Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antiarrhythmic Drugs - Classification and Mechanism of Action.
Uploaded by
SUMIT KUMAR DAS0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
92 views1 pageOriginal Title
Antiarrhythmic Drugs- Classification and Mechanism of Action.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
92 views1 pageAntiarrhythmic Drugs - Classification and Mechanism of Action.
Uploaded by
SUMIT KUMAR DASCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
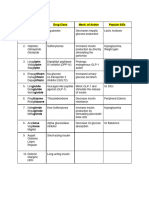
Antiarryhythmics Drugs
Classification and Mechanism of Action
Class- I Class- II Class- III Class- IV Other
+ + +
Na channel blocker B adrenoreceptor K channel blocker Ca channel blocker Antiarrythmic Drugs
Disopyramide, Flecainide Atenolol, Esmolol, Metoprolol Amiodarone, Dofetilide, Diltiazem, Verapamil Adenosine, Digoxin,
Lidocaine, Mexiletine Dronedarone, Ibutilide, Sotalol Magnesium sulfate
Procainamide, Propafenone,
Quinidine
Causes of Arrhythmia
1. Abnormal Automaticity- SA node shows the fastest rate of phase 4 depolarization and therefore, exhibits a
Nerve Impulse higher rate of discharge than that occurring in other pacemaker cells exhibiting automaticity
2. Abnormality in impulse conduction- Impulse from higher pacemaker centers are normally conducted down
pathways that bifurcate o activate the entire ventricular surface. A phenomenon is called reentry may occur if
Normal Conduction Unidirectional Block unidirectional block occurs. Reference- Lippincott (Pharmacology) 6th Edition
Ventricle Wall
Block
E Mail- solutionpharmacy@gmail.com & Reach solution at- www.facebook.com/pharmavideo/
You might also like
- Anti Arrhythmic DrugsDocument12 pagesAnti Arrhythmic DrugsMunazza QuraishiNo ratings yet
- Classification of Drugs PDFDocument15 pagesClassification of Drugs PDFmuhammad ihtisham ul hassanNo ratings yet
- Biologically Active Amines Found in Man: Their Biochemistry, Pharmacology, and Pathophysiological ImportanceFrom EverandBiologically Active Amines Found in Man: Their Biochemistry, Pharmacology, and Pathophysiological ImportanceNo ratings yet
- Abbreviation of PharmacologyDocument59 pagesAbbreviation of PharmacologyMohamed Abo EmadNo ratings yet
- Human Tumours Secreting Catecholamines: Clinical and Physiopathological Study of the PheochromocytomasFrom EverandHuman Tumours Secreting Catecholamines: Clinical and Physiopathological Study of the PheochromocytomasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Antiarrhythmic Agent - WikipediaDocument23 pagesAntiarrhythmic Agent - WikipediaSai Jeevan SampathiraoNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic AgentsDocument45 pagesAntiarrhythmic AgentsSoh Kae SiangNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii: Drugs For Arrhythmia: ObjectivesDocument3 pagesUnit Ii: Drugs For Arrhythmia: ObjectivesJosa Camille BungayNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument46 pagesAntiarrhythmic DrugsHUZAIFA YAMAANNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Important Things To RememberDocument5 pagesPharmacology Important Things To RememberHydie100% (1)
- PHARMACOLOGY HighlightedDocument37 pagesPHARMACOLOGY HighlightedEmeroot RootNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 2 NotesDocument21 pagesPharmacology 2 Notesgnikap_deleonNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument10 pagesAntiarrhythmic DrugsGauri RautNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Therapy of Arrhythmias (09.11.16)Document46 pagesPharmacological Therapy of Arrhythmias (09.11.16)Mariana CabralNo ratings yet
- In The Name of Allah, The Compassionate, The MercifulDocument59 pagesIn The Name of Allah, The Compassionate, The MercifulMuhammad AkbarNo ratings yet
- AnticoagulantsDocument64 pagesAnticoagulantsnainapattnaikNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Pharmacology: Mary Whyte Marshall, MSN, RN, BCDocument58 pagesNCLEX Pharmacology: Mary Whyte Marshall, MSN, RN, BCPeiling LiangNo ratings yet
- 4.03 Anti-Arrhythmic Drugs PDFDocument8 pages4.03 Anti-Arrhythmic Drugs PDFKarl ChavezNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Bjorn C. Knollmann and Dan M. RodenDocument24 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs: Bjorn C. Knollmann and Dan M. RodenNurul HidayahNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Dr. Pradeepa H D Clinical PharmacologistDocument16 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs: Dr. Pradeepa H D Clinical PharmacologistpradeephdNo ratings yet
- IA Hotline0115 3DEBF4D037254Document2 pagesIA Hotline0115 3DEBF4D037254ahmedsobhNo ratings yet
- Kontraindikasi Obat MGDocument2 pagesKontraindikasi Obat MGMuhammad Naqvi Al FarisiNo ratings yet
- IV Drug CompDocument5 pagesIV Drug CompWil Lester100% (1)
- Conduction Defects & ArrythmiasDocument73 pagesConduction Defects & Arrythmiasadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs by ZebDocument40 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs by ZebFazl UllahNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias!Document49 pagesArrhythmias!mospala285No ratings yet
- Classification of The DrugsDocument50 pagesClassification of The DrugsGlena SalamNo ratings yet
- Applied Pharma (NLE)Document2 pagesApplied Pharma (NLE)Maginalyn CangasNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Patches - Design and Current Approaches To Painless Drug DeliveryDocument19 pagesTransdermal Patches - Design and Current Approaches To Painless Drug DeliveryCiontu ValentinNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Antiarrhythmic Drugs - RecordedDocument33 pagesPharmacology of Antiarrhythmic Drugs - RecordedSarah SabtiNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument17 pagesAntiarrhythmic DrugsTarek G MustafaNo ratings yet
- Patches PDFDocument20 pagesPatches PDFMadalina CalcanNo ratings yet
- GI Bleeding - Drugs Known To Cause Bleeding PDFDocument1 pageGI Bleeding - Drugs Known To Cause Bleeding PDFdurgesh pushkarNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemDocument32 pagesDrugs Affecting The Cardiovascular SystemSARAH DIANA ROSE S. MANALILINo ratings yet
- Harrison TablesDocument163 pagesHarrison Tablesfrancieudo1No ratings yet
- سندDocument10 pagesسندAshkan AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument20 pagesAntiarrhythmic DrugsMd FcpsNo ratings yet
- Table Major Drug Interactions With AntimicrobialsDocument2 pagesTable Major Drug Interactions With AntimicrobialsYasmin ElsobkyNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of ArrhythmiasDocument37 pagesDrugs Used in The Treatment of ArrhythmiasChipego ChiyaamaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0749070421000890 MainDocument27 pages1 s2.0 S0749070421000890 MainEliseu AmaralNo ratings yet
- 2 Pharmacology of ChemotherapeuticsDocument34 pages2 Pharmacology of ChemotherapeuticsTilaye GebruNo ratings yet
- 2011 Article 151Document5 pages2011 Article 151dgracereid_693082078No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 AntiarrhythmicsDocument51 pagesLecture 5 AntiarrhythmicsjawadNo ratings yet
- 69.-AntiarrythmiticsDocument16 pages69.-AntiarrythmiticsireneNo ratings yet
- نسخة ANTI-ARRHYTHMICDocument49 pagesنسخة ANTI-ARRHYTHMICManWol JangNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - ReviewerDocument12 pagesPharmacology - ReviewerMissy NaguitNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agents: University of Negros Occidental-RecoletosDocument66 pagesAdrenergic Agents: University of Negros Occidental-Recoletosmary grace trinidadNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Glycosides, Antiarrhythemic Drugs-Dr - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, LecturerDocument15 pagesCardiac Glycosides, Antiarrhythemic Drugs-Dr - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, Lecturerjibachha sahNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument29 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias Cardiac ArrhythmiasgowthamNo ratings yet
- Guaranteed To Pass: Exam Tidbits in Easy To Digest, Bite Sized MorselsDocument2 pagesGuaranteed To Pass: Exam Tidbits in Easy To Digest, Bite Sized MorselsCarl LeeNo ratings yet
- Guaranteed To Pass: Exam Tidbits in Easy To Digest, Bite Sized MorselsDocument2 pagesGuaranteed To Pass: Exam Tidbits in Easy To Digest, Bite Sized MorselsAmberNo ratings yet
- Guaranteed To Pass: Exam Tidbits in Easy To Digest, Bite Sized MorselsDocument2 pagesGuaranteed To Pass: Exam Tidbits in Easy To Digest, Bite Sized MorselsAmberNo ratings yet
- Anti-Arrhythmic DrugsDocument45 pagesAnti-Arrhythmic Drugssultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Fixed Drug EruptionsDocument16 pagesFixed Drug EruptionsAnonymous 2BC7omLaWCNo ratings yet
- 1 DRUGS For HYPERTENSIONDocument1 page1 DRUGS For HYPERTENSIONApril Ann HortilanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Drugs Used in ArrhythymiasDocument27 pagesChapter 4 Drugs Used in ArrhythymiasKaye ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Poison & Antidote Chart IWK Regional Poison Cen PDFDocument1 pagePoison & Antidote Chart IWK Regional Poison Cen PDFdeeptiNo ratings yet