- June 2014 p1 CSECDocument14 pagesJune 2014 p1 CSECRomani OsbourneNo ratings yet
- Specimen 2019 With AnswerDocument34 pagesSpecimen 2019 With AnswerGiovanniNo ratings yet
- Answered CXC Cells QuestionsDocument10 pagesAnswered CXC Cells QuestionsKeelah BennNo ratings yet
- Sea Mathematics 2006Document22 pagesSea Mathematics 2006Clemencia GuerraNo ratings yet
- Bio Sheme of WorksDocument3 pagesBio Sheme of Worksreeta ramNo ratings yet
- May Pen High Integrated Science Exam ReviewDocument16 pagesMay Pen High Integrated Science Exam ReviewCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MarkschemeudatedDocument21 pagesUnit 1 MarkschemeudatedCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Types of Asexual ReproductionDocument3 pagesTypes of Asexual ReproductionCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- MAY PEN HIGH SCHOOL INTEGRATED SCIENCE EXAMDocument11 pagesMAY PEN HIGH SCHOOL INTEGRATED SCIENCE EXAMCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- MAY PEN HIGH SCHOOL END OF TERM EXAMDocument14 pagesMAY PEN HIGH SCHOOL END OF TERM EXAMCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- May Pen High School Mid Term Exam: Integrated Science Form 3Document8 pagesMay Pen High School Mid Term Exam: Integrated Science Form 3CHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- End of Term Exam: Integrated Science Form 1: Name: - TeacherDocument7 pagesEnd of Term Exam: Integrated Science Form 1: Name: - TeacherCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Form 5 EndoftermbiologyexamdecemberDocument16 pagesForm 5 EndoftermbiologyexamdecemberCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- May Pen High School Midterm Exam: Form 4: Integrated ScienceDocument7 pagesMay Pen High School Midterm Exam: Form 4: Integrated ScienceCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Form 4 HSBDocument6 pagesForm 4 HSBCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Form 1 Integrated Science MidtermDocument9 pagesForm 1 Integrated Science MidtermCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Test: Sawaiwittayakarn School Grade 7: M 1/1, 1/2, 1/3 and 1/4 ClassDocument6 pagesTest: Sawaiwittayakarn School Grade 7: M 1/1, 1/2, 1/3 and 1/4 ClassCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Form 3 Midterm TestDocument6 pagesForm 3 Midterm TestCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Form 5 EndoftermhumanandsocialbiodecemberDocument13 pagesForm 5 EndoftermhumanandsocialbiodecemberCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Name: - Teacher: - Instruction: This Paper Consists of Three Sections. Answer All Questions in All Section. Section Marks Total A 20 B C 10 Total 75Document3 pagesName: - Teacher: - Instruction: This Paper Consists of Three Sections. Answer All Questions in All Section. Section Marks Total A 20 B C 10 Total 75CHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- May Pen High School End of Term ExamDocument4 pagesMay Pen High School End of Term ExamCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Name: - TeacherDocument10 pagesName: - TeacherCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam: ENGLISH CourseDocument13 pagesMidterm Exam: ENGLISH CourseCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- ENGLISH Course Midterm Exam M-5/1, 5/2, 5/3, 6/1 6/2 6/3Document13 pagesENGLISH Course Midterm Exam M-5/1, 5/2, 5/3, 6/1 6/2 6/3CHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- TEACHER EMPLOYMENT QUESTIONNAIREDocument2 pagesTEACHER EMPLOYMENT QUESTIONNAIRECHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Form 4 INTESCI COMPLETEDocument10 pagesMidterm Exam Form 4 INTESCI COMPLETECHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Form 5 HSB COMPLETEDocument11 pagesMidterm Exam Form 5 HSB COMPLETECHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam: Total Section A Multiple Choice 40 Section B Picture Dictation 10 Section C Conversation 10 Score Total 60Document12 pagesMidterm Exam: Total Section A Multiple Choice 40 Section B Picture Dictation 10 Section C Conversation 10 Score Total 60CHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Human and Social Biology Form 4Document9 pagesHuman and Social Biology Form 4CHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Test: Sawaiwittayakarn School Grade 8: 2/1, 2/2, 2/3 and 2/4 Class: - Name: - Total - /38Document8 pagesTest: Sawaiwittayakarn School Grade 8: 2/1, 2/2, 2/3 and 2/4 Class: - Name: - Total - /38CHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Form 5 INTESCIENCE COMPLETEDocument9 pagesMidterm Exam Form 5 INTESCIENCE COMPLETECHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Integrated Science Form 4 Final ExamDocument14 pagesIntegrated Science Form 4 Final ExamCHRISTOPHER SCALE100% (1)
- Sba Book GradeDocument2 pagesSba Book GradeCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Form 4 GENBIO COMPLETEDocument9 pagesMidterm Exam Form 4 GENBIO COMPLETECHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy WorksheetDocument2 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy WorksheetCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- ISO 18001 ChecklistDocument7 pagesISO 18001 ChecklistRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of Water TherapyDocument5 pagesThe Benefits of Water TherapyJohn Paul CordovaNo ratings yet
- Protein Electrophoresis, Immunofixation, and Immunodisplacement in Clinical Diagnosis. 2nd Edition, May 2011Document182 pagesProtein Electrophoresis, Immunofixation, and Immunodisplacement in Clinical Diagnosis. 2nd Edition, May 2011Zia Uddin100% (3)
- Lengua Extranjera (Inglés) Examen A PDFDocument1 pageLengua Extranjera (Inglés) Examen A PDFJoseManuelLabordaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Antibacterial Antiinflammatory and Skinwhitening Effect of Centella Asiatica L Urban2018journal of Plant BiotechnologyOpen AccessDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Antibacterial Antiinflammatory and Skinwhitening Effect of Centella Asiatica L Urban2018journal of Plant BiotechnologyOpen AccessRika DestianaNo ratings yet
- 8 Week Powerlifting IntroDocument3 pages8 Week Powerlifting Introlachlan Gill02No ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan: Effective?) - The Blood Pressure WillDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching Plan: Effective?) - The Blood Pressure WillphoebeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Drugs and Their EffectsDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Drugs and Their EffectsJerica Jaz F. VergaraNo ratings yet
- Form 6: Application For LeaveDocument7 pagesForm 6: Application For LeaveTina Marie TiongcoNo ratings yet
- Record Retention ChartDocument2 pagesRecord Retention ChartVatsalPatelNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plants For The Treatment of Nervios Anxiety and Depression in Mexican Traditional Medicine - 2014 - Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia PDFDocument18 pagesMedicinal Plants For The Treatment of Nervios Anxiety and Depression in Mexican Traditional Medicine - 2014 - Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia PDFGabriela OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter - Meghan L. ShalvoyDocument1 pageCover Letter - Meghan L. ShalvoyMeghan Equality ShalvoyNo ratings yet
- Effect of Tyrosine Supplementation On Clinical and Healthy Populations (Jongkees Et Al.)Document8 pagesEffect of Tyrosine Supplementation On Clinical and Healthy Populations (Jongkees Et Al.)Danny QuishpiNo ratings yet
- Best Practices in Health and NutritionDocument5 pagesBest Practices in Health and NutritionMary Rose Fernando AngelesNo ratings yet
- The Standard - 2014-07-30Document71 pagesThe Standard - 2014-07-30jorina8070% (1)
- James Andretich Resume #2Document2 pagesJames Andretich Resume #2Abbey DavisNo ratings yet
- Complications of SinusitisDocument81 pagesComplications of SinusitisDrravikumar BhandariNo ratings yet
- Concrete Pouring & Compacting MethodDocument18 pagesConcrete Pouring & Compacting MethodDragu SorinNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Respiratory SystemDocument57 pagesPathology of The Respiratory SystemAngelic khanNo ratings yet
- CCRN-PCCN Review RenalDocument11 pagesCCRN-PCCN Review RenalGiovanni MictilNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Dislocation Physiotherapy StagesDocument13 pagesShoulder Dislocation Physiotherapy StagesSahoo PRASANTANo ratings yet
- Barangay Health Services NC IIDocument113 pagesBarangay Health Services NC IIMairem Barruga100% (2)
- Jurnal Efektifitas Matras DekubitusDocument9 pagesJurnal Efektifitas Matras DekubitusIhsan Nur MahmudiNo ratings yet
- DG Document Requirements Reference SheetDocument7 pagesDG Document Requirements Reference SheetJosé Larragaña OsunaNo ratings yet
- 240-62946386 Vehicle Driver Safety Management Procedure PDFDocument22 pages240-62946386 Vehicle Driver Safety Management Procedure PDFMAdrianRumayar100% (1)
- PSORIASISDocument9 pagesPSORIASISDianne BernardoNo ratings yet
- October 23, 2015 Strathmore TimesDocument28 pagesOctober 23, 2015 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesNo ratings yet
- T-Nation Yoke TrainingDocument11 pagesT-Nation Yoke TrainingJoseph Glaser100% (1)
- Composition and Regulation of Body FluidsDocument32 pagesComposition and Regulation of Body FluidsAndriKusumaNo ratings yet
- 11 cсынып емтихан сурактарыDocument6 pages11 cсынып емтихан сурактарыakzharNo ratings yet