0% found this document useful (0 votes)
878 views1 pageAnaphylaxis Management Protocol Guide
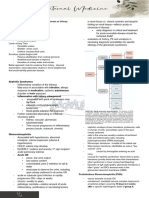
This document provides information on diagnosing and treating anaphylaxis. It defines anaphylaxis as a sudden onset of airway, breathing, or circulation problems, often accompanied by skin changes like rashes. The first steps are to call for help, remove any triggers if possible, lay the patient flat, and give an intramuscular injection of adrenaline. Vital signs and oxygen levels should then be monitored. If there is no response, a second dose of adrenaline can be given after 5 minutes along with intravenous fluids. For refractory cases, the refractory anaphylaxis algorithm should be followed.
Uploaded by
Shawn Gaurav JhaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
878 views1 pageAnaphylaxis Management Protocol Guide
This document provides information on diagnosing and treating anaphylaxis. It defines anaphylaxis as a sudden onset of airway, breathing, or circulation problems, often accompanied by skin changes like rashes. The first steps are to call for help, remove any triggers if possible, lay the patient flat, and give an intramuscular injection of adrenaline. Vital signs and oxygen levels should then be monitored. If there is no response, a second dose of adrenaline can be given after 5 minutes along with intravenous fluids. For refractory cases, the refractory anaphylaxis algorithm should be followed.
Uploaded by
Shawn Gaurav JhaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd