Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circuit Diagram:: Experiment No: 1 Title: Calibration of A Milliammeter As A Voltmeter. Objectives
Uploaded by
Asrar Hussain BhatOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circuit Diagram:: Experiment No: 1 Title: Calibration of A Milliammeter As A Voltmeter. Objectives
Uploaded by
Asrar Hussain BhatCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No: 1
TITLE: CALIBRATION OF A MILLIAMMETER AS A VOLTMETER.
OBJECTIVES:
To calibrate a milliammeter as a voltmeter with the help of a substandard voltmeter
To draw the calibration curve and correction curve for the given milliammeter.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
0-250mA
560Ω/1A
0-300V
1500Ω/0.5A
LIST OF APPARATUS:
Sl No Item Range Maker Maker’s No
THEORY:
Referring to the figure, let R is the external resistance connected in series with the milliammeter, Ra is
the internal resistance of the milliammeter. If V be the voltage drop across the above combination due to
circuit current I, then it can be shown that
V= (R + Ra). I
V
(R + Ra) = K
I
K is a constant, assuming constant external resistance.
If Vn is the voltmeter reading to which the milliammeter is to be calibrated for full-scale deflection of In
(milliamps), then constant,
K=Vn/In (volts/milliampere)
The voltage equivalent, Veq , to any intermediate milliammeter reading I, is
Veq=K.I (volts).
For milliammeter reading I,
Error = Veq -V (volts)
Correction = V- Veq = - Error (volts)
where V is the substandard voltmeter reading
CURVES:
i) Calibration Curve: Milliammeter reading on X-axis, Substandard voltmeter reading on Y-axis.
ii) Correction Curve: Milliammeter reading on X-axis, Correction on Y-axis.
NOTE: GRAPHS ARE POINT TO POINT LINEAR
PROCEDURE:
1) Connect the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram.
2) Note the zero setting of the instruments.
3) Adjust the potential divider to obtain zero output voltage and put the external series resistance R
at maximum value (so as to protect the milliammeter). Put on supply.
4) Increase the output voltage slowly up to that voltage (say 200 volts) to which the milliammeter is
to be calibrated.
5) Adjust the external resistance R to obtain full-scale deflection of the milliammeter (In). Note the
voltmeter reading. If it is different from the previously adjusted value then adjust both the
potential divider and the series resistance R to obtain the voltage (Vn) while the milliammeter
gives full-scale deflection.
6) Note the final reading (after adjustments) of Step 5. Decrease the output voltage (with the help of
potential divider) in steps up to the zero reading in the milliammeter. Note the instruments
reading in each step. Take ten sets of readings.
EXPERIMENTAL OBSERVATIONS AND RESULTS:
K=Vn/In (volts/milliamps)
Sl No Substandard Voltmeter Milliammeter Equivalent Voltage Correction
Reading Reading
V (volts) I (mA) Veq=K.I V- Veq (volts)
REPORT:
1. Draw the calibration curve & correction curve of the milliammeter using scale (join point
to point).
2. Define Equivalent Voltage. Show sample calculations.
3. What do you mean by calibration?
4. What is a rheostat? How is it used and why? Draw and explain with reference to the given
circuit diagram.
You might also like
- Characteristic Curve of Zener DiodeDocument2 pagesCharacteristic Curve of Zener DiodeSatyam TripãthìNo ratings yet
- Exp2 - Calibration of Ammeter & VoltmeterDocument4 pagesExp2 - Calibration of Ammeter & VoltmeterKEREN EVANGELINE I (RA1913011011002)No ratings yet
- Experiment 12-Resonance Lab ReportDocument8 pagesExperiment 12-Resonance Lab ReportShahzad JameelNo ratings yet
- Measure Unknown Inductance Using Maxwell BridgeDocument2 pagesMeasure Unknown Inductance Using Maxwell Bridgemigman99No ratings yet
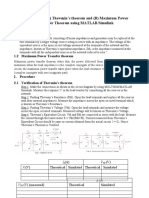
- Verification of (A) Thevenin's Theorem and (B) Maximum Power Transfer Theorem Using MATLAB/SimulinkDocument3 pagesVerification of (A) Thevenin's Theorem and (B) Maximum Power Transfer Theorem Using MATLAB/SimulinkSuhana SinghNo ratings yet
- Experiment 24: The Potentiometer: PurposeDocument6 pagesExperiment 24: The Potentiometer: PurposekirtiNo ratings yet
- NDW Series Computer Controlled Torsion Testing MachineDocument5 pagesNDW Series Computer Controlled Torsion Testing Machinegosaye desalegnNo ratings yet
- Inverse Laplace Transform Lecture-3Document22 pagesInverse Laplace Transform Lecture-3SingappuliNo ratings yet
- Bapatla Engineering College EEE Lab ExperimentsDocument44 pagesBapatla Engineering College EEE Lab Experimentspardhu_y4No ratings yet
- Acc ManualDocument44 pagesAcc ManualDevendra VelhalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7: Voltmeter Using PMMC: I. ObjectivesDocument9 pagesExperiment 7: Voltmeter Using PMMC: I. ObjectivesJam MagatNo ratings yet
- EE-306 Electromechanical Devices Lab ManualDocument79 pagesEE-306 Electromechanical Devices Lab ManualKhaled HassanNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Circuit BasicsDocument26 pagesRectifier Circuit BasicsShiny SinghalNo ratings yet
- Experiment No-7 Fil LampDocument2 pagesExperiment No-7 Fil LampAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- 15ecl48 VTU Raghudathesh RC Wein Bridge OscillatorsDocument7 pages15ecl48 VTU Raghudathesh RC Wein Bridge OscillatorsraghudatheshgpNo ratings yet
- ChronoamperometryDocument7 pagesChronoamperometrybettypaz89100% (1)
- Lab 6 - Maximum Power Transfer and PF Improvement - 2012Document5 pagesLab 6 - Maximum Power Transfer and PF Improvement - 2012劉成No ratings yet
- Plot V-I Characteristics of SCRDocument13 pagesPlot V-I Characteristics of SCRU V Durgarao100% (1)
- Node and Mesh Circuit Analysis MethodsDocument20 pagesNode and Mesh Circuit Analysis MethodsMurat GülerNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2005Document18 pagesCircuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2005Muhammad Umair50% (2)
- Diploma ELECTRICAl 6th Sem SylDocument21 pagesDiploma ELECTRICAl 6th Sem SylAadil Ashraf KhanNo ratings yet
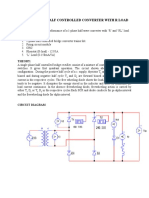
- Single Phase Half Controlled Converter With R LoadDocument3 pagesSingle Phase Half Controlled Converter With R LoadB ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- EE6201 Circuit Theory Regulation 2013 Lecture Notes PDFDocument251 pagesEE6201 Circuit Theory Regulation 2013 Lecture Notes PDFrajNo ratings yet
- PYP100 Lab ManualDocument231 pagesPYP100 Lab ManualSIDDHARTH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Measuring Instruments and Circuit Elements Lab ExperimentDocument38 pagesMeasuring Instruments and Circuit Elements Lab ExperimentSaif KhanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Lab ManualDocument38 pagesElectrical Circuit Lab Manualecessec67% (3)
- 6 Measurement of Ripple Factor of RectifiersDocument5 pages6 Measurement of Ripple Factor of Rectifierskarthiksubramanian940% (1)
- PLANKS CONSTANT ExperimentDocument7 pagesPLANKS CONSTANT ExperimentHuman Error (Sid)No ratings yet
- Test 1 - Sept16 AnswerDocument5 pagesTest 1 - Sept16 AnswerFarah IzzatiNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 5Document7 pagesExperiment # 5Abdullah TahirNo ratings yet
- Cathodic Disbondment Mul Tiple Channel Testing Unit MODEL #CD-16Document10 pagesCathodic Disbondment Mul Tiple Channel Testing Unit MODEL #CD-16Masood AlamNo ratings yet
- Wireless Stepper Motor ControlDocument2 pagesWireless Stepper Motor ControlHarsha100% (1)
- Embedded System Lab ManualDocument67 pagesEmbedded System Lab Manualsaim100% (1)
- Experiment No.02 To Observe The Characteristics of A Half Wave RectifierDocument4 pagesExperiment No.02 To Observe The Characteristics of A Half Wave RectifierWaqas MughalNo ratings yet
- Abes Engineering College, Ghaziabad: Department of Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument80 pagesAbes Engineering College, Ghaziabad: Department of Electronics & Communication EngineeringJayan GoelNo ratings yet
- Ohmmeters Class NotesDocument4 pagesOhmmeters Class NotesnitishbgmNo ratings yet
- Optical FiberDocument6 pagesOptical FiberSarveenaNo ratings yet
- Luo ConverterDocument6 pagesLuo ConverterAndrei CocorNo ratings yet
- Diode Clippers: 1. Positive Clipper and Negative ClipperDocument6 pagesDiode Clippers: 1. Positive Clipper and Negative ClipperBibek ThapaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank S&TDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank S&Tarvind r0% (1)
- EE6201 Circuit Theory Regulation 2013 Lecture Notes PDFDocument257 pagesEE6201 Circuit Theory Regulation 2013 Lecture Notes PDFVenkatesan Swamy100% (1)
- Lab1-Introduction To DSO ND FGDocument11 pagesLab1-Introduction To DSO ND FGHamza AliNo ratings yet
- Chebyshev Analog FilterDocument24 pagesChebyshev Analog FilternguyenphuonghuyNo ratings yet
- Retardation TestDocument5 pagesRetardation TestAnkit Shetty100% (1)
- WCU Engineering Lab ReportDocument8 pagesWCU Engineering Lab Reportallan_zirconia444No ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL SCIENCES - IDocument39 pagesELECTRICAL SCIENCES - IGanesh DharmireddyNo ratings yet
- Nano Fluid Volume PercentageDocument35 pagesNano Fluid Volume PercentageMuthiah Chidambaram Muthiah100% (1)
- Simplified Analysis of Graetz CircuitDocument42 pagesSimplified Analysis of Graetz CircuitKaran Singhania100% (3)
- Tangent GalvanometerDocument19 pagesTangent GalvanometerChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- First Order Active Filters (LPF, HPF) : (A) Low Pass FilterDocument12 pagesFirst Order Active Filters (LPF, HPF) : (A) Low Pass FilterVRNo ratings yet
- DTC PPTDocument17 pagesDTC PPTmanoranjanottaNo ratings yet
- A Network Theorem Dual to Miller's TheoremDocument5 pagesA Network Theorem Dual to Miller's TheoremSiddhant Jain0% (1)
- Circuit Diagram:: Experiment No: 2 Title: Calibration of A Milli Voltmeter As An Ammeter. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesCircuit Diagram:: Experiment No: 2 Title: Calibration of A Milli Voltmeter As An Ammeter. ObjectivesAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Experiment B6 Aim: Apparatus:: Characteristics of DiodeDocument9 pagesExperiment B6 Aim: Apparatus:: Characteristics of DiodeAnurag BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic InstrumentationDocument26 pagesElectrical & Electronic InstrumentationKamal PhyNo ratings yet
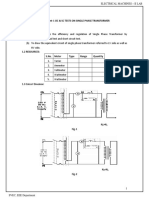
- 1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase TransformerDocument6 pages1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase Transformerchandrakanth100% (3)
- Lab 3 Resistance & Ohm's LawDocument4 pagesLab 3 Resistance & Ohm's LawDouglas RyanNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit FundamentalsDocument19 pagesElectric Circuit FundamentalsSana NgaNo ratings yet
- Fow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEEDocument12 pagesFow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEERobert Fow JOENo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram:: Experiment No: 7 (A) Title: Study of R-L-C Series Circuit. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesCircuit Diagram:: Experiment No: 7 (A) Title: Study of R-L-C Series Circuit. ObjectivesAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram:: Experiment No: 2 Title: Calibration of A Milli Voltmeter As An Ammeter. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesCircuit Diagram:: Experiment No: 2 Title: Calibration of A Milli Voltmeter As An Ammeter. ObjectivesAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Experiment No-7 Fil LampDocument2 pagesExperiment No-7 Fil LampAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram:: Experiment No: 3 Title: Characteristics of Filament Lamp ObjectivesDocument2 pagesCircuit Diagram:: Experiment No: 3 Title: Characteristics of Filament Lamp ObjectivesAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering Lab Manual FOR Ii Semester B.E Assam Engineering CollegeDocument13 pagesBasic Electrical & Electronics Engineering Lab Manual FOR Ii Semester B.E Assam Engineering CollegeAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Lab Questions and BooksDocument3 pagesLab Questions and BooksAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
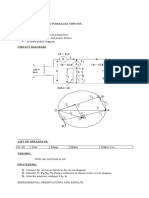
- Experiment No-6 (B) RLC ParallelDocument3 pagesExperiment No-6 (B) RLC ParallelAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Experiment No-6 (B) RLC ParallelDocument3 pagesExperiment No-6 (B) RLC ParallelAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Best Selling Home Appliances and Electronics ListingDocument2 pagesBest Selling Home Appliances and Electronics ListingAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Lab Manual FOR First/Second Semester B.E Assam Engineering CollegeDocument20 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Lab Manual FOR First/Second Semester B.E Assam Engineering CollegeAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Asrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Experiment No-7 Fil LampDocument2 pagesExperiment No-7 Fil LampAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Principal Assam Engineering College: Date: 23-Jun-2021Document2 pagesPrincipal Assam Engineering College: Date: 23-Jun-2021Asrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- GZT 4 TH Sem Fina BacklogDocument113 pagesGZT 4 TH Sem Fina BacklogAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Chapter - I: Per Unit (PU) Representation of Power System Elements (Contd)Document9 pagesChapter - I: Per Unit (PU) Representation of Power System Elements (Contd)Asrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Z-Bus Building Algorithm: Network Representation 1,2,3,4-Nodes Let 1 Be The Reference Node A, B, C, D, e - ElementsDocument17 pagesZ-Bus Building Algorithm: Network Representation 1,2,3,4-Nodes Let 1 Be The Reference Node A, B, C, D, e - ElementsAsrar Hussain BhatNo ratings yet
- Electrical Isolator PDFDocument23 pagesElectrical Isolator PDFLimuel OlandriaNo ratings yet
- hf9000 PDFDocument116 pageshf9000 PDFjunebug172100% (1)
- Ultrafast Soft Recovery Diode BulletinDocument7 pagesUltrafast Soft Recovery Diode BulletinStevenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GeomagneticDocument349 pagesIntroduction To GeomagneticMuhamad SafiiNo ratings yet
- On GeneratorDocument55 pagesOn GeneratorDileep Reddy91% (11)
- Fundamentals of Mechatronics 1st Edition Jouaneh Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesFundamentals of Mechatronics 1st Edition Jouaneh Solutions Manualqefoni100% (1)
- Tutorial 1 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 PDFAbu RectifyNo ratings yet
- T Are A Potencial Electrico 2016Document4 pagesT Are A Potencial Electrico 2016Servando De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument40 pagesInternship ReportSudharshan GovindanNo ratings yet
- TIH 025-030 Bearing HeatermanualDocument106 pagesTIH 025-030 Bearing HeatermanualcoupercouperNo ratings yet
- VR6Document20 pagesVR6nebiyouNo ratings yet
- EMI and AC - Question File PDFDocument37 pagesEMI and AC - Question File PDFAryan GoyalNo ratings yet
- 25854224Document5 pages25854224Fajar SodiqNo ratings yet
- Lecture35 Ch12 CoherenceDocument25 pagesLecture35 Ch12 Coherencepavan457No ratings yet
- Chapter 34Document46 pagesChapter 34Latelo MoseaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Thumb of RulesDocument18 pagesElectrical Thumb of Rulesameeri143No ratings yet
- System Voltage Suggested Arrester RatingDocument26 pagesSystem Voltage Suggested Arrester RatinggilbertomjcNo ratings yet
- Human Levers and Equilibrium ConceptsDocument27 pagesHuman Levers and Equilibrium ConceptsLeighton JamesNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 9th Edition Serway Test BankDocument23 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 9th Edition Serway Test Bankninhletitiaqt3100% (29)
- Mag Lev 1Document4 pagesMag Lev 1jyotsu16pansareNo ratings yet
- What's The 4 Generation?: Diagnostic Test System For Power Apparatus Condition AssessmentDocument2 pagesWhat's The 4 Generation?: Diagnostic Test System For Power Apparatus Condition AssessmentVictor Jose Romero FernandezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesLesson 1 IntroductionShiela Amiral BisanaNo ratings yet
- AQA A Level Physics Equation SheetDocument5 pagesAQA A Level Physics Equation SheetCamila Lorenzoni100% (2)
- Powerit MV Air Insulated Motor Control: Featuring Advance and Safegear TechnologyDocument72 pagesPowerit MV Air Insulated Motor Control: Featuring Advance and Safegear TechnologyRaja Bharath DonthiNo ratings yet
- Electrodynamic Wheel (EDW) Magnetic Levitation Using COMSOL MultiphyiscsDocument17 pagesElectrodynamic Wheel (EDW) Magnetic Levitation Using COMSOL MultiphyiscsCamilo Ortega ManjarresNo ratings yet
- BTS 412 B2Document15 pagesBTS 412 B2KSNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document5 pagesUnit 2Mahesh SinghNo ratings yet
- RefDocument75 pagesRefagrawalvishal990% (1)
- Auxiliary Units For 7SR23 Catalogue Sheet PDFDocument12 pagesAuxiliary Units For 7SR23 Catalogue Sheet PDFSteven RodriquezNo ratings yet